算法(Algorithms)第4版 练习 1.5.3
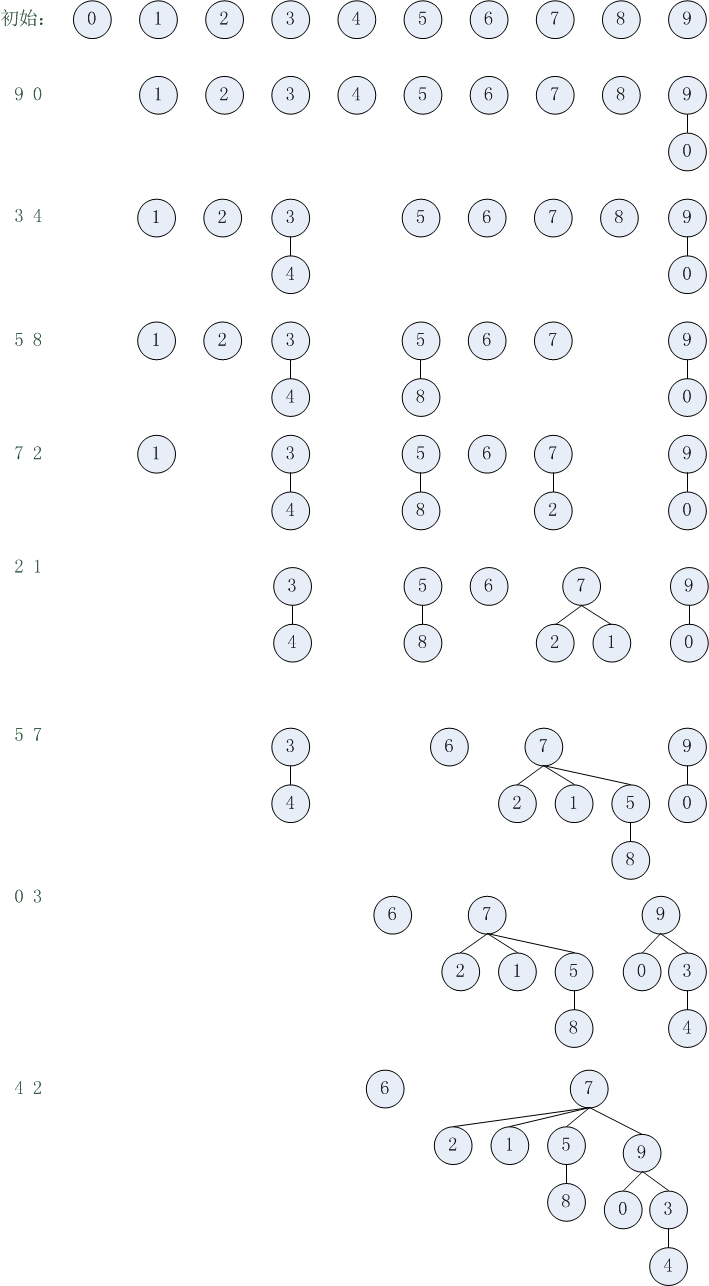
id数组和treesize数组变化情况:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
10 components
9 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
9 components
3 4
9 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
8 components
5 8
9 1 2 3 3 5 6 7 9
1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2
7 components
7 2
9 1 3 3 5 6 7 5 9
1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2
6 components
2 1
9 7 3 3 5 6 7 5 9
1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2
5 components
5 7
9 7 7 3 3 6 7 5 9
1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2
4 components
0 3
9 7 7 3 7 6 7 5 9
1 1 1 2 1 2 1 5 1
3 components
4 2
9 7 7 9 3 7 6 7 5
1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 4
2 components
森林图:
操作次数分析:
find函数每次访问数组次数是1 + 2 * depth
connected函数每次调用两次find函数
union函数每次调用两次find函数(如果两个连接点不在同一个树的话,则多一次数组访问)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//initialize N components
int N = StdIn.readInt();
UFWeightedQuickUnion uf = new UFWeightedQuickUnion(N);
StdOut.println(uf);
while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if(uf.connected(p, q)) {//ignore if connected
StdOut.println(p + " " + q + " is connected");
continue;
}
uf.union(p, q);//connect p and q
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
StdOut.println(uf);
}
}
对于这个client,对每个数据对,都调用一次connected函数和union函数。
下边对数组访问次数进行分析:
9 0:9和0的深度都为0,find访问数组次数为1,connected为2 * 1, union为2 * 1 + 5,总的为2 * 1 + 2 * 1 + 5
3 4:3和4的深度都为0,find访问数组次数为1,connected为2 * 1, union为2 * 1 + 5,总的为2 * 1 + 2 * 1 + 5
5 8:5和8的深度都为0,find访问数组次数为1,connected为2 * 1, union为2 * 1 + 5,总的为2 * 1 + 2 * 1 + 5
7 2:7和2的深度都为0,find访问数组次数为1,connected为2 * 1, union为2 * 1 + 5,总的为2 * 1 + 2 * 1 + 5
2 1:2的深度为1,1的深度为0。find访问数组次数分别为3、1,connected为3 + 1, union为3 + 1 + 5,总的为3 + 1 +3 + 1 + 5
5 7:5的深度为0,7的深度为0。find访问数组次数分别为1、1,connected为1 + 1, union为1 + 1 + 5,总的为1 + 1 +1 + 1 + 5
0 3:0的深度为1,3的深度为0。find访问数组次数分别为3、1,connected为3 + 1, union为3 + 1 + 5,总的为3 + 1 +3 + 1 + 5
4 2:4的深度为2,2的深度为1。find访问数组次数分别为5、3,connected为5 + 3, union为5 + 3 + 5,总的为5 + 3 +5 + 3 + 5
源代码:
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class UFWeightedQuickUnion { private int[] id;//parent link(site indexed)
private int[] treesize;//size of component for roots(site indexed)
private int count;//number of components public UFWeightedQuickUnion(int N) { count = N; id = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i; treesize = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
treesize[i] = 1; } public int count() {
return count;
} public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
} public int find(int p) { while(p != id[p])
p = id[p]; return p; } public void union(int p, int q) { int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q); if(pRoot == qRoot)
return; //make smaller root point to larger one
if(treesize[pRoot] < treesize[qRoot]) {
id[pRoot] = qRoot;
treesize[qRoot] += treesize[pRoot];
} else {
id[qRoot] = pRoot;
treesize[pRoot] += treesize[qRoot];
} count--; } @Override
public String toString() {
String s = ""; for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
s += id[i] + " ";
}
s += "\n"; for(int i = 0; i < treesize.length; i++) {
s += treesize[i] + " ";
}
s += "\n" + count + " components"; return s;
} public static void main(String[] args) { //initialize N components
int N = StdIn.readInt();
UFWeightedQuickUnion uf = new UFWeightedQuickUnion(N);
StdOut.println(uf); while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) { int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt(); if(uf.connected(p, q)) {//ignore if connected
StdOut.println(p + " " + q + " is connected");
continue;
} uf.union(p, q);//connect p and q
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
StdOut.println(uf);
} } }
算法(Algorithms)第4版 练习 1.5.3的更多相关文章
- 1.2 Data Abstraction(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.2.1 package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.St ...
