Tomcat启动过程源码解读
根据Tomcat源码来看一下Tomcat启动过程都做了什么
部分代码为主要流程代码,删去了try-catch以及一些校验逻辑,方便理解主流程
先来一张启动过程时序图,了解一下启动顺序
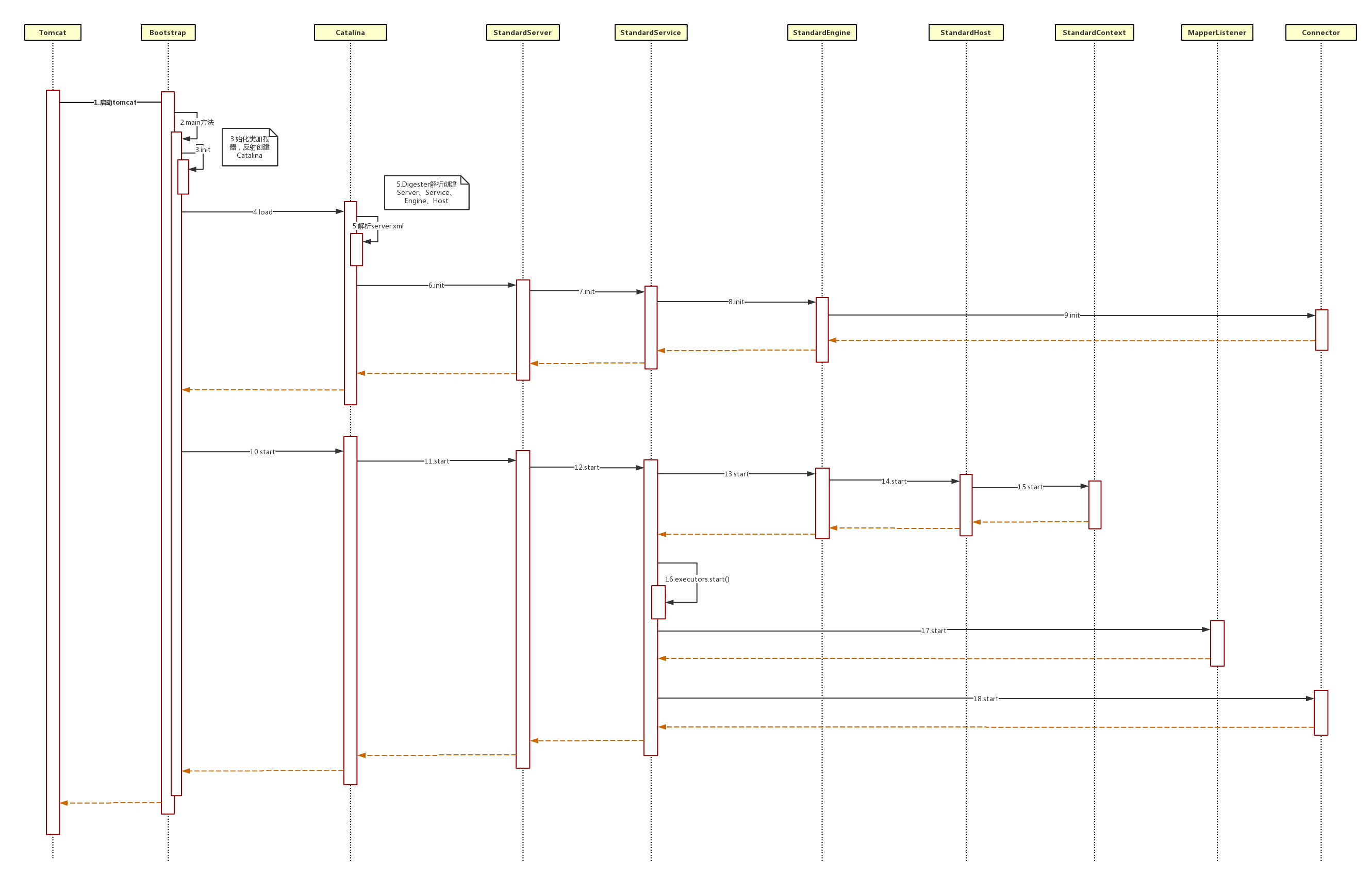
Tomcat启动的入口类:org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#main
main方法是整个tomcat启动时的入口。在main方法中,使用bootstrap.init()来初始化类加载器和创建Catalina实例,然后再启动Catalina线程。
public static void main(String args[]) {
if (daemon == null) {
// Don't set daemon until init() has completed
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap;
} else {
// When running as a service the call to stop will be on a new
// thread so make sure the correct class loader is used to prevent
// a range of class not found exceptions.
