算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.4
写在前面
整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
这一节内容可能会用到的库文件有 Measurement 和 TestCase,同样在 Github 上可以找到。
善用 Ctrl + F 查找题目。
习题&题解
1.4.1
解答
即为证明组合计算公式:
C(N, 3)
= N! / [(N - 3)! × 3!]
= [(N - 2) * (N - 1) * N] / 3!
= N(N - 1)(N - 2) / 6
显然 N 必须大于等于 3。
N = 3 时公式正确,只有一种组合。
N = 4 时公式正确,只有四种组合。
扩展到 N+1 个数,将 N = N + 1 代入,可得:
(N + 1)N(N - 1) / 6
N + 1 个数能组成的三位数组合可以这样理解
前 N 个数中取三个数的所有组合 +多出的一个数和前 N 个数中的任意取两个数的所有组合
即为 N(N-1)(N - 2) / 6 + C(N, 2)
变形后即为(N + 1)N(N - 1) / 6
得证。
1.4.2
解答
将 a[i] + a[j] + a[k] 改为 (long)a[i] + a[j] + a[k] 即可。
此时整个式子将按照精度最高(也就是 long)的标准计算。
long.MaxValue = 9223372036854775807 > int.MaxValue * 3 = 6442450941
代码
- namespace Measurement
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用暴力方法寻找数组中和为零的三元组。
- /// </summary>
- public static class ThreeSum
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 输出所有和为零的三元组。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">输入数组。</param>
- public static void PrintAll(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = i + ; j < n; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = j + ; k < n; ++k)
- {
- if ((long)a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == )
- {
- Console.WriteLine($"{a[i]} + {a[j]} + {a[k]}");
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 计算和为零的三元组的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">输入数组。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static int Count(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- int count = ;
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = i + ; j < n; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = j + ; k < n; ++k)
- {
- if ((long)a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == )
- {
- count++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.3
解答
见代码,这里贴出绘图函数,窗体只是在得到测试结果之后简单调用以下这两个函数。
代码
- public static void PaintLinear(double[] testResult)
- {
- //新建一个绘图窗口
- Form2 linear = new Form2();
- linear.Show();
- //新建画布
- Graphics canvas = linear.CreateGraphics();
- //获取窗口区域
- Rectangle rect = linear.ClientRectangle;
- //计算单位长度(十等分)
- int unitY = rect.Height / ;
- int unitX = rect.Width / ;
- //获取中心区域(上下左右增加 10% 的内补)
- Rectangle center = new Rectangle(rect.X + unitX, rect.Y + unitY, unitX * , unitY * );
- //绘制坐标系
- canvas.DrawLine(Pens.Black, center.X, center.Y, center.X, center.Y + center.Height);
- canvas.DrawLine(Pens.Black, center.X, center.Y + center.Height, center.X + center.Width, center.Y + center.Height);
- //对 X 轴 10 等分,对 Y 轴 10 等分
- int xaxisUnit = center.Width / ;
- int yaxisUnit = center.Height / ;
- //标记 X 轴坐标值
- for (int i = ; i <= ; i += i)
- {
- canvas.DrawString(i + "N", linear.Font, Brushes.Black, center.X + i * xaxisUnit, center.Y + center.Height);
- }
- //反转坐标系
- canvas.TranslateTransform(, linear.ClientRectangle.Height);
- canvas.ScaleTransform(, -);
- //计算单位长度
- double Unit = center.Height / testResult[];
- //标记
- PointF[] result = new PointF[];
- for (int i = , j = ; i < && j <= ; ++i, j += j)
- {
- result[i] = new PointF(center.X + j * xaxisUnit, (float)(center.Y + Unit * testResult[i]));
- }
- //链接
- canvas.DrawLines(Pens.Black, result);
- canvas.Dispose();
- }
- public static void PaintLogarithm(double[] testResult)
- {
- //新建一个绘图窗口
- Form2 log = new Form2();
- log.Show();
- //新建画布
- Graphics canvas = log.CreateGraphics();
- //获取窗口区域
- Rectangle rect = log.ClientRectangle;
- //计算单位长度(十等分)
- int unitY = rect.Height / ;
- int unitX = rect.Width / ;
- //获取中心区域(上下左右增加 10% 的内补)
- Rectangle center = new Rectangle(rect.X + unitX, rect.Y + unitY, unitX * , unitY * );
- //绘制坐标系
- canvas.DrawLine(Pens.Black, center.X, center.Y, center.X, center.Y + center.Height);
- canvas.DrawLine(Pens.Black, center.X, center.Y + center.Height, center.X + center.Width, center.Y + center.Height);
- //对 X 轴 10 等分,对 Y 轴 10 等分
- int xaxisUnit = center.Width / ;
- int yaxisUnit = center.Height / ;
- //标记 X 轴坐标值
- for (int i = ; i <= ; i += i)
- {
- canvas.DrawString(i + "N", log.Font, Brushes.Black, center.X + i * xaxisUnit, center.Y + center.Height);
- }
- //反转坐标系
- canvas.TranslateTransform(, log.ClientRectangle.Height);
- canvas.ScaleTransform(, -);
- //计算单位长度
- double Unit = center.Height / testResult[];
- //标记
- PointF[] result = new PointF[];
- for (int i = , j = ; i < && j <= ; ++i, j += j)
- {
- result[i] = new PointF(center.X + j * xaxisUnit, (float)(center.Y + Unit * testResult[i]));
- }
- //链接
- canvas.DrawLines(Pens.Black, result);
- canvas.Dispose();
- }
1.4.4
解答
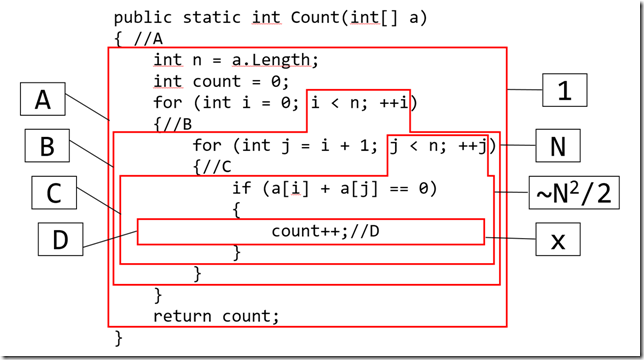
代码分块↑
时间分析↓

1.4.5
解答
类似于取极限的做法。
a. N
b. 1
c. 1
d. 2N3
e. 1
f. 2
g. N100
1.4.6
解答
a. N + N/2 + N/4 + … = ~2N,线性。
b. 1 + 2 + 4 + … = ~2N,线性。
c. logN * N,线性对数。
1.4.7
解答
最外层循环进行了 N 次比较。
次外层循环进行了 N^2 次比较。
最里层循环进行了 N^3 次比较。
内部 if 语句进行了 N^3 次比较。
if 内部进行了 N(N-1) 次加法。
加起来,~2N^3。
1.4.8
解答
平方级别:直接二层循环遍历一遍。
线性对数:只遍历一遍数组,在遍历过程中用二分查找确认在剩余数组中是否有相等的整数。
代码
- /// <summary>
- /// 暴力查找数组中相等的整数对。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">需要查找的数组。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static int CountEqual(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- int count = ;
- for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
- {
- for (int j = i + ; j < n; j++)
- {
- if (a[i] == a[j])
- count++;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
暴力算法↑
二分查找算法↓
- /// <summary>
- /// 利用 Array.Sort 进行优化的查找相等整数对算法。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">需要查找的数组。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static int CountEqualLog(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- int count = ;
- Array.Sort(a);
- int dup = ; // dup = 重复元素数量-1
- for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
- {
- while (a[i - ] == a[i])
- {
- dup++;
- i++;
- }
- count += dup * (dup + ) / ;
- dup = ;
- }
- return count;
- }
1.4.9
解答

1.4.10
解答
修改二分查找的结束条件,找到后仍然向左侧寻找,如果还能找到更小的,则返回较小的下标;否则返回当前下标。
代码
- namespace _1._4._10
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- public class BinarySearch
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用递归方法进行二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">关键字。</param>
- /// <param name="a">查找范围。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找的起始下标。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找的结束下标。</param>
- /// <returns>返回下标,如果没有找到则返回 -1。</returns>
- public static int Rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi)
- {
- if (hi < lo)
- return -;
- int mid = (hi - lo) / + lo;
- if (a[mid] == key)
- {
- int mini = Rank(key, a, lo, mid - );
- if (mini != -)
- return mini;
- return mid;
- }
- else if (a[mid] < key)
- {
- return Rank(key, a, mid + , hi);
- }
- else
- {
- return Rank(key, a, lo, mid - );
- }
- }
- }
- }
1.4.11
解答
这里给出官网上的 Java 实现:StaticSETofInts.java。
howMany() 可以用二分查找实现,在找到一个值后继续向两侧查找,最后返回找到的次数。
代码
- using System;
- namespace Measurement
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 有序数组,能够快速查找并自动维护其中的顺序。
- /// </summary>
- public class StaticSETofInts
- {
- private int[] a;
- /// <summary>
- /// 用一个数组初始化有序数组。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="keys">源数组。</param>
- public StaticSETofInts(int[] keys)
- {
- this.a = new int[keys.Length];
- for (int i = ; i < keys.Length; ++i)
- {
- this.a[i] = keys[i];
- }
- Array.Sort(this.a);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查数组中是否存在指定元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">要查找的值。</param>
- /// <returns>存在则返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
- public bool Contains(int key)
- {
- return Rank(key, , this.a.Length - ) != -;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回某个元素在数组中存在的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <returns>返回某个元素在数组中存在的数量。</returns>
- public int HowMany(int key)
- {
- int hi = this.a.Length - ;
- int lo = ;
- return HowMany(key, lo, hi);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回某个元素在数组中存在的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找起始下标。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找结束下标。</param>
- /// <returns>返回某个元素在数组中存在的数量。</returns>
- private int HowMany(int key, int lo, int hi)
- {
- int mid = Rank(key, lo, hi);
- if (mid == -)
- return ;
- else
- {
- return + HowMany(key, lo, mid - ) + HowMany(key, mid + , hi);
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找的起始下标。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找的结束下标。</param>
- /// <returns>返回关键值的下标,如果不存在则返回 -1。</returns>
- public int Rank(int key, int lo, int hi)
- {
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = (hi - lo) / + lo;
- if (key < this.a[mid])
- hi = mid - ;
