react 16 渲染整理
背景
老的react架构在渲染时会有一些性能问题,从setstate到render,程序一直在跑,一直到render完成。才能继续下一步操作。如果组件比较多,或者有复杂的计算逻辑,这之间的消耗的时间是比较多的。
假设更新一个组件需要1ms,如果有200个组件要更新,那就需要200ms,这200ms之间是不能响应的。如果这时候用户在input框输入什么东西,表现出来的就是明显的卡顿。
React这样的调度策略对动画的支持也不好。如果React更新一次状态,占用浏览器主线程的时间超过16.6ms,就会被人眼发觉前后两帧不连续,呈现出动画卡顿。
Fiber
react团队经过两年的工作,重写了react中核心算法reconciliation。并在v16版本中发布了这个新的特性。为了区别之前和之后的reconciler,通常将之前的reconciler称为stack reconciler,重写后的称为fiber reconciler,简称为Fiber。
区别
最大的变化就是支持了任务帧,把各个任务都增加了优先级,同步和异步。比如用户输入input是优先级比较高的,它可以打断低优先级的任务。
比如再处理dom diff的时候耗时严重,fiber任务处理大概会有50ms的帧时长,超过这个时间就会先去看看有没高优任务去做。然后回来做低优先级任务。
- 优先级高的任务可以中断低优先级的任务。
- 还增加了异步任务,调用requestIdleCallback api,浏览器空闲的时候执行。(不过用户操作默认是同步的,暂时还没开放这个特性)
- dom diff树变成了链表,一个dom对应两个fiber(一个链表),对应两个队列,这都是为找到被中断的任务,重新执行而设计的。
渲染流程
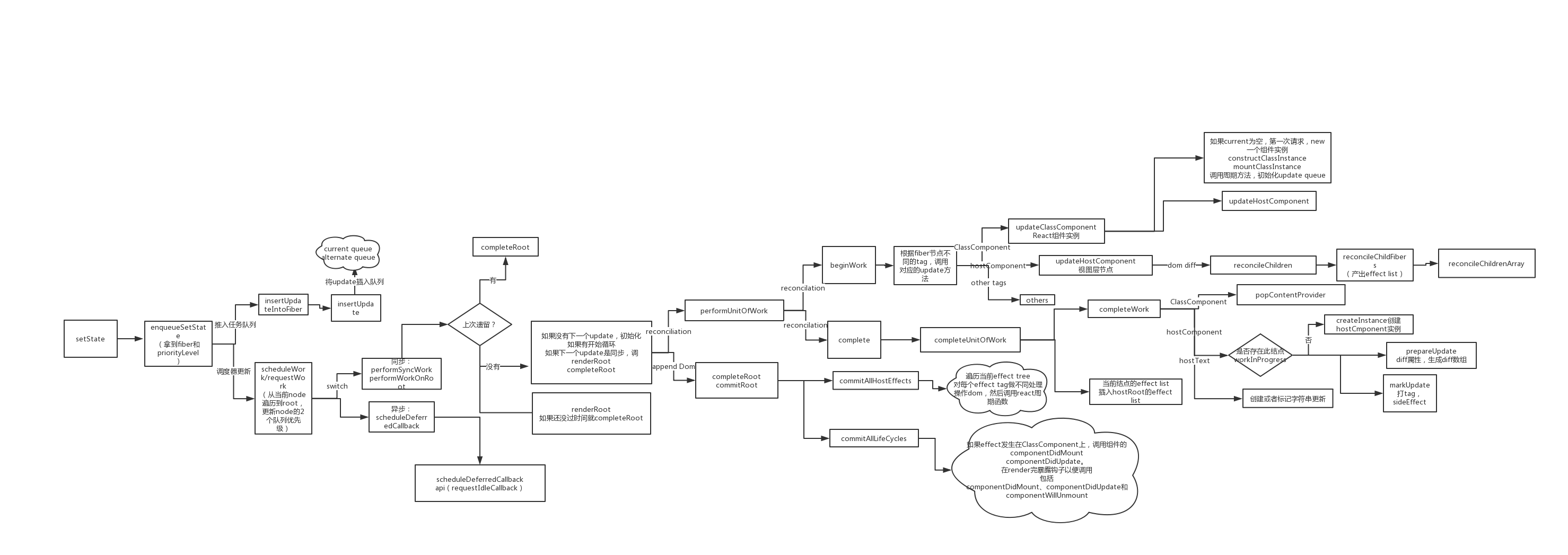
scheduleWork - requestWork - 同步/异步 - performSyncWork- performWork - performWorkOnRoot -
renderRoot/completeRoot - workLoop-performUnitOfWork-beginWork/completeUnitOfWork -updateClassComponent-reconcileChildrenAtExpirationTime- reconcileChildFibers-reconcileChildrenArray
源码基于react v16.3.0 (8e3d94ff)
setstate
Component.prototype.setState = function(partialState, callback) {
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, 'setState');
};
enqueueSetState
主要是把任务插入fiber的update queue,然后调度任务
enqueueSetState(instance, partialState, callback) {
const fiber = ReactInstanceMap.get(instance);
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(fiber);
const update = {
expirationTime,
partialState,
callback,
isReplace: false,
isForced: false,
capturedValue: null,
next: null,
};
insertUpdateIntoFiber(fiber, update);
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
},
insertUpdateIntoFiber
插入fiber两棵树的update queue
每个react 结点都有2个fiber链表,一个叫current fiber,一个叫alternate fiber,而每个链表又对应两个updateQueue。
而currentFiber.alternate = alternateFiber; alternateFiber.alternate = currentFiber。通过alternate属性连接起来。初始化的时候,alternate fiber是current fiber 的clone。
处理diff的时候,操作的是alternateFiber,处理完diff,让currentFiber = alternateFiber;这样一个处理就完成了。
scheduleWork
scheduleWork会更新每个节点的优先级,然后循环到root,以后的操作都从root开始遍历。
- expirationTime 优先级 expirationTime 不为 1 的时候,则其值越低,优先级越高。
{
NoWork: 0, // No work is pending.
SynchronousPriority: 1, // For controlled text inputs. Synchronous side-effects.
