Candidate Generation and LUNA16 preprocessing
在这个kernel中,我们将讨论有助于更好地理解问题陈述和数据可视化的方法。 我还将提供有用的资源和信息的链接。
此脚本是用Python编写的。 我建议人们在桌面上安装anaconda,因为here提到了它的优点。 本教程中用于读取,处理和可视化数据的库是matplotlib,numpy,skimage和pydicom.。
图像大小(z,512,512),其中z是CT扫描中的切片数量,取决于扫描仪的分辨率。 由于计算能力的限制,这样的大图像不能直接送到卷积网络中。 因此,我们将不得不找到更可能患有癌症的地区。 我们将通过首先分割肺部,然后去除低强度区域来缩小我们的搜索空间。
在本教程中,我们将首先读入数据集并对其进行可视化。 之后,我们将分割肺部结构,然后使用图像处理方法在CT扫描中找到感兴趣的区域(可能的癌症区域)。 接下来我将介绍如何预处理LUNA16数据集,用于UNet等训练架构的分割和候选分类。
肺结构的分割是非常具有挑战性的问题,因为在肺部区域不存在同质性,在肺部结构,不同扫描仪和扫描协议中密度相似。 分割的肺可以进一步用于发现肺部结节候选者和感兴趣的区域,这可能有助于更好地分类CT扫描。 发现肺结节区域是一个非常困难的问题,因为附着在血管上的结节或者存在于肺区域的边界处。 肺结节候选者可以通过切割周围的三维体素并通过可以在LUNA16数据集上训练的3D CNNs进一步用于分类。 LUNA 16数据集具有每个CT扫描中的结节的位置,因此对于训练分类器将是有用的。
Reading a CT Scan
输入文件夹有三件事,一个是sample_images文件夹,它具有CT扫描样本。 stage1_labels.csv包含阶段1训练集图像的癌症基础事实,stage1_sample_submission.csv显示阶段1的提交格式。
In [1]:
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
import skimage, os
from skimage.morphology import ball, disk, dilation, binary_erosion, remove_small_objects, erosion, closing, reconstruction, binary_closing
from skimage.measure import label,regionprops, perimeter
from skimage.morphology import binary_dilation, binary_opening
from skimage.filters import roberts, sobel
from skimage import measure, feature
from skimage.segmentation import clear_border
from skimage import data
from scipy import ndimage as ndi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection
import dicom
import scipy.misc
import numpy as np # Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory from subprocess import check_output
print(check_output(["ls", "../input"]).decode("utf8"))
#上面两句话是无法在windows下执行的(没有ls的binay文件)
import os
cwd = os.getcwd()
file_path=cwd+'/input'
print(os.listdir(file_path))
结果:
['sample_images', 'stage1_labels.csv', 'stage1_sample_submission.csv']
每个三维CT扫描由多个切片组成,其数目取决于扫描仪的分辨率,每个切片都有一个与之关联的实例号,它告诉从顶部切片的索引。 CT扫描的所有dicom文件都在CT扫描名称的一个文件夹内。 现在我们将读取扫描的所有dicom切片,然后根据它们的实例编号堆叠它们以获得3D肺部CT扫描图像。
sample_images文件夹大约有20个文件夹,每个文件夹对应一个CT扫描。 在文件夹里面有很多dicom文件。
In [2]:
image_path=file_path+'/sample_images'
print(os.listdir(image_path))
结果:
['00cba091fa4ad62cc3200a657aeb957e', '0a099f2549429d29b32f349e95fb2244', '0a0c32c9e08cc2ea76a71649de56be6d', '0a38e7597ca26f9374f8ea2770ba870d', '0acbebb8d463b4b9ca88cf38431aac69', '0b20184e0cd497028bdd155d9fb42dc9', '0bd0e3056cbf23a1cb7f0f0b18446068', '0c0de3749d4fe175b7a5098b060982a1', '0c37613214faddf8701ca41e6d43f56e', '0c59313f52304e25d5a7dcf9877633b1', '0c60f4b87afcb3e2dfa65abbbf3ef2f9', '0c98fcb55e3f36d0c2b6507f62f4c5f1', '0c9d8314f9c69840e25febabb1229fa4', '0ca943d821204ceb089510f836a367fd', '0d06d764d3c07572074d468b4cff954f', '0d19f1c627df49eb223771c28548350e', '0d2fcf787026fece4e57be167d079383', '0d941a3ad6c889ac451caf89c46cb92a', '0ddeb08e9c97227853422bd71a2a695e', '0de72529c30fe642bc60dcb75c87f6bd']
每个CT扫描由多个以DICOM格式提供的2D切片组成。 首先,我将读取CT扫描的随机dicom文件。 读取图像文件后,我们将用0更新-2000的亮度值,因为它们是落在扫描仪边界之外的像素。
