使用 BeanDefinition 描述 Spring Bean
什么是BeanDefinition
在Java中,一切皆对象。在JDK中使用java.lang.Class来描述类这个对象。
在Spring中,存在bean这样一个概念,那Spring又是怎么抽象bean这个概念,用什么类来描述bean这个对象呢?Spring使用BeanDefinition来描述bean。
BeanDefinition

BeanDefinition继承了AttributeAccessor和BeanMetadataElement接口。在Spring中充斥着大量的各种接口,每种接口都拥有不同的能力,某个类实现了某个接口,也就相应的拥有了某种能力。
AttributeAccessor
顾名思义,这是一个属性访问者,它提供了访问属性的能力。
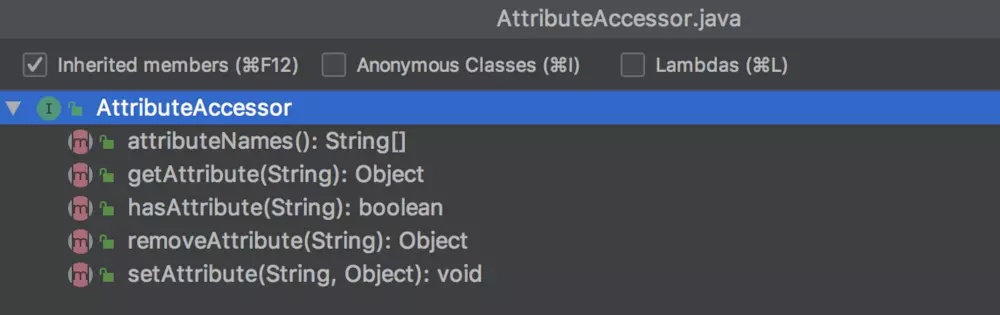
BeanMetadataElement
BeanMetadataElement中只有一个方法,用来获取元数据元素的配置源对象:
public interface BeanMetadataElement {
@Nullable
Object getSource();
}
BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition接口是Spring对bean的抽象。
我们可以从源码中可以看出,Spring是怎么描述一个bean:
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: "singleton".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
*
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: "prototype".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
*
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// Modifiable attributes
/**
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName);
/**
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getParentName();
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
*
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName);
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
*
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
@Nullable
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
*
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(@Nullable String scope);
/**
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
@Nullable
String getScope();
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn);
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
*
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName);
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
*
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName);
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
*
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean.
*
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
*
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
/**
* Return if there are property values values defined for this bean.
*
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* Set the name of the initializer method.
*
* @since 5.1
*/
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName);
/**
* Return the name of the initializer method.
*
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName();
/**
* Set the name of the destroy method.
*
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName);
/**
* Return the name of the destroy method.
*
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName();
/**
* Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
*
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
* @since 5.1
*/
void setRole(int role);
/**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
*
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole();
/**
* Set a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDescription(@Nullable String description);
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
String getDescription();
// Read-only attributes
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
*
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
*
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
* @since 3.0
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotatedBeanDefinition 继承了BeanDefinition,拓展了BeanDefinition接口的能力:
BeanDefinition常见实现类
- ChildBeanDefinition
- RootBeanDefinition
- GenericBeanDefinition
- AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
- ScannedGenericBeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionBuilder
BeanDefinitionBuilder是Builder模式的应用。通过这个类我们可以方便的构建BeanDefinition的实例对象。举个例子:
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(OrderService.class)
//这里的属性名是根据setter方法
.addPropertyReference("dao", "orderDao")
.setInitMethodName("init")
.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
.getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition("orderService", beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
//do nothing
}
}
关于BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,这里先简单介绍一下,详细的我们后面再说。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,同时又增加了一个新的方法BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,该方法允许程序员通过代码编码的方式手动往程序中注册BeanDefinition。
实例中的具体程序已上传到github:https://github.com/shenjianeng/spring-code-study
欢迎关注公众号:

使用 BeanDefinition 描述 Spring Bean的更多相关文章
- spring bean的重新加载
架构体系 在谈spring bean的重新加载前,首先我们来看看spring ioc容器. spring ioc容器主要功能是完成对bean的创建.依赖注入和管理等功能,而这些功能的实现是有下面几个组 ...
- 0003 - 基于xml的Spring Bean 的创建过程
一.目录 前言 创建 Bean 容器 加载 Bean 定义 创建 Bean Spring Bean 创建过程中的设计模式 总结 二.前言 2.1 Spring 使用配置 ApplicationCont ...
