程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(三)第二周测验
6. 学生信息处理程序
总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 1024kB
描述
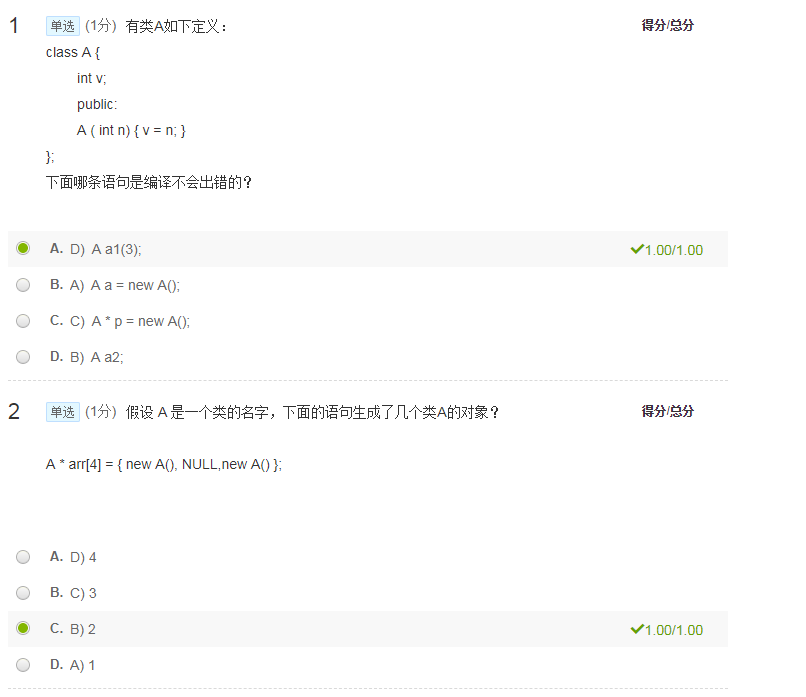
实现一个学生信息处理程序,计算一个学生的四年平均成绩。 要求实现一个代表学生的类,并且类中所有成员变量都是【私有的】。 补充下列程序中的 Student 类以实现上述功能。 #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std; class Student {
// 在此处补充你的代码
}; int main() {
Student student; // 定义类的对象
student.input(); // 输入数据
student.calculate(); // 计算平均成绩
student.output(); // 输出数据
}
输入
输入数据为一行,包括:
姓名,年龄,学号,第一学年平均成绩,第二学年平均成绩,第三学年平均成绩,第四学年平均成绩。
其中姓名为由字母和空格组成的字符串(输入保证姓名不超过20个字符,并且空格不会出现在字符串两端),年龄、学号和学年平均成绩均为非负整数。信息之间用逗号隔开。
输出
输出一行数据,包括:
姓名,年龄,学号,四年平均成绩。
信息之间用逗号隔开。
样例输入
Tom Hanks,18,7817,80,80,90,70
样例输出
Tom Hanks,18,7817,80
提示
必须用类实现,其中所有成员变量都是私有的。
输出结果中,四年平均成绩不一定为整数。
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Student {
private:
char name[20];
int id,age;
float a,b,c,d;
char ch;
public:
void input()
{
cin.get(name, 21, ','); //看补充
cin>>ch>>age>>ch>>id>>ch>>a>>ch>>b>>ch>>c>>ch>>d;
};
float calculate()
{
float sum=a+b+c+d;
return sum/4;
};
bool t()
{
float sum=(a+b+c+d)/4;
int a=sum;
if (a==sum)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void output()
{
float mid=calculate();
cout<<name<<","<<age<<","<<id<<",";
if (t()==false)
{
printf("%.1f",mid);//没有给iomanip头文件,只能选择C语言输出
}
else
printf("%.0f",mid);
}
}; int main() {
Student student; // 定义类的对象
student.input(); // 输入数据
student.calculate(); // 计算平均成绩
student.output(); // 输出数据
}
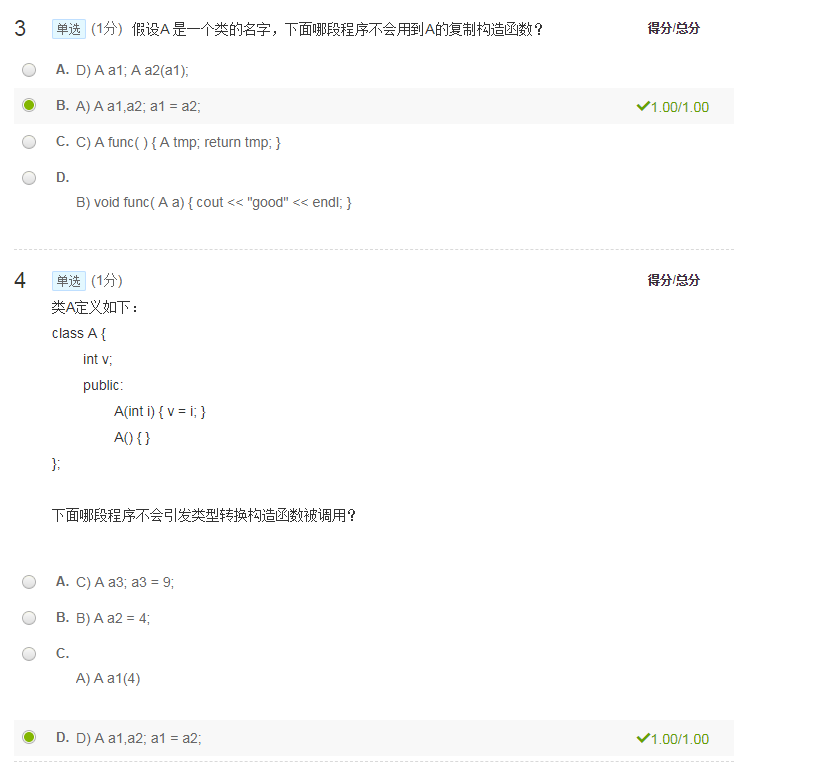
7.奇怪的类复制
描述
程序填空,使其输出9 22 5 #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Sample {
public:
int v;
// 在此处补充你的代码
};
void PrintAndDouble(Sample o)
{
cout << o.v;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Sample a(5);
Sample b = a;
PrintAndDouble(b);
Sample c = 20;
PrintAndDouble(c);
