spring深入学习(四)-----spring aop
AOP概述
aop其实就是面向切面编程,举个例子,比如项目中有n个方法是对外提供http服务的,那么如果我需要对这些http服务进行响应时间的监控,按照传统的方式就是每个方法中添加相应的逻辑,但是这些逻辑是重复的,我无非是需要记录请求的时间以及响应时间,另外可能需要加上请求入参以及响应出参。这时候就可以把这些http服务看成切面,通过aop的方式在方法前和方法后去做点什么操作。
aop的实现者有很多,包括AspectJ、Spring AOP等等,当然我们重点就放在Spring aop上了。
在spring中,aop可以由jdk动态代理或cglib实现,这地方的示例可以看下本人之前的文章了动态代理
jdk动态代理跟cglib有个重要的区别就是jdk动态代理的类必须要实现了某个接口,但是cglib则没这个要求。
针对cglib,举例如下:
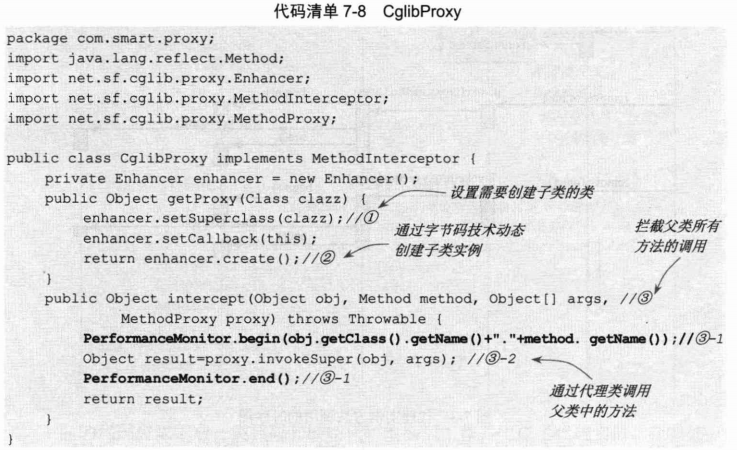
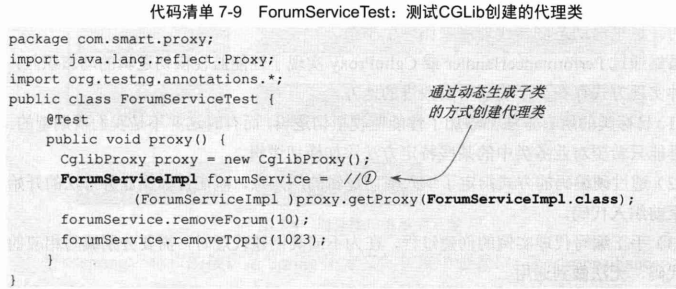
spring aop简单示例
业务代码
@Component("knight")
public class BraveKnight {
public void saying(){
System.out.println("我是骑士..(切点方法)");
}
}
package com.cjh.aop2; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 注解方式声明aop
* 1.用@Aspect注解将类声明为切面(如果用@Component("")注解注释为一个bean对象,那么就要在spring配置文件中开启注解扫描,<context:component-scan base-package="com.cjh.aop2"/>
* 否则要在spring配置文件中声明一个bean对象)
* 2.在切面需要实现相应方法的前面加上相应的注释,也就是通知类型。
* 3.此处有环绕通知,环绕通知方法一定要有ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数传入,然后执行对应的proceed()方法,环绕才能实现。
*/
@Component("annotationTest")
@Aspect
public class AnnotationTest {
//定义切点
@Pointcut("execution(* *.saying(..))")
