基于WordNet的英文同义词、近义词相似度评估及代码实现
源码地址:https://github.com/XBWer/WordSimilarity
1.确定要解决的问题及意义
在基于代码片段的分类过程中,由于程序员对数据变量名的选取可能具有一定的规范性,在某一特定业务处理逻辑代码中,可能多个变量名之间具有关联性或相似性(如“trade”(商品交易)类中,可能存在“business”,“transaction”,“deal”等同义词),在某些情况下,它们以不同的词语表达了相同的含义。因此,为了能够对代码片段做出更加科学的类别判断,更好地识别这些同义词,我们有必要寻找一种能够解决避免由于同义词的存在而导致误分类的方法。说白了,就是要去判断词语之间的相似度(即确定是否为近义词),并找出代码段中出现次数最多的一组语义。
2.要达到的效果
即在给定的代码段中,能够发现哪些词是属于同义词,并且能够实现分类。
Eg.public static void function(){
String trade=”money”;
Int deal=5;
Long long business=0xfffffff;
Boolen transaction=TRUE;
……
}
Output:同义词有:trade,deal,business,transaction
这段代码很可能与trade有关
3.初识WordNet
问题确定了之后,通过网上的搜索,发现了WordNet和word2vec这两个相关的词汇。(后知后觉,这本身就是一个找近义词的过程)
3.1 WordNet是什么
首先,来看WordNet。搜了一下相关介绍:
WordNet是一个由普林斯顿大学认识科学实验室在心理学教授乔治·A·米勒的指导下建立和维护的英语字典。开发工作从1985年开始,从此以后该项目接受了超过300万美元的资助(主要来源于对机器翻译有兴趣的政府机构)。
由于它包含了语义信息,所以有别于通常意义上的字典。WordNet根据词条的意义将它们分组,每一个具有相同意义的字条组称为一个synset(同义词集合)。WordNet为每一个synset提供了简短,概要的定义,并记录不同synset之间的语义关系。