- else if (key > this.a[mid])
- lo = mid + ;
- else
- return mid;
- }
- return -;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.12
解答
由于两个数组都是有序的,可以同时进行比较。
设 i, j 分别为两个数组的下标。
如果 a[i] == a[j],i 和 j 都向后移动一位。
如果 a[i] != a[j],比较小的那个向后移动一位。
循环直到某个数组遍历完毕。
这样最后的时间复杂度 ~2N
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._12
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.12
- *
- * 编写一个程序,有序打印给定的两个有序数组(含有 N 个 int 值) 中的所有公共元素,
- * 程序在最坏情况下所需的运行时间应该和 N 成正比。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] a = new int[] { , , , };
- int[] b = new int[] { , , , , , };
- //2N 次数组访问,数组 a 和数组 b 各遍历一遍
- for (int i = , j = ; i < a.Length && j < b.Length; )
- {
- if (a[i] < b[j])
- {
- i++;
- }
- else if (a[i] > b[j])
- {
- j++;
- }
- else
- {
- Console.WriteLine($"Common Element:{a[i]}, First index: (a[{i}], b[{j}])");
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
1.4.13
解答
对象的固定开销用 Object 表示。
a. Accumulator
使用 1.2.4.3 节给出的实现。
= int * 1 + double + Object * 1
= 4 * 1 + 8 + 16 * 1 = 32
b. Transaction
= string * 1 + Date * 1 + double * 1 + Object * 1
= (40 + 16 + 4 + 4 + 2N) * 1 + (8 + 32) * 1 + 8 * 1 + 16 * 1
= 128 + 2N
c. FixedCapacityStackOfStrings
= string[] * 1 + string * N + int * 1 + Object * 1
= 24 * 1 + N * (64 + 2C) + 4 * 1 + 16 * 1
= N * (64 + 2C) + 44
= N * (64 + 2C) + 48(填充)
d.Point2D
= double * 2 + Object * 1
= 8 * 2 + 16 * 1
= 32
e.Interval1D
= double * 2 + Object * 1
= 8 * 2 + 16 * 1
= 32
f.Interval2D
= Interval1D * 2 + Object * 1
= (8 + 24) * 2 + 16 * 1
= 80
g.Double
= double * 1 + Object * 1
= 8 * 1 + 16 * 1
= 24
1.4.14
解答
这里给出暴力方法,将最内侧循环换成二分查找即为优化版本。
代码
- using System;
- namespace Measurement
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用暴力方法查找数组中和为零的四元组。
- /// </summary>
- public static class FourSum
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 输出数组中所有和为 0 的四元组。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">包含所有元素的数组。</param>
- public static void PrintAll(long[] a)
- {
- int N = a.Length;
- for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = i + ; j < N; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = j + ; k < N; ++k)
- {
- for (int l = k + ; l < N; ++l)
- {
- if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] + a[l] == )
- {
- Console.WriteLine($"{a[i]} + {a[j]} + {a[k]} + {a[l]} = 0");
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 计算和为零的四元组的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">包含所有元素的数组。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static int Count(long[] a)
- {
- int N = a.Length;
- int cnt = ;
- for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = i + ; j < N; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = j + ; k < N; ++k)
- {
- for (int l = k + ; l < N; ++l)
- {
- if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] + a[l] == )
- {
- cnt++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return cnt;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.15
解答
由于数组已经排序(从小到大),负数在左侧,正数在右侧。
TwoSumFaster
设最左侧下标为 lo,最右侧下标为 hi。
如果 a[lo] + a[hi] > 0, 说明正数太大,hi--。
如果 a[lo] + a[hi] < 0,说明负数太小,lo++。
否则就找到了一对和为零的整数对,lo++, hi--。
ThreeSumFaster
对于数组中的每一个数 a,ThreeSum 问题就等于求剩余数组中所有和为 -a 的 TwoSum 问题。
只要在 TwoSumFaster 外层再套一个循环即可。
代码
- /// <summary>
- /// TwoSum 的快速实现。(线性级别)
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">需要查找的数组范围。</param>
- /// <returns>数组中和为零的整数对数量。</returns>
- static int TwoSumFaster(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = a.Length - ;
- int count = ;
- while (lo < hi)
- {
- if (a[lo] + a[hi] == )
- {
- count++;
- lo++;
- hi--;
- }
- else if (a[lo] + a[hi] < )
- {
- lo++;
- }
- else
- {
- hi--;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// ThreeSum 的快速实现。(平方级别)
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">需要查找的数组范围。</param>
- /// <returns>数组中和为零的三元组数量。</returns>
- static int ThreeSumFaster(int[] a)
- {
- int count = ;
- for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
- {
- int lo = i + ;
- int hi = a.Length - ;
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- if (a[lo] + a[hi] + a[i] == )
- {
- count++;
- lo++;
- hi--;
- }
- else if (a[lo] + a[hi] + a[i] < )
- {
- lo++;
- }
- else
- {
- hi--;
- }
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
1.4.16
解答
先将数组从小到大排序,再遍历一遍即可得到差距最小的两个数。
排序算法需要消耗 NlogN,具体见 MSDN:Array.Sort 方法 (Array)。
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._16
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.16
- *
- * 最接近一对(一维)。
- * 编写一个程序,给定一个含有 N 个 double 值的数组 a[],
- * 在其中找到一对最接近的值:两者之差(绝对值)最小的两个数。
- * 程序在最坏情况下所需的运行时间应该是线性对数级别的。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- //总运行时间: NlogN + N = NlogN
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- double[] a = new double[] { 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 0.8, };
- Array.Sort(a);//Nlog(N) 具体见 https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/6tf1f0bc(v=vs.110).aspx 备注部分
- double minDiff = double.MaxValue;
- double minA = ;
- double minB = ;
- for (int i = ; i < a.Length - ; ++i)//N
- {
- if (a[i + ] - a[i] < minDiff)
- {
- minA = a[i];
- minB = a[i + ];
- minDiff = a[i + ] - a[i];
- }
- }
- Console.WriteLine($"Min Pair: {minA} {minB}, Min Value: {minDiff}");
- }
- }
- }
1.4.17
解答
遍历找到最小值和最大值即可。
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._17
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.17
- *
- * 最遥远的一对(一维)。
- * 编写一个程序,给定一个含有 N 个 double 值的数组 a[],
- * 在其中找到一对最遥远的值:两者之差(绝对值)最大的两个数。
- * 程序在最坏情况下所需的运行时间应该是线性级别的。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- double[] a = new double[] { 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 0.8, };
- double min = int.MaxValue;
- double max = int.MinValue;
- for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
- {
- if (a[i] > max)
- {
- max = a[i];
- }
- if (a[i] < min)
- {
- min = a[i];
- }
- }
- Console.WriteLine($"MaxDiff Pair: {min} {max}, Max Difference: {Math.Abs(max - min)}");
- }
- }
- }
1.4.18
解答
和二分查找的方式类似,先确认中间的值是否是局部最小,如果不是,则向较小的一侧二分查找。
在三个数中比较得到最小值需要两次比较,因此最坏情况下为 ~2lgN 次比较。
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._18
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- var a = new int[] { , , , , };
- Console.WriteLine(LocalMinimum(a));
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 寻找数组的局部最小元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">寻找范围。</param>
- /// <returns>局部最小元素的值。</returns>
- static int LocalMinimum(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = a.Length - ;
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = (hi - lo) / + lo;
- int min = mid;
- // 取左中右最小值的下标
- if (mid != hi && a[min] >= a[mid + ])
- min = mid + ;
- if (mid != lo && a[min] >= a[mid - ])
- min = mid - ;
- if (min == mid)
- return mid;
- if (min > mid)
- lo = min;
- else
- hi = min;
- }
- return -;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.19
解答
算法过程类似于 “滑雪”,从数值较高的一侧向周围数值较小的一侧移动,直到到达“山谷”(局部最小)。
首先在中间行搜索最小值,再将最小值与其上下两个元素比较,如果不满足题意,则“滑向”较小的一侧,矩阵被分为了两半(上下两侧)。
在较小的一侧,找到中间列的最小值,再将最小值与其左右两个元素比较,如果不满足题意,类似的移动到较小的一侧(左右两侧)。
现在查找范围缩小到了原来矩阵的四分之一,递归的进行上述操作,最后可以得到答案。
每次查找最小值都是对行/列进行遍历,遍历耗时和 N 成正比。
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._19
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.19
- *
- * 矩阵的局部最小元素。
- * 给定一个含有 N^2 个不同整数的 N×N 数组 a[]。
- * 设计一个运行时间和 N 成正比的算法来找出一个局部最小元素:
- * 满足 a[i][j] < a[i+1][j]、a[i][j] < a[i][j+1]、a[i][j] < a[i-1][j] 以及 a[i][j] < a[i][j-1] 的索引 i 和 j。
- * 程序运行时间在最坏情况下应该和 N 成正比。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- // 先查找 N/2 行中的最小元素,并令其与上下元素比较,
- // 如果不满足题意,则向相邻的最小元素靠近再次查找
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[,] matrix = new int[, ]
- {
- { , , , , },
- { , , , , },
- { , , , , },
- { , , , , },
- { , , , , }
- };
- Console.WriteLine(MinimumRow(matrix, , , , ));
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 在矩阵中间行查找局部最小。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="matrix">矩阵。</param>
- /// <param name="rowStart">实际查找范围的行起始。</param>
- /// <param name="rowLength">实际查找范围的行结尾。</param>
- /// <param name="colStart">实际查找范围的列起始。</param>
- /// <param name="colLength">实际查找范围的列结尾。</param>
- /// <returns>矩阵中的局部最小元素。</returns>
- static int MinimumRow(int[,] matrix, int rowStart, int rowLength, int colStart, int colLength)
- {
- int min = int.MaxValue;
- if (rowLength < )
- return int.MaxValue;
- int mid = rowStart + rowLength / ;
- int minCol = ;
- // 获取矩阵中间行的最小值
- for (int i = ; i < colLength; ++i)
- {
- if (min > matrix[mid, colStart + i])
- {
- min = matrix[mid, colStart + i];
- minCol = i;
- }
- }
- // 检查是否满足条件
- if (matrix[mid, minCol] < matrix[mid - , minCol] && matrix[mid, minCol] < matrix[mid + , minCol])
