多线程间通信之AutoResetEvent和ManualResetEvent的原理分析和开发示例
AutoResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信。 通常,当线程需要独占访问资源时使用该类。
线程通过调用 AutoResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 来等待信号。 如果 AutoResetEvent 为非终止状态,则线程会被阻止,并等待当前控制资源的线程通过调用 Set 来通知资源可用。
调用 Set 向 AutoResetEvent 发信号以释放等待线程。 AutoResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到一个正在等待的线程被释放,然后自动返回非终止状态。 如果没有任何线程在等待,则状态将无限期地保持为终止状态。
如果当 AutoResetEvent 为终止状态时线程调用 WaitOne,则线程不会被阻止。 AutoResetEvent 将立即释放线程并返回到非终止状态。
ManualResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信。 通常,此通信涉及一个线程在其他线程进行之前必须完成的任务。
当一个线程开始一个活动(此活动必须完成后,其他线程才能开始)时,它调用 Reset 以将 ManualResetEvent 置于非终止状态。 此线程可被视为控制 ManualResetEvent。 调用 ManualResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 的线程将阻止,并等待信号。 当控制线程完成活动时,它调用Set 以发出等待线程可以继续进行的信号。 并释放所有等待线程。
一旦它被终止,ManualResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到它被手动重置。 即对 WaitOne 的调用将立即返回。
可以通过将布尔值传递给构造函数来控制 ManualResetEvent 的初始状态,如果初始状态处于终止状态,为 true;否则为 false。
ManualResetEvent 也可以同 staticWaitAll 和 WaitAny 方法一起使用。
生活中的例子
AutoResetEvent :在上海坐地铁,检票口有个刷卡的通道,一次只能一个人刷卡后通过,而我过后,它又是关闭的,另一个人又得再刷卡.一次操作,只有一个事件,这时就是非终止状态,一般是用来同步访问资源.
ManualResetEvent :公司园区的大门很大,一次可以多人通过。
ManualResetEvent和AutoResetEvent 比较
ManualResetEvent和AutoResetEvent都继承自EventWaitHandler,它们的唯一区别就在于父类 EventWaitHandler的构造函数参数EventResetMode不同,这样我们只要弄清了参数EventResetMode值不同时,EventWaitHandler类控制线程同步的行为有什么不同,两个子类也就清楚了。
共同点:
A、Set方法将事件状态设置为终止状态,允许一个或多个等待线程继续;Reset方法将事件状态设置为非终止状态,导致线程阻止;WaitOne阻止当前线程,直到当前线程的WaitHandler收到事件信号。
B、可以通过构造函数的参数值来决定其初始状态,若为true则事件为终止状态从而使线程为非阻塞状态,为false则线程为阻塞状态。
C、如果某个线程调用WaitOne方法,则当事件状态为终止状态时,该线程会得到信号,继续向下执行。
不同点:
A、AutoResetEvent.WaitOne()每次只允许一个线程进入,当某个线程得到信号后,AutoResetEvent会自动又将信号置为不发送状态,则其他调用WaitOne的线程只有继续等待,也就是说AutoResetEvent一次只唤醒一个线程;
B、ManualResetEvent则可以唤醒多个线程,因为当某个线程调用了ManualResetEvent.Set()方法后,其他调用WaitOne的线程获得信号得以继续执行,而ManualResetEvent不会自动将信号置为不发送。
C、也就是说,除非手工调用了ManualResetEvent.Reset()方法,则ManualResetEvent将一直保持有信号状态,ManualResetEvent也就可以同时唤醒多个线程继续执行。
先看下AutoResetEvent 的代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
namespace System.Threading { using System; using System.Security.Permissions; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; [HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)] [System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)] public sealed class AutoResetEvent : EventWaitHandle { public AutoResetEvent(bool initialState) : base(initialState,EventResetMode.AutoReset){ } } } |
再来看下EventWaitHandle的代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
|
namespace System.Threading { using System; using System.Threading; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using System.Security.Permissions; using System.IO; using Microsoft.Win32; using Microsoft.Win32.SafeHandles; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; using System.Runtime.Versioning; #if !FEATURE_PAL using System.Security.AccessControl; #endif [HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)] [ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public class EventWaitHandle : WaitHandle { [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.None)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine, ResourceScope.Machine)] public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode) : this(initialState,mode,null) { } [SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name) { if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) { throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); } SafeWaitHandle _handle = null; switch(mode) { case EventResetMode.ManualReset: _handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(null, true, initialState, name); break; case EventResetMode.AutoReset: _handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(null, false, initialState, name); break; default: throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_InvalidFlag",name)); }; if (_handle.IsInvalid) { int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); _handle.SetHandleAsInvalid(); if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); __Error.WinIOError(errorCode, ""); } SetHandleInternal(_handle); } [SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name, out bool createdNew) #if !FEATURE_PAL : this(initialState, mode, name, out createdNew, null) { } [SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] public unsafe EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name, out