UVa 1451 Average - 斜率优化
A DNA sequence consists of four letters, A, C, G, and T. The GC-ratio of a DNA sequence is the number of Cs and Gs of the sequence divided by the length of the sequence. GC-ratio is important in gene finding because DNA sequences with relatively high GC-ratios might be good candidates for the starting parts of genes. Given a very long DNA sequence, researchers are usually interested in locating a subsequence whose GC-ratio is maximum over all subsequences of the sequence. Since short subsequences with high GC-ratios are sometimes meaningless in gene finding, a length lower bound is given to ensure that a long subsequence with high GC-ratio could be found. If, in a DNA sequence, a 0 is assigned to every A and T and a 1 to every C and G, the DNA sequence is transformed into a binary sequence of the same length. GC-ratios in the DNA sequence are now equivalent to averages in the binary sequence.
| Position Index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| Sequence | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
For the binary sequence above, if the length lower bound is 7, the maximum average is 6/8 which happens in the subsequence [7,14]. Its length is 8, which is greater than the length lower bound 7. If the length lower bound is 5, then the subsequence [7,11] gives the maximum average 4/5. The length is 5 which is equal to the length lower bound. For the subsequence [7,11], 7 is its starting index and 11 is its ending index.
Given a binary sequence and a length lower bound L, write a program to find a subsequence of the binary sequence whose length is at least L and whose average is maximum over all subsequences of the binary sequence. If two or more subsequences have the maximum average, then find the shortest one; and if two or more shortest subsequences with the maximum average exist, then find the one with the smallest starting index.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 000) and L (1 ≤ L ≤ 1, 000) which are the length of a binary sequence and a length lower bound, respectively. In the next line, a string, binary sequence, of length n is given.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. Print the starting and ending index of the subsequence.
Sample Input
Sample Output
按照题目意思,可以想出用前缀和,这样从i到j的平均数就可以表示为(sum[j] - sum[i - 1]) / j - i + 1,仔细一看,这长得不是很向斜率的公式吗?
那么我们可以把第i个字符抽象成平面上的点(i, sum[i]),题目就可以转换成已知平面上有N个点,找到两个点的横坐标的之差大于等于L,且斜率最大。然而这并没有什么用,因为刚刚要用O(n2)解决的问题,现在还是要用O(n2)来解决。不着急,来看看下面。
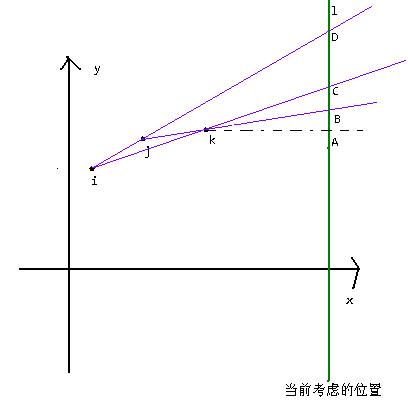
现在要确定以点p为结束位置的最优的起点,那么假如有i, j, k三个候选点,点p在直线l上。
- 如果点p在线段AB上,那么点i是最优的
- 如果点p在线段BC上,那么点i还是最优的
- 如果点p在线段CD上,那么点k还是最优的
- 如果点p在点D上方,那么点k还是最优的
于是,可以试问点j的意义。既然没有意义,那就把它删掉吧,于是最后的折线成了这样↓
由于sum是递增的,所以对于两个存在于折线上的两个点i, j(i < j),如果i更优,那么还是i更优,如果j更优,那么i不会再更优(于是可以愉快地把i,pop()掉了)
所以处理以r为右端点的时候,先用点r - L删掉上凸点(维护斜率的递增),再把点r - L塞进去(push_back()),最后删掉队首没有第二个元素更优的队首,然后取出当前队首,更新答案。
由于这个队列允许队首删除,队尾插入和删除,所要实现双端队列(不要学习我封装)(似乎是单调队列)。
由于每个元素至多会被插入队列1次,从队列中删除1次,所以时间复杂度为O(n),总时间复杂度为O(n)(常数又被省略掉了)
Code(无限wa后的ac代码)
/**
* uva
* Problem#1451
* Accepted
* Time:60ms
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
#define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b))
#define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b))
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u){
char x;
int aFlag = ;
while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-');
if(x == '-'){
aFlag = -;
x = getchar();
}
for(u = x - ''; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = u * + x - '');
ungetc(x, stdin);
u *= aFlag;
} template<typename T>
class IndexedDeque{
public:
T* list;
int pfront;
int prear;
IndexedDeque():list(NULL), pfront(), prear(){ }
IndexedDeque(int size):pfront(), prear(){
list = new T[size];
}
void push_front(T x){ list[--pfront] = x; }
void push_back(T x) { list[prear++] = x; }
void pop_front() { ++pfront; }
void pop_back() { --prear; }
T front() { return list[pfront]; }
T rear() { return list[prear - ]; }
T& operator [](int pos){ return list[pfront + pos]; }
int size() { return prear - pfront; }
}; int T;
int n, L;
int* sum;
char* str;
IndexedDeque<int> que; inline int segsum(int from, int end){ return sum[end] - sum[from - ]; }
inline int cmpSlope(int l1, int r1, int l2, int r2){ return (segsum(l1, r1) * (r2 - l2 + )) - (segsum(l2, r2) * (r1 - l1 + )); } inline void init(){
readInteger(n);
readInteger(L);
str = new char[(const int)(n + )];
sum = new int[(const int)(n + )];
que = IndexedDeque<int>(n * );
scanf("%s", str);
} inline void solve(){
sum[] = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
sum[i + ] = sum[i] + str[i] - ''; int resl = , resr = L;
for(int i = L; i <= n; i++){
while(que.size() > && cmpSlope(que[que.size() - ], i - L, que[que.size() - ], i - L) >= )
que.pop_back();
que.push_back(i - L + );
while(que.size() > && cmpSlope(que[], i, que[], i) <= )
que.pop_front(); int temp = cmpSlope(que.front(), i, resl, resr);
if(temp > || (temp == && resr - resl > i - que.front())){
resl = que.front(), resr = i;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", resl, resr);
} inline void clear(){
delete[] sum;
delete[] str;
delete[] que.list;
} int main(){
readInteger(T);
while(T--){
init();
solve();
clear();
}
return ;
}
UVa 1451 Average - 斜率优化的更多相关文章
- UVA 1451 Average平均值 (数形结合,斜率优化)
摘要:数形结合,斜率优化,单调队列. 题意:求一个长度为n的01串的子串,子串长度至少为L,平均值应该尽量大,多个满足条件取长度最短,还有多个的话,取起点最靠左. 求出前缀和S[i],令点Pi表示(i ...