WordNet的开发有两个目的:
它既是一个字典,又是一个辞典,它比单纯的辞典或词典都更加易于使用。
支持自动的文本分析以及人工智能应用。
WordNet内部结构
在WordNet中,名词,动词,形容词和副词各自被组织成一个同义词的网络,每个同义词集合都代表一个基本的语义概念,并且这些集合之间也由各种关系连接。(一个多义词将出现在它的每个意思的同义词集合中)。在WordNet的第一版中(标记为1.x),四种不同词性的网络之间并无连接。WordNet的名词网络是第一个发展起来的。
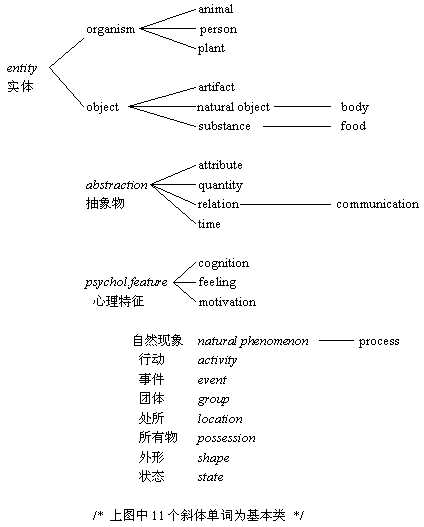
名词网络的主干是蕴涵关系的层次(上位/下位关系),它占据了关系中的将近80%。层次中的最顶层是11个抽象概念,称为基本类别始点(unique beginners),例如实体(entity,“有生命的或无生命的具体存在”),心理特征(psychological feature,“生命有机体的精神上的特征)。名词层次中最深的层次是16个节点。
(wikipedia)
通俗地来说,WordNet是一个结构化很好的知识库,它不但包括一般的词典功能,另外还有词的分类信息。目前,基于WordNet的方法相对来说比较成熟,比如路径方法 (lch)、基于信息论方法(res)等。(详见参考文献)
3.2 WordNet的安装与配置
有了WordNet ,也就等于是有了我们所要的单词库。所以,暂时先不考虑相似度的计算,把WordNet下载下来再说。
参考http://hi.baidu.com/buptyoyo/item/f13dfe463c061e3afb896028。顺利地下载,安装以及跑demo。
之后,一起来看一下WordNet的文件结构:

bin目录下,有可执行文件WordNet 2.1.exe:
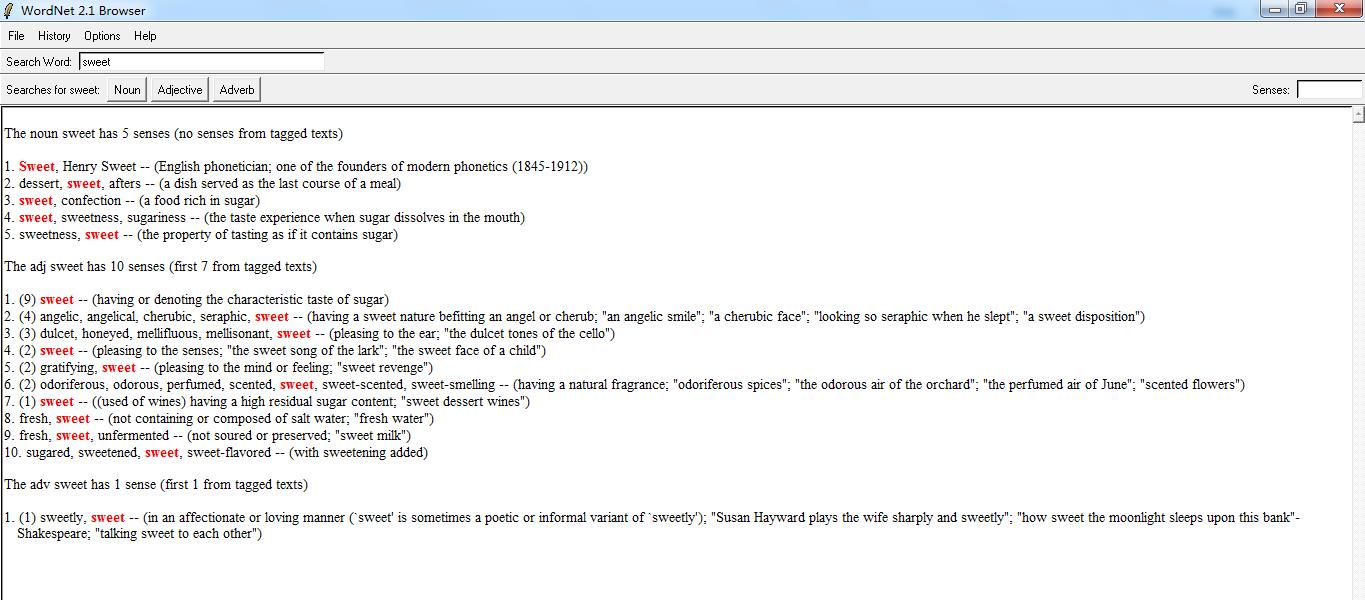

