Gym 100952J&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest J. Polygons Intersection【计算几何求解两个凸多边形的相交面积板子题】
J. Polygons Intersection
We will not waste your time, it is a straightforward problem. Given multiple polygons, calculate the area of their intersection. For simplicity, there will be exactly 2 polygons both of them are convex, given in the counterclockwise order and have non-zero areas. Furthermore, in one polygon a vertex won't be on the sides of the other one. The figure below demonstrates the first test case.
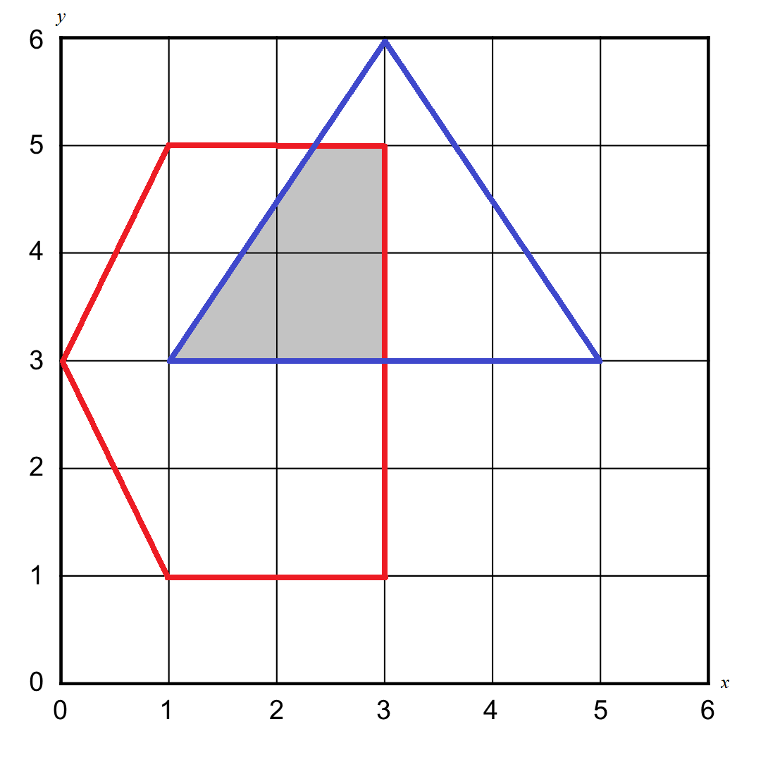
The first line of the input will be a single integer T, the number of test cases (1 ≤ T ≤ 20). each test case contains two integers (3 ≤ N, M ≤ 40) Then a line contains N pairs of integers xi, yi (-1000 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 1000) coordinates of the ith vertex of polygon A, followed by a line contains M pairs of integers xj, yj (-1000 ≤ xj, yj ≤ 1000) coordinates of the jth vertex of polygon B. The coordinates are separated by a single space.
For each test case, print on a single line, a single number representing the area of intersection, rounded to four decimal places.
2
5 3
0 3 1 1 3 1 3 5 1 5
1 3 5 3 3 6
3 3
-1 -1 -2 -1 -1 -2
1 1 2 1 1 2
2.6667
0.0000
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/gym/100952/problem/J
题意:给2个凸多边形,求相交面积
思路:板子题,学习一下!
下面给出AC代码:
#include "iostream"
#include "string.h"
#include "stack"
#include "queue"
#include "string"
#include "vector"
#include "set"
#include "map"
#include "algorithm"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "math.h"
#define ll long long
#define bug(x) cout<<x<<" "<<"UUUUU"<<endl;
#define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define mp(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
using namespace std;
const long long INF = 1e18+1LL;
const int inf = 1e9+1e8;
const int N=1e5+;
#define maxn 510
const double eps=1E-;
int sig(double d){
return(d>eps)-(d<-eps);
}
struct Point{
double x,y; Point(){}
Point(double x,double y):x(x),y(y){}
bool operator==(const Point&p)const{
return sig(x-p.x)==&&sig(y-p.y)==;
}
};
double cross(Point o,Point a,Point b){
return(a.x-o.x)*(b.y-o.y)-(b.x-o.x)*(a.y-o.y);
}
double area(Point* ps,int n){
ps[n]=ps[];
double res=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
res+=ps[i].x*ps[i+].y-ps[i].y*ps[i+].x;
}
return res/2.0;
}
int lineCross(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point&p){
double s1,s2;
s1=cross(a,b,c);
s2=cross(a,b,d);
if(sig(s1)==&&sig(s2)==) return ;
if(sig(s2-s1)==) return ;
p.x=(c.x*s2-d.x*s1)/(s2-s1);
p.y=(c.y*s2-d.y*s1)/(s2-s1);
return ;
}
//多边形切割
//用直线ab切割多边形p,切割后的在向量(a,b)的左侧,并原地保存切割结果
//如果退化为一个点,也会返回去,此时n为1
void polygon_cut(Point*p,int&n,Point a,Point b){
static Point pp[maxn];
int m=;p[n]=p[];
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
if(sig(cross(a,b,p[i]))>) pp[m++]=p[i];
if(sig(cross(a,b,p[i]))!=sig(cross(a,b,p[i+])))
lineCross(a,b,p[i],p[i+],pp[m++]);
}
n=;
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
if(!i||!(pp[i]==pp[i-]))
p[n++]=pp[i];
while(n>&&p[n-]==p[])n--;
}
//---------------华丽的分隔线-----------------//
//返回三角形oab和三角形ocd的有向交面积,o是原点//
double intersectArea(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d){
Point o(,);
int s1=sig(cross(o,a,b));
int s2=sig(cross(o,c,d));
if(s1==||s2==)return 0.0;//退化,面积为0
if(s1==-) swap(a,b);
if(s2==-) swap(c,d);
Point p[]={o,a,b};
int n=;
polygon_cut(p,n,o,c);
polygon_cut(p,n,c,d);
polygon_cut(p,n,d,o);
double res=fabs(area(p,n));
if(s1*s2==-) res=-res;return res;
}
//求两多边形的交面积
double intersectArea(Point*ps1,int n1,Point*ps2,int n2){
if(area(ps1,n1)<) reverse(ps1,ps1+n1);
if(area(ps2,n2)<) reverse(ps2,ps2+n2);
ps1[n1]=ps1[];
ps2[n2]=ps2[];
double res=;
for(int i=;i<n1;i++){
for(int j=;j<n2;j++){
res+=intersectArea(ps1[i],ps1[i+],ps2[j],ps2[j+]);
}
}
return res;//assumeresispositive!
