Hello 2018 A,B,C,D
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The following problem is well-known: given integers n and m, calculate
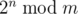 ,
,
where 2n = 2·2·...·2 (n factors), and 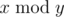 denotes the remainder of division of x by y.
denotes the remainder of division of x by y.
You are asked to solve the "reverse" problem. Given integers n and m, calculate
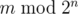 .
.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 108).
The second line contains a single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 108).
Output a single integer — the value of 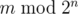 .
.
4
42
10
1
58
0
98765432
23456789
23456789
In the first example, the remainder of division of 42 by 24 = 16 is equal to 10.
In the second example, 58 is divisible by 21 = 2 without remainder, and the answer is 0.
思路:
直接用题目讲的公式套
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
ll mod(ll x,ll y){
return x - (x/y)*y;
}
int main()
{
int n;
ll m;
cin>>n>>m;
cout<<mod(m,pow(,n))<<endl;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Consider a rooted tree. A rooted tree has one special vertex called the root. All edges are directed from the root. Vertex u is called a child of vertex v and vertex v is called a parent of vertex u if there exists a directed edge from v to u. A vertex is called a leaf if it doesn't have children and has a parent.
Let's call a rooted tree a spruce if its every non-leaf vertex has at least 3 leaf children. You are given a rooted tree, check whether it's a spruce.
The definition of a rooted tree can be found here.
The first line contains one integer n — the number of vertices in the tree (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000). Each of the next n - 1 lines contains one integer pi (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) — the index of the parent of the i + 1-th vertex (1 ≤ pi ≤ i).
Vertex 1 is the root. It's guaranteed that the root has at least 2 children.
Print "Yes" if the tree is a spruce and "No" otherwise.
4
1
1
1
Yes
7
1
1
1
2
2
2
No
8
1
1
1
1
3
3
3
Yes
The first example:
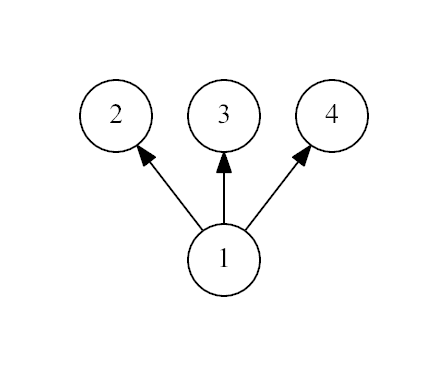
The second example:
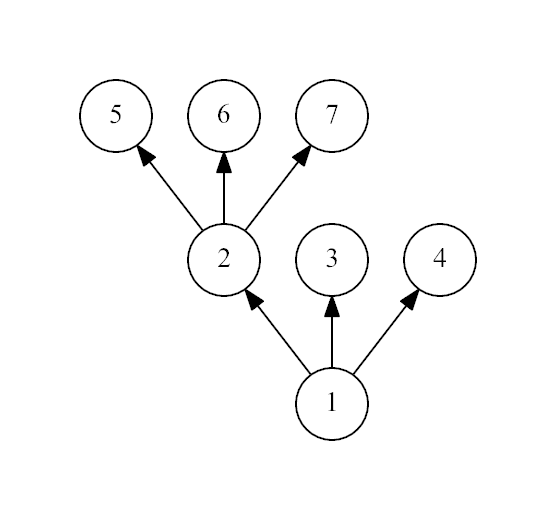
It is not a spruce, because the non-leaf vertex 1 has only 2 leaf children.