# Any results you write to the current directory are saved as output.
def loadFileInformation(filename):
information = {}
ds = dicom.read_file(filename)
information['PatientID'] = ds.PatientID
information['PatientName'] = ds.PatientName
information['PatientBirthDate'] = ds.PatientBirthDate
return information random_dcm_path=image_path+'/00cba091fa4ad62cc3200a657aeb957e/38c4ff5d36b5a6b6dc025435d62a143d.dcm'
# print(loadFileInformation(random_dcm_path))
lung = dicom.read_file(random_dcm_path) slice = lung.pixel_array
slice[slice == -2000] = 0
plt.imshow(slice, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.show()
结果:
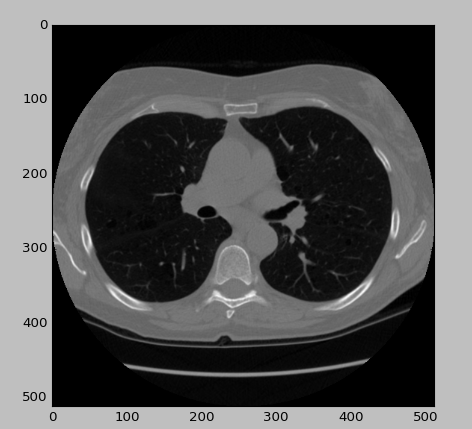
def read_ct_scan(folder_name):
# Read the slices from the dicom file
slices = [dicom.read_file(folder_name + '/'+filename) for filename in os.listdir(folder_name)] # Sort the dicom slices in their respective order
slices.sort(key=lambda x: int(x.InstanceNumber)) # Get the pixel values for all the slices
slices = np.stack([s.pixel_array for s in slices])
slices[slices == -2000] = 0
return slices
某个病人CT_path=image_path+'/00cba091fa4ad62cc3200a657aeb957e'
