数据结构 -- 链表(LinkedList)
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。
每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
相比于线性表顺序结构,操作复杂。由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到O(1)的复杂度,比另一种线性表顺序表快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要O(n)的时间,而线性表和顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是O(logn)和O(1)。
二、链表种类
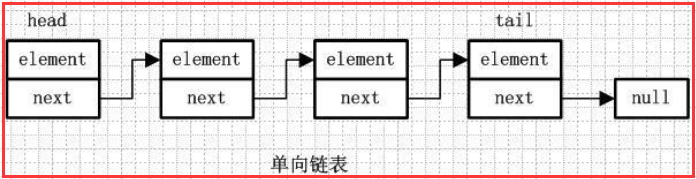
1.1)单向链表:
element:用来存放元素
next:用来指向下一个节点元素
通过每个结点的指针指向下一个结点从而链接起来的结构,最后一个节点的next指向null。
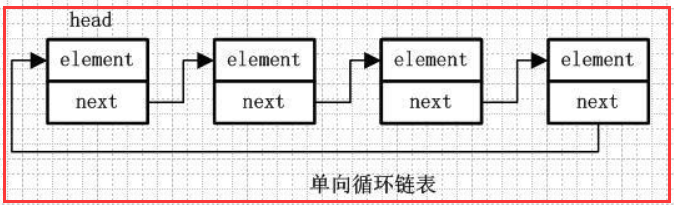
1.2)单向循环链表
element、next 跟前面一样
在单向链表的最后一个节点的next会指向头节点,而不是指向null,这样存成一个环
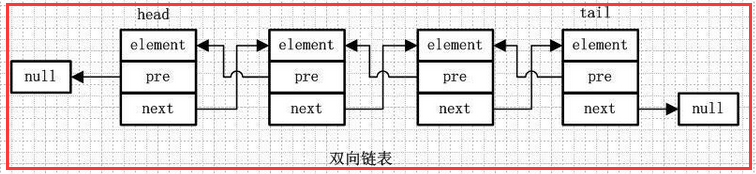
1.3)双向链表
element:存放元素
pre:用来指向前一个元素
next:指向后一个元素
双向链表是包含两个指针的,pre指向前一个节点,next指向后一个节点,但是第一个节点head的pre指向null,最后一个节点的tail指向null。
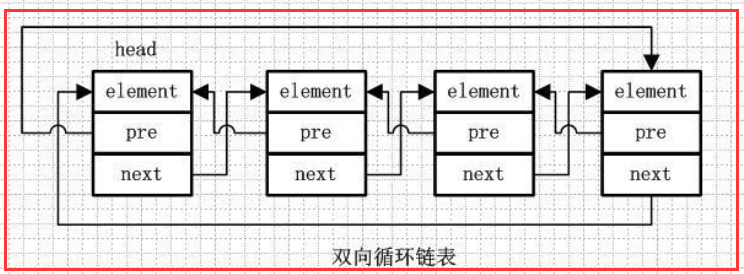
1.4)双向循环链表
element、pre、next 跟前面的一样
第一个节点的pre指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点,也形成一个“环”。
时间复杂度
(1)添加操作:O(n)
① addLast(e): O(n) ②addFirst(e): O(1) ③add(index, e): O(n/2)=O(n)
(2)删除操作:O(n)
① removeLast(e): O(n) ②removeFirst(e): O(1) ③remove(index, e): O(n/2)=O(n)
(3)查找操作:O(n)
① get(index): O(n) ②contains(e): O(n)
(4)修改操作:O(n)
① set(index,e): O(n)
三、代码实现
单链表的实现
图解如下:
插入
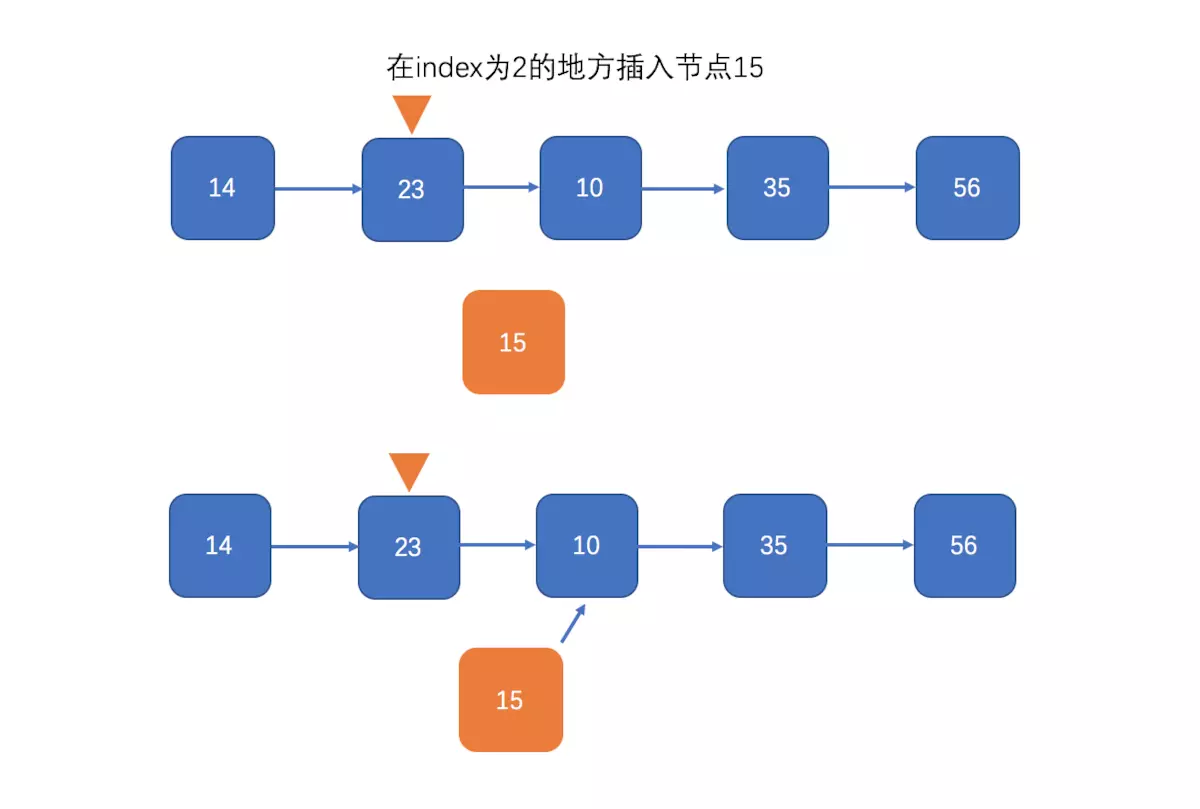
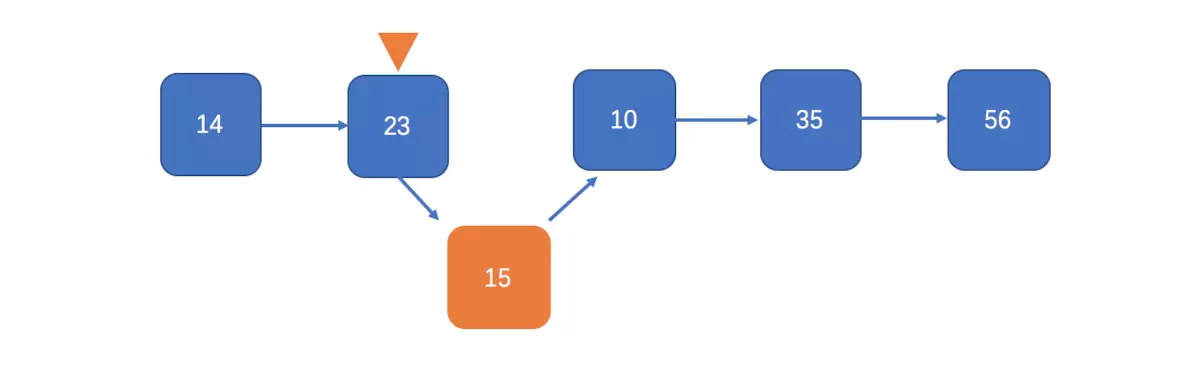
删除
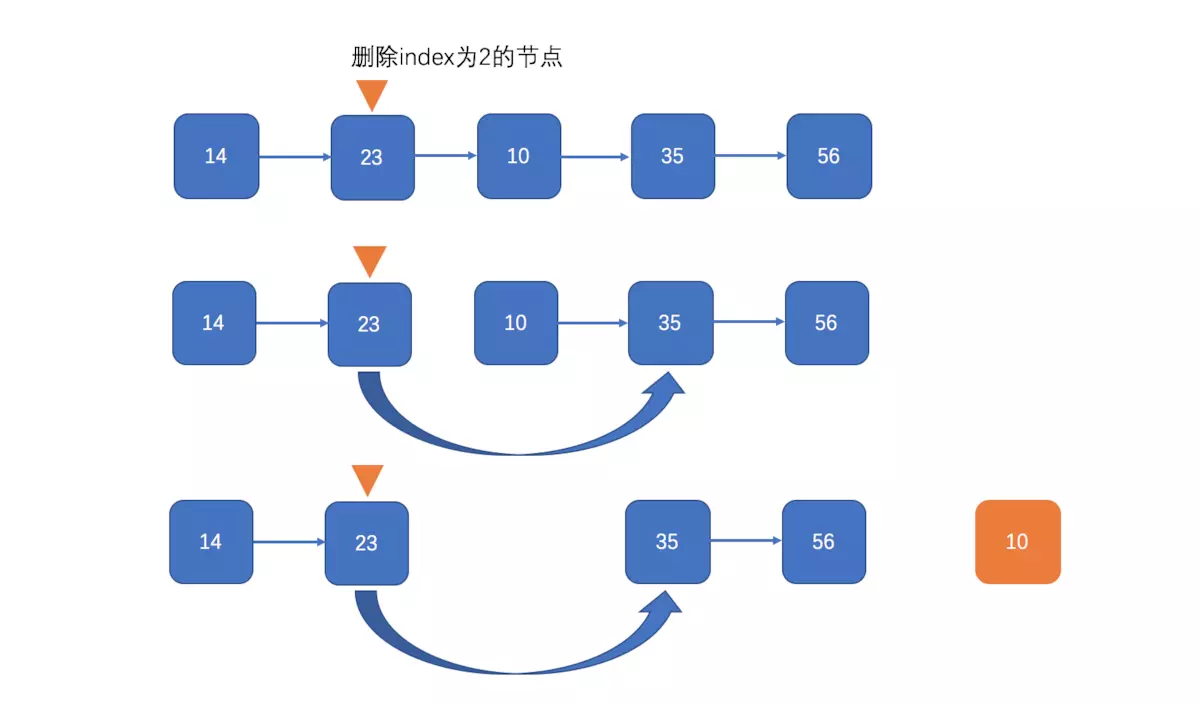
代码
public class LinkedList<E> {
//链表节点,使用内部类
private class Node{
public E e; //当前节点内容
public Node next; //指向下一个节点
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e,null);
}
public Node(){
this(null,null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点,位于第一位置的前一个位置
private int size;//链表元素个数
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for (int i=0; i<index; i++){
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e,prev.next);
size ++;
}
//在链表 表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0,e);
}
//在链表 尾部添加新的元素e
public void addList(E e){
add(size,e);
}
//获得链表的第index位置的元素. 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index Illegal");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i =0; i<index; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
}
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
public void set(int index,E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index Illegal");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i=0; i<index; i++){
cur =cur.next;
}
cur.e = e;
}
//查找链表中是否包含元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.e.equals(e))
return true;
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
