web常见效果之轮播图
轮播图的展示效果是显而易见:
HTML代码如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head> <body> <div id="container">
<div id="list" style="left: -600px;">
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="2" />
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="3" />
<img src="img/4.jpg" alt="4" />
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="5" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="5" />
</div>
<div id="buttons">
<span index="1" class="on"></span>
<span index="2"></span>
<span index="3"></span>
<span index="4"></span>
<span index="5"></span>
</div>
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="next" class="arrow">></a>
</div> </body> </html>
疑问一:为什么用id?
方便获取被操作的元素
疑问二:为什么轮播图加类“on”?
为了方便操作,如果加了"on",即说明当前图片正在轮播
疑问三:
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a> //href="javascript:;" 是为了防止多次点击,并且为了防止跳出链接
//id = prev 是为了获取操作
//class = arrow 是属于左右移动
//<是左括号 "<" ,属于web安全符号
疑问四:为什么加了一个单独的样式,style = left: -600px;
<div id="list" style="left: -600px;">
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="2" />
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="3" />
<img src="img/4.jpg" alt="4" />
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="5" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="5" />
</div>
为了实现轮播图偏移量。
CSS代码如下
* {
margin:;
padding:;
text-decoration: none;
}
body {
padding: 20px;
}
#container {
position: relative;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
}
#list {
position: absolute;
z-index:;
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
}
#list img {
float: left;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
}
#buttons {
position: absolute;
left: 250px;
bottom: 20px;
z-index:;
height: 10px;
}
#buttons span {
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border: 1px solid #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #333;
cursor: pointer;
}
#buttons .on {
background: orangered;
}
.arrow {
position: absolute;
top: 180px;
z-index:;
display: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 39px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .3);
cursor: pointer;
}
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .7);
}
#container:hover .arrow {
display: block;
}
#prev {
left: 20px;
}
#next {
right: 20px;
}
疑问一:谈论一下绝对定位和相对定位?
position: relative 是相对定位
position: absolute是绝对定位
如果父元素没有被赋予相对定位,那么子元素的绝对定位是基于网页的!
疑问二:为什么用.7? 而不是0.7
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .7);
}
为了方便书写,可以用.7替代0.7。
疑问三:父元素用相对定位,子元素为什么一定要用绝对定位?
父元素:
#container {
position: relative;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
}
子元素:
#list {
position: absolute;
z-index:;
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
}
如何区分父元素和子元素 , 即包括起来的,如下图所示
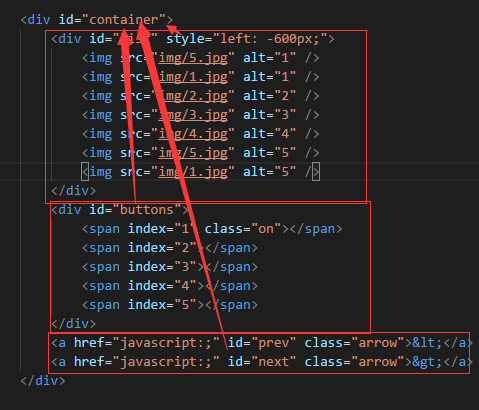
所有元素的父元素就是 container
所有绝对定位都是相对于父元素 container
JS代码如下
window.onload = function() {
var container = document.getElementById('container');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
var imgLen= document.getElementTagName('img');
var buttons = document.getElementById('buttons').getElementsByTagName('span');
var prev = document.getElementById('prev');
var next = document.getElementById('next');
var index = 1;
var timer;
function animate(offset) {
//获取的是style.left,是相对左边获取距离,所以第一张图后style.left都为负值,
//且style.left获取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整转化为数字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + 'px';
//无限滚动判断
if (newLeft > -600) {
list.style.left = -3000 + 'px';
}
if (newLeft < -3000) {
list.style.left = -600 + 'px';
}
}
function play() {
//重复执行的定时器
timer = setInterval(function() {
next.onclick();
}, 2000)
}
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
function buttonsShow() {
//将之前的小圆点的样式清除
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == "on") {
buttons[i].className = "";
}
}
//数组从0开始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = "on";
}
prev.onclick = function() {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function() {
//由于上边定时器的作用,index会一直递增下去,我们只有5个小圆点,所以需要做出判断
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1
}
animate(-600);
buttonsShow();
};
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
(function(i) {
buttons[i].onclick = function() {
/* 这里获得鼠标移动到小圆点的位置,用this把index绑定到对象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由于这里的index是自定义属性,需要用到getAttribute()这个DOM2级方法,去获取自定义index的属性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute('index'));
var offset = 600 * (index - clickIndex); //这个index是当前图片停留时的index
animate(offset);
index = clickIndex; //存放鼠标点击后的位置,用于小圆点的正常显示
buttonsShow();
}
})(i)
}
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
play();
}
疑问一:为什么用window.onload?