ct_scan = read_ct_scan(某个病人CT_path)
为了可视化切片,我们将必须绘制它们。 matplotlib用于绘制切片。 plot_ct_scan函数将三维CT扫描图像数组作为输入,并绘制等间距切片。 CT扫描是灰度图像,即每个像素的值是单个样本,这意味着它仅携带强度信息。
def plot_ct_scan(scan):
f, plots = plt.subplots(int(scan.shape[0] / 20) + 1, 4, figsize=(25, 25))
for i in range(0, scan.shape[0], 5):
plots[int(i / 20), int((i % 20) / 5)].axis('off')
plots[int(i / 20), int((i % 20) / 5)].imshow(scan[i], cmap=plt.cm.bone)
plot_ct_scan(ct_scan)
plt.show()
结果:
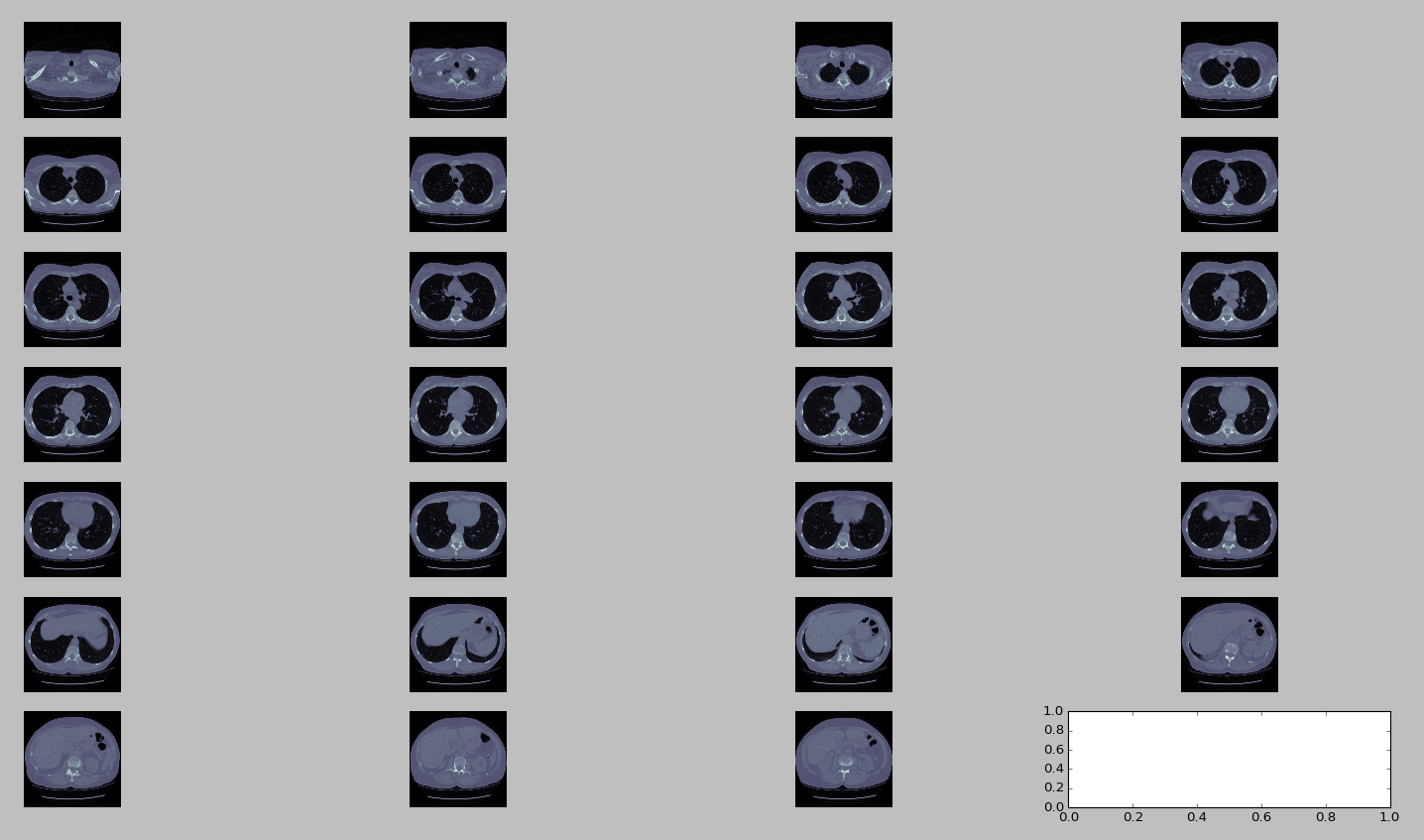
Segmentation of Lungs
在阅读CT扫描之后,预处理的第一步就是肺结构的分割,因为显然感兴趣的区域位于肺内。 可以看出,肺部是CT扫描中较暗的区域。 肺内的明亮区域是血管或空气。 在所有地方使用604(-400HU)的阈值,因为在实验中发现它工作得很好。 我们从CT扫描图像的每个切片中分割出肺部结构,尽量不要放过附着在肺壁上的可能区域。 有一些可能附着在肺壁上的结节。
我将首先解释一个常见的方法,使用简单的图像处理和形态学操作来分割肺部,然后将给文献的良好链接提供参考和总结。
def get_segmented_lungs(im, plot=False):
'''
This funtion segments the lungs from the given 2D slice.
'''
if plot == True:
f, plots = plt.subplots(8, 1, figsize=(5, 40))
'''
Step 1: Convert into a binary image.
'''
binary = im < 604
if plot == True:
plots[0].axis('off')
plots[0].imshow(binary, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 2: Remove the blobs connected to the border of the image.