// 从链表中删除index(0-based)位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E remove(int index){
if (index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++){
prev = prev.next;
}
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
//删除retNode节点,则它的下一个节点指引就不需要了,设置null,让GC干活
retNode.next = null;
size --;
return retNode.e;
}
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
public void removeElement(E e){
Node prev = dummyHead;
while (prev != null){
if (prev.next.e.equals(e)){
break;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
if (prev.next != null){
Node delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
size --;
}
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while( cur != null){
stringBuilder.append(cur + "- >");
cur = cur.next;
}
stringBuilder.append("null");
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
测试代码
public class LinkedListTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
for (int i=0; i< 10; i++){
linkedList.add(i,i*10);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.remove(1);
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.removeElement(50);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}
//测试结果
0- >null
0- >10- >null
0- >10- >20- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >null
0- >10- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null
0- >20- >30- >40- >50- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null //删除第二个位置的10
0- >20- >30- >40- >60- >70- >80- >90- >null //删除指定元素50
链表实现队列
import com.wj.queue.Queue; //Queue连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11808221.html
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next; public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e=e;
this.next = next;
} public Node(){
this(null,null);
} public Node(E e){
this(e,null);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
} private Node head, tail; //指针队首和队尾
private int size; //数据个数 public LinkedListQueue(){
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
} @Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
} @Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} //入队
@Override
public void enqueue(Object o) {
if (tail == null){
tail = new Node((E) o);
head = tail;
}else {
tail.next = new Node((E) o);
tail = tail.next;
}
size++;
}
//出队
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
}
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next;
retNode.next = null;
if (head == null){
tail = null;
}
size--;
return retNode.e;
}
//返回队首元素
@Override