AnimationPriority: 2, // Needs to complete before the next frame.
HighPriority: 3, // Interaction that needs to complete pretty soon to feel responsive.
LowPriority: 4, // Data fetching, or result from updating stores.
OffscreenPriority: 5, // Won't be visible but do the work in case it becomes visible.
};
function scheduleWork(fiber: Fiber, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
return scheduleWorkImpl(fiber, expirationTime, false);
}
function scheduleWorkImpl(
fiber: Fiber,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
isErrorRecovery: boolean,
) {
recordScheduleUpdate(); // 记录更新,实际啥也没干
let node = fiber;
while (node !== null) {
// Walk the parent path to the root and update each node's
// expiration time.
// 更新每个node的优先级
if (
node.expirationTime === NoWork ||
node.expirationTime > expirationTime
) {
node.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
if (node.alternate !== null) {
if (
node.alternate.expirationTime === NoWork ||
node.alternate.expirationTime > expirationTime
) {
node.alternate.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
}
if (node.return === null) {
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
const root: FiberRoot = (node.stateNode: any);
if (
!isWorking &&
nextRenderExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
expirationTime < nextRenderExpirationTime
) {
// This is an interruption. (Used for performance tracking.)
interruptedBy = fiber;
resetStack();
}
if (
// If we're in the render phase, we don't need to schedule this root
// for an update, because we'll do it before we exit...
!isWorking ||
isCommitting ||
// ...unless this is a different root than the one we're rendering.
nextRoot !== root
) {
// Add this root to the root schedule.
requestWork(root, expirationTime);
}
} else {
}
return;
}
}
node = node.return;
}
}
requestWork
同步执行performSyncWork,异步执行scheduleCallbackWithExpiration,
scheduleCallbackWithExpiration会调浏览器的requestidlecallback,在浏览器空闲的时候进行处理。
react还对这个api做了polyfill
function requestWork(root: FiberRoot, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
if (isRendering) {
return;
}
if (isBatchingUpdates) { // 这里是BatchingUpdates的处理。
// Flush work at the end of the batch.
if (isUnbatchingUpdates) {
// ...unless we're inside unbatchedUpdates, in which case we should
// flush it now.