bool createdNew, EventWaitHandleSecurity eventSecurity) #endif { if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) { throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); } Win32Native.SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES secAttrs = null; #if !FEATURE_PAL // For ACL's, get the security descriptor from the EventWaitHandleSecurity. if (eventSecurity != null) { secAttrs = new Win32Native.SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES(); secAttrs.nLength = (int)Marshal.SizeOf(secAttrs); byte[] sd = eventSecurity.GetSecurityDescriptorBinaryForm(); byte* pSecDescriptor = stackalloc byte[sd.Length]; Buffer.memcpy(sd, 0, pSecDescriptor, 0, sd.Length); secAttrs.pSecurityDescriptor = pSecDescriptor; } #endif SafeWaitHandle _handle = null; Boolean isManualReset; switch(mode) { case EventResetMode.ManualReset: isManualReset = true; break; case EventResetMode.AutoReset: isManualReset = false; break; default: throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_InvalidFlag",name)); }; _handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(secAttrs, isManualReset, initialState, name); int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); if (_handle.IsInvalid) { _handle.SetHandleAsInvalid(); if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); __Error.WinIOError(errorCode, name); } createdNew = errorCode != Win32Native.ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS; SetHandleInternal(_handle); } private EventWaitHandle(SafeWaitHandle handle) { SetHandleInternal(handle); } [SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] public static EventWaitHandle OpenExisting(string name) { #if !FEATURE_PAL return OpenExisting(name, EventWaitHandleRights.Modify | EventWaitHandleRights.Synchronize); } [SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] [ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] [ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] public static EventWaitHandle OpenExisting(string name, EventWaitHandleRights rights) { #endif // !FEATURE_PAL if (name == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("name", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentNull_WithParamName")); } if(name.Length == 0) { throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_EmptyName"), "name"); } if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) { throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); }#if FEATURE_PAL SafeWaitHandle myHandle = Win32Native.OpenEvent(Win32Native.EVENT_MODIFY_STATE | Win32Native.SYNCHRONIZE, false, name);#else SafeWaitHandle myHandle = Win32Native.OpenEvent((int) rights, false, name); #endif if (myHandle.IsInvalid) { int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); if(Win32Native.ERROR_FILE_NOT_FOUND == errorCode || Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_NAME == errorCode) throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(); if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); //this is for passed through Win32Native Errors __Error.WinIOError(errorCode,""); } return new EventWaitHandle(myHandle); } public bool Reset() { bool res = Win32Native.ResetEvent(safeWaitHandle); if (!res) __Error.WinIOError(); return res; } public bool Set() { bool res = Win32Native.SetEvent(safeWaitHandle); if (!res) __Error.WinIOError(); return res; }#if !FEATURE_PAL public EventWaitHandleSecurity GetAccessControl() { return new EventWaitHandleSecurity(safeWaitHandle, AccessControlSections.Access | AccessControlSections.Owner | AccessControlSections.Group); } public void SetAccessControl(EventWaitHandleSecurity eventSecurity) { if (eventSecurity == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("eventSecurity"); eventSecurity.Persist(safeWaitHandle); } #endif } } |
再来看下ManualResetEvent的代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
namespace System.Threading { using System; using System.Security.Permissions; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; [HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)][System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)] public sealed class ManualResetEvent : EventWaitHandle { public ManualResetEvent(bool initialState) : base(initialState,EventResetMode.ManualReset){} } } |
其实这两个的差别就是AutoResetEvent是base(initialState,EventResetMode.AutoReset)而ManualResetEvent是base(initialState,EventResetMode.ManualReset).