public E getFront() {
if (isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
}
return head.e;
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("Queue: front ");
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null){
stringBuilder.append(cur + "- >");
cur = cur.next;
}
stringBuilder.append("NULL tail");
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
测试类
public class LinkedListQueueTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueue linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue();
for (int i=0; i<10; i++){
linkedListQueue.enqueue(i); //入队
System.out.println(linkedListQueue);
if (i % 3 ==0){
linkedListQueue.dequeue(); //符合条件,出队
}
}
}
}
//测试结果
Queue: front 0- >NULL tail
Queue: front 1- >NULL tail
Queue: front 1- >2- >NULL tail
Queue: front 1- >2- >3- >NULL tail
Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >NULL tail
Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >5- >NULL tail
Queue: front 2- >3- >4- >5- >6- >NULL tail
Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >NULL tail
Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >8- >NULL tail
Queue: front 3- >4- >5- >6- >7- >8- >9- >NULL tail
链表实现栈
import com.wj.stack.Stack; //详情连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11809042.html
public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private LinkedList<E> linkedList; public LinkedListStack(){
linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return linkedList.getSize();
} @Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return linkedList.isEmpty();
} //压入
public void push(Object o) {
linkedList.addFirst((E) o);
}
//移除
@Override
public E pop() {
return linkedList.removeFirst();
}
//返回栈首元素
@Override
public E peek() {
return linkedList.getFirst();
} public String toString(){
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("Stack: top ");
stringBuilder.append(linkedList);
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
测试类
public class LinkedListStackTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListStack stack = new LinkedListStack();
for (int i =0; i< 10; i++){
stack.push(i); //压入
System.out.println(stack);
}
System.out.println("=============");
stack.pop(); //移除
System.out.println(stack);
}
}
//测试结果
Stack: top 0- >null
Stack: top 1- >0- >null
Stack: top 2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
Stack: top 9- >8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null //将第一个移除
=============
Stack: top 8- >7- >6- >5- >4- >3- >2- >1- >0- >null
四、效率对比
栈的对比