- {
- return matrix[mid, minCol];
- }
- // 如果不满足则向较小一侧移动
- if (matrix[mid - , minCol] > matrix[mid + , minCol])
- {
- return MinimumCol(matrix, rowStart, rowLength, mid + , colLength / + );
- }
- else
- {
- return MinimumCol(matrix, rowStart, rowLength, colStart, colLength / + );
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 在矩阵中间列查找局部最小。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="matrix">矩阵。</param>
- /// <param name="rowStart">实际查找范围的行起始。</param>
- /// <param name="rowLength">实际查找范围的行结尾。</param>
- /// <param name="colStart">实际查找范围的列起始。</param>
- /// <param name="colLength">实际查找范围的列结尾。</param>
- /// <returns>矩阵中的局部最小元素。</returns>
- static int MinimumCol(int[,] matrix, int rowStart, int rowLength, int colStart, int colLength)
- {
- int min = int.MaxValue;
- int n = matrix.GetLength();
- int mid = n / ;
- int minRow = ;
- // 获取矩阵中间列最小值
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- if (min > matrix[i, mid])
- {
- min = matrix[i, mid];
- minRow = i;
- }
- }
- // 检查是否满足条件
- if (matrix[minRow, mid] < matrix[minRow, mid - ] && matrix[minRow, mid] < matrix[minRow, mid + ])
- {
- return matrix[minRow, mid];
- }
- // 如果不满足则向较小一侧移动
- if (matrix[minRow, mid - ] > matrix[minRow, mid + ])
- {
- return MinimumRow(matrix, mid + , rowLength / + , colStart, colLength);
- }
- else
- {
- return MinimumRow(matrix, rowStart, rowLength / + , colStart, colLength);
- }
- }
- }
- }
1.4.20
解答
首先给出 BitMax 类的官方 Java 实现:BitonicMax.java。
我们使用这个类生成双调数组,并使用其中的 Max() 方法找到双调数组的最大值。
找到最大值之后分别对左右两侧进行二分查找,注意对于升序和降序的数组二分查找的实现有所不同。
代码
BitonicMax 类
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._20
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 双调查找类。
- /// </summary>
- public class BitonicMax
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 生成双调数组。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="N">数组的大小。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static int[] Bitonic(int N)
- {
- Random random = new Random();
- int mid = random.Next(N);
- int[] a = new int[N];
- for (int i = ; i < mid; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = a[i - ] + + random.Next();
- }
- if (mid > )
- {
- a[mid] = a[mid - ] + random.Next() - ;
- }
- for (int i = mid + ; i < N; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = a[i - ] - - random.Next();
- }
- return a;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 寻找数组中的最大值。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">查找范围。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找起始下标。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找结束下标。</param>
- /// <returns>返回数组中最大值的下标。</returns>
- public static int Max(int[] a, int lo, int hi)
- {
- if (lo == hi)
- {
- return hi;
- }
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (a[mid] < a[mid + ])
- {
- return Max(a, mid + , hi);
- }
- if (a[mid] > a[mid + ])
- {
- return Max(a, lo, mid);
- }
- return mid;
- }
- }
- }
主程序
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._20
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.20
- *
- * 双调查找。
- * 如果一个数组中的所有元素是先递增后递减的,则称这个数组为双调的。
- * 编写一个程序,给定一个含有 N 个不同 int 值的双调数组,判断它是否含有给定的整数。
- * 程序在最坏情况下所需的比较次数为 ~3lgN
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] a = BitonicMax.Bitonic();
- int max = BitonicMax.Max(a, , a.Length - );
- int key = a[];
- int leftside = BinarySearchAscending(a, key, , max);
- int rightside = BinarySearchDescending(a, key, max, a.Length - );
- if (leftside != -)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(leftside);
- }
- else if (rightside != -)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(rightside);
- }
- else
- {
- Console.WriteLine("No Result");
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 对升序数组的二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">升序数组。</param>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找的左边界。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找的右边界。</param>
- /// <returns>返回找到关键值的下标,如果没有找到则返回 -1。</returns>
- static int BinarySearchAscending(int[] a, int key, int lo, int hi)
- {
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (a[mid] < key)
- {
- lo = mid + ;
- }
- else if (a[mid] > key)
- {
- hi = mid - ;
- }
- else
- {
- return mid;
- }
- }
- return -;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 对降序数组的二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">升序数组。</param>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找的左边界。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找的右边界。</param>
- /// <returns>返回找到关键值的下标,如果没有找到则返回 -1。</returns>
- static int BinarySearchDescending(int[] a, int key, int lo, int hi)
- {
- while (lo < hi)
- {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (a[mid] > key)
- {
- lo = mid + ;
- }
- else if (a[mid] < key)
- {
- hi = mid - ;
- }
- else
- {
- return mid;
- }
- }
- return -;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.21
解答
直接将 Contains() 实现为二分查找即可。
代码
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查数组中是否存在指定元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">要查找的值。</param>
- /// <returns>存在则返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
- public bool Contains(int key)
- {
- return Rank(key, , this.a.Length - ) != -;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="key">关键值。</param>
- /// <param name="lo">查找的起始下标。</param>
- /// <param name="hi">查找的结束下标。</param>
- /// <returns>返回关键值的下标,如果不存在则返回 -1。</returns>
- public int Rank(int key, int lo, int hi)
- {
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = (hi - lo) / + lo;
- if (key < this.a[mid])
- hi = mid - ;
- else if (key > this.a[mid])
- lo = mid + ;
- else
- return mid;
- }
- return -;
- }
1.4.22
解答
普通二分查找是通过除法不断减半缩小搜索范围。
这里我们用斐波那契数列来缩小范围。
举个例子,例如数组大小是 100,比它大的最小斐波那契数是 144。
斐波那契数列如下:0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144
我们记 F(n) = 144,F(n-1) = 89, F(n-2) = 55。
我们先查看第 0 + F(n-2) 个数,如果比关键值小则直接将范围缩小到 [55, 100];否则则在[0, 55]之间查找。
之后我们令 n = n-1。
递归上述过程即可完成查找。
代码
- /// <summary>
- /// 使用斐波那契数列进行的查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">查找范围。</param>
- /// <param name="key">关键字。</param>
- /// <returns>返回查找到的关键值下标,没有结果则返回 -1。</returns>
- static int rank(int[] a, int key)
- {
- // 使用斐波那契数列作为缩减范围的依据
- int Fk = ;
- int Fk_1 = ;
- int Fk_2 = ;
- // 获得 Fk,Fk需要大于等于数组的大小,复杂度 lgN
- while (Fk < a.Length)
- {
- Fk = Fk + Fk_1;
- Fk_1 = Fk_1 + Fk_2;
- Fk_2 = Fk - Fk_1;
- }
- int lo = ;
- // 按照斐波那契数列缩减查找范围,复杂度 lgN
- while (Fk_2 >= )
- {
- int i = lo + Fk_2 > a.Length - ? a.Length - : lo + Fk_2;
- if (a[i] < key)
- {
- lo = lo + Fk_2;
- }
- else if (a[i] == key)
- {
- return i;
- }
- Fk = Fk_1;
- Fk_1 = Fk_2;
- Fk_2 = Fk - Fk_1;
- }
- return -;
- }
1.4.23
解答
根据书中的提示,将二分查找中判断相等的条件改为两个数的差小于等于 1/N2。
代码
- // 将二分查找中的相等判定条件修改为差值小于 x,其中 x = 1/N^2。
- /// <summary>
- /// 二分查找。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">查找范围。</param>
- /// <param name="key">关键字。</param>
- /// <returns>结果的下标,没有结果时返回 -1。</returns>
- static int BinarySearch(double[] a, double key)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = a.Length - ;
- double threshold = 1.0 / (a.Length * a.Length);
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (Math.Abs(a[mid] - key) <= threshold)
- {
- return mid;
- }
- else if (a[mid] < key)
- {
- lo = mid + ;
- }
- else
- {
- hi = mid - ;
- }
- }
- return -;
- }
1.4.24
解答
第一问:二分查找即可。
第二问:
按照第 1, 2, 4, 8,..., 2^k 层顺序查找,一直到 2^k > F,
随后在 [2^(k - 1), 2^k] 范围中二分查找。
代码
这里建立了一个结构体用于返回测试结果:
- struct testResult
- {
- public int F;// 找到的 F 值。
- public int BrokenEggs;// 打碎的鸡蛋数。
- }
用于测试的方法:
- /// <summary>
- /// 扔鸡蛋,没碎返回 true,碎了返回 false。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="floor">扔鸡蛋的高度。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static bool ThrowEgg(int floor)
- {
- return floor <= F;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 第一种方案。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">大楼。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static testResult PlanA(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = a.Length - ;
- int mid = ;
- int eggs = ;
- testResult result = new testResult();
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (ThrowEgg(mid))
- {
- lo = mid + ;
- }
- else
- {
- eggs++;
- hi = mid - ;
- }
- }
- result.BrokenEggs = eggs;
- result.F = hi;
- return result;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 第二种方案。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">大楼。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static testResult PlanB(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = ;
- int mid = ;
- int eggs = ;
- testResult result = new testResult();