nextFlushedRoot = root;
nextFlushedExpirationTime = Sync;
performWorkOnRoot(root, Sync, false);
}
return;
}
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
performSyncWork();
} else {
scheduleCallbackWithExpiration(expirationTime);
}
}
performSyncWork 主要的任务调度
这里会找到高优任务先执行。
同步任务会直接调用performWorkOnRoot进行下一步,
异步任务也会调performWorkOnRoot,但处理不太一样
如果有上次遗留的任务,留到空闲时运行
function performSyncWork() {
performWork(Sync, false, null);
}
function performWork(
minExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
isAsync: boolean,
dl: Deadline | null,
) {
deadline = dl;
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (isAsync) {
while (
nextFlushedRoot !== null &&
nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
(minExpirationTime === NoWork ||
minExpirationTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime) &&
(!deadlineDidExpire ||
recalculateCurrentTime() >= nextFlushedExpirationTime)
) {
performWorkOnRoot(
nextFlushedRoot,
nextFlushedExpirationTime,
!deadlineDidExpire,
);
findHighestPriorityRoot();
}
} else {
while (
nextFlushedRoot !== null &&
nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
(minExpirationTime === NoWork ||
minExpirationTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime)
) {
performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, false);
findHighestPriorityRoot();
}
}
if (deadline !== null) {
callbackExpirationTime = NoWork;
callbackID = -1;
}
// If there's work left over, schedule a new callback.
if (nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork) {
scheduleCallbackWithExpiration(nextFlushedExpirationTime);
}
// Clean-up.
deadline = null;
deadlineDidExpire = false;
finishRendering();
}
performWorkOnRoot (异步任务和同步任务的异同)
如果有上次遗留,直接调用completeRoot进到渲染阶段。如果没有就调renderRoot开始reconcilation阶段。
异步任务主要是渲染的时候判断一下时间,如果没时间了,先把finishedWork赋给全局,下次循环处理。
function performWorkOnRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
isAsync: boolean,
) {
isRendering = true;
// Check if this is async work or sync/expired work.
if (!isAsync) {
// Flush sync work.
let finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// This root is already complete. We can commit it.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
root.finishedWork = null;
finishedWork = renderRoot(root, expirationTime, false);
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// We've completed the root. Commit it.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
}
}
} else {
// Flush async work.
let finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// This root is already complete. We can commit it.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
root.finishedWork = null;
finishedWork = renderRoot(root, expirationTime, true);
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// We've completed the root. Check the deadline one more time
// before committing.
if (!shouldYield()) {
// Still time left. Commit the root.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
// There's no time left. Mark this root as complete. We'll come
// back and commit it later.
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
}
}
}
}
isRendering = false;
}
renderRoot
如果是第一次进入,会创建一个nextUnitOfWork。
nextUnitOfWork是每个工作的粒度。
然后调用workLoop
function renderRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
isAsync: boolean,
): Fiber | null {
isWorking = true;
// Check if we're starting from a fresh stack, or if we're resuming from
// previously yielded work.
if (
expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime ||
root !== nextRoot ||
nextUnitOfWork === null
) {
// Reset the stack and start working from the root.
resetStack();
nextRoot = root;
nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime;
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(
nextRoot.current,
null,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork;
}
let didFatal = false;
startWorkLoopTimer(nextUnitOfWork);
do {
try {
workLoop(isAsync);
} catch (thrownValue) {
// ...
}
break;
} while (true);
// We're done performing work. Time to clean up.
// ...
}
workLoop
异步任务在处理的时候会调用shouldYield,shouldYield会判断是不是已经超时了,超时暂时先不做。
function workLoop(isAsync) {
if (!isAsync) {
// Flush all expired work.
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until the deadline runs out of time.
