View.findViewById()和Activity.findViewById()区别
在网上看见View.findViewById() 和 Activity.findViewById()执行效率不一样
使用Activity.findViewById()如:
TextView tv_inner_1 = (TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.tv_inner_1);
TextView tv_inner_2 = (TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.tv_inner_2);
使用View.findViewById() 如:
View layout_outer = this.findViewById(R.id.layout_outer);
TextView tv_inner_1 = (TextView)layout_outer.findViewById(R.id.tv_inner_1);
TextView tv_inner_2 = (TextView)layout_outer.findViewById(R.id.tv_inner_2);
他们都是针对下面同一个xml
<LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout id="@+id/layout_outer">
<TextView id="@+id/tv_inner_1"/>
<TextView id="@+id/tv_inner_2"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
自从学习android的hello world开始
我们就知道了这样一个函数findViewById(),他已经成为了家喻户晓,坑蒙拐骗,杀人越货必备的一个函数(好吧,这句是扯淡)
但一直用也没细致研究过它,直到写程序的时候发现一个由这个函数引起的一个莫名其妙的bug,遂决定好好研究下次函数~
我们调用的findViewById()函数其实有两种(目前我只看到两种,不确定还有没有其他的),一种是Activity类中findViewById()函数
另外一种是View类中定义的findViewById()函数
一般我们在oncreate()方法中使用的(**view)findViewById(R.id.**)既是调用的Activity中的findViewById()函数
而在其他情况写出的***view.findViewById()中调用的是view类中的findViewById()
分别看一下源代码中的实现方法及介绍
Activity类中定义的findViewById()
/**
* Finds a view that was identified by the id attribute from the XML that
* was processed in {@link #onCreate}.
*
* @return The view if found or null otherwise.
*/
public View findViewById(int id) {
return getWindow().findViewById(id);
}
/**
* Retrieve the current {@link android.view.Window} for the activity.
* This can be used to directly access parts of the Window API that
* are not available through Activity/Screen.
*
* @return Window The current window, or null if the activity is not
* visual.
*/
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}
这里可以看出这个函数是在寻找在xml中定义的指定id的对象
View类中的findViewById()
/**
* Look for a child view with the given id. If this view has the given
* id, return this view.
*
* @param id The id to search for.
* @return The view that has the given id in the hierarchy or null
*/
public final View findViewById(int id) {
if (id < 0) {
return null;
}
return findViewTraversal(id);
/**
* {@hide}
* @param id the id of the view to be found
* @return the view of the specified id, null if cannot be found
*/
protected View findViewTraversal(int id) {
if (id == mID) {
return this;
}
return null;
}
从这里可以看出我们是从一个view的child view中寻找指定id的对象,所以即使几个layout的XML文件中的View的id号相同的话,只要他们没有相同的父节点,或有相同的父亲节点,但不在父节点及以上节点调用findViewById通过id来查找他们就是没有问题。(这句引用自这里http://www.2cto.com/kf/201204/127404.html)
使用这个函数的常见问题:
1.既然Activity中的findViewById()是从R.java中寻找东西,那么我们就要杜绝相同名字的控件
今天自己的bug就是因为这个产生的

说到控件的命名,今天还有一个小发现
仔细看下边两段代码代码
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
< /LinearLayout>
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
< /LinearLayout>
一段里边Layout没有id这个参数,一段里边有id,虽然代码不同但在outline中显示出来都是
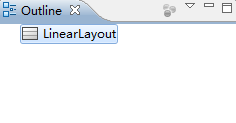
这样在第一种情况下R.id中可以找到LinearLayout这个控件,第二种是没有的哈,这些也是以后要注意的细节
2.在调用view中的findViewById()一定要想好父View是谁!即**view.findViewById()中的**view要找对,如果没有找对父View,返回基本都是null了
View.findViewById()和Activity.findViewById()区别的更多相关文章
- view和activity的区别
activity相当于控制部分,view相当于显示部分.两者之间是多对多的关系,所有东西必须用view来显示. viewGroup继承自view,实现了ViewManager,ViewParent接 ...