- while (ThrowEgg(hi))
- {
- lo = hi;
- hi *= ;
- }
- eggs++;
- if (hi > a.Length - )
- {
- hi = a.Length - ;
- }
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- if (ThrowEgg(mid))
- {
- lo = mid + ;
- }
- else
- {
- eggs++;
- hi = mid - ;
- }
- }
- result.BrokenEggs = eggs;
- result.F = hi;
- return result;
- }
1.4.25
解答
第一问:
第一个蛋按照 √(N), 2√(N), 3√(N), 4√(N),..., √(N) * √(N) 顺序查找直至碎掉。这里扔了 k 次,k <= √(N)。
k-1√(N) ~ k√(N) 顺序查找直至碎掉,F 值就找到了。这里最多扔 √(N) 次。
第二问:
按照第 1, 3, 6, 10,..., 1/2k^2 层顺序查找,一直到 1/2k^2 > F,
随后在 [1/2k^2 - k, 1/2k^2] 范围中顺序查找。
代码
这里我们同样定义了一个结构体:
- struct testResult
- {
- public int F;// 测试得出的 F 值
- public int BrokenEggs;// 碎掉的鸡蛋数。
- public int ThrowTimes;// 扔鸡蛋的次数。
- }
之后是测试用的方法:
- /// <summary>
- /// 扔鸡蛋,没碎返回 true,碎了返回 false。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="floor">扔鸡蛋的高度。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static bool ThrowEgg(int floor)
- {
- return floor <= F;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 第一种方案。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">大楼。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static testResult PlanA(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = ;
- int eggs = ;
- int throwTimes = ;
- testResult result = new testResult();
- while (ThrowEgg(hi))
- {
- throwTimes++;
- lo = hi;
- hi += (int)Math.Sqrt(a.Length);
- }
- eggs++;
- if (hi > a.Length - )
- {
- hi = a.Length - ;
- }
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- if (!ThrowEgg(lo))
- {
- eggs++;
- break;
- }
- throwTimes++;
- lo++;
- }
- result.BrokenEggs = eggs;
- result.F = lo - ;
- result.ThrowTimes = throwTimes;
- return result;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 第二种方案。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">大楼。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static testResult PlanB(int[] a)
- {
- int lo = ;
- int hi = ;
- int eggs = ;
- int throwTimes = ;
- testResult result = new testResult();
- for (int i = ; ThrowEgg(hi); ++i)
- {
- throwTimes++;
- lo = hi;
- hi += i;
- }
- eggs++;
- if (hi > a.Length - )
- {
- hi = a.Length - ;
- }
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- if (!ThrowEgg(lo))
- {
- eggs++;
- break;
- }
- lo++;
- throwTimes++;
- }
- result.BrokenEggs = eggs;
- result.F = lo - ;
- result.ThrowTimes = throwTimes;
- return result;
- }
1.4.26
解答

1.4.27
解答
实现比较简单,想象两个栈背靠背接在一起,左侧栈负责出队,右侧栈负责入队。
当左侧栈为空时就把右侧栈中的元素倒到左侧栈,这个过程是 O(n) 的。
但在这个过程之前必然有 n 个元素入栈,均摊后即为 O(1)。
代码
- namespace _1._4._27
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用两个栈模拟的队列。
- /// </summary>
- /// <typeparam name="Item">队列中的元素。</typeparam>
- class StackQueue<Item>
- {
- Stack<Item> H;//用于保存出队元素
- Stack<Item> T;//用于保存入队元素
- /// <summary>
- /// 构造一个队列。
- /// </summary>
- public StackQueue()
- {
- this.H = new Stack<Item>();
- this.T = new Stack<Item>();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将栈 T 中的元素依次弹出并压入栈 H 中。
- /// </summary>
- private void Reverse()
- {
- while (!this.T.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.H.Push(this.T.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将一个元素出队。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item Dequeue()
- {
- //如果没有足够的出队元素,则将 T 中的元素移动过来
- if (this.H.IsEmpty())
- {
- Reverse();
- }
- return this.H.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将一个元素入队。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要入队的元素。</param>
- public void Enqueue(Item item)
- {
- this.T.Push(item);
- }
- }
- }
1.4.28
解答
每次入队的时候将队列倒转,这样入队的元素就是第一个了。
代码
- namespace _1._4._28
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用一条队列模拟的栈。
- /// </summary>
- /// <typeparam name="Item">栈中保存的元素。</typeparam>
- class QueueStack<Item>
- {
- Queue<Item> queue;
- /// <summary>
- /// 初始化一个栈。
- /// </summary>
- public QueueStack()
- {
- this.queue = new Queue<Item>();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 向栈中添加一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item"></param>
- public void Push(Item item)
- {
- this.queue.Enqueue(item);
- int size = this.queue.Size();
- // 倒转队列
- for (int i = ; i < size - ; ++i)
- {
- this.queue.Enqueue(this.queue.Dequeue());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从栈中弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item Pop()
- {
- return this.queue.Dequeue();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 确定栈是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.queue.IsEmpty();
- }
- }
- }
1.4.29
解答
和用两个栈实现队列的方法类似。
push 的时候把右侧栈内容倒到左侧栈,之后再入栈。
pop 的时候也做相同操作,右侧栈内容进左侧栈,之后再出栈。
enqueue 的时候则将左侧栈内容倒到右侧栈,之后再入队。
代码
- namespace _1._4._29
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用两个栈模拟的 Steque。
- /// </summary>
- /// <typeparam name="Item">Steque 中的元素类型。</typeparam>
- class StackSteque<Item>
- {
- Stack<Item> H;
- Stack<Item> T;
- /// <summary>
- /// 初始化一个 Steque
- /// </summary>
- public StackSteque()
- {
- this.H = new Stack<Item>();
- this.T = new Stack<Item>();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 向栈中添加一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item"></param>
- public void Push(Item item)
- {
- ReverseT();
- this.H.Push(item);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将 T 中的元素弹出并压入到 H 中。
- /// </summary>
- private void ReverseT()
- {
- while (!this.T.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.H.Push(this.T.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将 H 中的元素弹出并压入到 T 中。
- /// </summary>
- private void ReverseH()
- {
- while (!this.H.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.T.Push(this.H.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从 Steque 中弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item Pop()
- {
- ReverseT();
- return this.H.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 在 Steque 尾部添加一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item"></param>
- public void Enqueue(Item item)
- {
- ReverseH();
- this.T.Push(item);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查 Steque 是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.H.IsEmpty() && this.T.IsEmpty();
- }
- }
- }
1.4.30
解答
steque 作为队列的头部,stack 作为队列的尾部。
pushLeft:直接 push 到 steque 中即可。
pushRight:如果 stack 为空,则直接 enqueue 到 steque 中,否则就 push 到 stack 中。
popLeft:如果 steque 为空,则将 stack 中的元素倒到 steque 中去(steque.push(stack.pop())),然后再从 steque 中 pop。
popRight:如果 stack 为空,则将 steque 中的元素倒到 stack 中去,然后再从 stack 中 pop。
代码
- namespace _1._4._30
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用一个栈和一个 Steque 模拟的双向队列。
- /// </summary>
- /// <typeparam name="Item">双向队列中保存的元素类型。</typeparam>
- class Deque<Item>
- {
- Stack<Item> stack;//代表队列尾部
- Steque<Item> steque;//代表队列头部
- /// <summary>
- /// 创建一条空的双向队列。
- /// </summary>
- public Deque()
- {
- this.stack = new Stack<Item>();
- this.steque = new Steque<Item>();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 在左侧插入一个新元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要插入的元素。</param>
- public void PushLeft(Item item)
- {
- this.steque.Push(item);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将栈中的内容移动到 Steque 中。
- /// </summary>
- private void StackToSteque()
- {
- while (!this.stack.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.steque.Push(this.stack.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将 Steque 中的内容移动到栈中。
- /// </summary>
- private void StequeToStack()
- {
- while (!this.steque.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.stack.Push(this.steque.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从双向队列左侧弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item PopLeft()
- {
- if (this.steque.IsEmpty())
- {
- StackToSteque();
- }
- return this.steque.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 向双向队列右侧添加一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要插入的元素。</param>
- public void PushRight(Item item)
- {
- if (this.stack.IsEmpty())
- {
- this.steque.Enqueue(item);
- }
- else
- {
- this.stack.Push(item);
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从双向队列右侧弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item PopRight()
- {
- if (this.stack.IsEmpty())
- {
- StequeToStack();
- }
- return this.stack.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 判断队列是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.stack.IsEmpty() && this.steque.IsEmpty();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回队列中元素的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public int Size()
- {
- return this.stack.Size() + this.steque.Size();
- }
- }
- }
1.4.31
解答
三个栈分别命名为左中右。
左侧栈和右侧栈负责模拟队列,和用两个栈模拟队列的方法类似。
由于是双向队列,左栈和右栈会频繁的倒来倒去,因此每次都只倒一半的元素可以有效减少开销。
有一侧栈为空时,另一侧栈中上半部分先移动到中间栈中,下半部分倒到另一侧栈里,再从中间栈拿回上半部分元素。