可以看到,WordNet对所有的英文单词都进行的分类,并且形成了一棵语义树。在本例中,entity——>abstract entity——>abstraction——>attribute——>state——>feeling——> emotion——>love;
从叶子节点到根节点
WordNet名次分类中的25个基本类:
dict目录里面存放的就是资源库了,可以看到,它以形容词,副词,名词,动词来分类:
doc为WordNet的用户手册文件文件夹
lib为WordNet软件使用Windows资源的函数库
src为源码文件夹
4.解决问题的大致思路
我们首先以 WordNet 的词汇语义分类作为基础,抽取出其中的同义词,然后采用基于向量空间的方法计算出相似度。工作流程如下:
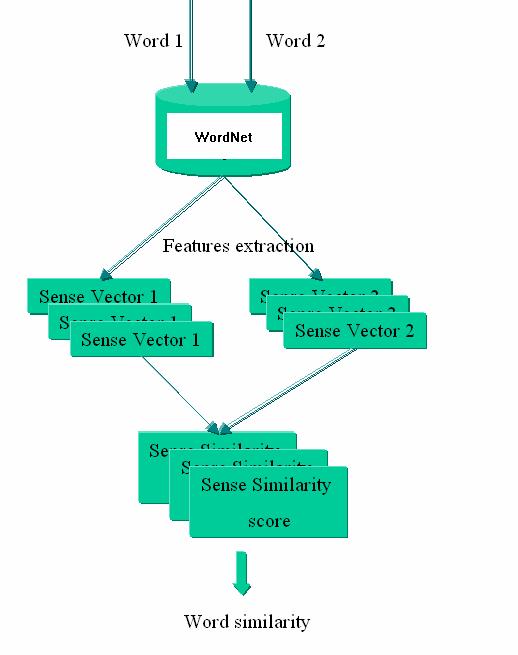
5.基于WordNet的相似度计算
以下摘自:《基于WordNet的英语词语相似度计算》
5.1 特征提取

5.2 意义相似度和词语相似度的计算


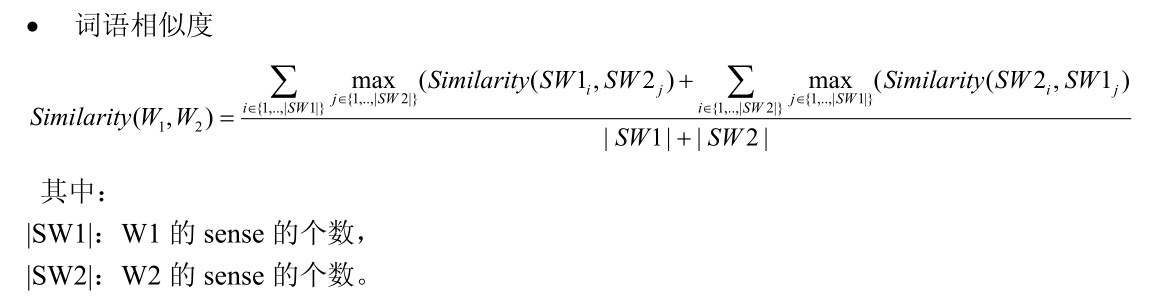
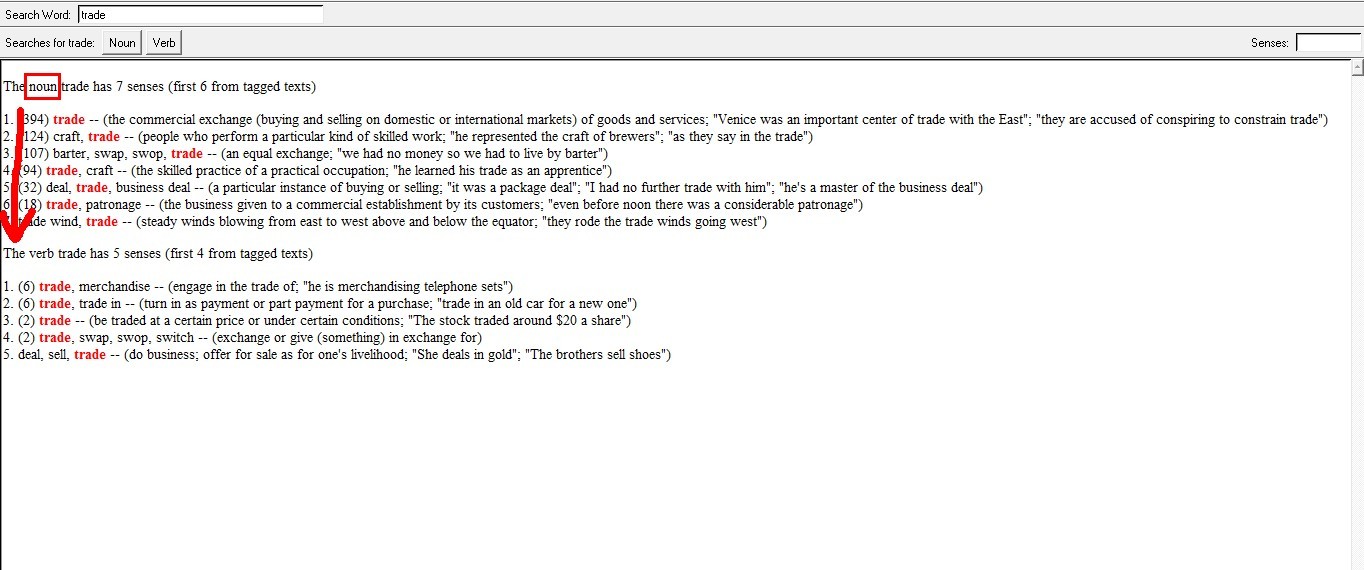
6.实现效果
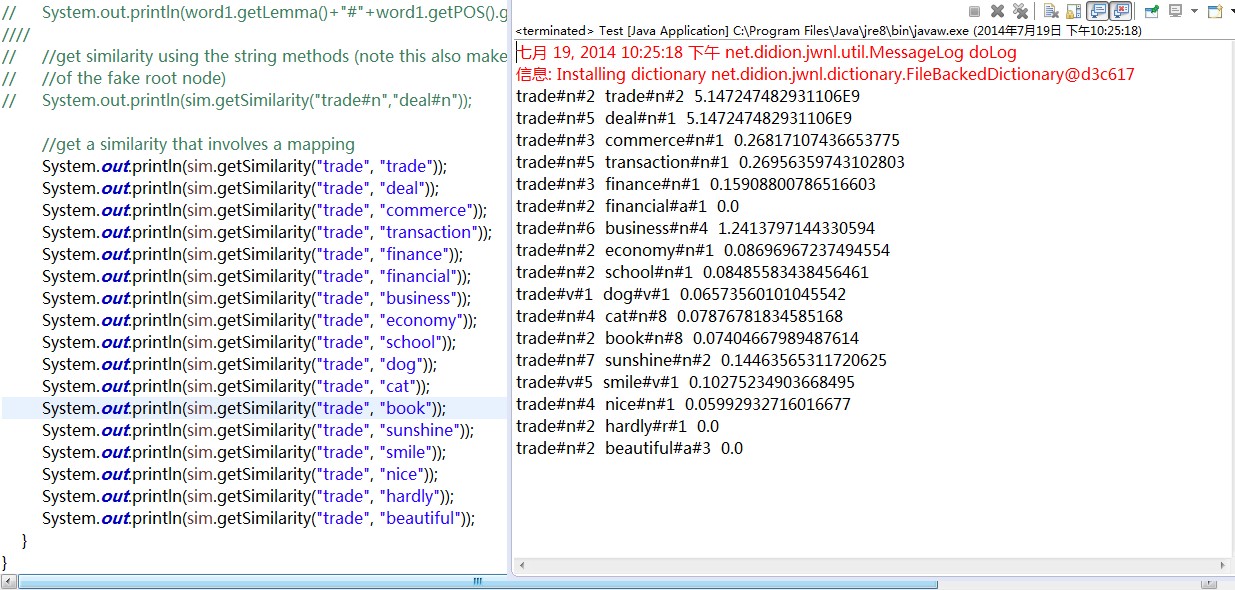
与“trade”的相似度比较:
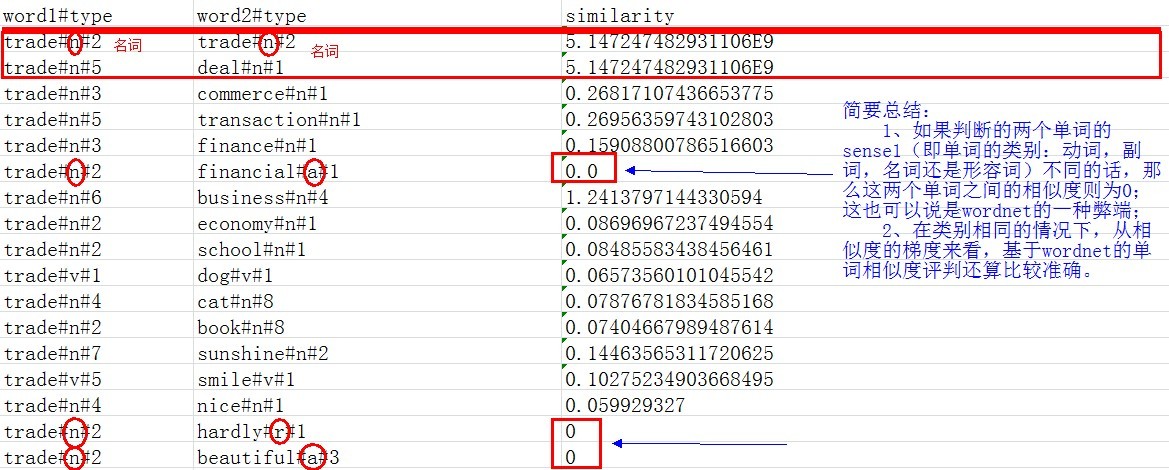 分析:
分析:
先看第一组:trade vs trade
自己和自己当然是相似度100%
再看第二组:trade#n#5 vs deal#n#1
相似度竟然和第一组是一样的!根据结果,trade作为名词时,它的第5种含义和deal作为名词时的第1种含义是完全相似的。让我们去库里看个究竟:
trade#n#5:

deal#n#1:
再来看一组不是很好理解的:
trade#n#7 vs deal#n#2
他们的相似度达到了0.14+,算是比较高的了,这是为什么呢?