'''
cleared = clear_border(binary)
if plot == True:
plots[1].axis('off')
plots[1].imshow(cleared, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 3: Label the image.
'''
label_image = label(cleared)
if plot == True:
plots[2].axis('off')
plots[2].imshow(label_image, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 4: Keep the labels with 2 largest areas.
'''
areas = [r.area for r in regionprops(label_image)]
areas.sort()
if len(areas) > 2:
for region in regionprops(label_image):
if region.area < areas[-2]:
for coordinates in region.coords:
label_image[coordinates[0], coordinates[1]] = 0
binary = label_image > 0
if plot == True:
plots[3].axis('off')
plots[3].imshow(binary, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 5: Erosion operation with a disk of radius 2. This operation is
seperate the lung nodules attached to the blood vessels.
'''
selem = disk(2)
binary = binary_erosion(binary, selem)
if plot == True:
plots[4].axis('off')
plots[4].imshow(binary, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 6: Closure operation with a disk of radius 10. This operation is
to keep nodules attached to the lung wall.
'''
selem = disk(10)
binary = binary_closing(binary, selem)
if plot == True:
plots[5].axis('off')
plots[5].imshow(binary, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 7: Fill in the small holes inside the binary mask of lungs.
'''
edges = roberts(binary)
binary = ndi.binary_fill_holes(edges)
if plot == True:
plots[6].axis('off')
plots[6].imshow(binary, cmap=plt.cm.bone)
'''
Step 8: Superimpose the binary mask on the input image.
'''
get_high_vals = binary == 0
im[get_high_vals] = 0
if plot == True:
plots[7].axis('off')
plots[7].imshow(im, cmap=plt.cm.bone) return im
get_segmented_lungs函数分割CT扫描的二维切片。 为了更好的可视化和理解代码和应用操作,我已经输出切片。
get_segmented_lungs(ct_scan[71], True)
plt.show()
结果:

现在,我将逐片分割整个CT扫描并显示CT扫描的一些切片。
def segment_lung_from_ct_scan(ct_scan):