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null==daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Unwrap the Exception for clearer error reporting
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
bootstrap.init()方法,用于初始化容器相关,首先创建类加载器,然后通过反射创建org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina实例:
public void init() throws Exception {
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
Class<?> startupClass =
catalinaLoader.loadClass
("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
之后Bootstrap的demon.start()方法就会调用Catalina的start方法。
Catalina实例执行start方法。这里有两个点,一个是load()加载server.xml配置、初始化Server的过程,一个是getServer().start()开启服务、初始化并开启一系列组件、子容器的过程。
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
load方法解析server.xml配置文件,并加载Server、Service、Connector、Container、Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper一系列的容器。加载完成后,调用getServer().start()来开启一个新的Server。
下面先看load方法怎么加载组件和容器的:
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void load() { long t1 = System.nanoTime(); initDirs(); // Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming(); // Create and execute our Digester
Digester digester = createStartDigester(); InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
file = configFile();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
digester.parse(inputSource); getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile()); // Stream redirection
initStreams(); // Start the new server
getServer().init();
}
首先利用Digester类解析server.xml文件,得到容器的配置,并创建相应的对象,并关联父子容器。依次创建的是StandardServer、StandardService、StandardEngine、StandardHost。
然后拿到StandardServer实例调用init()方法初始化Tomcat容器的一系列组件。一些容器初始化的的时候,都会调用其子容器的init()方法,初始化它的子容器。顺序是StandardServer、StandardService、StandardEngine、Connector。每个容器都在初始化自身相关设置的同时,将子容器初始化。
这里插入一个Tomcat中生命周期的概念。在初始化、开启一系列组件、容器的过程中,由tomcat'管理的组件和容器,都有一个共同的特点,都实现了org.apache.catalina.Lifecycle接口,由Tomcat管理其生命周期。Lifecycle提供一种统一的管理对象生命周期的接口。通过Lifecycle、LifecycleListener、LifecycleEvent,Catalina实现了对tomcat各种组件、容器统一的启动和停止的方式。
在Tomcat服务开启过程中启动的一些列组件、容器,都继承了org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase这个抽象类,其中的init()、start() 方法、stop() 方法,为其子类实现了统一的start和stop管理。方法中具体的initInternal()、startInternal() 和stopInternal() 方法,交由子类自己实现。
看一下LifecycleBase的init()和start()的实现吧:
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException {
if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, null, false);
initInternal();
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, null, false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null, false);
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("lifecycleBase.initFail",toString()), t);
}
}
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) ||
LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
Exception e = new LifecycleException();
log.debug(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()), e);
} else if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()));
}
return;
}
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
} else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
startInternal();
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT);
} else {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null, false);
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.startFail", toString()), t);
}
}
可以看到,init()和start()方法里,调用了initInternal()方法、startInternal()方法和stop()方法,这三者最终会走子类的具体实现。
上面的StandardServer的初始化过程就是一个活生生的例子。在Catalina的load过程中,getServer().init()方法就是LifecycleBase中的init()方法,调用initInternal()时是走的StandardServer的实现,StandardServer的initInternal()中会调用StandardServer的init()方法,进行子容器的初始化。然后依次初始化。
看一下代码,了解一下StandardServer中的initInternal()实现。
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors
* to bind to restricted ports under Unix operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // Register global String cache
// Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers
// present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache
// will be registered under multiple names
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache"); // Register the MBeanFactory
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory"); // Register the naming resources
globalNamingResources.init(); // Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared
// class loaders
if (getCatalina() != null) {
ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader();
// Walk the class loader hierarchy. Stop at the system class loader.
// This will add the shared (if present) and common class loaders
while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) {
URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs();
for (URL url : urls) {
if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
try {
File f = new File (url.toURI());
if (f.isFile() &&
f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f);
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
cl = cl.getParent();
}
}
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
}
再举一个具体的例子:
回到刚才的启动过程中,getServer().start()开启服务的方法,实际就是上面提到的LifecycleBase中的start()方法。其中,会调用org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#initInternal方法,初始化Server并调用Service的init方法。org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer在其实现的startInternal() 中,开启naming resources和services,调用service的start方法,开启所有service,调用其service的startInternal()方法。
下面看一下StandardServer中的startInternal()的实现:
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
}
}
这里的service,是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService的实例。
总结一下启动的Tomcat启动的过程
在Catalina的load方法里,就已经调用了StandardServer里的init方法,一层一层初始化了globalNamingResources,StandardService--》StandardEngine,executors,MapperListener,Connector--》CoyoteAdapter,protocolHandler。至此就将tomcat的catalina中的组件、容器初始化完成。 接下来就是调用start方法一层一层开启,StandardServer的startInternal方法,按层次start:globalNamingResources,StandardService--》StandardEngine,executors,MapperListener,Connector--》StandardHost,StandardContext,protocolHandler。顺序基本同init过程。StandardEngine在start时,会init子容器,并调用子容器的start方法。子容器依次这样init、start,就开启了StandardHost和StandardContext。
参考文章:
tomcat源码分析-http请求在Container中的执行路线
tomcat源码解析(一)--启动与Server.xml文件的解析
Tomcat启动过程源码解读的更多相关文章
- Spring IOC容器启动流程源码解析(四)——初始化单实例bean阶段
目录 1. 引言 2. 初始化bean的入口 3 尝试从当前容器及其父容器的缓存中获取bean 3.1 获取真正的beanName 3.2 尝试从当前容器的缓存中获取bean 3.3 从父容器中查找b ...