window.onload = function() {
//是为了方便在图片等必须的加载完以后再执行
}
疑问二:为什么不把功能合在一起呢?
奉行:单一职责
疑问三:为什么要首先获取元素?
window.onload = function() {
var container = document.getElementById('container');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
var buttons = document.getElementById('buttons').getElementsByTagName('span');
var prev = document.getElementById('prev');
var next = document.getElementById('next');
var index = 1;
var timer;
}
获取完元素以后,才可以操作,所以你首先要想好要用到的。
疑问四:为什么那么多功能函数呢,用一个也可以的,不是吗?
window.onload = function() {
function animate(offset) {
//动画
}
function play() {
//开始
}
function stop() {
//结束
}
function buttonsShow() {
//显示按钮(小圆点)
}
}
单一职责,即功能单一,与其它功能不耦合。
function animate(offset) {
//获取的是style.left,是相对左边获取距离,所以第一张图后style.left都为负值,
//且style.left获取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整转化为数字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + 'px';
//无限滚动判断
if (newLeft > -600) {
list.style.left = -3000 + 'px';
}
if (newLeft < -3000) {
list.style.left = -600 + 'px';
}
}
function play() {
//重复执行的定时器
timer = setInterval(function() {
next.onclick();
}, 2000)
}
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
function buttonsShow() {
//将之前的小圆点的样式清除
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == "on") {
buttons[i].className = "";
}
}
//数组从0开始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = "on";
}
疑问五:prev(上),next(下)
prev.onclick = function() {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function() {
//由于上边定时器的作用,index会一直递增下去,我们只有5个小圆点,所以需要做出判断
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1
}
animate(-600);
buttonsShow();
};
点击后图片会向左移或者右移...
疑问四:闭包?
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
(function(i) {
buttons[i].onclick = function() {
/* 这里获得鼠标移动到小圆点的位置,用this把index绑定到对象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由于这里的index是自定义属性,需要用到getAttribute()这个DOM2级方法,去获取自定义index的属性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute('index'));
var offset = 600 * (index - clickIndex); //这个index是当前图片停留时的index
animate(offset);
index = clickIndex; //存放鼠标点击后的位置,用于小圆点的正常显示
buttonsShow();
}
})(i)
}
闭包格式:
(function(i) {
//这里放代码
})(i)
为什么需要闭包?
为了不让代码被全局污染,和普通的代码没有什么区别。
疑问五:container.onmouseover = stop / container.onmouseout = play 什么意思?
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
为了放在图片上,轮播不再继续,暂停在某张图片上。
疑问六:
play();
为什么最后放了一个 play() ,play() 函数如果想要被执行,就必须调用!
优化
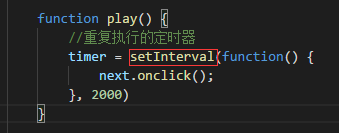
一.
IE9以下可以用 setInterval
IE9以上可以用 requestAnimactionFrame
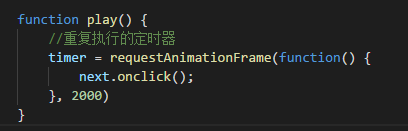
你可以判断浏览器内核再决定用setInterval 或 requestAnimactionFrame !
二.

这里可以修改一下,改成,再添加一个轮播图更简单
三.
这里可以用js改为动态的增加,根据图片的数量
四.