return np.asarray([get_segmented_lungs(slice) for slice in ct_scan])
segmented_ct_scan = segment_lung_from_ct_scan(ct_scan)
plot_ct_scan(segmented_ct_scan)
plt.show()
结果:
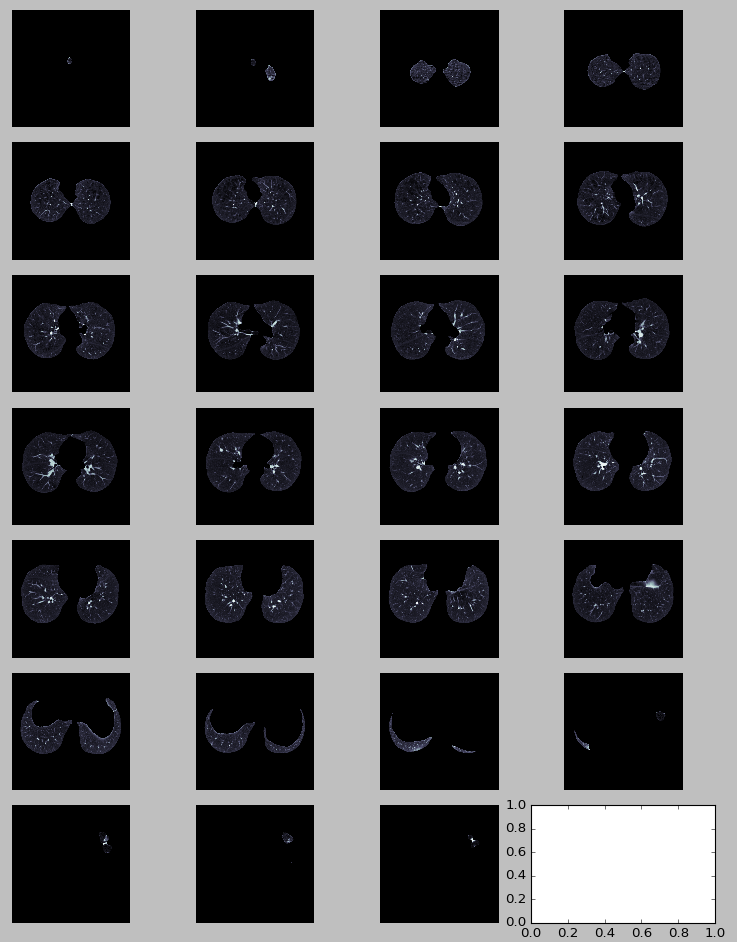
Nodule Candidate/Region of Interest Generation
在从CT扫描图像中分割出肺部结构之后,我们的任务是找到具有结节的候选区域,因为搜索空间非常大。 而且由于计算的局限性,整幅图像不能直接用3D CNNs进行分类,需要找到可能的癌症区域并对其进行分类。 在实验中发现,所有的兴趣区域的强度> 604(-400 HU)。 所以,我们使用这个阈值来过滤较暗的区域。 这大大减少了候选人数量,保留了召回率高的重要区域。 然后我们将所有候选点分类以减少误报。
segmented_ct_scan[segmented_ct_scan < 604] = 0
plot_ct_scan(segmented_ct_scan)
plt.show()
结果:

过滤后,由于血管仍然有很多噪音。 因此,我们进一步删除两个最大的连接组件( remove the two largest connected component)。
selem = ball(2)
binary = binary_closing(segmented_ct_scan, selem) label_scan = label(binary) areas = [r.area for r in regionprops(label_scan)]
areas.sort() for r in regionprops(label_scan):
max_x, max_y, max_z = 0, 0, 0
min_x, min_y, min_z = 1000, 1000, 1000 for c in r.coords:
max_z = max(c[0], max_z)
max_y = max(c[1], max_y)
max_x = max(c[2], max_x) min_z = min(c[0], min_z)
min_y = min(c[1], min_y)
min_x = min(c[2], min_x)
if (min_z == max_z or min_y == max_y or min_x == max_x or r.area > areas[-3]):
for c in r.coords:
segmented_ct_scan[c[0], c[1], c[2]] = 0
else:
index = (max((max_x - min_x), (max_y - min_y), (max_z - min_z))) / (min((max_x - min_x), (max_y - min_y), (max_z - min_z)))
plot_3d函数绘制CT扫描的3D numpy数组。
In [14]:
def plot_3d(image, threshold=-300):
# Position the scan upright,
# so the head of the patient would be at the top facing the camera
p = image.transpose(2, 1, 0)
p = p[:, :, ::-1] verts, faces = measure.marching_cubes(p, threshold) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # Fancy indexing: `verts[faces]` to generate a collection of triangles
mesh = Poly3DCollection(verts[faces], alpha=0.1)
face_color = [0.5, 0.5, 1]
mesh.set_facecolor(face_color)
ax.add_collection3d(mesh) ax.set_xlim(0, p.shape[0])