这样可以确保接下来的 pop 操作一定是常数级别的。
代码
- namespace _1._4._31
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用三个栈模拟的双向队列。
- /// </summary>
- /// <typeparam name="Item">双向队列中的元素。</typeparam>
- class Deque<Item>
- {
- Stack<Item> left;
- Stack<Item> middle;
- Stack<Item> right;
- /// <summary>
- /// 构造一条新的双向队列。
- /// </summary>
- public Deque()
- {
- this.left = new Stack<Item>();
- this.middle = new Stack<Item>();
- this.right = new Stack<Item>();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 向双向队列左侧插入一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要插入的元素。</param>
- public void PushLeft(Item item)
- {
- this.left.Push(item);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 向双向队列右侧插入一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要插入的元素。</param>
- public void PushRight(Item item)
- {
- this.right.Push(item);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 当一侧栈为空时,将另一侧的下半部分元素移动过来。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="source">不为空的栈。</param>
- /// <param name="destination">空栈。</param>
- private void Move(Stack<Item> source, Stack<Item> destination)
- {
- int n = source.Size();
- // 将上半部分元素移动到临时栈 middle
- for (int i = ; i < n / ; ++i)
- {
- this.middle.Push(source.Pop());
- }
- // 将下半部分移动到另一侧栈中
- while (!source.IsEmpty())
- {
- destination.Push(source.Pop());
- }
- // 从 middle 取回上半部分元素
- while (!this.middle.IsEmpty())
- {
- source.Push(this.middle.Pop());
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查双端队列是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.right.IsEmpty() && this.middle.IsEmpty() && this.left.IsEmpty();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从右侧弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item PopRight()
- {
- if (this.right.IsEmpty())
- {
- Move(this.left, this.right);
- }
- return this.right.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从左侧弹出一个元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item PopLeft()
- {
- if (this.left.IsEmpty())
- {
- Move(this.right, this.left);
- }
- return this.left.Pop();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回双端队列的大小。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public int Size()
- {
- return this.left.Size() + this.middle.Size() + this.right.Size();
- }
- }
- }
1.4.32
解答
首先,不需要扩容数组的的操作都只需访问数组一次,M 次操作就是 M 次访问。
随后我们有性质, M 次栈操作后额外复制访问数组的次数小于 2M。
这里简单证明,设 M 次操作之后栈的大小为 n,那么额外访问数组的次数为:
S = n/2 + n/4 + n/8 +...+ 2 < n
为了能使栈大小达到 n,M 必须大于等于 n/2
因此 2M >= n > S,得证。
因此我们可以得到 M 次操作后访问数组次数的总和 S' = S + M < 3M
1.4.33
解答
Integer = 4(int) + 8(对象开销) = 12
Date = 3 * 4(int * 3) + 8(对象开销) = 20
Counter = 4(String 的引用) + 4(int) + 8(对象开销) = 16
int[] = 8(对象开销) + 4(数组长度) + 4N = 12 + 4N
double[] = 8(对象开销) + 4(数组长度) + 8N = 12 + 8N
double[][] = 8(对象开销) + 4(数组长度) + 4M(引用) + M(12 + 8N)(M 个一维数组) = 12 + 16M + 8MN
String = 8(对象开销) + 3*4(int * 3) + 4(字符数组的引用) = 24
Node = 8(对象开销) + 4*2(引用*2) = 16
Stack = 8(对象开销) + 4(引用) + 4(int) = 16
1.4.34
解答
1. 第一种方案,类似于二分查找,先猜测左边界(lo),再猜测右边界(hi),如果边界值猜中的话直接返回,否则:
如果右边界比较热,那么左边界向右边界靠,lo=mid;否则,右边界向左边界靠,hi=mid。其中,mid = lo + (hi – lo)/2。
每次二分查找都要猜测两次,~2lgN。
2. 第二种方案,假设上次猜测值为 lastGuess,本次即将要猜测的值为 nowGuess,通过方程:
(lastGuess + nowGuess)/2 = (lo + hi)/2
可以求得 nowGuess,具体可以查看示意图:
数字是猜测顺序,黑色范围是猜测值的范围(lastGuess 和 nowGuess),绿色的是实际查找的范围(lo 和 hi)。
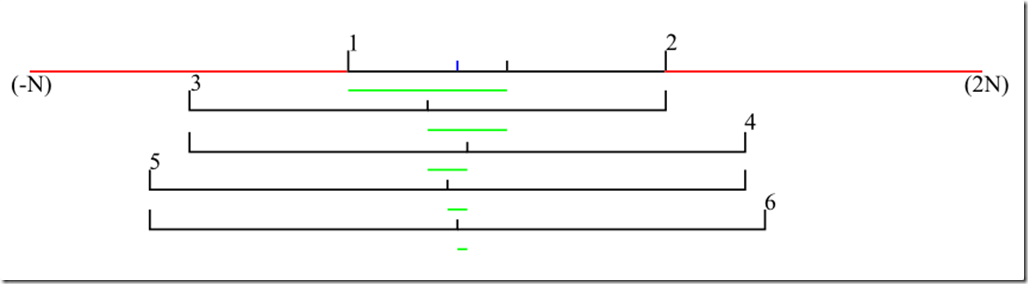
代码
首先是 Game 类
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._34
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 某次猜测的结果。
- /// </summary>
- enum GuessResult
- {
- Hot = , // 比上次猜测更接近目标。
- Equal = , // 猜中目标。
- Cold = -, // 比上次猜测更远离目标。
- FirstGuess = - // 第一次猜测。
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 游戏类。
- /// </summary>
- class Game
- {
- public int N { get; } // 目标值的最大范围。
- public int SecretNumber { get; } // 目标值。
- public int LastGuess { get; private set; } // 上次猜测的值
- /// <summary>
- /// 构造函数,新开一局游戏。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="N">目标值的最大范围。</param>
- public Game(int N)
- {
- Random random = new Random();
- this.N = N;
- this.SecretNumber = random.Next(N - ) + ;
- this.LastGuess = -;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 猜测,根据与上次相比更为接近还是远离目标值返回结果。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="guess">本次的猜测值</param>
- /// <returns>接近或不变返回 Hot,远离则返回 Cold,猜中返回 Equal。</returns>
- public GuessResult Guess(int guess)
- {
- if (guess == this.SecretNumber)
- {
- return GuessResult.Equal;
- }
- if (this.LastGuess == -)
- {
- this.LastGuess = guess;
- return GuessResult.FirstGuess;
- }
- int lastDiff = Math.Abs(this.LastGuess - this.SecretNumber);
- this.LastGuess = guess;
- int nowDiff = Math.Abs(guess - this.SecretNumber);
- if (nowDiff > lastDiff)
- {
- return GuessResult.Cold;
- }
- else
- {
- return GuessResult.Hot;
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 重置游戏,清空上次猜测的记录。目标值和最大值都不变。
- /// </summary>
- public void Restart()
- {
- this.LastGuess = -;
- }
- }
- }
之后是实际测试的方法:
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._34
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.34
- *
- * 热还是冷。
- * 你的目标是猜出 1 到 N 之间的一个秘密的整数。
- * 每次猜完一个整数后,你会直到你的猜测距离该秘密整数是否相等(如果是则游戏结束)。
- * 如果不相等,你会知道你的猜测相比上一次猜测距离秘密整数是比较热(接近),还是比较冷(远离)。
- * 设计一个算法在 ~2lgN 之内找到这个秘密整数,然后设计一个算法在 ~1lgN 之内找到这个秘密整数。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 某种方案的测试结果,包含猜测结果和尝试次数。
- /// </summary>
- struct TestResult
- {
- public int SecretNumber;// 猜测到的数字。
- public int TryTimes;// 尝试次数。
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Game game = new Game();
- TestResult A = PlayGameA(game);
- game.Restart();
- TestResult B = PlayGameB(game);
- Console.WriteLine($"SecretNumber:{game.SecretNumber}");
- Console.WriteLine("TestResultA:");
- Console.WriteLine($"SecretNumber:{A.SecretNumber}, TryTimes:{A.TryTimes}");
- Console.WriteLine();
- Console.WriteLine("TestResultB:");
- Console.WriteLine($"SecretNumber:{B.SecretNumber}, TryTimes:{B.TryTimes}");
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 方案一,用二分查找实现,需要猜测 2lgN 次。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="game">用于猜测的游戏对象。</param>
- /// <returns>返回测试结果,包含猜测结果和尝试次数。</returns>
- static TestResult PlayGameA(Game game)
- {
- TestResult result;
- result.TryTimes = ;
- result.SecretNumber = ;
- GuessResult guessResult;
- int hi = game.N;
- int lo = ;
- // 利用二分查找猜测,2lgN
- while (lo <= hi)
- {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- guessResult = game.Guess(lo);
- result.TryTimes++;
- if (guessResult == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.SecretNumber = lo;
- return result;
- }
- guessResult = game.Guess(hi);
- result.TryTimes++;
- if (guessResult == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.SecretNumber = hi;
- return result;
- }
- else if (guessResult == GuessResult.Hot)
- {
- lo = mid;
- }
- else
- {
- hi = mid;
- }
- }
- return result;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 方案二,根据 (lastGuess + nowGuess)/2 = (lo + hi) / 2 确定每次猜测的值。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="game">用于猜测的游戏对象。</param>
- /// <returns>返回测试结果,包含猜测结果和尝试次数。</returns>
- static TestResult PlayGameB(Game game)
- {
- TestResult result;
- result.TryTimes = ;
- result.SecretNumber = ;
- GuessResult guessResult;
- int hi = game.N;
- int lo = ;
- bool isRightSide = true;
- // 第一次猜测
- guessResult = game.Guess();
- result.TryTimes++;
- if (guessResult == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.SecretNumber = ;
- return result;
- }
- while (lo < hi)
- {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ;
- int nowGuess = (lo + hi) - game.LastGuess;
- guessResult = game.Guess(nowGuess);
- result.TryTimes++;
- if (guessResult == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.SecretNumber = nowGuess;
- break;
- }
- else if (guessResult == GuessResult.Hot)
- {
- if (isRightSide)
- {
- lo = mid;
- }
- else
- {
- hi = mid;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if (isRightSide)
- {
- hi = mid;
- }
- else
- {
- lo = mid;
- }
- }
- isRightSide = !isRightSide;
- if (hi - lo <= )
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- if (game.Guess(lo) == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.TryTimes++;
- result.SecretNumber = lo;
- }
- else if (game.Guess(hi) == GuessResult.Equal)
- {
- result.TryTimes++;
- result.SecretNumber = hi;
- }
- return result;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.35
解答
1. 一个 Node 对象包含一个 int(泛型 Item) 的引用和下一个 Node 对象的引用。push 操作创建新 Node 对象时会创建一个引用。
因此对于第一种情况,压入 n 个 int 类型的元素创建了 N 个 Node 对象,创建了 2N 个引用。
2. 比起上一种情况,每个 Node 对象多包含了一个指向 Integer 的引用。
因此对于第二中情况,压入 n 个 int 类型的元素创建了 N 个 Node 对象和 N 个 Integer 对象,比起第一种情况多创建了 N 个引用。
