Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) C. Alyona and the Tree dfs
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alyona decided to go on a diet and went to the forest to get some apples. There she unexpectedly found a magic rooted tree with root in the vertex 1, every vertex and every edge of which has a number written on.
The girl noticed that some of the tree's vertices are sad, so she decided to play with them. Let's call vertex v sad if there is a vertex u in subtree of vertex v such that dist(v, u) > au, where au is the number written on vertex u, dist(v, u) is the sum of the numbers written on the edges on the path from v to u.
Leaves of a tree are vertices connected to a single vertex by a single edge, but the root of a tree is a leaf if and only if the tree consists of a single vertex — root.
Thus Alyona decided to remove some of tree leaves until there will be no any sad vertex left in the tree. What is the minimum number of leaves Alyona needs to remove?
In the first line of the input integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) is given — the number of vertices in the tree.
In the second line the sequence of n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) is given, where ai is the number written on vertex i.
The next n - 1 lines describe tree edges: ith of them consists of two integers pi and ci (1 ≤ pi ≤ n, - 109 ≤ ci ≤ 109), meaning that there is an edge connecting vertices i + 1 and pi with number ci written on it.
Print the only integer — the minimum number of leaves Alyona needs to remove such that there will be no any sad vertex left in the tree.
9
88 22 83 14 95 91 98 53 11
3 24
7 -8
1 67
1 64
9 65
5 12
6 -80
3 8
5
The following image represents possible process of removing leaves from the tree:
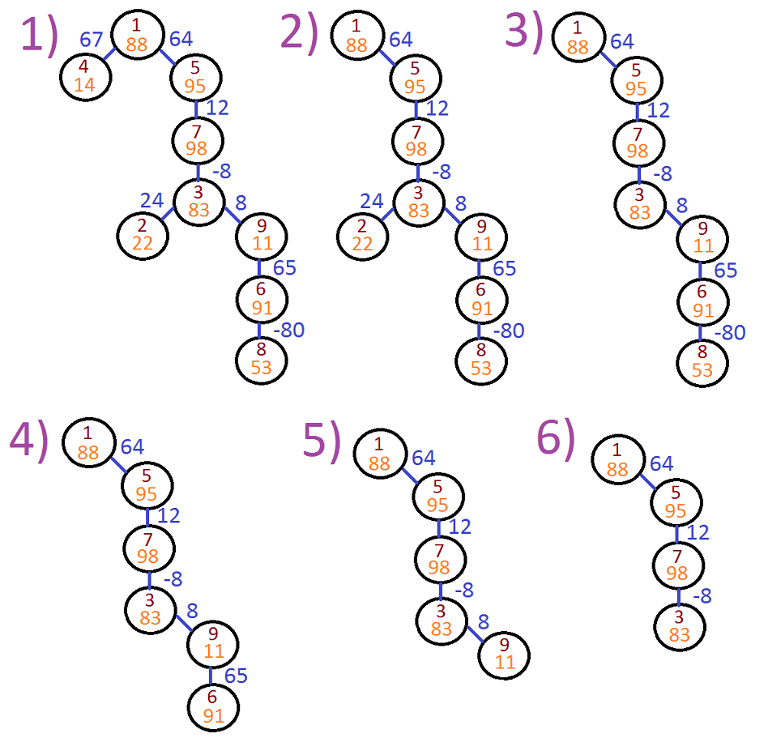
思路:dfs一波,找到sad的点,去掉sad为根的树;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define esp 0.00000000001
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+;
ll a[N];
vector<pair<int,int > >edge[N];
int getnum(int u)
{
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<edge[u].size();i++)
ans+=getnum(edge[u][i].first);
return ans+;
}
int dfs(int u,ll dis)
{
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<edge[u].size();i++)
{
if(a[edge[u][i].first]<dis+edge[u][i].second)
ans+=getnum(edge[u][i].first);
else
ans+=dfs(edge[u][i].first,max(dis+edge[u][i].second,0LL));
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int x,y,z,i,t;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(i=;i<=x;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=;i<x;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
edge[u].push_back(make_pair(i+,v));
}
int ans=dfs(,);
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alyona decided to go on a diet and went to the forest to get some apples. There she unexpectedly found a magic rooted tree with root in the vertex 1, every vertex and every edge of which has a number written on.
The girl noticed that some of the tree's vertices are sad, so she decided to play with them. Let's call vertex v sad if there is a vertex u in subtree of vertex v such that dist(v, u) > au, where au is the number written on vertex u, dist(v, u) is the sum of the numbers written on the edges on the path from v to u.