- view和activity的区别(转)
activity相当于控制部分,view相当于显示部分.两者之间是多对多的关系,所有东西必须用view来显示. viewGroup继承自view,实现了ViewManager,ViewParent接口 ...
- Android: Custom View和include标签的区别
Custom View, 使用的时候是这样的: <com.example.home.alltest.view.MyCustomView android:id="@+id/customV ...
- 关于android编程中service和activity的区别
一. 绝大部分情况下,Service的作用是用来“执行”后台的.耗时的.重要的任务,三者缺一不可,而最重要的原因是第三点:要执行重要的任务. 因为当一个进程启动了Service后,进程的优先级变高了, ...
- 【android-tips】如何在view中取得activity对象
(转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/buptgshengod) 今天想实现在view中返回上一个activity的功能,想了半天.因为在虽然view是包含于一个activity ...
- js架构设计模式——MVVM模式下,ViewModel和View,Model有什么区别
MVVM模式下,ViewModel和View,Model有什么区别 Model:很简单,就是业务逻辑相关的数据对象,通常从数据库映射而来,我们可以说是与数据库对应的model. View:也很简单,就 ...
- inflate, findViewById与setContentView的区别与联系
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentV ...
- inflate, findViewById与setContentView的区别与联系 分类: H1_ANDROID 2014-04-18 22:54 1119人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentV ...
- Android View的onTouchEvent和OnTouch区别
还是以自定义的TestButton为例. 我们可以通过重写onTouchEvent方法来处理诸如down move up的消息: public class TestButton extends But ...
随机推荐
- CSS 清除浮动 clear 属性
CSS 清除浮动 clear 属性用于设定元素哪一侧不允许有其他浮动元素(而并非取消元素的浮动). 可能的取值如下: 取值 说明 none 默认值,允许两侧都有浮动元素 left 左侧不允许有其他浮动 ...
- (一) ffmpeg filter学习-使用流程
FFMPEG中有一个类库:libavfilter.该类库提供了各种视音频过滤器.之前一直没有怎么使用过这个类库,最近看了一下它的使用说明,发现还是很强大的,有很多现成的filter供使用,完成视频的处 ...
- windows上操作git基本命令
今天准备整理一下代码,重温一下Git的基本命令,好久不用忘得差不多了. 1. 进入某个目录: 进入D盘,然后进入D盘的名为git的文件夹: $ cd D: $ cd Git 2. 返回上一级目录: $ ...
- 【剑指offer】输入一颗二叉树的根节点,判断是不是平衡二叉树,C++实现
原创博文,转载请注明出处! # 题目 # 举例 # 思路 由平衡二叉树的定义可知,判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树的关键在于判断任意结点是否是平衡结点.后序遍历二叉树,判断节点的子树是否平衡并计算节点的子树 ...
- ubuntu安装依赖:0.8.1-1ubuntu4.4 正要被安装以及vm nested解决方法
刚才在ubuntu10.04虚拟机上安装kvm,提示0.8.1-1ubuntu4.4 正要被安装,查了一下,有一种解决方法: 进入“系统->系统管理->更新管理器->设置”,在弹出的 ...
- crt,excrt学习总结
\(crt,Chinese\ Remainder\ Theorem\) 概述 前置技能:同余基础性质,\(exgcd\). \(crt\),中国剩余定理.用于解决模数互质的线性同余方程组.大概长这样: ...
- 接口结构+一个selenium例子
大家今天可以先建一个项目目录,明天我们在码代码: 我看好多朋友都在看selenium方面的东西,在这里给大家一个和讯网自动发文章的selenium代码,有兴趣的朋友可以试试,船长已亲测可用,不明白的地 ...
- Linux下Apache服务器配置
Linux下Apache服务器配置 相关包: httpd-2.2.3-29.e15.i386.rpm //主程序包 httpd-devel-2.2.3-29.e15.i ...
- 使用PHP类库PHPqrCode生成二维码
PHPqrCode是一个PHP二维码生成类库,利用它可以轻松生成二维码,官网提供了下载和多个演示demo, 查看地址:http://phpqrcode.sourceforge.net/. 下载官 ...
- js核心知识
枚举属性: var o = {x:1} console.log("x" in o);//true console.log("toString" in o);// ...