- UVA 1451 Average
A DNA sequence consists of four letters, A, C, G, and T. The GC-ratio of a DNA sequence is the numbe ...
- UVA - 1451 Average (斜率优化)
题意:由01组成的长度为n的子串,AT由0表示,GC由1表示,求一段长度大于等于L且GC率最高的子串的起始终止坐标,若GC率相同,取长度较小,若长度相同,取起始坐标最小. 分析: 1.一个子串(i+1 ...
- HDU 2993 MAX Average Problem dp斜率优化
MAX Average Problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
- MAX Average Problem(斜率优化dp)
MAX Average Problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
- 【UVA 1451】Average
题 题意 求长度为n的01串中1占总长(大于L)的比例最大的一个子串起点和终点. 分析 前缀和s[i]保存前i个数有几个1,[j+1,i] 这段区间1的比例就是(s[i]-s[j])/(i-j),于是 ...
- HDU 2993 MAX Average Problem(斜率优化DP)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2993 题目大意:给定一个长度为n(最长为10^5)的正整数序列,求出连续的最短为k的子序列平均值的最大 ...
- UVALive 4726 Average ——(斜率优化DP)
这是第一次写斜率优化DP= =.具体的做法参照周源论文<浅谈数形结合思想在信息学竞赛中的应用>.这里仅提供一下AC的代码. 有两点值得注意:1.我这个队列的front和back都是闭区间的 ...
- 斜率优化dp(POJ1180 Uva1451)
学这个斜率优化dp却找到这个真心容易出错的题目,其中要从n倒过来到1的确实没有想到,另外斜率优化dp的算法一开始看网上各种大牛博客自以为懂了,最后才发现是错了. 不过觉得看那些博客中都是用文字来描述, ...
随机推荐
- Python:字符串处理函数
split() / join() 拆分和组合 #split() 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片(拆分),默认空格符 lan = "python ruby c c++ swift" ...
- 单例模式:Qt本身就提供了专门的宏 Q_GLOBAL_STATIC 通过这个宏不但定义简单,还可以获得线程安全性
标题起的是有点大 主要是工作和学习中,遇到些朋友,怎么说呢,代码不够Qt化 可能是由于他们一开始接触的是 Java MFC 吧 接触 Qt 7个年头了 希望我的系列文章能抛砖引玉吧 单例模式 很多人洋 ...
- idea 创建的maven+spring+mybatis项目整合 报错无法创建bean
报错如下: Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with n ...
- sublime eslint 和 jshint的安装与使用
jshint简介 jslint是一javascript的语法检测,众多前端自动化工具都又用到,编辑器也用到jshint. webstorm很强大,自身带有,但是我使用的电脑带不动.sublime或者a ...
- HTTP API响应数据规范整理
概述 本文档为本人对长期开发API接口所整理的经验总结,如有不完善或不合理的地方,望各位多提意见. 文档目的为规范服务器端API接口,便于服务器端与客户端代码重用.服务器端和客户端可根据实际所定义规范 ...
- Python中的__init__.py的作用
当用 import 导入该目录时,会执行 __init__.py 里面的代码 因此在__init__.py文件中,把深层的包的路径缩短,别的地方就可以在引用到目录级别时引到深层的包.
- Mac SVN版本从1.9降到1.8
假设系统已安装brew,在终端执行下列命令: brew update brew install subversion18 echo 'export PATH="/usr/local/opt/ ...
- 使用Python2.7 POST 数据到 onenet 平台
功能 发送数据名称为SENSORID(这里用TEST测试),数值为VALUE(这里用49值做测试)的数据,发送到自己的onenet对应设备 效果发送成功 代码 # -*- coding: utf-8 ...
- linux locate
locate命令查找文件比find速度快很多,locate是在linux下实现快速查找文件的工具.相应的windows下有everything功能也很强大. [root@wuzhigang lib]# ...
- yii2关联查询两组一对一
public function getMember1(){ return $this->hasOne(Member::className(), ['wechat_id' => ...