3. 对于数组来说,创建对象只有扩容时重新创建数组对象一种情况,对于 N 次 push 操作只需要 lgN 次扩容,因此创建的对象为 lgN 个。
每次扩容都需要重新创建引用,(4 + 8 +...+ 2N)(扩容) + N(每次 push 操作) = 5N - 4 = ~5N
4. 创建引用和上题一样,创建对象则多出了装箱过程,每次 push 都会新建一个 Integer 对象,N + lgN = ~N。
1.4.36
解答
1. N 个 Node<int> 对象的空间开销
= N * (16(对象开销) + 4(int) + 8(下一个 Node 的引用) + 4(填充字节)) = 32N
2. 比起上一题来说,空间开销变为
= N * (16(Node 对象开销) + 8(Integer 对象引用) + (16(Integer 对象开销) + 4(int) + 4(填充字节)) + 8(下一个对象的引用) = 32N + 24N = 56N。
3. 如果不扩容则是 4N,N 个元素最多可以维持 4N 的栈空间(少于四分之一将缩小)。
4. 比起上一题,数组元素变成了引用每个占用 8 字节,还要额外加上 Integer 对象的每个 24 字节。
= (8 + 24)N ~ (8 * 4 + 24)N
1.4.37
解答
数据量比较大时才会有比较明显的差距。
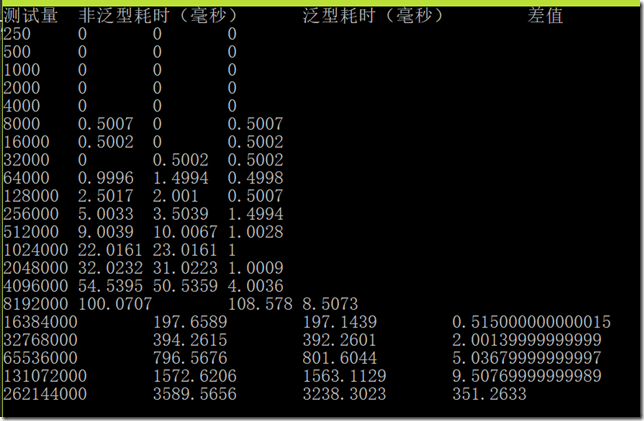
代码
FixedCapacityStackOfInts,根据 FixedCapacityOfString 修改而来:
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- namespace _1._4._37
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 固定大小的整型数据栈。
- /// </summary>
- class FixedCapacityStackOfInts : IEnumerable<int>
- {
- private int[] a;
- private int N;
- /// <summary>
- /// 默认构造函数。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="capacity">栈的大小。</param>
- public FixedCapacityStackOfInts(int capacity)
- {
- this.a = new int[capacity];
- this.N = ;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查栈是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.N == ;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查栈是否已满。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsFull()
- {
- return this.N == this.a.Length;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将一个元素压入栈中。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要压入栈中的元素。</param>
- public void Push(int item)
- {
- this.a[this.N] = item;
- this.N++;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从栈中弹出一个元素,返回被弹出的元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public int Pop()
- {
- this.N--;
- return this.a[this.N];
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回栈顶元素(但不弹出它)。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public int Peek()
- {
- return this.a[this.N - ];
- }
- public IEnumerator<int> GetEnumerator()
- {
- return new ReverseEnmerator(this.a);
- }
- IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
- {
- return GetEnumerator();
- }
- private class ReverseEnmerator : IEnumerator<int>
- {
- private int current;
- private int[] a;
- public ReverseEnmerator(int[] a)
- {
- this.current = a.Length;
- this.a = a;
- }
- int IEnumerator<int>.Current => this.a[this.current];
- object IEnumerator.Current => this.a[this.current];
- void IDisposable.Dispose()
- {
- this.current = -;
- this.a = null;
- }
- bool IEnumerator.MoveNext()
- {
- if (this.current == )
- return false;
- this.current--;
- return true;
- }
- void IEnumerator.Reset()
- {
- this.current = this.a.Length;
- }
- }
- }
- }
FixedCapacityStack<Item>
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- namespace _1._4._37
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 固定大小的栈。
- /// </summary>
- class FixedCapacityStack<Item> : IEnumerable<Item>
- {
- private Item[] a;
- private int N;
- /// <summary>
- /// 默认构造函数。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="capacity">栈的大小。</param>
- public FixedCapacityStack(int capacity)
- {
- this.a = new Item[capacity];
- this.N = ;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查栈是否为空。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsEmpty()
- {
- return this.N == ;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查栈是否已满。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public bool IsFull()
- {
- return this.N == this.a.Length;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 将一个元素压入栈中。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="item">要压入栈中的元素。</param>
- public void Push(Item item)
- {
- this.a[this.N] = item;
- this.N++;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 从栈中弹出一个元素,返回被弹出的元素。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item Pop()
- {
- this.N--;
- return this.a[this.N];
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回栈顶元素(但不弹出它)。
- /// </summary>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public Item Peek()
- {
- return this.a[this.N - ];
- }
- public IEnumerator<Item> GetEnumerator()
- {
- return new ReverseEnmerator(this.a);
- }
- IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
- {
- return GetEnumerator();
- }
- private class ReverseEnmerator : IEnumerator<Item>
- {
- private int current;
- private Item[] a;
- public ReverseEnmerator(Item[] a)
- {
- this.current = a.Length;
- this.a = a;
- }
- Item IEnumerator<Item>.Current => this.a[this.current];
- object IEnumerator.Current => this.a[this.current];
- void IDisposable.Dispose()
- {
- this.current = -;
- this.a = null;
- }
- bool IEnumerator.MoveNext()
- {
- if (this.current == )
- return false;
- this.current--;
- return true;
- }
- void IEnumerator.Reset()
- {
- this.current = this.a.Length;
- }
- }
- }
- }
测试函数:
- using System;
- using Measurement;
- namespace _1._4._37
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// FixedCapacityStackOfInts 测试类。
- /// </summary>
- public static class DoubleTest
- {
- private static readonly int MAXIMUM_INTEGER = ;
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回对 n 个随机整数的栈进行 n 次 push 和 n 次 pop 所需的时间。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="n">随机数组的长度。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static double TimeTrial(int n)
- {
- int[] a = new int[n];
- FixedCapacityStackOfInts stack = new FixedCapacityStackOfInts(n);
- Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next(-MAXIMUM_INTEGER, MAXIMUM_INTEGER);
- }
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Push(a[i]);
- }
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Pop();
- }
- return timer.ElapsedTimeMillionSeconds();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回对 n 个随机整数的栈进行 n 次 push 和 n 次 pop 所需的时间。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="n">随机数组的长度。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static double TimeTrialGeneric(int n)
- {
- int[] a = new int[n];
- FixedCapacityStack<int> stack = new FixedCapacityStack<int>(n);
- Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next(-MAXIMUM_INTEGER, MAXIMUM_INTEGER);
- }
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Push(a[i]);
- }
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Pop();
- }
- return timer.ElapsedTimeMillionSeconds();
- }
- }
- }
主函数:
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._37
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.37
- *
- * 自动装箱的性能代价。
- * 通过实验在你的计算机上计算使用自动装箱所付出的性能代价。
- * 实现一个 FixedCapacityStackOfInts,
- * 并使用类似 DoublingRatio 的用例比较它和泛型 FixedCapacityStack 在进行大量 push() 和 pop() 时的性能。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("测试量\t非泛型耗时(毫秒)\t泛型耗时(毫秒)\t差值");
- for (int n = ; true; n += n)
- {
- double time = DoubleTest.TimeTrial(n);
- double timeGeneric = DoubleTest.TimeTrialGeneric(n);
- Console.WriteLine($"{n}\t{time}\t{timeGeneric}\t{Math.Abs(time - timeGeneric)}");
- }
- }
- }
- }
1.4.38
解答
把 DoublingTest 中调用的函数稍作修改即可。
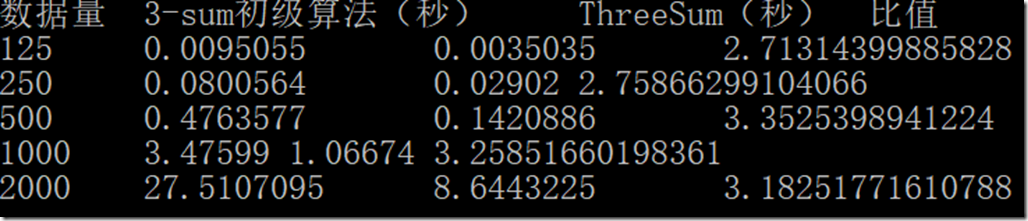
代码
ThreeSum 测试类
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._38
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// ThreeSum 测试类。
- /// </summary>
- public static class DoubleTest
- {
- private static readonly int MAXIMUM_INTEGER = ;
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回对 n 个随机整数的数组进行一次 ThreeSum 所需的时间。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="n">随机数组的长度。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static double TimeTrial(int n)
- {
- int[] a = new int[n];
- Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next(-MAXIMUM_INTEGER, MAXIMUM_INTEGER);
- }
- Measurement.Stopwatch timer = new Measurement.Stopwatch();
- ThreeSum.Count(a);
- return timer.ElapsedTime();
- }
- }
- }
ThreeSum
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._38
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 用暴力方法寻找数组中和为零的三元组。
- /// </summary>
- public static class ThreeSum
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 输出所有和为零的三元组。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">输入数组。</param>
- public static void PrintAll(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = ; j < n; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = ; k < n; ++k)
- {
- if (i < j && j < k)
- {
- if ((long)a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == )
- {
- Console.WriteLine($"{a[i]} + {a[j]} + {a[k]}");
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 计算和为零的三元组的数量。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">输入数组。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static int Count(int[] a)