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYield()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}
function shouldYield() {
if (deadline === null) {
return false;
}
if (deadline.timeRemaining() > timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork) {
// Disregard deadline.didTimeout. Only expired work should be flushed
// during a timeout. This path is only hit for non-expired work.
return false;
}
deadlineDidExpire = true;
return true;
}
performUnitOfWork (reconcilation阶段)
reconcilation又分两步
1是beginWork,beginWork会开始处理组件,针对不同组件不同处理。包括dom diff
2 是completeUnitOfWork,completeUnitOfWork会对begin work产生的effect list进行一些处理。
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
startWorkTimer(workInProgress);
let next = beginWork(current, workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
if (next === null) {
next = completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
return next;
}
beginWork
主要是对react 组件进行一些操作。和调用一些生命周期,
我们主要关注classComponent,就是react的组件
HostConponent在浏览器下就是dom
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
if (
workInProgress.expirationTime === NoWork ||
workInProgress.expirationTime > renderExpirationTime
) {
return bailoutOnLowPriority(current, workInProgress);
}
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case FunctionalComponent:
return updateFunctionalComponent(current, workInProgress);
case ClassComponent:
return updateClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case HostComponent:
return updateHostComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
case HostText:
return updateHostText(current, workInProgress);
case ForwardRef:
return updateForwardRef(current, workInProgress);
case Fragment:
return updateFragment(current, workInProgress);
case Mode:
return updateMode(current, workInProgress);
case ContextProvider:
return updateContextProvider(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
case ContextConsumer:
return updateContextConsumer(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
default:
invariant(
false,
'Unknown unit of work tag. This error is likely caused by a bug in ' +
'React. Please file an issue.',
);
}
}
updateClassComponent
mount组件,构建组件实例,调用生命周期比如willMount,初始化组件的的updateQueue。
- updateClassInstance中,如果props不一致,会调willReceiveProps方法,然后checkShouldCompoentUpdate,也就是
shouldCompoentUpdate。 - finishClassComponent中,会判断之前的shouldUpdate,如果是true就要调用组件的render,产出children,然后对children进行dom diff。
function updateClassComponent(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {
// Push context providers early to prevent context stack mismatches.
// During mounting we don't know the child context yet as the instance doesn't exist.
// We will invalidate the child context in finishClassComponent() right after rendering.
const hasContext = pushLegacyContextProvider(workInProgress);
let shouldUpdate;
if (current === null) {
if (workInProgress.stateNode === null) {
// In the initial pass we might need to construct the instance.
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, workInProgress.pendingProps);
mountClassInstance(workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
shouldUpdate = true;
} else {
// In a resume, we'll already have an instance we can reuse.
shouldUpdate = resumeMountClassInstance(
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
} else {
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
let didCaptureError = false;
const updateQueue = workInProgress.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue !== null && updateQueue.capturedValues !== null) {
shouldUpdate = true;
didCaptureError = true;
}
return finishClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
shouldUpdate,
hasContext,
didCaptureError,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
reconcileChildFibers (virtul dom diff)
finishClassComponent会调用reconcileChildFibers进行dom diff。
function reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChild: any,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
if (
typeof newChild === 'object' &&
newChild !== null &&
newChild.type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE &&
newChild.key === null
) {
newChild = newChild.props.children;
}
// Handle object types
const isObject = typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null;
if (isObject) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
expirationTime,
),
);
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSinglePortal(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
expirationTime,
),
);
}
}
if (typeof newChild === 'string' || typeof newChild === 'number') {
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
'' + newChild,
expirationTime,
),
);
}
if (isArray(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
expirationTime,
);
}
if (getIteratorFn(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenIterator(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
expirationTime,
);
}
}
reconcileChildrenArray
大部分情况是reconcileChildrenArray,就那这个来说。
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChildren: Array<*>,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
let resultingFirstChild: Fiber | null = null;
let previousNewFiber: Fiber | null = null;
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
let newIdx = 0;
let nextOldFiber = null;
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
// 没有采用两端同时对比,受限于Fiber列表的单向结构
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot( // 生成新的fiber
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
expirationTime,
);
//如果在遍历中发现key值不相等的情况,则直接跳出第一轮遍历
if (newFiber === null) {
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (oldFiber && newFiber.alternate === null) {
// 我们找到了匹配的节点,但我们并不保留当前的Fiber,所以我们需要删除当前的子节点
// We matched the slot, but we didn't reuse the existing fiber, so we
// need to delete the existing child.
deleteChild(returnFiber, oldFiber);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
// 记录上一个更新的子节点
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
if (newIdx === newChildren.length) {
// 我们已经遍历完了所有的新节点,直接删除剩余旧节点
// We've reached the end of the new children. We can delete the rest.