The third example:
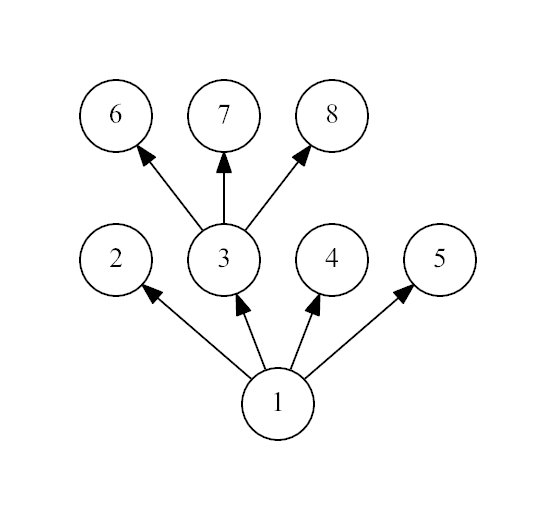
思路:
我是直接算出叶子节点的数量,再由这些叶子节点推出父节点的子节点数量,每个非叶子节点的父节点都要有3个以上的叶子节点。有个特殊判断就是没有叶子节点的除了叶子结点还有在中间的节点
这些节点的子节点全部为非叶子节点,要特判下。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[],b[],c[];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
cin>>a[i];
b[a[i]]++;
}
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
if(b[i]==){
c[a[i]]++;
}
}
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
if(c[i]!=&&c[i]<){
cout<<"No"<<endl; return ;
}
if(b[i]!=&&c[i]==){
cout<<"No"<<endl; return ;
}
}
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A New Year party is not a New Year party without lemonade! As usual, you are expecting a lot of guests, and buying lemonade has already become a pleasant necessity.
Your favorite store sells lemonade in bottles of n different volumes at different costs. A single bottle of type i has volume 2i - 1 liters and costs ci roubles. The number of bottles of each type in the store can be considered infinite.
You want to buy at least L liters of lemonade. How many roubles do you have to spend?
The first line contains two integers n and L (1 ≤ n ≤ 30; 1 ≤ L ≤ 109) — the number of types of bottles in the store and the required amount of lemonade in liters, respectively.
The second line contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 109) — the costs of bottles of different types.
Output a single integer — the smallest number of roubles you have to pay in order to buy at least L liters of lemonade.
4 12
20 30 70 90
150
4 3
10000 1000 100 10
10
4 3
10 100 1000 10000
30
5 787787787
123456789 234567890 345678901 456789012 987654321
44981600785557577
In the first example you should buy one 8-liter bottle for 90 roubles and two 2-liter bottles for 30 roubles each. In total you'll get 12 liters of lemonade for just 150 roubles.
In the second example, even though you need only 3 liters, it's cheaper to buy a single 8-liter bottle for 10 roubles.
In the third example it's best to buy three 1-liter bottles for 10 roubles each, getting three liters for 30 roubles.
思路:
因为数据的特殊性(每个瓶子都是2^i-1)我们可以将L转换为2进制,逐位递推,因为相邻两个瓶子容量差距为1倍那么第i位花费最少的情况就是取a[i],a[i-1]*2中最小的,同时如果a[i]<a[i-1]那么肯定i-1位是优先选择a[i],这样就求出了每一位最优的情况,那么当L转换为2进制的时候,如果位数上为1就优先取值,如果为0的话就要和前面的值判断下,如果当前位数的最优解小于之前的最优解那么直接覆盖掉之前的就行了因为i位的容量为2^i,大于前面所有容量之和,且花费更少那么肯定优先选i位代表的瓶子。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll unsigned long long int main()
{
ll n,m,a[];
ll ans = ;
cin>>n>>m;
cin>>a[];
for(int i = ;i < n; i++){
cin>>a[i];
a[i] = min(a[i],*a[i-]);
a[i-] = min(a[i],a[i-]);
}
for(int i = n;i < ;i ++){
a[i] = *a[i-];
}
for(int i = ;i < ;i ++){
if(m & (<<i)) ans += a[i];
ans = min(ans,a[i+]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are preparing for an exam on scheduling theory. The exam will last for exactly T milliseconds and will consist of n problems. You can either solve problem i in exactly ti milliseconds or ignore it and spend no time. You don't need time to rest after solving a problem, either.
Unfortunately, your teacher considers some of the problems too easy for you. Thus, he assigned an integer ai to every problem i meaning that the problem i can bring you a point to the final score only in case you have solved no more than ai problems overall (including problem i).
Formally, suppose you solve problems p1, p2, ..., pk during the exam. Then, your final score s will be equal to the number of values of jbetween 1 and k such that k ≤ apj.
You have guessed that the real first problem of the exam is already in front of you. Therefore, you want to choose a set of problems to solve during the exam maximizing your final score in advance. Don't forget that the exam is limited in time, and you must have enough time to solve all chosen problems. If there exist different sets of problems leading to the maximum final score, any of them will do.