- 1.1 BASIC PROGRAMMING MODEL(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.1.1 private static void exercise111() { StdOut.println("1.1.1:"); StdOut.println((0+15)/ ...
- ubuntu命令行下java工程编辑与算法(第四版)环境配置
ubuntu命令行下java工程编辑与算法(第四版)环境配置 java 命令行 javac java 在学习算法(第四版)中的实例时,因需要安装配套的java编译环境,可是在编译java文件的时候总是 ...
- 配置算法(第4版)的Java编译环境
1. 下载 1.1 JDK http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html选择“Windows x64 180.5 ...
- 算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.3.49 用 6 个栈实现一个 O(1) 队列
因为这个解法有点复杂,因此单独开一贴介绍. 那么这里就使用六个栈来解决这个问题. 这个算法来自于这篇论文. 原文里用的是 Pure Lisp,不过语法很简单,还是很容易看懂的. 先导知识——用两个栈模 ...
- 在Eclipse下配置算法(第四版)运行环境
第一步:配置Eclipse运行环境 Eclipse运行环境配置过程是很简单的,用过Eclipse进行java开发或学习的同学应该都很熟悉这个过程了. 配置过程: (1)系统环境:Windows7 64 ...
- 排序算法总结(C语言版)
排序算法总结(C语言版) 1. 插入排序 1.1 直接插入排序 1.2 Shell排序 2. 交换排序 2.1 冒泡排序 2.2 快速排序 3. 选择 ...
- 算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1 写在前面 整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csh ...
- 《算法》第四版 IDEA 运行环境的搭建
<算法>第四版 IDEA 运行环境的搭建 新建 模板 小书匠 在搭建之初,我是想不到会出现如此之多的问题.我看了网上的大部分教程,都是基于Eclipse搭建的,还没有使用IDEA搭建的教程 ...
- 常见排序算法题(java版)
常见排序算法题(java版) //插入排序: package org.rut.util.algorithm.support; import org.rut.util.algorithm.Sor ...
随机推荐
- mv 命令 简要
1.mv test.txt test1.txt 给文件重命名 2.mv test.txt aaDir 将test.txt文件移动到aaDir文件夹中 3.mv -t /hom ...
- Hadoop环境搭建1_JDK+SSH
1 前言: Hadoop 最早是为了在Linux 平台上使用而开发的,但是Hadoop 在UNIX.Windows 和Mac OS X 系统上也运行良好.不过,在Windows 上运行Hadoop 稍 ...
- chef简介
Chef 的简单介绍 Chef 主要分为三个部分 Chef Server.Workstation 以及 Chef Client.用户在 Workstation 上编写 Cookbook.然后,通过 k ...
- BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第11章节--为Office和SP解决方式开发集成Apps Office新的App模型
BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第11章节--为Office和SP解决方式开发集成Apps Office新的App模型 Office 2 ...
- drupal7 使用(hook_preprocess_HOOK)向各个主题模版里面传递变量
函数地址:hook_preprocess_HOOK 1 首先解释下hook_preprocess_HOOK这个钩子的含义: hook _ preprocess _ H ...
- 百度地图API简介
百度地图API简介 在此申明不是我写的,用的是别人的,仅限自己学习 百度地图移动版API(Android)是一套基于Android设备的应用程序接口,通过该接口,可以轻松的访问百度服务和数据,构建功能 ...
- uiwebview 屏幕自适应 -- 根据 内容适应或者 webview适应
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface ViewController : UIViewController<UIWebViewDelegate,UISe ...
- c_str()方法使用
语法: const char *c_str(); c_str()函数返回一个指向正规C字符串的指针常量, 内容与本string串相同. 这是为了与c语言兼容,在c语言中没有string类型,故必须通过 ...
- [笔记]我的Linux入门之路 - 02.***-Qt5配置
作为一个学习中的程序员,查wiki等,***肯定是刚需.况且没有它很多东西都下不下来.我在windows环境下使用的是shadowsocks,那么在linux下也使用它. 一.SS版本 SS版本众多, ...
- [闲来无事,从头再来][C51篇]导读
目 的: 通过学习C51,熟悉单片机,熟悉C语言,熟悉单片机系统的外部电路. 方 法: 通过看书和使用板子做实验来进行学习 参考资料: <新概念51单片机C语言教程& ...