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
return resultingFirstChild;
}
if (oldFiber === null) {
// 如果旧节点先遍历完,则按顺序插入剩余的新节点
// If we don't have any more existing children we can choose a fast path
// since the rest will all be insertions.
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = createChild(
returnFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
expirationTime,
);
if (!newFiber) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
// TODO: Move out of the loop. This only happens for the first run.
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}
// 把子节点都设置快速查找的map映射集
const existingChildren = mapRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
// 使用map查找需要保存或删除的节点
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = updateFromMap(
existingChildren,
returnFiber,
newIdx,
newChildren[newIdx],
expirationTime,
);
if (newFiber) {
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (newFiber.alternate !== null) {
// 新的Fiber也是一个工作线程,但是如果已有当前的实例,那我们就可以复用这个Fiber,
// 我们要从Map中删除这个新的,避免准备复用的Fiber被删除
existingChildren.delete(
newFiber.key === null ? newIdx : newFiber.key,
);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
// Any existing children that weren't consumed above were deleted. We need
// to add them to the deletion list.
// 到此所有剩余的Map的节点都将被删除,加入删除队列
existingChildren.forEach(child => deleteChild(returnFiber, child));
}
// 最终返回Fiber子节点列表的第一个节点
return resultingFirstChild;
}
可以看到其实删除节点并不是直接删除而是打个Deletion的tag。生成effect list
function deleteChild(returnFiber: Fiber, childToDelete: Fiber): void {
const last = returnFiber.lastEffect;
if (last !== null) {
last.nextEffect = childToDelete;
returnFiber.lastEffect = childToDelete;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = childToDelete;
}
childToDelete.nextEffect = null;
childToDelete.effectTag = Deletion;
}
completeUnitOfWork
在dom diff之后会有一个收尾工作大概就是effect的各种处理,就是workLoop之后的completeUnitOfWork函数。
同步effect list到 current 的host root 树。
调用completeWork
function completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
while (true) {
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
const returnFiber = workInProgress.return;
const siblingFiber = workInProgress.sibling;
if ((workInProgress.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect) {
// This fiber completed.
let next = completeWork(
current,
workInProgress,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
resetExpirationTime(workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
if (next !== null) {
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
if (__DEV__ && ReactFiberInstrumentation.debugTool) {
ReactFiberInstrumentation.debugTool.onCompleteWork(workInProgress);
}
// If completing this work spawned new work, do that next. We'll come
// back here again.
return next;
}
// 将当前fiber子树上的effect list 插入到当前hostRoot 树的effectlist中
if (
returnFiber !== null &&
// Do not append effects to parents if a sibling failed to complete
(returnFiber.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect
) {
// Append all the effects of the subtree and this fiber onto the effect
// list of the parent. The completion order of the children affects the
// side-effect order.
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
if (workInProgress.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress.lastEffect;
}
// If this fiber had side-effects, we append it AFTER the children's
// side-effects. We can perform certain side-effects earlier if
// needed, by doing multiple passes over the effect list. We don't want
// to schedule our own side-effect on our own list because if end up
// reusing children we'll schedule this effect onto itself since we're
// at the end.
const effectTag = workInProgress.effectTag;
// Skip both NoWork and PerformedWork tags when creating the effect list.
// PerformedWork effect is read by React DevTools but shouldn't be committed.
if (effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress;
}
}
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
return siblingFiber;
} else if (returnFiber !== null) {
// If there's no more work in this returnFiber. Complete the returnFiber.
workInProgress = returnFiber;
continue;
} else {
// We've reached the root.
isRootReadyForCommit = true;
return null;
}
} else {
// This fiber did not complete because something threw. Pop values off
// the stack without entering the complete phase. If this is a boundary,
// capture values if possible.
const next = unwindWork(workInProgress);
// Because this fiber did not complete, don't reset its expiration time.
if (workInProgress.effectTag & DidCapture) {
// Restarting an error boundary
stopFailedWorkTimer(workInProgress);
} else {
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
}
if (next !== null) {
stopWorkTimer(workInProgress);
if (__DEV__ && ReactFiberInstrumentation.debugTool) {
ReactFiberInstrumentation.debugTool.onCompleteWork(workInProgress);
}
// If completing this work spawned new work, do that next. We'll come
// back here again.