AutoResetEvent是操作单个线程的,而ManualResetEvent可以操作多个线程.
AutoResetEvent开发示例
在主线程运行后,新开一个新线程,由新线程来控制主线程的等待和执行.
类关系图
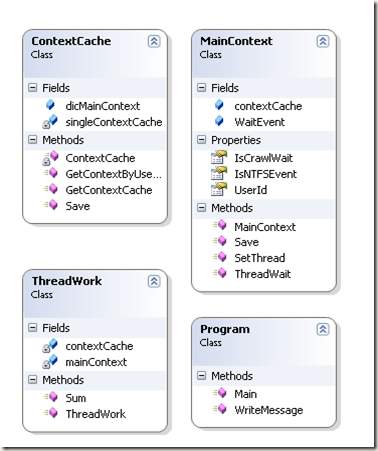
代码实现
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
|
//===============================================================================//作者:Spring Yang//日期:2011-10-12//===============================================================================namespace TestMultipleThread{ using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading; public class ThreadWork { private MainContext mainContext; private ContextCache contextCache; public ThreadWork() { contextCache = ContextCache.GetContextCache(); mainContext = contextCache.GetContextByUserId("001"); } public void Sum() { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("this is thread ID {0} execute", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread.Sleep(10); } if (mainContext != null && mainContext.IsCrawlWait == false) { mainContext.IsNTFSEvent = true; while (mainContext.IsCrawlWait) { Thread.Sleep(25); } Console.WriteLine("main thread is wait"); Thread.Sleep(10000); Console.WriteLine("main thread is start"); mainContext.IsNTFSEvent = false; mainContext.SetThread(); } } } class Program { public static void Main() { MainContext mainContext = new MainContext("001"); mainContext.Save(); //新开一个线程 ThreadWork threadWork = new ThreadWork(); ThreadStart myThreadDelegate = new ThreadStart(threadWork.Sum); Thread myThread = new Thread(myThreadDelegate); myThread.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { if (mainContext.IsNTFSEvent) mainContext.ThreadWait(); Thread.Sleep(10); } Console.WriteLine("main Thread continue"); Thread.Sleep(100000); } public void WriteMessage() { Console.WriteLine("Stop the main thread."); } } public class MainContext { public string UserId { get; set; } //设置 AutoResetEvent public AutoResetEvent WaitEvent; public ContextCache contextCache; //设置线程等待 public void ThreadWait() { if (WaitEvent == null) WaitEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); if (IsNTFSEvent) { IsCrawlWait = true; WaitEvent.WaitOne(); } } public MainContext(string userID) { UserId = userID; IsCrawlWait = false; IsNTFSEvent = false; contextCache = ContextCache.GetContextCache(); } public void Save() { contextCache.Save(UserId, this); } public void SetThread() { if (!IsNTFSEvent && IsCrawlWait) { IsCrawlWait = false; WaitEvent.Set(); } } public bool IsCrawlWait { get; set; } public bool IsNTFSEvent { get; set; } } //单例模式,保存到内存中 public class ContextCache { public Dictionary<string, MainContext> dicMainContext = new Dictionary<string, MainContext>(); public void Save(string userId, MainContext mainContext) { dicMainContext.Add(userId, mainContext); } private static ContextCache singleContextCache; public MainContext GetContextByUserId(string userId) { MainContext context; dicMainContext.TryGetValue(userId, out context); return context; } private ContextCache() { } public static ContextCache GetContextCache() { if (singleContextCache == null) { singleContextCache = new ContextCache(); } return singleContextCache; } }} |
运行结果

参考资料:
1、MSDN
2、C#多线程:深入了解线程同步lock,Monitor,Mutex,同步事件和等待句柄(中) 地址: http://dongguojun.iteye.com/blog/960586
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/springyangwc/archive/2011/10/12/2208991.html
多线程间通信之AutoResetEvent和ManualResetEvent的原理分析和开发示例的更多相关文章
- 多线程间通信之AutoResetEvent和ManualResetEvent的原理分析
AutoResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信. 通常,当线程需要独占访问资源时使用该类. 线程通过调用 AutoResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 来等待信号. 如果 AutoRe ...