The first line contains two integers n and T (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105; 1 ≤ T ≤ 109) — the number of problems in the exam and the length of the exam in milliseconds, respectively.
Each of the next n lines contains two integers ai and ti (1 ≤ ai ≤ n; 1 ≤ ti ≤ 104). The problems are numbered from 1 to n.
In the first line, output a single integer s — your maximum possible final score.
In the second line, output a single integer k (0 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of problems you should solve.
In the third line, output k distinct integers p1, p2, ..., pk (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the indexes of problems you should solve, in any order.
If there are several optimal sets of problems, you may output any of them.
5 300
3 100
4 150
4 80
2 90
2 300
2
3
3 1 4
2 100
1 787
2 788
0
0
2 100
2 42
2 58
2
2
1 2
In the first example, you should solve problems 3, 1, and 4. In this case you'll spend 80 + 100 + 90 = 270 milliseconds, falling within the length of the exam, 300 milliseconds (and even leaving yourself 30 milliseconds to have a rest). Problems 3 and 1 will bring you a point each, while problem 4 won't. You'll score two points.
In the second example, the length of the exam is catastrophically not enough to solve even a single problem.
In the third example, you have just enough time to solve both problems in 42 + 58 = 100 milliseconds and hand your solutions to the teacher with a smile.
思路:
题目意思有点难懂,看了半天,给出 n m,一个代表题目数量,一个代表做题耗时加起来不得超过m,n组数据,每组有两个数 ,ai 和 ti,ti为耗时,ai不得小于已选题目的数量,如第一个样例中4不合格因为a4 = 2,而包括a4的时候一共选了3道题,所以a4不符合要求,这道题用优先队列来写的话会很方便,自定义个优先队列,ai为第一优先级,ti为第二优先级,ai小的优先,如果相同则ti大的优先,判断ai是否符合大于所选问题总数,队列中的ti之和是否小于等于规定的时间t,如果不符合要求就释放队首,再添加下一个问题进行判断,这样不断判下来,最后得到的就是符合要求的。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int x,y,id;
}a[];
struct cmp1{
bool operator()(const node &c,const node &d){
if(c.x!=d.x)return c.x>d.x;return c.y<d.y;
}
};
bool cmp2(node c,node d){
return c.y < d.y;
}
priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp1>q;
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = ;i < n;i ++){
cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y;
a[i].id = i + ;
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp2);
int m1 = m;
int ans = ;
for(int i = ;i < n; i++){
if(m1 < a[i].y) break;
if(ans < a[i].x){
m1 -= a[i].y;
q.push(a[i]);
ans ++;
}
while(!q.empty()&&q.top().x<ans){
ans --;
m1 += q.top().y;
q.pop();
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl<<ans<<endl;
while(!q.empty()){
cout<<q.top().id<<" ";
q.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
Hello 2018 A,B,C,D的更多相关文章
- 2018. The Debut Album
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=2018 真心爱过,怎么能彻底忘掉 题目大意: 长度为n的串,由1和2组成,连续的1不能超过a个,连续 ...
- Math.abs(~2018),掌握规律即可!
Math.abs(~2018) 某前端群的入门问题长姿势了,一个简单的入门问题却引发了我的思考,深深的体会到自己在学习前端技术的同时忽略遗忘了一些计算机的基础知识. 对于 JS Math对象没什么可说 ...
- 肖秀荣8套卷2018pdf下载|2018肖秀荣冲刺8套卷pdf下载电子版
肖秀荣8套卷2018pdf下载|2018肖秀荣冲刺8套卷pdf下载电子版 下载链接: https://u253469.ctfile.com/fs/253469-229815828
- 2018年的UX设计师薪酬预测,你能拿多少?
以下内容由Mockplus团队翻译整理,仅供学习交流,Mockplus是更快更简单的原型设计工具. 一个经验丰富的设计师完全可以根据地区和专业来可以预期薪酬之间的差距,其中悬殊最高可达80K. 本 ...