trade#n#7:

sunshine#n#2:

相信聪明的你一定明白了为什么。
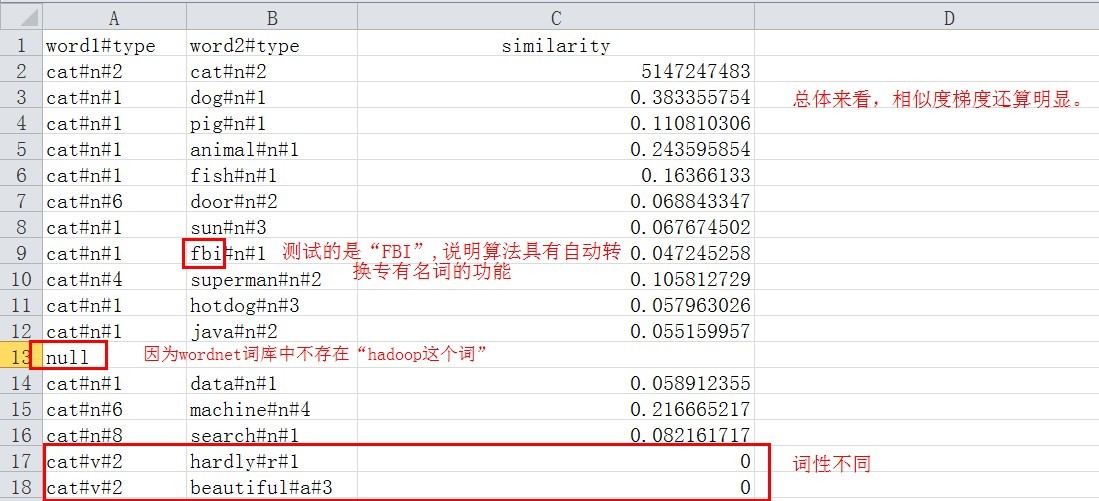
与“cat”的相似度比较:
7.代码分析
工程结构图:
test.java
- package JWordNetSim.test;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- import net.didion.jwnl.JWNL;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.IndexWord;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.POS;
- import net.didion.jwnl.dictionary.Dictionary;
- import shef.nlp.wordnet.similarity.SimilarityMeasure;
- /**
- * A simple test of this WordNet similarity library.
- * @author Mark A. Greenwood
- */
- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
- //在运行代码前,必须在本机上安装wordnet2.0,只能装2.0,装了2.1会出错
- JWNL.initialize(new FileInputStream("D:\\JAVAProjectWorkSpace\\jwnl\\JWordNetSim\\test\\wordnet.xml"));
- //建议一个映射去配置相关参数
- Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<String,String>();
- //the simType parameter is the class name of the measure to use
- params.put("simType","shef.nlp.wordnet.similarity.JCn");
- //this param should be the URL to an infocontent file (if required
- //by the similarity measure being loaded)
- params.put("infocontent","file:D:\\JAVAProjectWorkSpace\\jwnl\\JWordNetSim\\test\\ic-bnc-resnik-add1.dat");
- //this param should be the URL to a mapping file if the
- //user needs to make synset mappings
- params.put("mapping","file:D:\\JAVAProjectWorkSpace\\jwnl\\JWordNetSim\\test\\domain_independent.txt");
- //create the similarity measure
- SimilarityMeasure sim = SimilarityMeasure.newInstance(params);
- //取词
- // Dictionary dict = Dictionary.getInstance();
- // IndexWord word1 = dict.getIndexWord(POS.NOUN, "trade"); //这里把trade和dog完全定义为名词来进行处理
- // IndexWord word2 = dict.getIndexWord(POS.NOUN,"dog"); //
- //
- // //and get the similarity between the first senses of each word
- // System.out.println(word1.getLemma()+"#"+word1.getPOS().getKey()+"#1 " + word2.getLemma()+"#"+word2.getPOS().getKey()+"#1 " + sim.getSimilarity(word1.getSense(1), word2.getSense(1)));
- ////
- // //get similarity using the string methods (note this also makes use
- // //of the fake root node)
- // System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade#n","deal#n"));
- //get a similarity that involves a mapping
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "trade"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "deal"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "commerce"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "transaction"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "finance"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "financial"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "business"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "economy"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "school"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "dog"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "cat"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "book"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "sunshine"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "smile"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "nice"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "hardly"));
- System.out.println(sim.getSimilarity("trade", "beautiful"));
- }
- }
SimilarityMeasure.java
- package shef.nlp.wordnet.similarity;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.InputStreamReader;
- import java.net.URL;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.HashSet;
- import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Set;
- import net.didion.jwnl.JWNLException;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.IndexWord;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.POS;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.Synset;
- import net.didion.jwnl.dictionary.Dictionary;
- /**
- * An abstract notion of a similarity measure that all provided
- * implementations extend.
