吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression():
'''
加载用于回归问题的数据集
'''
#使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
# 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4
return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor()
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("Training score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Testing score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test)) # 获取分类数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
# 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor
test_GradientBoostingRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 n_estimators 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
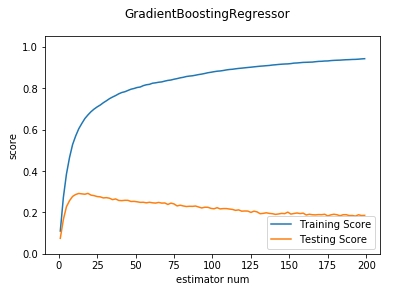
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_depth 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
maxdepths=np.arange(1,20)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for maxdepth in maxdepths:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_depth=maxdepth,max_leaf_nodes=None)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 learning_rate 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
learnings=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for learning in learnings:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(learning_rate=learning)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(learnings,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(learnings,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("learning_rate")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
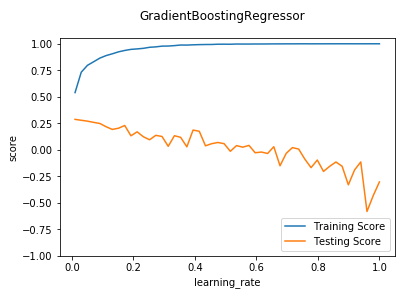
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 subsample 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
subsamples=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,num=20)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for subsample in subsamples:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(subsample=subsample)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(subsamples,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(subsamples,testing_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.set_xlabel("subsample")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
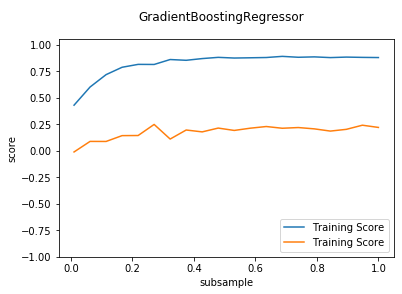
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随不同的损失函数和 alpha 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2)
########## 绘制 huber ######
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,1)
alphas=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,endpoint=False,num=5)
for alpha in alphas:
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss='huber',alpha=alpha)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:alpha=%f"%alpha)
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:alpha=%f"%alpha)
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4)
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.set_title("loss=%huber")
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
#### 绘制 ls 和 lad
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,2)
for loss in ['ls','lad']:
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss=loss)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:loss=%s"%loss)
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:loss=%s"%loss)
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4)
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.set_title("loss=ls,lad")
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
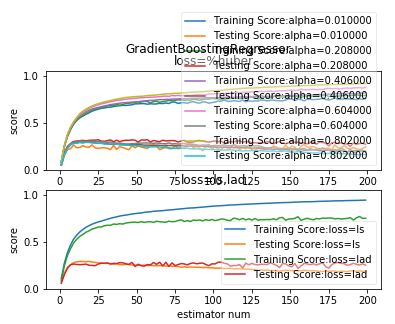
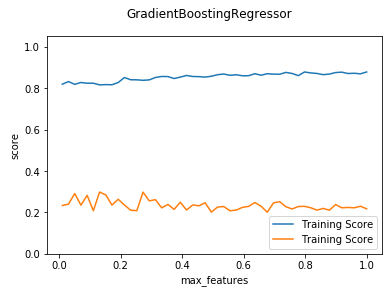
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_features 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
max_features=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for features in max_features:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_features=features)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_features")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestClassifier分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理字典学习模型
from sklearn.decomposition import DictionaryLearning #数据预处理字典学习DictionaryLearning模型 def test_Diction ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络感知机学习算法的应用
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn import neighbors, datasets from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络与原始感知机模型
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——分类决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——回归决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
随机推荐
- CodeForces 1144A
原题链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-1144A #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ...
- 非最大抑制,挑选和目标重叠框 yolo思想原理
非最大抑制,挑选和目标重叠框 yolo思想原理 待办 https://blog.csdn.net/shuzfan/article/details/52711706 根据分类器类别分类概率做排序,(框的 ...
- Codeforces 764C Timofey and a tree
Each New Year Timofey and his friends cut down a tree of n vertices and bring it home. After that th ...
- PATA-1151 LCA in a Binary Tree
题意:根据前序和中序建立树,寻找两个点的LCA. 我在之前的博客中写了关于LCA的多种求法. https://www.cnblogs.com/yy-1046741080/p/11505547.html ...
- path('<int:question_id>/vote/', views.vote, name='vote')中的<int:question_id>的含义
path('<int:question_id>/vote/', views.vote, name='vote')<int:question_id>用于匹配URL的值,并将扑捉到 ...
- Java单体应用 - 架构模式 - 02.MVC架构
原文地址:http://www.work100.net/training/monolithic-architecture-mvc.html 更多教程:光束云 - 免费课程 MVC架构 序号 文内章节 ...
- PHP程序员应该如何提升
PHP程序员应该如何提升 尤其不认可W3school之类的东西,不够深度,理解不深,比起这个更建议看官方文档,中文不清楚,看英文的. 入门视频:入门视频推荐:哈佛大学公开课:构建动态网站Beginne ...
- 题解【洛谷P5788】【模板】单调栈
题面 单调栈模板题. 单调栈与单调队列一样,都是维护了一段区间内的顺序. 然后--这个题用一个栈维护一下贪心就没了. 具体参考这一篇题解 #include <bits/stdc++.h> ...
- Linux - Shell - 免密码登录
概述 简述 linux ssh 无密码登录 无能狂怒 最近真是不知道写啥了 环境 os centos7 1. 场景 场景 主机A 需要经常访问 主机B 每次访问, 都要输入一次 密码 问题 每次都输密 ...
- TODO:如何模拟cpu打满,磁盘打满,网卡打满
背景: 测试活动中,需要构造cpu打满.磁盘打满.网卡打满的场景 场景1:cpu打满 环境信息: 虚拟机,物理核数16个,每个物理核的虚拟核数1个,虚拟核数16个: [root@vm10-0-0-8 ...
