23-[模块]-subprocess模块
1.调用系统命令
我们经常需要通过Python去执行一条系统命令或脚本,系统的shell命令是独立于你的python进程之外的,每执行一条命令,就是发起一个新进程,通过python调用系统命令或脚本的模块在python2有os.system
>>> os.system('uname -a')
Darwin Alexs-MacBook-Pro.local 15.6.0 Darwin Kernel Version 15.6.0: Sun Jun 4 21:43:07 PDT 2017; root:xnu-3248.70.3~1/RELEASE_X86_64 x86_64
0
(1)os.system
>>> import os
>>> os.system('df -h')
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
C:/Program Files (x86)/cmder/vendor/git-for-windows 224G 86G 139G 39% /
D: 101G 1001M 100G 1% /d
E: 123G 129M 122G 1% /e
F: 122G 1.3G 121G 1% /f
G: 123G 3.6G 119G 3% /g
0
>>> os.system('uname')
MSYS_NT-6.1-WOW
0
>>>
(2)os.popen
>>> f = os.popen('df -h')
>>> f
<os._wrap_close object at 0x03501750>
>>> f.read()
'Filesystem
Size Used Avail Use%
Mounted on\n
C:/Program Files (x86)/cmder/vendor/git-for-windows 224G 86G 139G 39% /\n
D:
101G 1001M 100G 1% /d\n
E: 123G 129M 122G 1% /e\n
F: 122G 1.3G 121G 1% /f\n
G: 123G 3.6G 119G 3% /g\n'
>>>
>>> f.close()
>>>
(3)commands #python2
>>> import commands
>>> commands.getstatusoutput('df -h')
(0, '\xe6\x96\x87\xe4\xbb\xb6\xe7\xb3\xbb\xe7\xbb\x9f
\xe5\xae\xb9\xe9\x87\x8f \xe5\xb7\xb2\xe7\x94\xa8
\xe5\x8f\xaf\xe7\x94\xa8 \xe5\xb7\xb2\xe7\x94\xa8% \xe6\x8c\x82\xe8\xbd\xbd\xe7\x82\xb9\nudev
973M 0 973M 0% /dev\ntmpfs 199M 6.4M 192M 4%
/run\n/dev/sda1 21G 11G 8.8G 56% /\ntmpfs 992M 200K 992M
1% /dev/shm\ntmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock\ntmpfs
992M 0 992M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup\ntmpfs
199M 56K 199M 1% /run/user/1000')
>>>
这条命令的实现原理是什么呢?(视频中讲,解释进程间通信的问题...)
除了os.system可以调用系统命令,,commands,popen2等也可以,比较乱,于是官方推出了subprocess,目地是提供统一的模块来实现对系统命令或脚本的调用
2、subprocess模块
三种执行命令的方法
subprocess.run(*popenargs, input=None, timeout=None, check=False, **kwargs) #官方推荐
subprocess.call(*popenargs, timeout=None, **kwargs) #跟上面实现的内容差不多,另一种写法
subprocess.Popen() #上面各种方法的底层封装
(1)run()方法
功能:执行args参数所表示的命令,等待命令结束,并返回一个CompletedProcess类型对象。
Run command with arguments and return a CompletedProcess instance.The returned instance will have attributes args,
returncode, stdout and stderr. By default, stdout and stderr are not captured,
and those attributes will be None. Pass stdout=PIPE and/or stderr=PIPE in order to capture them. If check is True and the exit code was non-zero, it raises a CalledProcessError.
The CalledProcessError object will have the return code in the returncode attribute,
and output & stderr attributes if those streams were captured. If timeout is given, and the process takes too long, a TimeoutExpired exception will be raised. The other arguments are the same as for the Popen constructor.