- * @author Mark A. Greenwood
- */
- public abstract class SimilarityMeasure
- {
- /**
- * A mapping of terms to specific synsets. Usually used to map domain
- * terms to a restricted set of synsets but can also be used to map
- * named entity tags to appropriate synsets.
- */
- private Map<String,Set<Synset>> domainMappings = new HashMap<String,Set<Synset>>();
- /**
- * The maximum size the cache can grow to
- */
- private int cacheSize = 5000;
- /**
- * To speed up computation of the similarity between two synsets
- * we cache each similarity that is computed so we only have to
- * do each one once.
- */
- private Map<String,Double> cache = new LinkedHashMap<String,Double>(16,0.75f,true)
- {
- public boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<String,Double> eldest)
- {
- //if the size is less than zero then the user is asking us
- //not to limit the size of the cache so return false
- if (cacheSize < 0) return false;
- //if the cache has crown bigger than it's max size return true
- return size() > cacheSize;
- }
- };
- /**
- * Get a previously computed similarity between two synsets from the cache.
- * @param s1 the first synset between which we are looking for the similarity.
- * @param s2 the other synset between which we are looking for the similarity.
- * @return The similarity between the two sets or null
- * if it is not in the cache.
- */
- protected final Double getFromCache(Synset s1, Synset s2)
- {
- return cache.get(s1.getKey()+"-"+s2.getKey());
- }
- /**
- * Add a computed similarity between two synsets to the cache so that
- * we don't have to compute it if it is needed in the future.
- * @param s1 one of the synsets between which we are storring a similarity.
- * @param s2 the other synset between which we are storring a similarity.
- * @param sim the similarity between the two supplied synsets.
- * @return the similarity score just added to the cache.
- */
- protected final double addToCache(Synset s1, Synset s2, double sim)
- {
- cache.put(s1.getKey()+"-"+s2.getKey(),sim);
- return sim;
- }
- /**
- * Configures the similarity measure using the supplied parameters.
- * @param params a set of key-value pairs that are used to configure
- * the similarity measure. See concrete implementations for details
- * of expected/possible parameters.
- * @throws Exception if an error occurs while configuring the similarity measure.
- */
- protected abstract void config(Map<String,String> params) throws Exception;
- /**
- * Create a new instance of a similarity measure.
- * @param confURL the URL of a configuration file. Parameters are specified
- * one per line as key:value pairs.
- * @return a new instance of a similairy measure as defined by the
- * supplied configuration URL.
- * @throws Exception if an error occurs while creating the similarity measure.
- */
- public static SimilarityMeasure newInstance(URL confURL) throws Exception
- {
- //create map to hold the key-value pairs we are going to read from
- //the configuration file
- Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<String,String>();
- //create a reader for the config file
- BufferedReader in = null;
- try
- {
- //open the config file
- in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(confURL.openStream()));
- String line = in.readLine();
- while (line != null)
- {
- line = line.trim();
- if (!line.equals(""))
- {
- //if the line contains something then
- //split the data so we get the key and value
- String[] data = line.split("\\s*:\\s*",2);
- if (data.length == 2)
- {
- //if the line is valid add the two parts to the map
- params.put(data[0], data[1]);
- }
- else
- {
- //if the line isn't valid tell the user but continue on
- //with the rest of the file
- System.out.println("Config Line is Malformed: " + line);
- }
- }
- //get the next line ready to process
- line = in.readLine();
- }
- }
- finally
- {
- //close the config file if it got opened
- if (in != null) in.close();
- }
- //create and return a new instance of the similarity measure specified
- //by the config file
- return newInstance(params);
- }
- /**
- * Creates a new instance of a similarity measure using the supplied parameters.
- * @param params a set of key-value pairs which define the similarity measure.
- * @return the newly created similarity measure.
- * @throws Exception if an error occurs while creating the similarity measure.