// Since we're restarting, remove anything that is not a host effect
// from the effect tag.
next.effectTag &= HostEffectMask;
return next;
}
if (returnFiber !== null) {
// Mark the parent fiber as incomplete and clear its effect list.
returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = null;
returnFiber.effectTag |= Incomplete;
}
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
return siblingFiber;
} else if (returnFiber !== null) {
// If there's no more work in this returnFiber. Complete the returnFiber.
workInProgress = returnFiber;
continue;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
return null;
}
completeWork
比较长,不贴代码了。主要做的事情就是根据不同的component类型进行不同的处理。
重点是对HostComponent的props进行diff,并标记更新。
如果是react首次渲染,调用createInstance创建一个HostComponent。
如果已经存在HostComponent,检查节点是否需要更新,调用prepareUpdate,进行diff dom属性。
到此reconciliation阶段结束,主要负责产出effect list。
可以说reconcile的过程相当于是一个纯函数,输入是fiber节点,输出一个effect list。
因为纯函数的可预测性,让我们可以随时中断reconciliation阶段的执行,而不用担心side-effects给让组件状态和实际UI产生不一致
渲染阶段 completeRoot/commitRoot
function commitRoot(finishedWork: Fiber): ExpirationTime {
isWorking = true;
isCommitting = true;
startCommitTimer();
const root: FiberRoot = finishedWork.stateNode;
const committedExpirationTime = root.pendingCommitExpirationTime;
root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork;
const currentTime = recalculateCurrentTime();
// Reset this to null before calling lifecycles
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
let firstEffect;
if (finishedWork.effectTag > PerformedWork) {
// fiber的effect list只包括它子树中的effects,将节点的effect加到effect list链表中
if (finishedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
finishedWork.lastEffect.nextEffect = finishedWork;
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
} else {
firstEffect = finishedWork;
}
} else {
// There is no effect on the root.
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
}
// 做一些dom事件相关设置
prepareForCommit(root.containerInfo);
// Commit all the side-effects within a tree. We'll do this in two passes.
// The first pass performs all the host insertions, updates, deletions and
// ref unmounts.
nextEffect = firstEffect;
startCommitHostEffectsTimer();
while (nextEffect !== null) {
let didError = false;
let error;
try {
// 遍历fiber树的effect list,调用相关的生命周期,比如willUnmount。操作dom,完成渲染。
commitAllHostEffects();
} catch (e) {
didError = true;
error = e;
}
}
stopCommitHostEffectsTimer();
resetAfterCommit(root.containerInfo);
root.current = finishedWork;
nextEffect = firstEffect;
startCommitLifeCyclesTimer();
while (nextEffect !== null) {
let didError = false;
let error;
try {
// 再遍历effect list,如果effect发生在classComponent上,加调didMount和didUpdate方法。
// 如果发生在hostComponents上,会调用commitMount方法,主要是为了在render一个节点渲染之后做一些操作。比如input的auto-focus。
commitAllLifeCycles(root, currentTime, committedExpirationTime);
} catch (e) {
didError = true;
error = e;
}
}
isCommitting = false;
isWorking = false;
stopCommitLifeCyclesTimer();
stopCommitTimer();
if (typeof onCommitRoot === 'function') {
onCommitRoot(finishedWork.stateNode);
}
const remainingTime = root.current.expirationTime;
if (remainingTime === NoWork) {
// If there's no remaining work, we can clear the set of already failed
// error boundaries.
legacyErrorBoundariesThatAlreadyFailed = null;
}
return remainingTime;
}
react 16 渲染整理的更多相关文章
- React 16 服务端渲染的新特性
React 16 服务端渲染的新特性 React 16 中关于服务端渲染的新特性 快速介绍React 16 服务端渲染的新特性,包括数组.性能.流等 React 16 终于来了!
- React服务器渲染最佳实践
源码地址:https://github.com/skyFi/dva-starter React服务器渲染最佳实践 dva-starter 完美使用 dva react react-router,最好用 ...
- Facebook发布React 16 专利条款改为MIT开源协议
9 月 26 日,用于构建 UI 的 JavaScript 库 React 16 的最新版本上线. Facebook 最终在现有的两种 React 版本中选择了出现 bug 概率最少的一款.这次版本更 ...