import com.wj.stack.ArrayStack; //详情连接:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11809042.html
import com.wj.stack.Stack;
import java.util.Random;
public class StackEfficiency {
private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){
stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){
stack.pop();
} long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack();
double time1 = testStack(arrayStack,opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayStack - time1: " + time1); LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack();
double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack,opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListStack - time2: " + time2); }
}
//测试结果,添加和删除
ArrayStack - time1: 7.071363002
LinkedListStack - time2: 0.006395025
//说明数组的增删 效率要低于 链表。
//对于增删数组的时间复杂度是O(n),而链表是O(1)
队列的对比
import com.wj.queue.ArrayQueue;//详情:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11808221.html
import com.wj.queue.LoopQueue;
import com.wj.queue.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
public class MainQueue {
private static double testStack(Queue<Integer> queue, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){
queue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int i=0; i < opCount; i ++){
queue.dequeue();
} long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 1000000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue();
double time1 = testStack(arrayQueue,opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayStack - time1: " + time1); LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue();
double time2 = testStack(linkedListQueue,opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListStack - time2: " + time2); LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue();
double time3 = testStack(loopQueue,opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue - time3: " + time3);
}
}
//测试结果
ArrayQueue - time1: 368.014648575
LinkedListQueue - time2: 0.395344446
LoopQueue - time3: 0.045756219
//对于增删操作,数组(O(n))的时间复杂度高于链表队列和循环队列,所以数组最慢。
//链表和队列。队列增删只在队首和队尾,时间复杂度低于链表,所以循环队列要高于链表队列。
数据结构 -- 链表(LinkedList)的更多相关文章
- 模板 - 数据结构 - 链表/LinkedList
一个只供删除的双向链表,为了简单不再引入head节点,而且也不进行next的套娃操作.空间使用略微多了一些,但是无伤大雅. struct LinkedList { static const int M ...
- 数据结构之链表(LinkedList)(三)
数据结构之链表(LinkedList)(二) 环形链表 顾名思义 环形列表是一个首尾相连的环形链表 示意图 循环链表的特点是无须增加存储量,仅对表的链接方式稍作改变,即可使得表处理更加方便灵活. 看一 ...
- 数据结构之链表(LinkedList)(二)
数据结构之链表(LinkedList)(一) 双链表 上一篇讲述了单链表是通过next 指向下一个节点,那么双链表就是指不止可以顺序指向下一个节点,还可以通过prior域逆序指向上一个节点 示意图: ...