- */
- public static SimilarityMeasure newInstance(Map<String,String> params) throws Exception
- {
- //get the class name of the implementation we need to load
- String name = params.remove("simType");
- //if the name hasn't been specified then throw an exception
- if (name == null) throw new Exception("Must specifiy the similarity measure to use");
- //Get hold of the class we need to load
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Class<SimilarityMeasure> c = (Class<SimilarityMeasure>)Class.forName(name);
- //create a new instance of the similarity measure
- SimilarityMeasure sim = c.newInstance();
- //get the cache parameter from the config params
- String cSize = params.remove("cache");
- //if a cache size was specified then set it
- if (cSize != null) sim.cacheSize = Integer.parseInt(cSize);
- //get the url of the domain mapping file
- String mapURL = params.remove("mapping");
- if (mapURL != null)
- {
- //if a mapping file has been provided then
- //open a reader over the file
- BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((new URL(mapURL)).openStream()));
- //get the first line ready for processing
- String line = in.readLine();
- while (line != null)
- {
- if (!line.startsWith("#"))
- {
- //if the line isn't a comment (i.e. it doesn't start with #) then...
- //split the line at the white space
- String[] data = line.trim().split("\\s+");
- //create a new set to hold the mapped synsets
- Set<Synset> mappedTo = new HashSet<Synset>();
- for (int i = 1 ; i < data.length ; ++i)
- {
- //for each synset mapped to get the actual Synsets
- //and store them in the set
- mappedTo.addAll(sim.getSynsets(data[i]));
- }
- //if we have found some actual synsets then
- //store them in the domain mappings
- if (mappedTo.size() > 0) sim.domainMappings.put(data[0], mappedTo);
- }
- //get the next line from the file
- line = in.readLine();
- }
- //we have finished with the mappings file so close it
- in.close();
- }
- //make sure it is configured properly
- sim.config(params);
- //then return it
- return sim;
- }
- /**
- * This is the method responsible for computing the similarity between two
- * specific synsets. The method is implemented differently for each
- * similarity measure so see the subclasses for detailed information.
- * @param s1 one of the synsets between which we want to know the similarity.
- * @param s2 the other synset between which we want to know the similarity.
- * @return the similarity between the two synsets.
- * @throws JWNLException if an error occurs accessing WordNet.
- */
- public abstract double getSimilarity(Synset s1, Synset s2) throws JWNLException;
- /**
- * Get the similarity between two words. The words can be specified either
- * as just the word or in an encoded form including the POS tag and possibly
- * the sense number, i.e. cat#n#1 would specifiy the 1st sense of the noun cat.
- * @param w1 one of the words to compute similarity between.
- * @param w2 the other word to compute similarity between.
- * @return a SimilarityInfo instance detailing the similarity between the
- * two words specified.
- * @throws JWNLException if an error occurs accessing WordNet.
- */
- 253 public final SimilarityInfo getSimilarity(String w1, String w2) throws JWNLException
- {
- //Get the (possibly) multiple synsets associated with each word
- Set<Synset> ss1 = getSynsets(w1);
- Set<Synset> ss2 = getSynsets(w2);
- //assume the words are not at all similar
- SimilarityInfo sim = null;
- for (Synset s1 : ss1)
- 263 {
- 264 for (Synset s2 : ss2)
- 265 {
- 266 //for each pair of synsets get the similarity
- 267 double score = getSimilarity(s1, s2);
- 268
- 269 if (sim == null || score > sim.getSimilarity())
- 270 {
- 271 //if the similarity is better than we have seen before
- 272 //then create and store an info object describing the
- 273 //similarity between the two synsets
- 274 sim = new SimilarityInfo(w1, s1, w2, s2, score);
- 275 }
- 276 }
- 277 }
- //return the maximum similarity we have found
- return sim;
- }
- /**
- * Finds all the synsets associated with a specific word.
- * @param word the word we are interested. Note that this may be encoded
- * to include information on POS tag and sense index.
- * @return a set of synsets that are associated with the supplied word
- * @throws JWNLException if an error occurs accessing WordNet
- */
- private final Set<Synset> getSynsets(String word) throws JWNLException
- {
- //get a handle on the WordNet dictionary
- Dictionary dict = Dictionary.getInstance();
- //create an emptuy set to hold any synsets we find
- Set<Synset> synsets = new HashSet<Synset>();
- //split the word on the # characters so we can get at the
- //upto three componets that could be present: word, POS tag, sense index
- String[] data = word.split("#");
- //if the word is in the domainMappings then simply return the mappings
- if (domainMappings.containsKey(data[0])) return domainMappings.get(data[0]);
- if (data.length == 1)
- {
- //if there is just the word
- for (IndexWord iw : dict.lookupAllIndexWords(data[0]).getIndexWordArray())
- {
- //for each matching word in WordNet add all it's senses to
- //the set we are building up
- synsets.addAll(Arrays.asList(iw.getSenses()));
- }
- //we have finihsed so return the synsets we found
- return synsets;
- }
- //the calling method specified a POS tag as well so get that
- POS pos = POS.getPOSForKey(data[1]);
- //if the POS tag isn't valid throw an exception
- if (pos == null) throw new JWNLException("Invalid POS Tag: " + data[1]);
- //get the word with the specified POS tag from WordNet
- IndexWord iw = dict.getIndexWord(pos, data[0]);
- if (data.length > 2)
- {
- //if the calling method specified a sense index then
- //add just that sysnet to the set we are creating
- synsets.add(iw.getSense(Integer.parseInt(data[2])));
- }
- else
- {
- //no sense index was specified so add all the senses of
- //the word to the set we are creating
- synsets.addAll(Arrays.asList(iw.getSenses()));
- }
- //return the set of synsets we found for the specified word
- return synsets;
- }
- }
每个函数都有详细注解,大家应该都看的明白。
262~277的循环过程如下:
JCN.java
- /************************************************************************
- * Copyright (C) 2006-2007 The University of Sheffield *
- * Developed by Mark A. Greenwood <m.greenwood@dcs.shef.ac.uk> *
- * *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify *
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by *
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or *
- * (at your option) any later version. *
- * *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, *
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of *
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the *
- * GNU General Public License for more details. *
- * *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License *
- * along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software *
- * Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA. *
- ************************************************************************/
- package shef.nlp.wordnet.similarity;
- import net.didion.jwnl.JWNLException;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.Synset;
- 25 /**
- 26 * An implementation of the WordNet similarity measure developed by Jiang and
- 27 * Conrath. For full details of the measure see:
- 28 * <blockquote>Jiang J. and Conrath D. 1997. Semantic similarity based on corpus
- 29 * statistics and lexical taxonomy. In Proceedings of International
- 30 * Conference on Research in Computational Linguistics, Taiwan.</blockquote>
- 31 * @author Mark A. Greenwood
- 32 */
- public class JCn extends ICMeasure
- {
- /**
- * Instances of this similarity measure should be generated using the
- * factory methods of {@link SimilarityMeasure}.