Leaves of a tree are vertices connected to a single vertex by a single edge, but the root of a tree is a leaf if and only if the tree consists of a single vertex — root.
Thus Alyona decided to remove some of tree leaves until there will be no any sad vertex left in the tree. What is the minimum number of leaves Alyona needs to remove?
In the first line of the input integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) is given — the number of vertices in the tree.
In the second line the sequence of n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) is given, where ai is the number written on vertex i.
The next n - 1 lines describe tree edges: ith of them consists of two integers pi and ci (1 ≤ pi ≤ n, - 109 ≤ ci ≤ 109), meaning that there is an edge connecting vertices i + 1 and pi with number ci written on it.
Print the only integer — the minimum number of leaves Alyona needs to remove such that there will be no any sad vertex left in the tree.
9
88 22 83 14 95 91 98 53 11
3 24
7 -8
1 67
1 64
9 65
5 12
6 -80
3 8
5
The following image represents possible process of removing leaves from the tree:

Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) C. Alyona and the Tree dfs的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) C. Alyona and the Tree 水题
C. Alyona and the Tree 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/682/problem/C Description Alyona deci ...
- Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2)——C. Alyona and the Tree(树的DFS+逆向思维)
C. Alyona and the Tree time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) C. Alyona and the Tree
C. Alyona and the Tree time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #381 (Div. 1) B. Alyona and a tree dfs序 二分 前缀和
B. Alyona and a tree 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/739/problem/B Description Alyona has a tree ...
- Codeforces Round #381 (Div. 2) D. Alyona and a tree dfs序+树状数组
D. Alyona and a tree time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #381 (Div. 2) D. Alyona and a tree 树上二分+前缀和思想
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/740/problem/D D. Alyona and a tree time limit per test2 secondsm ...
- Codeforces Round #381 (Div. 2)D. Alyona and a tree(树+二分+dfs)
D. Alyona and a tree Problem Description: Alyona has a tree with n vertices. The root of the tree is ...
- Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) A B C 水 水 dfs序+dp
A. Alyona and Numbers time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #358 (Div. 2) E. Alyona and Triangles 随机化
E. Alyona and Triangles 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/682/problem/E Description You are given ...
随机推荐
- CentOS yum 安装node.js
第一步: curl --silent --location https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo bash - 第二步: sudo yum -y i ...
- 3D游戏引擎中常见的三维场景管理方法
对于一个有很多物体的3D场景来说,渲染这个场景最简单的方式就是用一个List将这些物体进行存储,并送入GPU进行渲染.当然,这种做法在效率上来说是相当低下的,因为真正需要渲染的物体应该是视椎体内的物体 ...
- JavaScript Object.defineProperty()方法详解
Object.defineProperty() 方法直接在一个对象上定义一个新属性,或者修改一个已经存在的属性, 并返回这个对象. 语法 Object.defineProperty(obj, prop ...
- 简明python教程八----输入/输出
通过创建一个file类的对象来打开一个文件,分别使用file类的read.readline或write方法来读写文件. 最后调用一个close方法来告诉Python我们完成了对文件的使用. poem= ...
- CF519 ABCD D. A and B and Interesting Substrings(map,好题)
A:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/519/A 水题没什么好说的. #include <iostream> #include <st ...
- JVM生命周期
JVM生命周期可以分为以下三个阶段 启动:任何class文件的main函数都可认为是jvm示例的起点. 运行:以main函数为起点,后续的线程都由它启动,包括守护线程和用户线程.main方法启动的线程 ...
- MySQL,sqlalchemy
Mariadb 数据库是一堆表的集合 主键 外键 索引 安装: Centos7 [root@host]# mysqladmin -u root password "new_password& ...
- ajax参数补充
ajax参数补充 contentType 当我们使用form表单提交数据时,有一个enctype属性,默认情况下不写 此时我们提交数据时,会默认将数据以application/x-www-form-u ...
- windows下mysql安装失败的一个解决案例
操作系统:windows8.1,之前安装过mysql,这次安装在配置的最后一部执行“Apply security settings”的过程中弹出经典错误: Access denied for user ...
- 20145316《Java程序设计》第二周学习总结
20145316<Java程序设计>第2周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 3.1.1 Java的类型 分为基本类型(Primitive type)和类类型(Class type) 基本类型: ...