- Flask框架整个流程源码解读
Flask框架整个流程源码解读 一.总的流程 运行Flask其本质是运行Flask对象中的__call__,而__call__本质调用wsgi_app的方法 wsgi_app方法 def wsgi_a ...
- Spark(五十一):Spark On YARN(Yarn-Cluster模式)启动流程源码分析(二)
上篇<Spark(四十九):Spark On YARN启动流程源码分析(一)>我们讲到启动SparkContext初始化,ApplicationMaster启动资源中,讲解的内容明显不完整 ...
- Spring IOC 容器预启动流程源码探析
Spring IOC 容器预启动流程源码探析 在应用程序中,一般是通过创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigApplicationConte ...
- Android系统默认Home应用程序(Launcher)的启动过程源码分析
在前面一篇文章中,我们分析了Android系统在启动时安装应用程序的过程,这些应用程序安装好之后,还须要有一个Home应用程序来负责把它们在桌面上展示出来,在Android系统中,这个默认的Home应 ...
- Android Content Provider的启动过程源码分析
本文參考Android应用程序组件Content Provider的启动过程源码分析http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6963418和 ...
- Elasticsearch6.3.2启动过程源码阅读记录
Elasticsearch6.3.2启动过程源码阅读记录 网上有很多关于es的源码分析,觉得自己技术深度还不够,所以这些文章只是看源码过程中的一个笔记,谈不上分析. 整个启动过程以类名.方法名,按顺序 ...
- Android Activity启动流程源码全解析(1)
前言 Activity是Android四大组件的老大,我们对它的生命周期方法调用顺序都烂熟于心了,可是这些生命周期方法到底是怎么调用的呢?在启动它的时候会用到startActivty这个方法,但是这个 ...
- Android Activity启动流程源码全解析(2)
接上之前的分析 ++Android Activity启动流程源码全解析(1)++ 1.正在运行的Activity调用startPausingLocked 一个一个分析,先来看看startPausing ...
随机推荐
- tomcat-users.xml 配置
一:tomcat6配置管理员信息 1:打开tomcat6下的~/conf/tomcat-users.xml文件,关于用户角色.管理员的信息都在这个配置文件中. 2:在配置文件<tomcat-us ...
- Struts2实现文件上传和下载,多文件上传,限制文件大小,限制文件类型
文件上传使用的包:commons-upload-xx.jar commons-io-xx.jar 一.实现文件上传: 1.在表单空间中添 ...
- 网页窗口logo图标设置
网站上的logo实际上是一个“**.ico”图片,比如说favicon.ico.实现步骤:第一步:制作favicon.ico,大小一般为16*16毫米(ico图片制作网址http://www.ico. ...
- Sql Server的艺术(七) SQL 数据插入操作
--用INSERT插入单行数据 在SQL中,可以通过INSERT...VALUES语句直接向数据库表中插入数据.可以整行,也可以部分列. 基本语法: INSERT INTO table_name [c ...
- C#常见问题总结(二)
1.erp系统可以在具有固定ip的拥有多层服务器的局域网中使用吗?如何使用 解决方法: 把ini.配置文件字符串中的服务器名改成服务器的,把debug文件夹拷到其他机器上就行,服务器上的服务器名是默认 ...
- Chrome浏览器调试Android的Webview
chrome://inspect Android:4.4+ Chrome 30+ 首次使用需要FQ
- LVS、Nginx和HAProxy负载均衡器对比总结
LVS特点: 1.抗负载能力强,使用IP负载均衡技术,只做分发,所以LVS本身并没有多少流量产生: 2.稳定性.可靠性好,自身有完美的热备方案:(如:LVS+Keepalived) 3.应用范围比较广 ...
- iOS学习——布局利器Masonry框架源码深度剖析
iOS开发过程中很大一部分内容就是界面布局和跳转,iOS的布局方式也经历了 显式坐标定位方式 --> autoresizingMask --> iOS 6.0推出的自动布局(Auto La ...
- MySQL Community Server 5.7安装详细步骤
mysql社区版安装配置步骤较繁琐,几经搜索之后才成功安装,此文将所有的安装步骤及安装过程中遇到的问题进行了总结 1. 下载MySQL社区版 最新版下载地址:https://dev.mysql ...
- 自动创建字符设备,不需mknod
自动创建设备文件 1.自动创建设备文件的流程 字符设备驱动模块 -->创建一个设备驱动class--->创建属于class的device--->调用mdev工具(自动完成)--> ...