}
//hdu-3060求两个任意简单多边形的并面积
Point ps1[maxn],ps2[maxn];
int n1,n2;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&n1,&n2);
for(int i=;i<n1;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&ps1[i].x,&ps1[i].y);
for(int i=;i<n2;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&ps2[i].x,&ps2[i].y);
double ans=intersectArea(ps1,n1,ps2,n2);
//ans=fabs(area(ps1,n1))+fabs(area(ps2,n2))-ans;//容斥
printf("%.4f\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
Gym 100952J&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest J. Polygons Intersection【计算几何求解两个凸多边形的相交面积板子题】的更多相关文章
- Gym 100952E&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest E. Arrange Teams【DFS+剪枝】
E. Arrange Teams time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standard inp ...
- Gym 100952F&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest F. Contestants Ranking【BFS+STL乱搞(map+vector)+优先队列】
F. Contestants Ranking time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:24 megabytes input:standar ...
- Gym 100952A&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest A. Who is the winner?【字符串,暴力】
A. Who is the winner? time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standard ...
- Gym 100952I&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest I. Mancala【模拟】
I. Mancala time limit per test:3 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input ou ...
- Gym 100952H&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest H. Special Palindrome【dp预处理+矩阵快速幂/打表解法】
H. Special Palindrome time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standard ...
- Gym 100952D&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest D. Time to go back【杨辉三角预处理,组合数,dp】
D. Time to go back time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard i ...
- Gym 100952C&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest C. Palindrome Again !!【字符串,模拟】
C. Palindrome Again !! time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standar ...
- Gym 100952G&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest G. The jar of divisors【简单博弈】
G. The jar of divisors time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standa ...
- Gym 100952B&&2015 HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest B. New Job【模拟】
B. New Job time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:64 megabytes input:standard input outp ...
随机推荐
- Java中 &&与&,||与|的区别
区别 && || 是逻辑运算,支持短路运算 & | 是位运算,不支持短路运算 短路运算 当有多个表达式时,左边的表达式值可以确定结果时,就再继续运算右边的表达式的值; 举例 ...
- 通过 JS 实现简单的拖拽功能并且可以在特定元素上禁止拖拽
前言 关于讲解 JS 的拖拽功能的文章数不胜数,我确实没有必要大费周章再写一篇重复的文章来吸引眼球.本文的重点是讲解如何在某些特定的元素上禁止拖拽.这是我在编写插件时遇到的问题,其实很多插件的拖拽功能 ...
- 669. Trim a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as `L`and `R`, trim the tree so t ...
- ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.2学习笔记[25] 官方第八章Analysis(空间查询)概览与解释
开森,最关注的空间分析章节终于到了,在空间查询那节逻辑性的代码简直要命(呵呵,空间分析的代码也要命...). 上目录截图: [Geodesic buffers(GeometryEngine)] 使用G ...
- bzoj 3653 [湖南集训]谈笑风生
题目描述 设 T 为一棵有根树,我们做如下的定义: • 设 a 和 b 为 T 中的两个不同节点.如果 a 是 b 的祖先,那么称"a 比 b 不知道高明到哪里去了". • 设 a ...
- 了解数组中的队列方法,DOM中节点的一些操作
队列的概念 栈是一种后进先出的结构,而队列是一种先进先出的结构.如银行排队,排在前面的人先办业务然后离开,后来的人站在最后.可以用队列的push()方法插入元素到队列的末尾,可以用shift()方法删 ...
- K:java中正则表达式的使用说明及其举例
从Java1.4起,java核心API就引入了java.util.regex程序包来处理正则表达式,并使用该包下的相关类进行字符串的匹配.搜索.提取.分析结构化内容等工作.需要注意的是,正则表达式本身 ...
- 一个IC软件工程师的2017年终工作总结
相比2016年的波澜起伏,2017多了一份平静和清淡.不过,平静的生活下,总有一颗飞向远方的心. 在这一年将近结束的时候,总结一下自己的工作,生活和学习.也顺便展望一下未来的2018,看看有哪些 美好 ...
- java 集合类基础问题汇总
1.Java集合类框架的基本接口有哪些? 参考答案 集合类接口指定了一组叫做元素的对象.集合类接口的每一种具体的实现类都可以选择以它自己的方式对元素进行保存和排序.有的集合类允许重复的键,有些不允许 ...
- 《深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级属性与最佳实践》读书笔记(更新中)
第一章:走进Java 概述 Java技术体系 Java发展史 Java虚拟机发展史 1996年 JDK1.0,出现Sun Classic VM HotSpot VM, 它是 Sun JDK 和 Ope ...