- 《数据结构与算法分析——C语言描述》ADT实现(NO.00) : 链表(Linked-List)
开始学习数据结构,使用的教材是机械工业出版社的<数据结构与算法分析——C语言描述>,计划将书中的ADT用C语言实现一遍,记录于此.下面是第一个最简单的结构——链表. 链表(Linked-L ...
- Python—数据结构——链表
数据结构——链表 一.简介 链表是一种物理存储上非连续,数据元素的逻辑顺序通过链表中的指针链接次序,实现的一种线性存储结构.由一系列节点组成的元素集合.每个节点包含两部分,数据域item和指向下一个节 ...
- (js描述的)数据结构[链表](4)
(js描述的)数据结构 [链表](4) 一.基本结构 二.想比于数组,链表的一些优点 1.内存空间不是必须连续的,可以充分利用计算机的内存,事项灵活的内存动态管理. 2.链表不必再创建时就确定大小,并 ...
- 数据结构和算法(Golang实现)(12)常见数据结构-链表
链表 讲数据结构就离不开讲链表.因为数据结构是用来组织数据的,如何将一个数据关联到另外一个数据呢?链表可以将数据和数据之间关联起来,从一个数据指向另外一个数据. 一.链表 定义: 链表由一个个数据节点 ...
- Redis数据结构—链表与字典的结构
目录 Redis数据结构-链表与字典的结构 链表 Redis链表节点的结构 Redis链表的表示 Redis链表用在哪 字典 Redis字典结构总览 Redis字典结构分解 Redis字典的使用 Re ...
- Redis数据结构—链表与字典
目录 Redis数据结构-链表与字典 链表 Redis链表节点的结构 Redis链表的表示 Redis链表用在哪 字典 Redis字典结构总览 Redis字典结构分解 哈希算法 解决键冲突 rehas ...
- 链表LinkedList、堆栈Stack、集合Set
链表LinkedList LinkedList 也像 ArrayList 一样实现了基本的 List 接口,但它在 List 中间执行插入和删除操作时比 ArrayList 更高效.然而,它在随机访问 ...
随机推荐
- gcc/g++ 链接库的编译与链接
GCC编译步骤 gcc -E t1.c -o t1.i 预处理 gcc -S t1.i -o t1.s 转成汇编语言 gcc -c t1.s -o t1.o 转成机器码 gcc t1.o -o t1. ...
- 10-5使用OpenType字体
http://www.missyuan.com/viewthread.php?tid=350835&extra=&page=1 现在当我们通过Photoshop.Word或其他应用程序 ...
- 在win10环境下配置spark和scala
在这里配置的是在命令行下运行spark的环境用来学习,最后结果如下,可运行简单的代码. 0.jdk.scala和spark的版本问题 有关版本如官网所示,我想要强调的是spark至今并不支持jdk11 ...
- JavaScript 取两位小数有效数字
a=2.33332.3333a.toFixed(2)"2.33"
- jmeter接口上传图片功能
图片上传需要选择Files Upload 输入下列参数: File Path:方法一,把图片放在bin目录下,直接输入图片名称:方法二,点击下图“Browse”按钮,选择一张需要上传的图片,地址将会自 ...
- springboot连接redis进行CRUD
springboot连接redis进行CRUD: 1.添加以下依赖: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</gr ...
- maven引入第三方jar包
maven有两种文件解析和分配策略,也就是我们常说的artifacts(依赖). 第一种是本地仓库,这是你缓存在本地的依赖.默认在${user.home}/.m2/repository目录下;当mav ...
- TopCoder SRM 582 Div 1 - Problem 1000 SemiPerfectPower
首先我们可以把答案差分,那么我们只需要求出\(1\)~\(x\)范围内的满足条件的数即可. 题目要求的应该是这个东西的个数: \(l \leq a*b^c \leq r(1 \le a < b) ...
- osg #ifdef _WIN32 osg
#ifdef _WIN32 #include <Windows.h> #endif // _WIN32 #include <osgViewer/Viewer> #include ...
- 算法习题---3.01猜数字游戏提示(UVa340)
一.题目 实现一个经典“猜数字”游戏.给定答案序列和用户猜的序列,统计有多少数字位置正确(A),有多少数字在两个序列都出现过但位置不对(B). 输入包含多组数据.每组输入第一行为序列长度n,第二行是答 ...