- Hello 2018, Bye 2017
2017年过去了,过去一年经历了太多,改变了好多好多,可以说人生进入了另一个阶段,有可能是成熟吧. 回顾2017 去年换了新工作,离开了将近工作了8年的公司,不带走一丝云彩,为其任劳任怨,最后没有任何 ...
- New Life With 2018
2017年转眼过去了.对自己来说.这一大年是迷茫和认知的一年.我的第一篇博客就这样记录下自己的历程吧 一:选择 从进入这一行到现在已经一年多了,2016年11月份就像所有的应届毕业生一样,都贼反感毕业 ...
- 2017 年终总结 & 2018 年度计划
不立几个 Flag,都不知道怎么作死 2017 年度计划完成情况: 1.健身时间不少于350天: 未完成 中断了22天,实际运动 343天 2.至少每个月看一本书: 及格 <切尔诺贝利的 ...
- [总结]-2018 w1
不想总结 2017,过去的就过去吧,不过自己在 2017 年还是收获了很多,最重要的就是赚钱.赚钱还是需要两把刷子,所以,2018 的小目标就是学习数据分析和机器学习.希望自己在这两个领域能搞点事情. ...
- 2018年手机应用UI设计趋势预测
用户需求瞬息万变,而手机软件UI设计为适应变化的用户需求,也相应的发生着变化.但是,这并不意味着用户需求和UI设计趋势就是无迹可寻的.事实上,根据前几年的手机app界面设计变化的特点,尤其是2017年 ...
- 2017 年的 人生 hard 模式终于结束了,2018年回归初心
2017 年的 人生 hard 模式终于结束了,2018年回归初心 2017年对于我个人来讲, 毫不夸张的说 算是近十年来除了高考那一年,最最惊心动魄的一年了,没有之一. >>>开篇 ...
随机推荐
- vxlan 简单理解 vs calico 网络模型
1.vxlan(virtual Extensible LAN)虚拟可扩展局域网,是一种overlay的网络技术,使用MAC in UDP的方法进 行封装,共50字节的封装报文头. 2.VTEP为虚拟机 ...
- Debian 鼠标左右手
环境:debian testing;xfce4桌面 在debian中想把鼠标改为左手操作,在设置中调整鼠标的按钮为左撇子根本没用!网上搜索后发现事实很简单,简单到不知该怎么说. 废话少说,放码过来. ...
- Windows控制程序网站带宽及Qos(TOS或DSCP)
[基于策略的 Qos]位置:gpedit.msc->本地计算机策略->用户配置->Windows 设置->基于策略的 Qos
- python_基础硬件知识
通过学习这一篇章的内容,回顾了<数字逻辑><计算机组成原理><操作系统> 这几门课的相关知识 有时候,总是要了解一些基本,才能更容易理解程序 以下是我的一些听课记录 ...
- 解决微云登陆出现wns login error的问题
原文首发我的主力博客 http://anforen.com/wp/2017/04/weiyunwns_login_error/ PC版微云客户端出现登陆出现wns login error 完全退出QQ ...
- 大数据入门第十二天——flume入门
一.概述 1.什么是flume 官网的介绍:http://flume.apache.org/ Flume is a distributed, reliable, and available servi ...
- 汇编 XOR运算
XOR运算 按位异或^ 一.按位异或^ 运算符^ 1^1=0;0^0=0; //相同则为0 0^1=1;1^0=1; //不相同为1 1101^0110=1011; // asm_XOR.c ...
- 汇编 inc 和 dec 指令
知识点: inc 加1指令 dec 减1指令 一.加一指令inc inc a 相当于 add a, //i++ 优点 速度比sub指令快,占用空间小 这条指令执行结果影响AF.OF.PF.SF.Z ...
- mfc 友元类
知识点 继承类成员的访问级别 友元类 继承访问控制: 基类 派生类(能否访问) public private protected 派生类类 派生类对象 派生类 派生类对象 派生类类 派生类对象 pri ...
- 【HNOI2018】游戏
题面 题解 这道题目到底有没有靠谱一点的解法啊... 有很多种\(\color{green}{\mathrm{AC}}\)的方法,设\(L[i],R[i]\)表示点\(i\)最左边和最右边能够到达的位 ...