- {
- int n = a.Length;
- int count = ;
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = ; j < n; ++j)
- {
- for (int k = ; k < n; ++k)
- {
- if (i < j && j < k)
- {
- if ((long)a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == )
- {
- count++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.39
解答
执行 N 次后取平均即可。
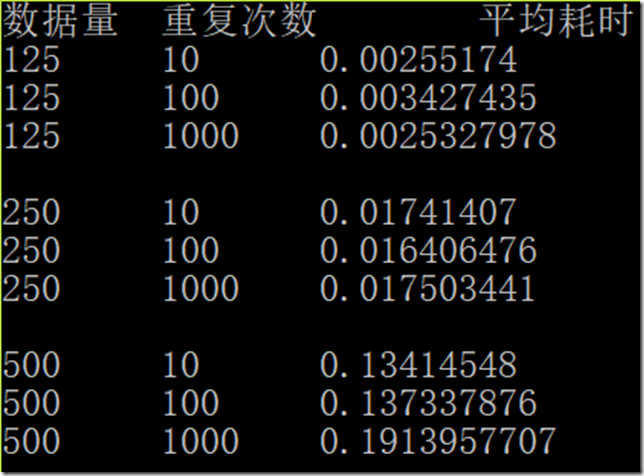
代码
修改后的 DoublingTest:
- using System;
- using Measurement;
- namespace _1._4._39
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// ThreeSum 测试类。
- /// </summary>
- public static class DoubleTest
- {
- private static readonly int MAXIMUM_INTEGER = ;
- /// <summary>
- /// 返回对 n 个随机整数的数组进行一次 ThreeSum 所需的时间。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="n">随机数组的长度。</param>
- /// <param name="repeatTimes">重复测试的次数。</param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- public static double TimeTrial(int n, int repeatTimes)
- {
- int[] a = new int[n];
- double sum = ;
- Random random = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next(-MAXIMUM_INTEGER, MAXIMUM_INTEGER);
- }
- for (int i = ; i < repeatTimes; ++i)
- {
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- ThreeSum.Count(a);
- sum += timer.ElapsedTime();
- }
- return sum / repeatTimes;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.40
解答
N 个数可组成的三元组的总数为:
C(N, 3) = N(N-1)(N-2)/3! = ~ (N^3)/6 (组合数公式)
[-M, M]中随机 N 次,有 (2M+1)^N 种随机序列(每次随机都有 2M+1 种可能)
按照分步计数方法,将随机序列分为和为零的三元组和其余 N-3 个数
这些序列中,和为零的三元组有 3M^2 + 3M + 1 种可能。
其他不为零的 N-3 个位置有 (2M+1)^(N-3) 种可能。
总共有 ((N^3)/6) * (3M^2 + 3M + 1) * (2M+1)^(N-3) 种可能性
平均值为:
[((N^3)/6) * (3M^2 + 3M + 1) * (2M+1)^(N-3)] / (2M+1)^N
N^3/16M
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._40
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.40
- *
- * 随机输入下的 3-sum 问题。
- * 猜测找出 N 个随机 int 值中和为 0 的整数三元组的数量所需的时间并验证你的猜想。
- * 如果你擅长数学分析,请为此问题给出一个合适的数学模型,
- * 其中所有值均匀的分布在 -M 和 M 之间,且 M 不能是一个小整数。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- // 数学模型
- //
- // N 个数可组成的三元组的总数为:
- // C(N, 3) = N(N-1)(N-2)/3! = ~ (N^3)/6 (组合数公式)
- // [-M, M]中随机 N 次,有 (2M+1)^N 种随机序列(每次随机都有 2M+1 种可能)
- // 按照分步计数方法,将随机序列分为和为零的三元组和其余 N-3 个数
- // 这些序列中,和为零的三元组有 3M^2 + 3M + 1 种可能。
- // 其他不为零的 N-3 个位置有 (2M+1)^(N-3) 种可能。
- // 总共有 ((N^3)/6) * (3M^2 + 3M + 1) * (2M+1)^(N-3) 种可能性
- // 平均值为:
- // [((N^3)/6) * (3M^2 + 3M + 1) * (2M+1)^(N-3)] / (2M+1)^N
- // (N^3) * (3M^2 + 3M + 1) / 6 * (2M+1)^3
- // ~ N^3 * 3M^2 / 6 * 8M^3
- // N^3/16M
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int M = ;
- for (int n = ; n < ; n += n)
- {
- Random random = new Random();
- int[] a = new int[n];
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next( * M) - M;
- }
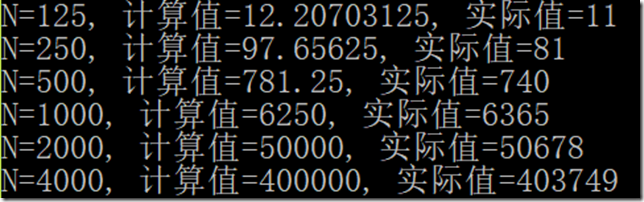
- Console.WriteLine($"N={n}, 计算值={Math.Pow(n, 3) / (16 * M)}, 实际值={ThreeSum.Count(a)}");
- }
- }
- }
- }
1.4.41
解答
代码
这里使用了委托来简化代码。
DoublingRatio
- using System;
- using Measurement;
- namespace _1._4._41
- {
- public delegate int Count(int[] a);
- static class DoublingRatio
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 从指定字符串中读入按行分割的整型数据。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="inputString">源字符串。</param>
- /// <returns>读入的整型数组</returns>
- private static int[] ReadAllInts(string inputString)
- {
- char[] split = new char[] { '\n' };
- string[] input = inputString.Split(split, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
- int[] a = new int[input.Length];
- for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = int.Parse(input[i]);
- }
- return a;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 使用给定的数组进行一次测试,返回耗时(毫秒)。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="Count">要测试的方法。</param>
- /// <param name="a">测试用的数组。</param>
- /// <returns>耗时(秒)。</returns>
- public static double TimeTrial(Count Count, int[] a)
- {
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- Count(a);
- return timer.ElapsedTimeMillionSeconds();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 对 TwoSum、TwoSumFast、ThreeSum 或 ThreeSumFast 的 Count 方法做测试。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="Count">相应类的 Count 方法</param>
- /// <returns>随着数据量倍增,方法耗时增加的比率。</returns>
- public static double Test(Count Count)
- {
- double ratio = ;
- double times = ;
- // 1K
- int[] a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._1Kints);
- double prevTime = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine("数据量\t耗时\t比值");
- Console.WriteLine($"1000\t{prevTime / 1000}\t");
- // 2K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._2Kints);
- double time = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"2000\t{time / 1000}\t{time / prevTime}");
- if (prevTime != )
- {
- ratio += time / prevTime;
- }
- else
- {
- times--;
- }
- prevTime = time;
- // 4K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._4Kints);
- time = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"4000\t{time / 1000}\t{time / prevTime}");
- if (prevTime != )
- {
- ratio += time / prevTime;
- }
- else
- {
- times--;
- }
- prevTime = time;
- // 8K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._8Kints);
- time = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"8000\t{time / 1000}\t{time / prevTime}");
- if (prevTime != )
- {
- ratio += time / prevTime;
- }
- else
- {
- times--;
- }
- prevTime = time;
- return ratio / times;
- }
- public static double TestTwoSumFast(Count Count)
- {
- double ratio = ;
- double times = ;
- // 8K
- int[] a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._8Kints);
- double prevTime = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine("数据量\t耗时\t比值");
- Console.WriteLine($"8000\t{prevTime / 1000}\t");
- // 16K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._16Kints);
- double time = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"16000\t{time / 1000}\t{time / prevTime}");
- if (prevTime != )
- {
- ratio += time / prevTime;
- }
- else
- {
- times--;
- }
- prevTime = time;
- // 32K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._32Kints);
- time = TimeTrial(Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"32000\t{time / 1000}\t{time / prevTime}");
- if (prevTime != )
- {
- ratio += time / prevTime;
- }
- else
- {
- times--;
- }
- prevTime = time;
- return ratio / times;
- }
- }
- }
主方法:
- using System;
- using Measurement;
- namespace _1._4._41
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.41
- *
- * 运行时间。
- * 使用 DoublingRatio 估计在你的计算机上用 TwoSumFast、TwoSum、ThreeSumFast 以及 ThreeSum 处理一个含有 100 万个整数的文件所需的时间。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] a = new int[];
- Random random = new Random();
- for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next() - ;
- }
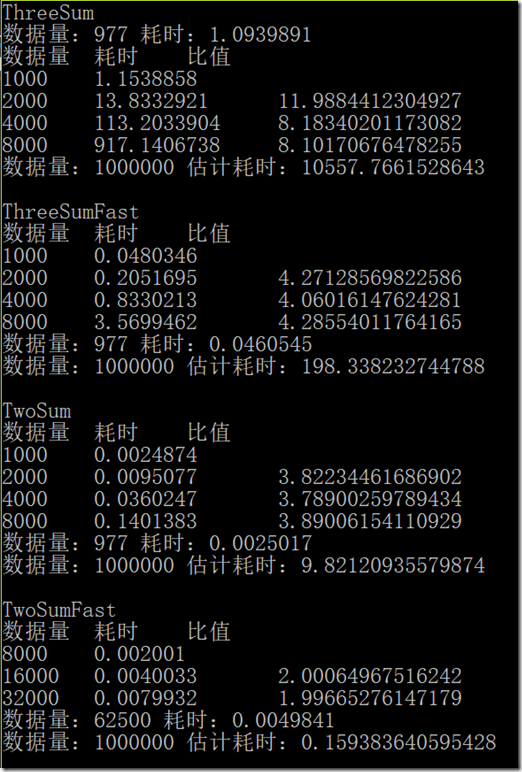
- // ThreeSum
- Console.WriteLine("ThreeSum");
- double time = DoublingRatio.TimeTrial(ThreeSum.Count, a);
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:977 耗时:{time / 1000}");
- double doubleRatio = DoublingRatio.Test(ThreeSum.Count);
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:1000000 估计耗时:{time * doubleRatio * 1024 / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine();
- //// ThreeSumFast
- Console.WriteLine("ThreeSumFast");
- time = DoublingRatio.TimeTrial(ThreeSumFast.Count, a);
- doubleRatio = DoublingRatio.Test(ThreeSumFast.Count);
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:977 耗时:{time / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:1000000 估计耗时:{time * doubleRatio * 1024 / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine();
- //// TwoSum
- Console.WriteLine("TwoSum");
- time = DoublingRatio.TimeTrial(TwoSum.Count, a);
- doubleRatio = DoublingRatio.Test(TwoSum.Count);
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:977 耗时:{time / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:1000000 估计耗时:{time * doubleRatio * 1024 / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine();
- // TwoSumFast
- // 速度太快,加大数据量
- a = new int[];
- for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next() - ;
- }
- Console.WriteLine("TwoSumFast");
- time = DoublingRatio.TimeTrial(TwoSumFast.Count, a);
- doubleRatio = DoublingRatio.TestTwoSumFast(TwoSumFast.Count);
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:62500 耗时:{time / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine($"数据量:1000000 估计耗时:{time * doubleRatio * 16 / 1000}");
- Console.WriteLine();
- }
- }
- }
1.4.42
解答
这里我们把时限设置为一小时,使用上一题的数据估计。
1.ThreeSum 暴力方法在输入倍增时耗时增加 2^3 = 8 倍。
1K 数据耗费了 1.15 秒,在一小时内(3600 秒)可以完成 2^3 = 8K 数据。
2.ThreeSumFast 方法在输入倍增时耗时增加 2^2 = 4 倍。
1K 数据耗费了 0.05 秒,在一小时内(3600 秒)可以完成 2^8 = 256K 数据。