public void sayings(){}
/**
* 前置通知(注解中的sayings()方法,其实就是上面定义pointcut切点注解所修饰的方法名,那只是个代理对象,不需要写具体方法,
* 相当于xml声明切面的id名,如下,相当于id="embark",用于供其他通知类型引用)
* <aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="mistrel">
<!-- 定义切点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *.saying(..))" id="embark"/>
<!-- 声明前置通知 (在切点方法被执行前调用) -->
<aop:before method="beforSay" pointcut-ref="embark"/>
<!-- 声明后置通知 (在切点方法被执行后调用) -->
<aop:after method="afterSay" pointcut-ref="embark"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
*/
@Before("sayings()")
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("注解类型前置通知");
}
//后置通知
@After("sayings()")
public void sayGoodbey(){
System.out.println("注解类型后置通知");
}
//环绕通知。注意要有ProceedingJoinPoint参数传入。
@Around("sayings()")
public void sayAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("注解类型环绕通知..环绕前");
pjp.proceed();//执行方法
System.out.println("注解类型环绕通知..环绕后");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 开启注解扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cjh.aop2"/>
<!-- 开启aop注解方式,此步骤不能少,这样java类中的aop注解才会生效 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
测试:
package com.cjh.aop2; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/cjh/aop2/beans.xml");
BraveKnight br = (BraveKnight) ac.getBean("knight");
br.saying();
}
}
自动创建代理
1、BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
通过名字就可以看出来是干嘛的,可以根据bean的名字来创建自动代理,示例如下:
业务类:
public interface UserService {
void print();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void print(){
System.out.println(getClass()+"#print");
}
}
拦截器:
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(getClass()+"调用方法前");
Object ret=invocation.proceed();
System.out.println(getClass()+"调用方法后");
return ret;
}
}
配置类:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
//要创建代理的目标Bean
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
//创建Advice或Advisor
@Bean
public Advice myMethodInterceptor(){
return new MyMethodInterceptor();
}
//使用BeanNameAutoProxyCreator来创建代理
@Bean
public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator(){
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator=new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator();
//设置要创建代理的那些Bean的名字
beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setBeanNames("userSer*");
//设置拦截链名字(这些拦截器是有先后顺序的)
beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setInterceptorNames("myMethodInterceptor");
return beanNameAutoProxyCreator;
}
}
测试:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService= applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.print();
}
}
自定义注解+BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
基于上面说的,对一些http接口做个响应时间监控,先以一个接口为例吧!
注解(PerformanceMonitor):
package com.ty.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; //代表此注解是运行过程中生效
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//此注解作用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface PerformanceMonitor {
String value() default "";
}
AnnotationController:
package com.ty.controller; import com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller
public class AnnotationController { @PerformanceMonitor
public String testServer() {
System.out.println("do someThing");
return "test";
}
}
BeanNameAutoProxyConfig:
package com.ty.configuration; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
public class BeanNameAutoProxyConfig { @Bean
public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator create() {
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator = new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator();
//为所有的controller创建自动动态代理
beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setBeanNames("*Controller");
//代理的具体的业务逻辑交给bean-----performanceInterceptor
beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setInterceptorNames("performanceInterceptor");
return beanNameAutoProxyCreator;
}
}
PerformanceInterceptor:
package com.ty.interceptor;
import com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.lang.reflect.Method; @Service
public class PerformanceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
//判断被代理类的方法上是否使用了@PerformanceMonitor注解
PerformanceMonitor performanceMonitor = methodInvocation.getMethod().getAnnotation(PerformanceMonitor.class);
if(performanceMonitor != null) {
//具体的代理逻辑,实现aop的效果
System.out.println("----------before----" + methodInvocation.getMethod().getName());
result = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("----------after----" + methodInvocation.getMethod().getName() + ";该笔调用耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - t1) + "ms");
}else {
//不使用该注解,则走原方法的调用逻辑
result = methodInvocation.proceed();
}
return result;
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--自动扫描包配置-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ty"/> <bean id="student" class="com.ty.beans.Student">
<!-- property代表的是set方法注入-->
<property name="age" value="27"></property>
<property name="name" value="马云"></property>
</bean> <bean id="school" class="com.ty.beans.School">
<!-- constructor代表的是构造器注入-->
<constructor-arg ref="student"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类:
package com.ty.beans; import com.ty.controller.AnnotationController;
import javafx.application.Application;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:applicationContext.xml" })
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class IOCTest { @Test
public void testAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
AnnotationController annotationController = (AnnotationController) context.getBean("annotationController");
annotationController.testServer();
}
}
运行结果:
----------before----testServer
do someThing
----------after----testServer;该笔调用耗时:8ms
这样也就实现了性能监控的目的,并且以后项目中所有的controller的接口,只要需要这个功能,加个注解即可。
@AspectJ
基于@AspectJ实现aop是相对简单的方式,上面也有类似的案例,下面详细的说说这个玩意。
aop主要包括切面、切入点、增强方法等核心组成部分。
1、切面
//用来声明这是一个AspectJ
@Aspect
//在此处声明一个Component 是因为Spring扫描注解并不能识别AspectJ 因此在此处声明,不必在applicationContext.xml配置bean标签了
@Component
public class ServiceLog {
。。。
}
2、切入点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.sample.service.impl..*.*(..))")