- Ioc容器beanDefinition-Spring 源码系列(1)
Ioc容器beanDefinition-Spring 源码系列(1) 目录: Ioc容器beanDefinition-Spring 源码(1) Ioc容器依赖注入-Spring 源码(2) Ioc容器 ...
- Spring之2:Spring Bean动态注册、删除
IoC容器的初始化包括BeanDefinition的Resource定位.载入和注册这三个基本的过程. 一.Resource定位.BeanDefinition的资源定位有resourceLoader通 ...
- Spring Bean的一生
Spring Bean的一生 When you work directly in Java, you can do anything you like with your objects and do ...
- 【转】spring bean 卸载
spring bean 卸载起因: 群里的一个朋友问到: 关于配置destory-method, springboot中 yml如何指定 首先介绍 bean卸载的三种形式 自定义destory-met ...
- 【Spring】IoC容器 - Spring Bean作用域Scope(含SpringCloud中的RefreshScope )
前言 上一章学习了[依赖来源],本章主要讨论SpringBean的作用域,我们这里讨论的Bean的作用域,很大程度都是默认只讨论依赖来源为[Spring BeanDefinition]的作用域,因为在 ...
- 大厂高频面试题Spring Bean生命周期最详解
Spring作为当前Java最流行.最强大的轻量级框架.Spring Bean的生命周期也是面试高频题,了解Spring Bean周期也能更好地帮助我们解决日常开发中的问题.程序员应该都知道Sprin ...
- Spring8:一些常用的Spring Bean扩展接口
前言 Spring是一款非常强大的框架,可以说是几乎所有的企业级Java项目使用了Spring,而Bean又是Spring框架的核心. Spring框架运用了非常多的设计模式,从整体上看,它的设计严格 ...
随机推荐
- 【linux】【qt5】【信号槽示例】
什么叫信号槽: 信号槽是 Qt 框架引以为豪的机制之一.所谓信号槽,实际就是观察者模式.当某个事件发生之后,比如,按钮检测到自己被点击了一下,它就会发出一个信号(signal).这种发出是没有目的的, ...
- 18牛客多校训练第二场 J farm
题意:一个n×m的农田, 每个小格子都有一种作物, 现在喷t次农药,每次农药覆盖一个矩形, 该矩形里面与农药类型不同的植物都会死掉, 求最后植物的死亡数是多少. 题解:二维树状数组. 每次喷农药的时候 ...
- 洛谷P5335 [THUSC2016]补退选 题解
传送门 一道字典树的例题吧 先说下思路前1,2两个条件都易满足,字典树插入修改即可,第三个条件可用动态数组来实现,存下它的size表示当前有几个节点经过(即人数),其下标表示第几次出现,里面存入操作次 ...
- 【Offer】[30] 【包含min函数的栈】
题目描述 思路分析 测试用例 Java代码 代码链接 题目描述 定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的min函数.在该栈中,调用min.push及pop的时间复杂度都是0(1). ...
- 060 Python必备库-从数据处理到人工智能
目录 一.概述 1.1 从数据处理到人工智能 二.Python库之数据分析 2.1 numpy 2.2 pandas 2.3 scipy 三.Python库之数据可视化 3.1 matplotlib ...
- Vert.x Web之Router
Vert.x Web 是一系列用于基于 Vert.x 构建 Web 应用的构建模块. Vert.x Web 的大多数特性被实现为了处理器(Handler),因此您随时可以实现您自己的处理器.我们预计随 ...
- 微服务SpringCloud之服务网关zuul一
前面学习了Eureka.Feign.Hystrix.Config,本篇来学习下API网关zuul.在微服务架构中,后端服务往往不直接开放给调用端,而是通过一个API网关根据请求的url,路由到相应的服 ...
- MongoDB的入门使用以及遇到的坑
一:MonoDB的简单介绍 MongoDB是一个介于关系型数据库与非关系型数据库中间的数据库,是使用C++进行编写的,他的优点是在支持的查询格式特别的强大,可以进行存储比较复杂的数据类型,支持建立索引 ...
- 关于git远程被覆盖的问题
有同事A和B,git远程版本为A0,两个人的本地项目已经跟远程同步.同事A先向git提交了3次,A1.A2.A3.git远程版本为A0.A1.A2.A3.同事B也向git提交了1次B1,但是同事B提交 ...
- Set集合、List集合
集合体系:Collection.Map接口 存储数量不等的多个对象,不能存储基本数据类型,如存储基本数据类型会自动装箱 ======================================== ...