任意图片上传,配合后台或者node进行自动重命名,实现拖入图片自动添加标签以及重命名图片。
之后,大家有什么优化意见以及想法,可以提出来,大家交流交流。
web常见效果之轮播图的更多相关文章
- Web前端JS实现轮播图原理
实现轮播图有很多方式,但是html的结构都是一样的.本文使用了Jquery框架,Dom操作更加方便灵活 html部分: <div class="banner"> < ...
- 移动web——bootstrap响应式轮播图
基本介绍 1.bootstrap有轮播图的模板,我们只需要改动下就行. 2.这里我们将介绍桌面版本和移动版本最后是综合版本 桌面版本 1.这里的图片设置是有窍门的,不再去添加img标签,而是作为a标签 ...
- 首页大屏广告效果 jquery轮播图淡入淡出
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- Jquery基础(动画效果的轮播图特效)
jquery文档准备的三种写法: $(document).ready(function() { }); $().ready(function() { }); $(function() { }); jq ...
- javascript写淡入淡出效果的轮播图
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 微信小程序从零开始开发步骤(五)轮播图
上一章完成页面自定义分享,这一章来说说轮播图,最常见的一个轮播图,中间带小圆点,自动轮播. Swiper是滑动特效插件,面向手机.平板电脑等移动终端.能实现触屏焦点图.触屏Tab切换.触屏多图切换等常 ...
- Jquery 轮播图简易框架
=====================基本结构===================== <div class="carousel" style="width: ...
- 原生js写简单轮播图方式1-从左向右滑动
轮播图就是让图片每隔几秒自动滑动,达到图片轮流播放的效果.轮播图从效果来说有滑动式的也有渐入式的,滑动式的轮播图就是图片从左向右滑入的效果,渐入式的轮播图就是图片根据透明度渐渐显示的效果,这里说的是实 ...
- JavaScript--缓动动画+轮播图
上效果: 实现步骤: 最重要的是运动公式!!! <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8 ...
随机推荐
- RestSharp使用总结
RestSharp是一个轻量的,不依赖任何第三方的组件或者类库的Http的组件.RestSharp具有以下的优点: 1.支持.NET 3.5+,Silverlight 4, Windows Pho ...
- 身为运维的你,怎么掌握python才不会失业
以前,我们都说Python是运维工程师的未来:现在,为什么大家都说不会Python的运维都将失业?运维必须懂开发,特别是python开发,已经形成大家的共识,不懂开发的运维,路会越走越窄. 而现在的情 ...
- JavaScript:在JS中截取字符串的方法
这篇主要说一说截取字符串的方法,用于帮助自己缕清方法的作用,参数的意义,返回值,是否对于原来的字符串进行了操作等. 在javascript中,常见的截取字符串的方法有slice().substring ...
- java 分页导出百万级数据到excel
最近修改了一个导出员工培训课程的历史记录(一年数据),导出功能本来就有的,不过前台做了时间限制(只能选择一个月时间内的),还有一些必选条件, 导出的数据非常有局限性.心想:为什么要做出这么多条件限制呢 ...
- [转载] epoll详解
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/xiajun07061225/article/details/9250579 什么是epoll epoll是什么?按照man手册的说法:是为处理大批量句 ...
- Ant的使用
Ant的使用 什么是Apache Ant Apache Ant是一个基于java的软件构建工具(build tool),理论上它有点类似C/C++的make工具 为什么要用ant? make, gnu ...
- Python之作用域
作用域测试例子: >>> a = 10 >>> def test(): ... a = 20 ... print a ... >>> a 10 & ...
- 69、django之Form组件
本篇导航: 小试牛刀 Form类 常用选择插件 自定义验证规则 初始化数据 Django的Form主要具有一下几大功能: 生成HTML标签 验证用户数据(显示错误信息) HTML Form提交保留上次 ...
- 用CRT查找内存泄漏
引用原文地址 : https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/x98tx3cf.aspx 1. 在program中严格按下面顺序include #define _ ...
- Tomcat:Can't load AMD 64-bit .dll on a IA 32 platform(问题记录)
从报错看,这主要是应为64位-32位不兼容导致的.好在,在报此错的情况下,tomcat还是跑起来了. 具体来说,从网上搜索的一些资料来看,应该是jdk版本与tomcat不一致 .tomcat我的是64 ...