- (十一)boost库之多线程间通信
(十一)boost库之多线程间通信 1.互斥锁 在编程中,引入了对象互斥锁的概念,来保证共享数据操作的完整性.每个对象都对应于一个可称为" 互斥锁" 的标记,这个标记用来保证在任一 ...
- Java 多线程间通信
JDK 1.5 以后, 将同步和锁封装成了对象, 并将操作锁的隐式方法定义到了该对象中, 将隐式动作变成了显示动作. Lock 接口 Lock 接口, 位于 java.util.concurrent. ...
- Java多线程间通信-解决安全问题、等待唤醒机制
/*1.增加一个知识点一个类怎么在所有的类中,让其它类来共同修改它的数据呢?可以用单例设计模式可以用静态可以在其它类中做一个构造函数,接受同一个对象,这样就可以实现对象 2.状态选择可以用数字0 1 ...
- java 多线程间通信(二)
传统的线程通信 Object提供了三个方法wait(), notify(), notifyAll()在线程之间进行通信,以此来解决线程间执行顺序等问题. wait():释放当前线程的同步监视控制器,并 ...
- java 多线程间通信(一)
synchronized同步 package com.test7; public class Run { public class MyObject { private int a; public M ...
- cuda多线程间通信
#include "cuda_runtime.h" #include "device_launch_parameters.h" #include <std ...
- wxpython多线程间通信
#!bin/bash/python # -*- coding=utf-8 -*- import time import wx from threading import Thread from wx. ...
- Android线程间通信更新UI的方法(重点分析EventBus)
Android的UI更新只能在UI线程中,即主线程.子线程中如果要进行UI更新,都是要通知主线程来进行. 几种实现方式总结如下,欢迎补充. 1.runOnUiThread() 子线程中持有当前Acti ...
随机推荐
- Jmeter-----图形监控
1.下载插件地址:https://jmeter-plugins.org/downloads/old/ 1)JmeterPlugins-Standard 插件:将JMeterPlugins.jar放到J ...
- JS模块化规范CMD之SeaJS
1. 在接触规范之前,我们用模块化来封装代码大多为如下: ;(function (形参模块名, 依赖项, 依赖项) { // 通过 形参模块名 修改模块 window.模块名 = 形参模块名 })(w ...
- IEEEXtreme 10.0 - Inti Sets
这是 meelo 原创的 IEEEXtreme极限编程大赛题解 Xtreme 10.0 - Inti Sets 题目来源 第10届IEEE极限编程大赛 https://www.hackerrank.c ...
- php极速后台开发框架LotusAdmin
组件:基于thinkphp5.0.12+layui2.1版本 演示站点:https://www.lotusadmin.top/账号 : admin密码:123456 官方QQ交流群:606645328 ...
- day2 购物商城
购物商城 商品展示.价格 买,加入购物车 付款,钱不够.(减商品,充值)
- java EE : http 协议之请求报文、响应报文
1 HTTP协议特点 1)客户端->服务端(请求request)有三部份 a)请求行 b)请求头 c)请求的内容,如果没有,就是空白字符 2)服务端->客户端(响应response)有三部 ...
- spring+atomikos+mybatis 多数据源事务(动态切换)
注:自动切换,是为不同的数据源,却要对应相同的dao层: 1.与无事务版的一样,创建DynamicDataSource类,继承AbstractRoutingDataSource package com ...
- Numpy存取文件
来自 Python科学计算 http://hyry.dip.jp/tech/book/page/scipy/numpy_file.html NumPy提供了多种存取数组内容的文件操作函数.保存数组数据 ...
- NHibernate示例
1. 下载相关资源: 下载NHibernate.下载地址: http://nhforge.org/Default.aspx 下载微软Northwind示例数据库,下载地址:http://www.mic ...
- 不愿看到Java开发者再做的10件事
William F. Buckley.Jr 曾经说过,“保守主义者是那些逆着历史潮流不断喊停的人,其他人都不愿意这么做或者对他们这么做显得没有耐性”.虽然我对此了解不多,但是每次看到有Java开发人员 ...