- */
- protected JCn()
- {
- //A protected constructor to force the use of the newInstance method
- }
- @Override public double getSimilarity(Synset s1, Synset s2) throws JWNLException
- {
- //if the POS tags are not the same then return 0 as this measure
- //only works with 2 nouns or 2 verbs.
- if (!s1.getPOS().equals(s2.getPOS())) return 0;
- //see if the similarity is already cached and...
- Double cached = getFromCache(s1, s2);
- //if it is then simply return it
- if (cached != null) return cached.doubleValue();
- //Get the Information Content (IC) values for the two supplied synsets
- double ic1 = getIC(s1);
- double ic2 = getIC(s2);
- //if either IC value is zero then cache and return a sim of 0
- if (ic1 == 0 || ic2 == 0) return addToCache(s1,s2,0);
- //Get the Lowest Common Subsumer (LCS) of the two synsets
- Synset lcs = getLCSbyIC(s1,s2);
- //if there isn't an LCS then cache and return a sim of 0
- if (lcs == null) return addToCache(s1,s2,0);
- //get the IC valueof the LCS
- double icLCS = getIC(lcs);
- //compute the distance between the two synsets
- //NOTE: This is the original JCN measure
- double distance = ic1 + ic2 - (2 * icLCS);
- //assume the similarity between the synsets is 0
- double sim = 0;
- if (distance == 0)
- {
- //if the distance is 0 (i.e. ic1 + ic2 = 2 * icLCS) then...
- //get the root frequency for this POS tag
- double rootFreq = getFrequency(s1.getPOS());
- if (rootFreq > 0.01)
- {
- //if the root frequency has a value then use it to generate a
- //very large sim value
- sim = 1/-Math.log((rootFreq - 0.01) / rootFreq);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- //this is the normal case so just convert the distance
- //to a similarity by taking the multiplicative inverse
- sim = 1/distance;
- }
- //cache and return the calculated similarity
- return addToCache(s1,s2,sim);
- }
- }
LIN.java
- package shef.nlp.wordnet.similarity;
- import net.didion.jwnl.JWNLException;
- import net.didion.jwnl.data.Synset;
- /**
- * An implementation of the WordNet similarity measure developed by Lin. For
- * full details of the measure see:
- * <blockquote>Lin D. 1998. An information-theoretic definition of similarity. In
- * Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Machine
- * Learning, Madison, WI.</blockquote>
- * @author Mark A. Greenwood
- */
- public class Lin extends ICMeasure
- {
- /**
- * Instances of this similarity measure should be generated using the
- * factory methods of {@link SimilarityMeasure}.
- */
- protected Lin()
- {
- //A protected constructor to force the use of the newInstance method
- }
- @Override public double getSimilarity(Synset s1, Synset s2) throws JWNLException
- {
- //if the POS tags are not the same then return 0 as this measure
- //only works with 2 nouns or 2 verbs.
- if (!s1.getPOS().equals(s2.getPOS())) return 0;
- //see if the similarity is already cached and...
- Double cached = getFromCache(s1, s2);
- //if it is then simply return it
- if (cached != null) return cached.doubleValue();
- //Get the Information Content (IC) values for the two supplied synsets
- double ic1 = getIC(s1);
- double ic2 = getIC(s2);
- //if either IC value is zero then cache and return a sim of 0
- if (ic1 == 0 || ic2 == 0) return addToCache(s1,s2,0);
- //Get the Lowest Common Subsumer (LCS) of the two synsets
- Synset lcs = getLCSbyIC(s1,s2);
- //if there isn't an LCS then cache and return a sim of 0
- if (lcs == null) return addToCache(s1,s2,0);
- //get the IC valueof the LCS
- double icLCS = getIC(lcs);
- //caluclaue the similarity score
- double sim = (2*icLCS)/(ic1+ic2);
- //cache and return the calculated similarity
- return addToCache(s1,s2,sim);
- }
- }
参考文献:
《基于维基百科的语义相似度计算》盛志超,陶晓鹏(复旦大学计算机科学技术学院);
《基于WordNet的英语词语相似度计算》颜伟,荀恩东(北京语言大学 语言信息处理研究所)
WordNet中的名词:http://ccl.pku.edu.cn/doubtfire/semantics/wordnet/c-wordnet/nouns-in-wordnet.htm
MIT的JWI(Java WordNet Interface)和JWNL(Java WordNet Library)比较
http://jxr19830617.blog.163.com/blog/static/163573067201301985219857/
http://jxr19830617.blog.163.com/blog/static/1635730672013019105255295/
基于WordNet的英文同义词、近义词相似度评估及代码实现的更多相关文章
- 【中文同义词近义词】词向量 vs 同义词近义词库
方案一:利用预训练好的词向量模型 优点: (1)能把词进行语义上的向量化(2)能得到词与词的相似度 缺点: (1)词向量的效果和语料库的大小和质量有较大的关系(2)用most_similar() 得到 ...