public void pc() {}
a、execution()是最常用的切点函数,整个表达式可以分为五个部分,其语法如下所示:
- execution(): 表达式主体。
- 第一个*号:表示返回类型,*号表示所有的类型。
- 包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.sample.service.impl包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
- 第二个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有的类。
- *(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。
b、@annotation
另外切入点中的execution()也可以用@Annotation代替,如下:
@AfterReturning("@annotation(com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor)")
public void needTestFun() {
System.out.println("可以对注明@PerformanceMonitor的方法进行增强");
}
对于所有注明@PerformanceMonitor的方法进行增强。
或者还有一种用法,可以方便拿到注解上的信息
@Around(value = "@annotation(apiOperation)")
public Object logApiCallInfo(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, ApiOperation apiOperation) {
//TODO 1、这里方便拿到注解的信息。不过注意@annotation(apiOperation)名称要与参数名称一致
String apiCode = apiOperation.value(); //TODO 调用业务接口
result = joinPoint.proceed(); //TODO 获取接口请求参数,并拼装成json,格式化输出
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
String[] parameterNames = methodSignature.getParameterNames();
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
if(parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length > 0 && args != null && args.length > 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; i++) {
jsonObject.put(parameterNames[i], args[i]);
}
//标准化输出
jsonObject.toJsonString();
}
}
3、增强方法
//环绕通知注解,pc()则是上面的pointcut切入点
@Around("pc()")
//环绕通知会多ProceedingJoinPoint这个参数
public Object log(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
。。。
}
- @Before
- @AfterReturning
- @Around
- @AfterThrowing
- @After
4、applicationContext.xml
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
spring深入学习(四)-----spring aop的更多相关文章
- (转)SpringMVC学习(四)——Spring、MyBatis和SpringMVC的整合
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/72231763 之前我整合了Spring和MyBatis这两个框架,不会的可以看我的文章MyBa ...
- Spring的第四天AOP之注解版
Spring的第四天AOP之注解版 ssm框架 spring 在上一篇博客中,介绍了Spring的AOP的xml版本的使用,在这篇博客中,我将介绍一下,注解版的使用. 常用注解 注解 通知 @Aft ...
- Spring Boot 项目学习 (四) Spring Boot整合Swagger2自动生成API文档
0 引言 在做服务端开发的时候,难免会涉及到API 接口文档的编写,可以经历过手写API 文档的过程,就会发现,一个自动生成API文档可以提高多少的效率. 以下列举几个手写API 文档的痛点: 文档需 ...
- Spring Cloud 学习 之 Spring Cloud Eureka(源码分析)
Spring Cloud 学习 之 Spring Cloud Eureka(源码分析) Spring Boot版本:2.1.4.RELEASE Spring Cloud版本:Greenwich.SR1 ...