ax.set_ylim(0, p.shape[1])
ax.set_zlim(0, p.shape[2])
In [15]:
plot_3d(segmented_ct_scan, 604)
plt.show()
结果:
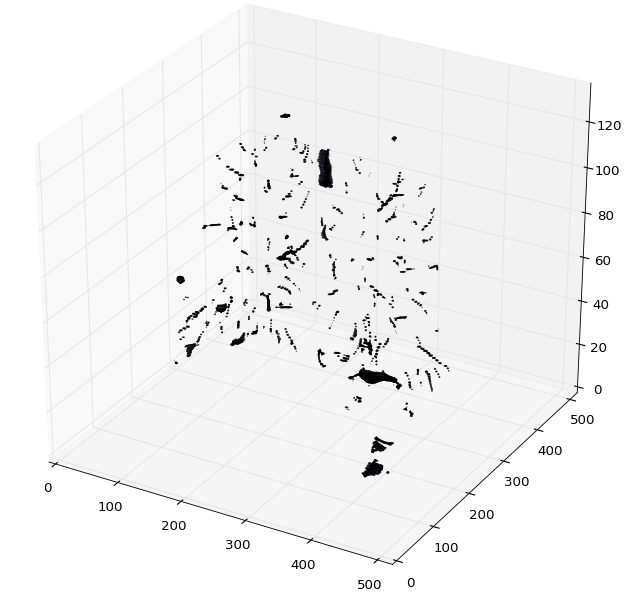
还有更多的方法可以去尝试获取感兴趣的区域。
1. 因为我们知道结节是球形的,所以左侧血管可以进一步使用形状特性进行过滤。
2. 可以进一步使用超像素(应该指的是加强分倍率)分割,并且可以在分割区域上应用形状属性。
3. 像UNet这样的CNN体系结构也可以用来生成候选感兴趣区域。
使用图像处理方法也有很多关于肺分割和结节候选生成的优秀论文。 我列出一些方法的小结:
- Automatic segmentation of lung nodules with growing neural gas and support vector machine-所提出的方法包括采集肺的计算机断层扫描图像(CT),通过提取胸腔,提取肺和重建实质的原始形状的技术减少感兴趣的体积。 之后,使用生长的神经气体(GNG)来限制比肺实质更密集的结构(结节,血管,支气管等)。 下一个阶段是类似肺结节的结构与其他结构如血管和支气管的分离。 最后,通过形状和纹理测量以及支持向量机将结构分类为结核或非结核。
- Automated Segmentation of Lung Regions using Morphological Operators in CT scan-get_segmented_lungs方法是这篇文章的一个小修改。 本文采用了604的门槛值。
- Pre-processing methods for nodule detection in lung CT- 本文采用点增强滤波器应用于体素数据的三维矩阵。 该3D滤波器试图确定每个体素的局部几何特性,计算Hessian矩阵的特征值并评估特意构建的“似然”函数,以区分线性,平面和球形物体的局部形态,将其建模为具有3D高斯部分 (Q. Li,S. Sone和K. Doi [6])。 通过将这种3D滤波器应用于人造图像,即使在将其叠加到非高斯区域的情况下,我们也验证了高斯样区域检测的效率。
- Lung Nodule Detection using a Neural Classifier:本文讨论了用于结节候选选择的点增强滤波器和用于假阳性发现减少的神经分类器。 该性能被评估为全自动计算机化的方法,用于在筛查CT中识别可能在视觉解释期间遗漏的肺癌的肺结节的检测。
接下来我将讨论关于LUNA16数据集的预处理,并用它来训练UNet模型。
UNET for Candidate Point Generation
目前深度学习方法在医学影像分割问题上取得了较好的效果。 一个非常有名的建筑是UNET,在我们的例子中可以用于结节候选点生成。 这些网络的培训使用注释数据集完成。 上述用于候选点生成的图像处理方法不需要任何训练数据。 我们使用LUNA16数据集来训练我们的UNET模型。
在LUNA16数据集中,每个CT扫描用结节点和用于生成二进制掩模的结节的半径来标注。 我将首先讨论LUNA16数据集的预处理。 在数据集中,CT扫描保存在“.mhd”文件中,SimpleITK用于读取图像。 我已经定义了三个功能:
Candidate Generation and LUNA16 preprocessing的更多相关文章
- 使用FP-Growth算法高效发现频繁项集【zz】
FP树构造 FP Growth算法利用了巧妙的数据结构,大大降低了Aproir挖掘算法的代价,他不需要不断得生成候选项目队列和不断得扫描整个数据库进行比对.为了达到这样的效果,它采用了一种简洁的数据结 ...
- 一起做RGB-D SLAM 第二季 (一)
小萝卜:师兄!过年啦!是不是很无聊啊!普通人的生活就是赚钱花钱,实在是很没意思啊! 师兄:是啊…… 小萝卜:他们都不懂搞科研和码代码的乐趣呀! 师兄:可不是嘛…… 小萝卜:所以今年过年,我们再做一个S ...
- 数据挖掘系列(2)--关联规则FpGrowth算法
上一篇介绍了关联规则挖掘的一些基本概念和经典的Apriori算法,Aprori算法利用频繁集的两个特性,过滤了很多无关的集合,效率提高不少,但是我们发现Apriori算法是一个候选消除算法,每一次消除 ...