3.TwoSum 暴力方法在输入倍增时耗时增加 2^2 = 4 倍。
8K 数据耗费了 0.14 秒,在一小时内(3600 秒)可以完成 2^10 = 1024K 数据。
4.TwoSumFast 在输入倍增时耗时增加 2^1 = 2 倍。
32K 数据耗费了 0.008 秒,在一小时内(3600 秒)可以完成 2^16 = 65536K 数据。
1.4.43
解答
代码
修改后的 DoublingRatio
- using System;
- using Measurement;
- namespace _1._4._43
- {
- static class DoublingRatio
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// 从指定字符串中读入按行分割的整型数据。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="inputString">源字符串。</param>
- /// <returns>读入的整型数组</returns>
- private static int[] ReadAllInts(string inputString)
- {
- char[] split = new char[] { '\n' };
- string[] input = inputString.Split(split, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
- int[] a = new int[input.Length];
- for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = int.Parse(input[i]);
- }
- return a;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 使用给定的数组对链栈进行一次测试,返回耗时(毫秒)。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">测试用的数组。</param>
- /// <returns>耗时(毫秒)。</returns>
- public static double TimeTrialLinkedStack(int[] a)
- {
- LinkedStack<int> stack = new LinkedStack<int>();
- int n = a.Length;
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Push(a[i]);
- }
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Pop();
- }
- return timer.ElapsedTimeMillionSeconds();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 使用给定的数组对数组栈进行一次测试,返回耗时(毫秒)。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">测试用的数组。</param>
- /// <returns>耗时(毫秒)。</returns>
- public static double TimeTrialDoublingStack(int[] a)
- {
- DoublingStack<int> stack = new DoublingStack<int>();
- int n = a.Length;
- Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Push(a[i]);
- }
- for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
- {
- stack.Pop();
- }
- return timer.ElapsedTimeMillionSeconds();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 对链栈和基于大小可变的数组栈做测试。
- /// </summary>
- public static void Test()
- {
- double linkedTime = ;
- double arrayTime = ;
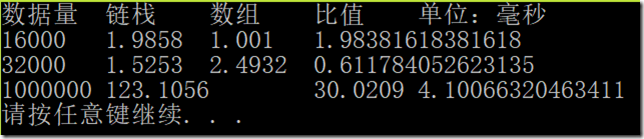
- Console.WriteLine("数据量\t链栈\t数组\t比值\t单位:毫秒");
- // 16K
- int[] a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._16Kints);
- linkedTime = TimeTrialLinkedStack(a);
- arrayTime = TimeTrialDoublingStack(a);
- Console.WriteLine($"16000\t{linkedTime}\t{arrayTime}\t{linkedTime / arrayTime}");
- // 32K
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._32Kints);
- linkedTime = TimeTrialLinkedStack(a);
- arrayTime = TimeTrialDoublingStack(a);
- Console.WriteLine($"32000\t{linkedTime}\t{arrayTime}\t{linkedTime / arrayTime}");
- // 1M
- a = ReadAllInts(TestCase.Properties.Resources._1Mints);
- linkedTime = TimeTrialLinkedStack(a);
- arrayTime = TimeTrialDoublingStack(a);
- Console.WriteLine($"1000000\t{linkedTime}\t{arrayTime}\t{linkedTime / arrayTime}");
- }
- }
- }
1.4.44
解答
每生成一个随机数都和之前生成过的随机数相比较。
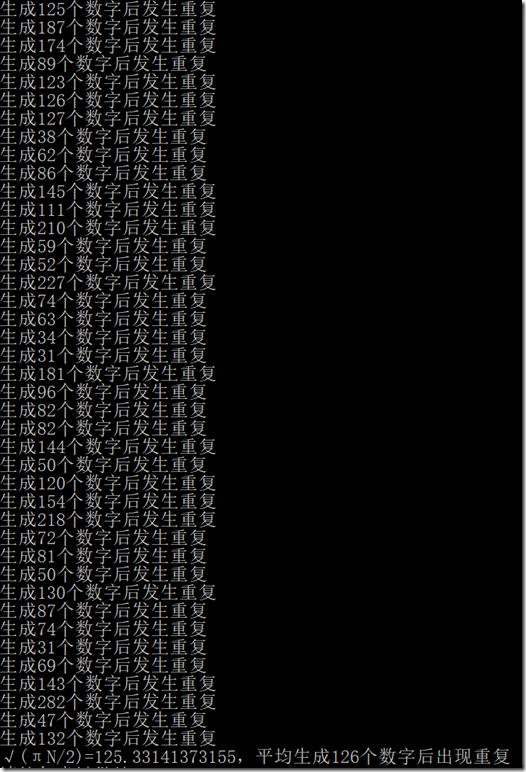
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._44
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.44
- *
- * 生日问题。
- * 编写一个程序,
- * 从命令行接受一个整数 N 作为参数并使用 StdRandom.uniform() 生成一系列 0 到 N-1 之间的随机整数。
- * 通过实验验证产生第一个重复的随机数之前生成的整数数量为 ~√(πN/2)。
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Random random = new Random();
- int N = ;
- int[] a = new int[N];
- int dupNum = ;
- int times = ;
- for (times = ; times < ; ++times)
- {
- for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = random.Next(N);
- if (IsDuplicated(a, i))
- {
- dupNum += i;
- Console.WriteLine($"生成{i + 1}个数字后发生重复");
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- Console.WriteLine($"√(πN/2)={Math.Sqrt(Math.PI * N / 2.0)},平均生成{dupNum / times}个数字后出现重复");
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查是否有重复的数字出现。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">需要检查的数组。</param>
- /// <param name="i">当前加入数组元素的下标。</param>
- /// <returns>有重复则返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
- static bool IsDuplicated(int[] a, int i)
- {
- for (int j = ; j < i; ++j)
- {
- if (a[j] == a[i])
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
1.4.45
解答
建立一个布尔数组,将每次随机出来的数作为下标,将相应位置的布尔值改为 true,每次随机都检查一遍这个数组是否都是 true。
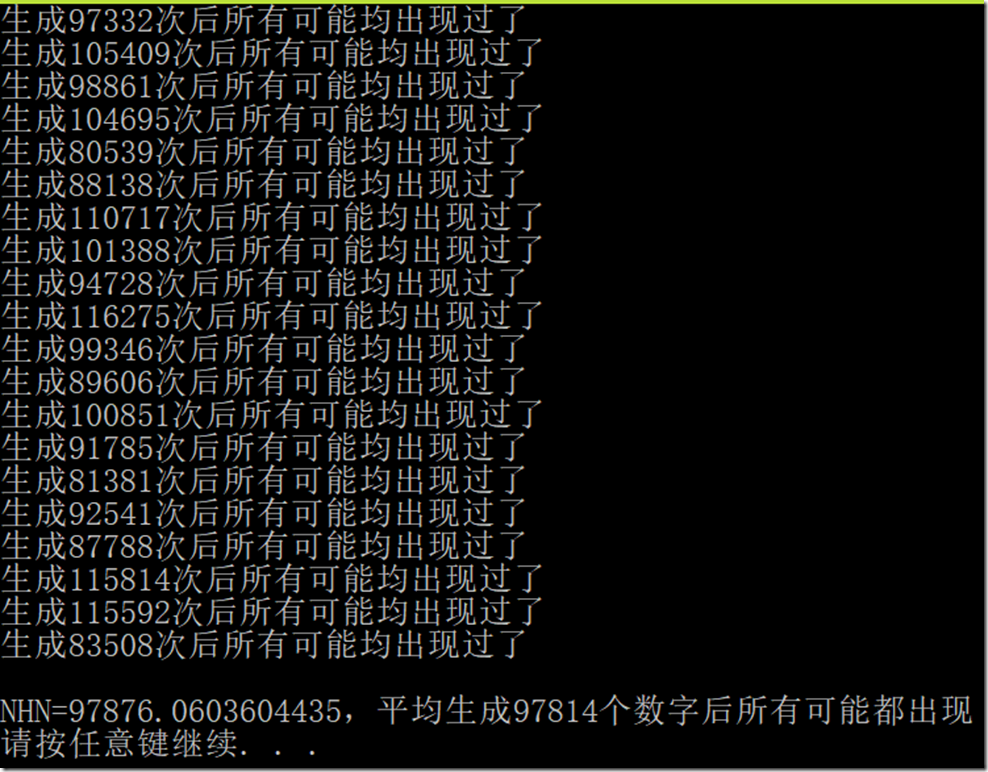
代码
- using System;
- namespace _1._4._45
- {
- /*
- * 1.4.45
- *
- * 优惠券收集问题。
- * 用和上一题相同的方式生成随机整数。
- * 通过实验验证生成所有可能的整数值所需生成的随机数总量为 ~NHN。
- * (这里的 HN 中 N 是下标)
- *
- */
- class Program
- {
- // HN 指的是调和级数
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Random random = new Random();
- int N = ;
- bool[] a = new bool[N];
- int randomSize = ;
- int times = ;
- for (times = ; times < ; ++times)
- {
- for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
- {
- a[i] = false;
- }
- for(int i = ; true; ++i)
- {
- int now = random.Next(N);
- a[now] = true;
- if (IsAllGenerated(a))
- {
- randomSize += i;
- Console.WriteLine($"生成{i}次后所有可能均出现过了");
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- Console.WriteLine($"\nNHN={N * HarmonicSum(N)},平均生成{randomSize / times}个数字后所有可能都出现");
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 计算 N 阶调和级数的和。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="N">调和级数的 N 值</param>
- /// <returns>N 阶调和级数的和。</returns>
- static double HarmonicSum(int N)
- {
- double sum = ;
- for (int i = ; i <= N; ++i)
- {
- sum += 1.0 / i;
- }
- return sum;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 检查所有数字是否都生成过了。
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="a">布尔数组。</param>
- /// <returns>全都生成则返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
- static bool IsAllGenerated(bool[] a)
- {
- foreach (bool i in a)
- {
- if (!i)
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- }
算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.4的更多相关文章
- 算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1 写在前面 整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csh ...
- 算法第四版 在Eclipse中调用Algs4库
首先下载Eclipse,我选择的是Eclipse IDE for Java Developers64位版本,下载下来之后解压缩到喜欢的位置然后双击Eclipse.exe启动 然后开始新建项目,File ...
- 算法第四版jar包下载地址
算法第四版jar包下载地址:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/
- 算法第四版-文字版-下载地址-Robert Sedgewick
下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/moshenglv/10777447 算法第四版,文字版,可复制,方便copy代码 目录: 第1章 基 础 ...... ...
- 二项分布。计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数(算法第四版1.1.27)
算法第四版35页问题1.1.27,估计用一下代码计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数: public static double binomial(int n,int ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之优先队列--Priority Queues
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.4优先队列(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:API 与初级实现 2:堆得定义 3:堆排序 4:事件驱动的仿真 优先队列最重要的操作就是删 ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之快速排序 QuickSort
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.3快速排序(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:快速排序 2:
- C程序设计(第四版)课后习题完整版 谭浩强编著
//复习过程中,纯手打,持续更新,觉得好就点个赞吧. 第一章:程序设计和C语言 习题 1.什么是程序?什么是程序设计? 答:程序就是一组计算机能识别和执行的指令.程序设计是指从确定任务到得到结果,写出 ...
- 算法第四版 coursera公开课 普林斯顿算法 ⅠⅡ部分 Robert Sedgewick主讲《Algorithms》
这是我在网上找到的资源,下载之后上传到我的百度网盘了. 包含两部分:1:算法视频的种子 2:字幕 下载之后,请用迅雷播放器打开,因为迅雷可以直接在线搜索字幕. 如果以下链接失效,请在下边留言,我再更新 ...
- 相似度分析,循环读入文件(加入了HanLP,算法第四版的库)
相似度分析的,其中的分词可以采用HanLP即可: http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1421978002609.htm /****************** ...
随机推荐
- linux开通端口允许其他机器访问
命令开通8080端口允许其他机器对linux的访问: iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
- jQuery中的$.getJSON、$.ajax、$.get、$.post的区别
jQuery中的$.getJSON.$.ajax.$.get.$.post的区别 使用见Flask(python)异步(ajax)返回json格式数据 ①.$.getJSON $.getJSON()是 ...
- 如何让模拟的json数据接口能够正常的在手机上有效果
1. 确保手机与PC在同一个ip网下 这里我是通过------------360随身WIFI,20块钱淘宝上卖的,外观像U盘一样的,直接插在电脑的USB上就能在PC上创建一个WiFi,手机连接上就可以 ...
- Python 多进程和进程池
一,前言 进程:是程序,资源集合,进程控制块组成,是最小的资源单位 特点:就对Python而言,可以实现真正的并行效果 缺点:进程切换很容易消耗cpu资源,进程之间的通信相对线程来说比较麻烦 线程:是 ...
- MATLAB绘制函数图
序言 Matlab可以根据用户给出的数据绘制相应的函数图.对于单个2D函数图,需要给出一个行向量x作为函数图上离散点集的横坐标,以及一个与x列数一样的横坐标y作为函数图上点集的纵坐标. 向量x和y的取 ...
- git删除和提交
//删除git分支git branch -D BranchNamegit branch -r -D origin/BranchNamegit push origin -d BranchName//提交 ...
- Xamarin.Forms 未能找到路径“x:\platforms”的一部分
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45500269/xamarin-android-common-targets-error-could-not-find-a-p ...
- 关于mysql分组查询
在mysql查询中,用到GROUP BY 根据某一字段分组之后,每组显示的结果都只有第一条,这样的结果通常不是我们想要的. GROUP_CONCAT('字段') 可以将每一组下面的这个字段所有的数 ...
- React-typescript-antd 常见问题
一.The key 'Accept' is not sorted alphabetically //tslint.json { "extends": ["tslint:r ...
- CLR 无法从 COM 上下文 0x208f68 转换为 COM 上下文 0x2090d8,这种状态已持续 60 秒
问题: CLR 无法从 COM 上下文 0x208f68 转换为 COM 上下文 0x2090d8,这种状态已持续 60 秒.拥有目标上下文/单元的线程很有可能执行的是非泵式等待或者在不发送 Wind ...