>>> import subprocess
>>> subprocess.run(['df','-h'])
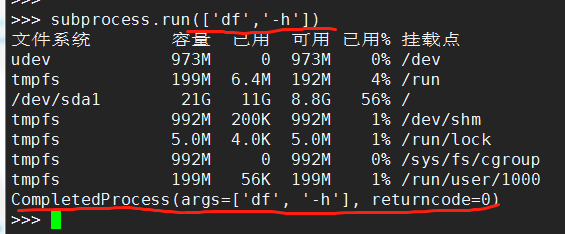
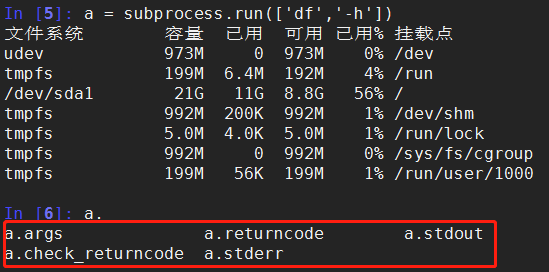
标准写法
subprocess.run(['df','-h'],stderr=subprocess.PIPE,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,check=True)
涉及到管道|的命令需要这样写
subprocess.run('df -h|grep disk1',shell=True) #shell=True的意思是这条命令直接交给系统去执行,不需要python负责解析
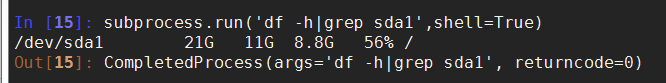

(2) call()方法
#执行命令,返回命令执行状态 , 0 or 非0
>>> retcode = subprocess.call(["ls", "-l"]) #执行命令,如果命令结果为0,就正常返回,否则抛异常
>>> subprocess.check_call(["ls", "-l"])
0 #接收字符串格式命令,返回元组形式,第1个元素是执行状态,第2个是命令结果
>>> subprocess.getstatusoutput('ls /bin/ls')
(0, '/bin/ls') #接收字符串格式命令,并返回结果
>>> subprocess.getoutput('ls /bin/ls')
'/bin/ls' #执行命令,并返回结果,注意是返回结果,不是打印,下例结果返回给res
>>> res=subprocess.check_output(['ls','-l'])
>>> res
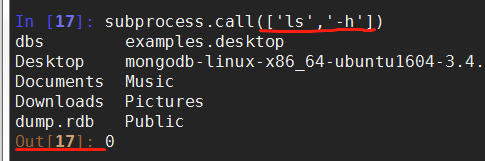
(3)Popen()方法
常用参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
下面这2条语句执行会有什么区别?
a=subprocess.run('sleep 10',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
a=subprocess.Popen('sleep 10',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
区别是Popen会在发起命令后立刻返回,而不等命令执行结果。这样的好处是什么呢?
如果你调用的命令或脚本 需要执行10分钟,你的主程序不需卡在这里等10分钟,可以继续往下走,干别的事情,每过一会,通过一个什么方法来检测一下命令是否执行完成就好了。
Popen调用后会返回一个对象,可以通过这个对象拿到命令执行结果或状态等,该对象有以下方法
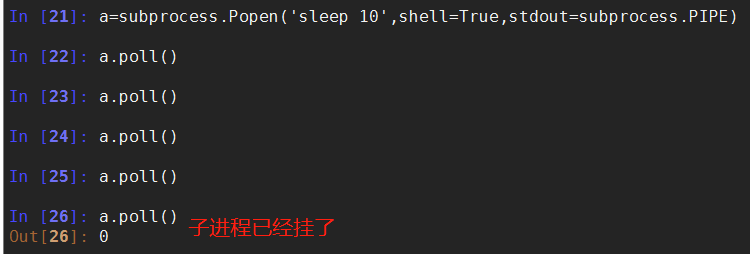
(1)poll()
Check if child process has terminated. Returns returncode
# 检查子进程是否死亡
(2)wait()
Wait for child process to terminate. Returns returncode attribute.
(3)terminate()、kill()
terminate()终止所启动的进程Terminate the process with SIGTERM kill() 杀死所启动的进程 Kill the process with SIGKILL
# 向文件写入数字
In [35]: a=subprocess.Popen('for i in $(seq 1 100);do sleep 1;echo $i >> /tmp/sleep.log;done',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE) # 文件内容
python@ubuntu:~$ tail -f /tmp/sleep.log
1
2
3
4
5
6 In [37]: a.pid #查看进程号
Out[37]: 7572 In [38]: a.kill() #停止写入
In [39]: a=subprocess.Popen('for i in $(seq 1 100);do sleep 1;echo $i >> /tmp/sleep.log;done',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
In [40]: a.pid
Out[40]: 7629
In [41]: import signal
In [42]: import os
In [45]: os.kill(7629,signal.SIGTERM)
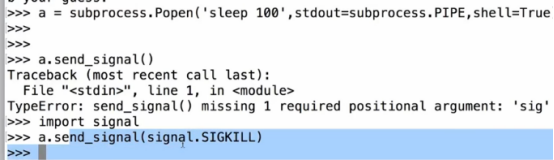
(4)发送系统信号
send_signal(signal.xxx)发送系统信号 pid 拿到所启动进程的进程号
(5)communicate()
communicate()与启动的进程交互,发送数据到stdin,并从stdout接收输出,然后等待任务结束
>>> a = subprocess.Popen('python3 guess_age.py',stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE,stdin=subprocess.PIPE,shell=True)
>>> a.communicate(b'')
(b'your guess:try bigger\n', b'')

23-[模块]-subprocess模块的更多相关文章
- s14 第5天 时间模块 随机模块 String模块 shutil模块(文件操作) 文件压缩(zipfile和tarfile)shelve模块 XML模块 ConfigParser配置文件操作模块 hashlib散列模块 Subprocess模块(调用shell) logging模块 正则表达式模块 r字符串和转译
时间模块 time datatime time.clock(2.7) time.process_time(3.3) 测量处理器运算时间,不包括sleep时间 time.altzone 返回与UTC时间 ...