- 八、频繁模式挖掘Frequent Pattern Mining
频繁模式挖掘(Frequent Pattern Mining): 频繁项集挖掘是通常是大规模数据分析的第一步,多年以来它都是数据挖掘领域的活跃研究主题.建议用户参考维基百科的association r ...
- FpGrowth算法
FpGrowth算法 频繁项集与关联规则挖掘(2)--FpGrowth算法 上一篇介绍了关联规则挖掘的一些基本概念和经典的Apriori算法,Aprori算法利用频繁集的两个特性,过滤了很多无关的 ...
- 关联规则算法之FP growth算法
FP树构造 FP Growth算法利用了巧妙的数据结构,大大降低了Aproir挖掘算法的代价,他不需要不断得生成候选项目队列和不断得扫描整个数据库进行比对.为了达到这样的效果,它采用了一种简洁的数据结 ...
- 关联分析:FP-Growth算法
关联分析又称关联挖掘,就是在交易数据.关系数据或其他信息载体中,查找存在于项目集合或对象集合之间的频繁模式.关联.相关性或因果结构.关联分析的一个典型例子是购物篮分析.通过发现顾客放入购物篮中不同商品 ...
- 用深度学习(DNN)构建推荐系统 - Deep Neural Networks for YouTube Recommendations论文精读
虽然国内必须FQ才能登录YouTube,但想必大家都知道这个网站.基本上算是世界范围内视频领域的最大的网站了,坐拥10亿量级的用户,网站内的视频推荐自然是一个非常重要的功能.本文就focus在YouT ...
- 挖掘频繁项集之FP-Growth算法
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/48918007 FP-Growth频繁项集挖掘算法(Frequent-Pattern Growth, 频 ...
随机推荐
- java统计文档中相同字符出现次数(超详细)
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { InputStream file = new ...
- @清晰掉 string.h之基础堵漏
一个标准的strcpy函数: 原本以为自己对strcpy还算比较了解,结果面试时还是悲剧了. 下面给出网上strcpy的得分版本: 2分 void strcpy( char *strDest, cha ...
- python jieba分词(结巴分词)、提取词,加载词,修改词频,定义词库 -转载
转载请注明出处 “结巴”中文分词:做最好的 Python 中文分词组件,分词模块jieba,它是python比较好用的分词模块, 支持中文简体,繁体分词,还支持自定义词库. jieba的分词,提取关 ...
- flask环境布署--废弃不用,只留作备份
[前置条件] 创建1个flask-demo,生成requirement.txt文件(下载好gunicorn),上传至git.创建demo参照:创建一个flask api-demo(响应体显示中文) g ...
- sql type subtype 统计
select * from testtable; type subtype value a sa 1b sb 1a sb errorb sa errora sb 1b sb 1c sa errorc ...
- gitlab在centos7.3上搭建
gitlab在centos7.3上搭建 最近接到gitlab+jenkins的任务,由于以前只接触过GitHub,并只是简单的使用,这里简单记录gitlab与jenkins搭建的 环境: centos ...
- 正则表达式断言(Assertions)
一 零宽正向先行断言 x(?=y) 仅匹配被y跟随的x. const regExp = /Jack(?=Sparrow|Dawson)/g; const str = 'JackJones JackSp ...
- psp周总结02
周日 周一 周二 周三 周四 周五 周六 所花时间 180 60 240 180 340 180 培训 代码量 186 65 157 86 200 200 博客量 1 1 了解的知识点 jsp页面 ...
- Chapter03 第二节 const限定符的使用
3.2 const限定符 const的作用:替代#define作为有类型检查的常量来使用.他的值被初始化后就固定了,成为一个只读变量,不能更改.(推荐使用特殊的命名规范来区分常量和非常量). cons ...
- 【Linux开发】Linux启动脚本设置
前言linux有自己一套完整的启动 体系,抓住了linux启动 的脉络,linux的启动 过程将不再神秘.阅读之前建议先看一下附图.本文中假设inittab中设置的init tree为:/etc/rc ...