- 安装elasticsearch及中文IK和近义词配置
安装elasticsearch及中文IK和近义词配置 安装java环境 java环境是elasticsearch安装必须的 yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk 安装elast ...
- python 近义词库包 synonyms 的使用
最近接触到nlp的一些东西,需要找出中文词语的近义词,也接触到了一个synonyms 的库, 分词,去停用词,word2vector 等 一些列nlp 的操作,还可以输出中文词语的近义词 https ...
- 安装elasticsearch-1.7.1及中文IK和近义词配置
安装elasticsearch及中文IK和近义词配置 https://www.cnblogs.com/yjf512/p/4789239.html 安装elasticsearch及中文IK和近义词配置 ...
- 【HICP Gauss】数据库 数据库管理(存储过程 函数 对象 近义词 触发器 事务类型)-9
存储过程存储过程在大新数据库系统中,一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集 存储在SQL数据库中 优势: SQL进行封装 调用方便 存储过程会进行编译 提升用户执行SQL语句集的速 ...
- LSF-SCNN:一种基于 CNN 的短文本表达模型及相似度计算的全新优化模型
欢迎大家前往腾讯云社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 本篇文章是我在读期间,对自然语言处理中的文本相似度问题研究取得的一点小成果.如果你对自然语言处理 (natural language proc ...
- paip.输入法英文词库的处理 python 代码 o4
paip.输入法英文词库的处理 python 代码 o4 目标是eng>>>中文>>atian 当输入非atian词的时候儿,能打印出 atian pinyin > ...
- 基于统计的无词典的高频词抽取(二)——根据LCP数组计算词频
接着上文[基于统计的无词典的高频词抽取(一)——后缀数组字典序排序],本文主要讲解高频子串抽取部分. 如果看过上一篇文章的朋友都知道,我们通过 快排 或 基数排序算出了存储后缀数组字典序的PAT数组, ...
- 基于虎书实现LALR(1)分析并生成GLSL编译器前端代码(C#)
基于虎书实现LALR(1)分析并生成GLSL编译器前端代码(C#) 为了完美解析GLSL源码,获取其中的信息(都有哪些in/out/uniform等),我决定做个GLSL编译器的前端(以后简称编译器或 ...
随机推荐
- C#之内存分配
在C#中,内存分成5个区,他们分别是堆.栈.自由存储区.全局/静态存储区和常量存储区. 栈,就是那些由编译器在需要的时候分配,在不需要的时候自动清楚的变量的存储区.里面的变量通常是局部变量.函数参数等 ...
- nodejs基础 -- express框架
Node.js Express 框架 Express 简介 Express 是一个简洁而灵活的 node.js Web应用框架, 提供了一系列强大特性帮助你创建各种 Web 应用,和丰富的 HTTP ...
- js作为参数,并且返回值;js的回调模式 callback
有这样一个情景,当我们弹出一个 prompt的时候,要求用户在文本框输入一个文字,然后点击确认,就可以拿到返回值 var temp=prompt("请输入您的名字"); a ...
- interproscan 软件对序列进行GO 注释
interproscan 软件实际上将对输入的查询序列和interpro 数据库中的序列去比对,将比对上的序列对应的GO信息作为查询序列的GO注释 在interpro 数据库中,每条蛋白质序列有一个唯 ...
- Linux 下 Nginx + JDK + Tomcat + MySQL 安装指南
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/smartbetter/article/details/52026342 Nginx 是一款高性能的 http 服务器/反向代理服务器/电子邮 ...
- [Learn AF3]第五章 App Framework 3组件之Drawer——Side Menu
Drawer——Side menu 组件名称:Drawer 说明:af3中的side menu和af2中有很大变化,af3中的side menu实际上是通过插件$.afui.drawer来实现 ...
- False 'Sharing Violation' Xcopy error message
今天想要将QC的新工具自动拷贝到p4 用户机器上使用,为了避免每次通知大家升级啊!!! 于是,我在程序里调用了bat文件,执行拷贝操作,想在默默的情况下替换更新新版本工具,结果我测试发现没能成功更新版 ...
- java http post上传文件
1.上传接口 @IgnoreToken @RequestMapping(value = "/upload/cpicFile", method = RequestMethod.POS ...
- springmvc 文件下载
1.使用servlet的API实现 参考:http://my.oschina.net/u/1394615/blog/311307 @RequestMapping("/download&quo ...
- iis6.0 default web site 无法启动
按照以往方式打开http://localhost/blog2/index.asp时,意外被提醒出现错误:http 404 无法找到文件.一时感觉不知所措,怎么会出现这样的问题? 近来还碰到了一个问题, ...