- Spring Cloud 学习 之 Spring Cloud Eureka(搭建)
Spring Boot版本:2.1.4.RELEASE Spring Cloud版本:Greenwich.SR1 文章目录 搭建服务注册中心: 注册服务提供者: 高可用注册中心: 搭建服务注册中心: ...
- [ SSH框架 ] Spring框架学习之三(AOP开发和注解的使用)
一.Spring 使用 AspectJ 进行 AOP 的开发:注解的方式 1.1 引入相关的jar包 1.2 引入spring的配置文件 <?xml version="1.0" ...
- Spring的学习(IoC,AOP)等
下面这个系列是非常好的例子: http://www.yiibai.com/spring/spring-3-hello-world-example.html 正在看,把一些基础夯实. IoC可以从下面一 ...
- spring boot 学习(四)Druid连接池的使用配置
Druid介绍 Druid是一个JDBC组件,druid 是阿里开源在 github 上面的数据库连接池,它包括三部分: * DruidDriver 代理Driver,能够提供基于Filter-Cha ...
- Spring Cloud学习笔记--Spring Boot初次搭建
1. Spring Boot简介 初次接触Spring的时候,我感觉这是一个很难接触的框架,因为其庞杂的配置文件,我最不喜欢的就是xml文件,这种文件的可读性很不好.所以很久以来我的Spring学习都 ...
随机推荐
- 一个suse11 sp1的crash工具版本问题
这几年排查的各种类型的crash也比较多了,各种类型的也算见过,但是排查这个crash,走了不该走的弯路,事后显得很low,为了防止自己犯类似错误,也同时提醒后人,记录之. 内核是suse11,sp1 ...
- 两个对象的 hashCode()或equals相同,equals或hashCode不一定相同--《案例演示》
两个对象的 hashCode()或equals相同,equals或hashCode不一定相同 1.两个对象的equals相同,hashCode不一定相同 在重写equals方法,未重写hashCode ...
- Habits of Considerate People
Habits of Considerate People体贴人的八种习惯哲学家亚瑟·叔本华曾经说过:“蜡之可贵,在于燃烧自己温暖他人,人之可贵,在于屈尊敬贤彬彬有礼”,事实的确如此.善意与体贴能够抚慰 ...
- java split方法
String a = "O|O||"; System.out.println(a.split("\\|").length); //["O", ...
- python基础系列教程,数学基础系列教程,数据分析系列教程,神经网络系列教程,深度学习系列视频教程分享交流
大家好,我是一个技术爱好者,目前对大数据人工智能很是痴迷,虽然学历只有高中,目前正在大踏步的向着人工智能狂奔,如果你也想学习,那就来吧 我的学习进度python基础(Numpy,pandas,matp ...
- KCF:High-Speed Tracking with Kernelized Correlation Filters 的翻译与分析(一)。分享与转发请注明出处-作者:行于此路
High-Speed Tracking with Kernelized Correlation Filters 的翻译与分析 基于核相关滤波器的高速目标跟踪方法,简称KCF 写在前面,之所以对这篇文章 ...
- C#中生成GUID的四种格式
var uuid = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); // 9af7f46a-ea52-4aa3-b8c3-9fd484c2af12 var uuidN = Guid.NewGu ...
- 复杂JSON对象的查询与合并
一个表里存放了全国各地地区.省.市.县区的数据,为了提高加载速度我保存成了本地的JSON文件 结构大致如下: [{ "text": "中华人民共和国", &qu ...
- Linux中Nginx安装教程
Nginx 是一个很强大的高性能Web和反向代理服务器,它具有很多非常优越的特性: 在连接高并发的情况下,Nginx是Apache服务器不错的替代品:Nginx在美国是做虚拟主机生意的老板们经常选择的 ...
- Android 网络编程的陷阱
陷阱一,不要在主线程或者UI线程中建立网络连接 Androd4.0以后,不允许在主线程中建立网络连接,不然会出现莫名其妙的程序退出情况.正确的做法是在主线程中,创建新的线程来运行网络连接程序. // ...