- React 16.x 新特性思维导图
React 16版本相对于以前的版本做了很大的改动,下面是我整理的React 16.x 新特性的思维导图文件,欢迎围观和指导:
- react 16 ssr的重构踩坑
ssr 服务端不能识别前端的window.特别是首屏渲染的数据需要用到window对象(比如href += location.search); 服务端不能加载图片,css文件. require.ext ...
- React 16 加载性能优化指南
关于 React 应用加载的优化,其实网上类似的文章已经有太多太多了,随便一搜就是一堆,已经成为了一个老生常谈的问题. 但随着 React 16 和 Webpack 4.0 的发布,很多过去的优化手段 ...
- 盘点 React 16.0 ~ 16.5 主要更新及其应用
目录 0. 生命周期函数的更新 1. 全新的 Content API 2. React Strict Mode 3. Portal 4. Refs 5. Fragment 6. 其他 7. 总结 生命 ...
- React 16.3.0 发布,构建用户界面的 JavaScript 库
React 16.3.0 已发布,React 是 Facebook 推出的一个为数据提供渲染为 HTML 视图,用来构建用户界面的开源 JavaScript 库. React 视图通常采用包含以自定义 ...
- React 服务器渲染原理解析与实践
第1章 服务器端渲染基础本章主要讲解客户端与服务器端渲染的概念,分析客户端渲染和服务器端渲染的利弊,带大家对服务器端渲染有一个粗浅认识. 1-1 课程导学1-2 什么是服务器端渲染1-3 什么是客户端 ...
随机推荐
- F#周报2019年第24期
新闻 ML.NET 1.1发布与模型构建器升级 .NET Core 3.0预览版6发布 尝试新的System.Text.Json API F#调用Infer.NET 匿名记录类型文档 了解FableC ...
- Node.js能解决什么问题?
一.使用Node.js能解决什么问题 对于PHP.JAVA.Python等服务端语言中,为每个客户端连接创建一个新的线程,而每个线程需要大约2M的内存,理论上,具有8GB内存的服务器可以同时连接的最大 ...
- ABP中文网的一些BUG
之前一些翻译了的文档没有及时更新.比如 IAsyncCrudAppService接口在很久之前的版本就已经改为了ICrudAppService,如果是在官网下载的最新实例中IAsyncCrudAppS ...
- Linux帮助——获取帮助
Linux帮助——获取帮助 摘要:本文主要学习了Linux众多命令中最基础的帮助命令. 介绍 作用 Linux的所有操作都可以通过命令行来完成,所以学习Linux最好从命令行开始.因为Linux的命令 ...
- DevExpress的TreeList怎样给树节点设置图标
场景 DevExpress的TreeList怎样设置数据源使其显示成单列树形结构: https://blog.csdn.net/BADAO_LIUMANG_QIZHI/article/details/ ...
- 学习shiro第一天
shiro是一个强大而且易用的安全框架(主要包括认证和授权),它比spring security更加简单,而且它不依赖于任何容器,可以和许多框架集成. shiro的核心是安全管理器(SecurityM ...
- 拥抱小程序,WeTest小程序全链路测试解决方案正式上线
背景 随着微信开放小程序开发功能,迅速在各个实体店抢占流量入口,广大商家看到了在线和离线的机会整合,利用小程序版本特点低成本进入市场,达到流量的获取和转化. 伴随着资本的进入,小程序开发市场也因此越来 ...
- HTTP Protocol
HTTP协议 1 HTTP请求状态码 当用户试图通过 HTTP 访问一台正在运行 Internet 信息服务 (IIS) 的服务器上的内容时,IIS 返回一个表示该请求的状态的数字代码.状态 ...
- SAP S4HANA BP事务代码初始界面的ROLE和Grouping配置
SAP S4HANA BP事务代码初始界面的ROLE和Grouping配置 SAP S/4 HANA系统里,创建供应商不再使用MK01/FK01/XK01等事务代码,而是使用BP事务代码. BP事务代 ...
- 车间如何数字化?MES系统来助力
对于生产过程复杂多变的离散制造企业而言,面临重重考验:生产作业计划频繁变更,制造工艺复杂,在生产过程中的临时插单.材料短缺等现象.通过MES制造执行管理解决方案,搭建协同管理平台,加强控制力.执行力和 ...