Sample d;
d = a;
cout << d.v;
return 0;
}
输入
无
输出
9
22
5
样例输入
None
样例输出
9
22
5
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Sample {
public:
int v;
Sample(int n=0)
{
v=n;
}
Sample(const Sample &x)
{
v=x.v+2;
}
};
void PrintAndDouble(Sample o) //作为函数参数时候会调用复制构造函数
{
cout << o.v;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Sample a(5);
Sample b = a;
PrintAndDouble(b);
Sample c = 20;
PrintAndDouble(c);
Sample d;
d = a;
cout << d.v;
return 0;
}
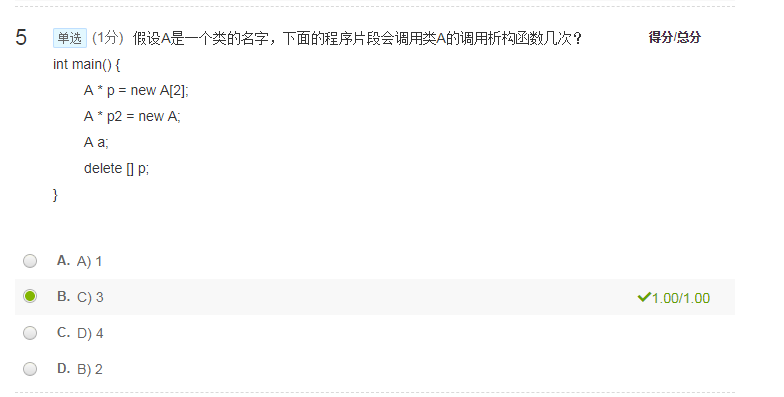
8.超简单的复数类
描述
下面程序的输出是: 3+4i
5+6i 请补足Complex类的成员函数。不能加成员变量。 #include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
private:
double r,i;
public:
void Print() {
cout << r << "+" << i << "i" << endl;
}
// 在此处补充你的代码
};
int main() {
Complex a;
a = "3+4i"; a.Print();
a = "5+6i"; a.Print();
return 0;
}
输入
无
输出
3+4i
5+6i
样例输入
无
样例输出
3+4i
5+6i
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
private:
double r,i;
public:
void Print()
{
cout << r << "+" << i << "i" << endl;
}
Complex() {};
Complex(char x[])
{
r=x[0]-'0';
i=x[2]-'0';
}
};
int main()
{
Complex a;
a = "3+4i";
a.Print();
a = "5+6i";
a.Print();
return 0;
}
9.哪来的输出
描述
程序填空,输出指定结果 #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int i;
A(int x) { i = x; }
// 在此处补充你的代码
};
int main()
{
A a(1);
A * pa = new A(2);
delete pa;
return 0;
}
输入
无
输出
2
1
样例输入
无
样例输出
2
1
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int i;
A(int x)
{
i = x;
}
~A()
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A a(1);
A * pa = new A(2);
delete pa;
return 0;
}
程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(三)第二周测验的更多相关文章
- 程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(一)第二周测验(2018春季)
编程题: 1:对齐输出 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 读入三个整数,按每个整数占8个字符的宽度,右对齐输出它们. 输入 只有一行,包含三个整数,整数之间以一个空格分 ...