- Python全栈之路----常用模块----subprocess模块
我们经常需要通过Python去执行一条系统命令或脚本,系统的shell命令是独立于你的python进程之外的,每执行一条命令,就是发起一个新进程,通过python调用系统命令或脚本的模块在python ...
- os模块,os.path模块,subprocess模块,configparser模块,shutil模块
1.os模块 os表示操作系统该模块主要用来处理与操作系统相关的操作最常用的文件操作打开 读入 写入 删除 复制 重命名 os.getcwd() 获取当前执行文件所在的文件夹路径os.chdir(&q ...
- os模块-subprocess 模块- configpaser 模块
一. os 模块 主要用于处理与操作系统相关操作,最常用文件操作 使用场景:当需要操作文件及文件夹(增,删,查,改) os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录 os.chdir('dirname') ...
- re模块,subprocess模块
""" RE是什么 正则 表达 式子 就是一些带有特殊含义的符号或者符号的组合 它的作用是对字符串进行过滤 在一堆字符串中找到你所关心的内容 你就需要告诉计算机你的过滤规 ...
- python hashlib模块 logging模块 subprocess模块
一 hashlib模块 import hashlib md5=hashlib.md5() #可以传参,加盐处理 print(md5) md5.update(b'alex') #update参数必须是b ...
- Python re模块 subprocess模块
re模块 内部实现不是Python 而是调用了c的库 re是什么 正则 表达 式子 就是一些带有特殊含义的符号或者符号的组合作用: 对字符串进行过滤 在一对字符串中找到所关心的内容 你就需要告诉计算机 ...
- python实现系统调用cmd命令的模块---subprocess模块
如果要python实现系统命令或者调用脚本,python中可以利用os或者subprocess模块实现: 一.os模块: # coding:utf-8 command = os.system('net ...
- python day 9: xlm模块,configparser模块,shutil模块,subprocess模块,logging模块,迭代器与生成器,反射
目录 python day 9 1. xml模块 1.1 初识xml 1.2 遍历xml文档的指定节点 1.3 通过python手工创建xml文档 1.4 创建节点的两种方式 1.5 总结 2. co ...
- configparser模块 subprocess 模块,xlrd 模块(表格处理)
今日内容: 1.configparser模块 2.subprocess模块 3.xlrd(读),xlwt(写) 表格处理 configparser模块 import configparser # co ...
随机推荐
- vim和xshell配色
xshell配色: http://www.hookr.cn/xshell-pei-se.html vim配色: 参考该文中的配置方法,包括设置256色等.http://www.cnblogs.com/ ...
- [翻译] SCViewShaker
SCViewShaker https://github.com/rFlex/SCViewShaker About A highly configurable UIView category for s ...
- [翻译] WPAttributedMarkup
WPAttributedMarkup https://github.com/nigelgrange/WPAttributedMarkup WPAttributedMarkup is a simple ...
- Celery学习--- Celery在项目中的使用
可以把celery配置成一个应用,注意连接文件命名必须为celery.py 目录格式如下 项目前提: 安装并启动Redis CeleryPro/celery.py [命名必须为celery.py] ...
- C# Socket编程 笔记,Socket 详解,入门简单
目录 一,网络基础 二,Socket 对象 三,Bind() 绑定与 Connect() 连接 四,Listen() 监听请求连接 和 Accept() 接收连接请求 五,Receive() 与 Se ...
- Hadoop HBase概念学习系列之HBase里的列式数据库(十七)
列式数据库,从数据存储方式上有别于行式数据库,所有数据按列存取. 行式数据库在做一些列分析时,必须将所有列的信息全部读取出来 而列式数据库由于其是按列存取,因此只需在特定列做I/O即可完成查询与分析, ...
- windows命令行大全
命令简介 cmd是command的缩写.即命令行 . 虽然随着计算机产业的发展,Windows 操作系统的应用越来越广泛,DOS 面临着被淘汰的命运,但是因为它运行安全.稳定,有的用户还在使用,所以一 ...
- 【转】【Flex】#010 操作XML文件(E4X)
该教程转载来自于:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-14767524-id-2785506.html [看到这边文章的位置,具体原作者未知] 经过一些排版的修改,其他内 ...
- Spring 源码阅读之BeanFactory
1. BeanFactory 的结构体系如下: 2. XmlBeanFactory ,装载Spring配置信息 package org.springframework.beans.factory.xm ...
- Ubuntu中文目录文件夹改为英文
打开终端,在终端中输入命令: export LANG=en_US xdg-user-dirs-gtk-update 在弹出的窗口中询问是否将目录转化为英文路径,同意并关闭. 在终端中输入命令: exp ...