- 程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(二)第二周测验(2018春季)
递归算法: 1:全排列 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 给定一个由不同的小写字母组成的字符串,输出这个字符串的所有全排列. 我们假设对于小写字母有'a' < ' ...
- 程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(三)第一周测验
作业题: 7. 填空(2分)简单的swap 通过码是 ( 请参考公告中的“关于编程作业的说明”完成编程作业(请注意,编程题都要求提交通过码,在openjudge上提交了程序并且通过以后,就可以下载到通 ...
- 【吴恩达课后测验】Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第二周测验【中英】
[中英][吴恩达课后测验]Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第二周测验 第2周测验 - 神经网络基础 神经元节点计算什么? [ ]神经元节点先计算激活函数,再计算线性函数(z = Wx + ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第五门课 序列模型(Sequence Models)-Week 2: Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings (第二周测验:自然语言处理与词嵌入)
Week 2 Quiz: Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings (第二周测验:自然语言处理与词嵌入) 1.Suppose you learn ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-Week 2 - Neural Network Basics(第二周测验 - 神经网络基础)
Week 2 Quiz - Neural Network Basics(第二周测验 - 神经网络基础) 1. What does a neuron compute?(神经元节点计算什么?) [ ] A ...
- 程序设计实习MOOC / 继承和派生——编程作业 第五周程序填空题1
描述 写一个MyString 类,使得下面程序的输出结果是: 1. abcd-efgh-abcd- 2. abcd- 3. 4. abcd-efgh- 5. efgh- 6. c 7. abcd- 8 ...
- 20165101刘天野 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》 结对编程练习_四则运算(第二周)
20165101刘天野 2017-2018-2 <Java程序设计> 结对编程练习_四则运算(第二周) 一.需求分析 能随机生成n道四则运算题目,n由使用者输入 支持分数运算 支持多运算符 ...
- 201871010105-曹玉中《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
201871010105-曹玉中<面向对象程序设计(Java)>第二周学习总结 项目 ...
随机推荐
- WEB入门之十二 jquery简介
学习内容 jQuery简介 搭建jQuery开发环境 jQuery基本选择器 能力目标 熟悉jQuery开发环境 能编写简单的jQuery代码 本章简介 在前面两章,我们学习了JavaScript面向 ...
- 音视频处理之PS封装的介绍与使用20180928
1.PS封装介绍MPEG2-PS是一种多路复用数字音频,视频等的封装容器.PS是Program Stream(程序流或节目流)的简称.程序流将一个或多个分组但有共同的时间基准的基本数据流(PES)合并 ...
- SQL Server优化的方法
SQL Server优化的方法<一> 查询速度慢的原因很多,常见如下几种: 1.没有索引或者没有用到索引(这是查询慢最常见的问题,是程序设计的缺陷) 2.I/O吞吐量小,形成了 ...
- cookie添加删除修改
//cookie添加 document.cookie="username=John Doe"; //添加过期时间 document.cookie="username1=J ...
- Git 配置环境及常用命令整理
一.Git教程网站 廖雪峰网站 易百GitHub命令:https://www.yiibai.com/git/git_clone.html 完成Windows环境命令下Git config配置 设置好之 ...
- element-ui 设置input的只读或禁用
只读:readonly 在data里定义:readonly: true, 然后在input框里加上readonly就可以了. 禁用:disabled 在data里定义:edit: true, 然后在i ...
- Dubbo学习笔记10:Dubbo服务消费方启动流程源码分析
同理我们看下服务消费端启动流程时序图: 在<Dubbo整体架构分析>一文中,我们提到服务消费方需要使用ReferenceConfig API来消费服务,具体是调用代码(1)get()方法来 ...
- python技巧 合并两个字典
python 3.5+ 版本 In [1]: a={'x':2,'y':4} In [2]: b={'c':1,'d':3} In [3]: c={'c':3,'y':6} In [4]: w={* ...
- 第5月第8天 jsonmodel
1. @implementation JSONValueTransformer (CustomTransformer) //时间戳转NSDate - (NSDate *)NSDateFromNSStr ...
- py-faster-rcnn代码阅读2-config.py
简介 该文件指定了用于fast rcnn训练的默认config选项,不能随意更改,如需更改,应当用yaml再写一个config_file,然后使用cfg_from_file(filename)导入以 ...
