linux磁盘管理系列-软RAID的实现
磁盘管理系列
linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html
linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_041_raid.html
linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_042_lvm.html
1 什么是RAID
RAID全称是独立磁盘冗余阵列(Redundant Array of Independent Disks),基本思想是把多个磁盘组合起来,组合一个磁盘阵列组,使得性能大幅提高。
RAID分为几个不同的等级,各个不同的等级均在数据可靠性及读写性能做了不同的权衡。实际工作中根据自己的业务需求选择不同的RAID方案。
2 RAID的实现方式
- 外接式磁盘阵列:通过扩展卡提供适配能力
- 内接式RAID:主板集成RAID控制器安装OS前在BIOS里配置
- 软件RAID:通过OS实现
3 标准的RAID
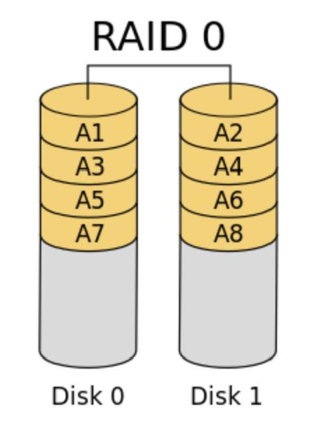
3.1 RAID0
RAID0称为条带化存储,将数据分段存储在各个磁盘中,读写均可以并行处理,因此读写速率为单个磁盘的N倍,没有冗余功能,任何一个磁盘的损坏就会导致的数据不可用。
3.2 RAID1
RADI1是镜像存储,没有数据校验,数据被同等的写入到2个或者多个磁盘中,写入速度相对慢, 但是读取速度比较快。

3.3 RAID 4
RADI4在RAID1的基础上,N个盘用于数据存储,另外加入了1个磁盘作为校验盘。一共N+1个盘,任何一个盘坏掉也不影响数据的访问
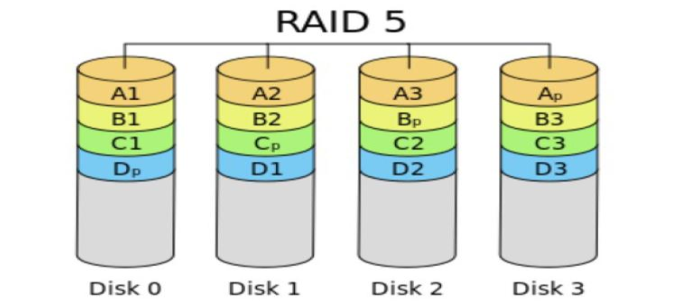
3.4 RAID 5
RAID5在RAID4的基础上,由原来的一个盘来存储校验数据,改为每个盘都有数据和校验信息的。
4 混合RAID
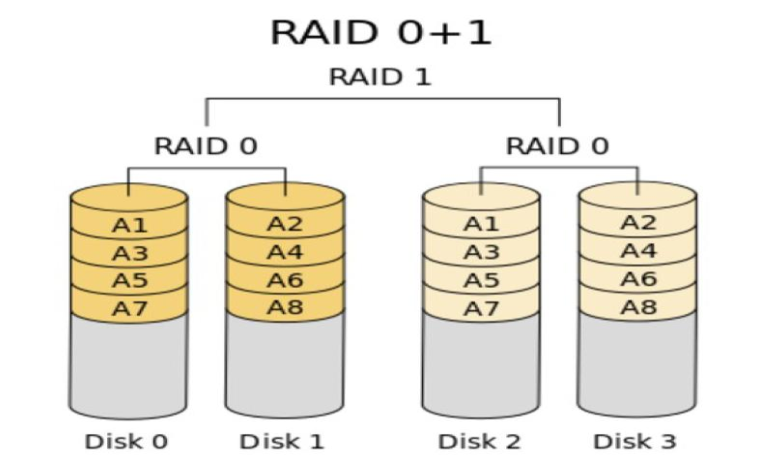
4.1 RAID01
先组成RAID0,然后组成RAID1.
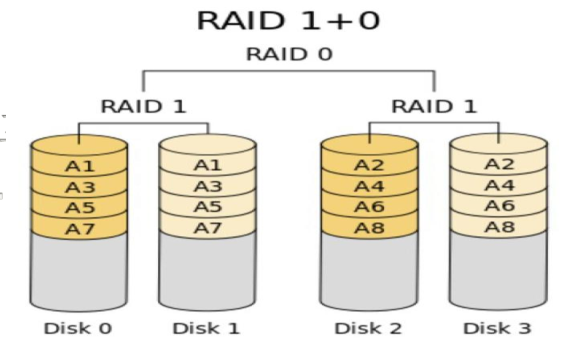
4.2 RAID10
先组成RAID1,然后组成RAID0
5 软RAID的实现
5.1 RAID5的实现
创建由三块硬盘组成的可用空间为2G的RAID5设备,要求其chunk大小为256k,文件系统为ext4,开机可自动挂载至/mydata目录
5.1.1 先看看我们的磁盘情况
[root@centos7 Bash]$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 128G 0 part
├─sda3 8:3 0 48.8G 0 part /
├─sda4 8:4 0 512B 0 part
└─sda5 8:5 0 19.5G 0 part /app
sdb 8:16 0 100G 0 disk
sdc 8:32 0 20G 0 disk
sdd 8:48 0 20G 0 disk
sde 8:64 0 20G 0 disk
sdf 8:80 0 20G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 8.1G 0 rom /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
这里我们使用sdb,sdc,sdd,每个盘创建一个主分区1G,构建RADI5.
5.1.2 根据实际情况分区
[root@centos7 Bash]$ fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x93d380cf. Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary ( primary, extended, free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (-, default ):
First sector (-, default ):
Using default value
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): +1G
Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set Command (m for help): t
Selected partition
Hex code (type L to list all codes): fd
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux raid autodetect' Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 107.4 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x93d380cf Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 fd Linux raid autodetect Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@centos7 Bash]$ fdisk /dev/sdc
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xc56b90d8. Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary ( primary, extended, free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (-, default ):
First sector (-, default ):
Using default value
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): +1G
Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set Command (m for help): t
Selected partition
Hex code (type L to list all codes): fd
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux raid autodetect' Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdc: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc56b90d8 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdc1 fd Linux raid autodetect Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@centos7 Bash]$ fdisk /dev/sdd
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x7e0900d8. Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary ( primary, extended, free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (-, default ):
First sector (-, default ):
Using default value
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): +1G
Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdd: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x7e0900d8 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdd1 Linux Command (m for help): t
Selected partition
Hex code (type L to list all codes): fd
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux raid autodetect' Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
5.1.3 创建raid
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mdadm -C /dev/md5 -a yes -l -n /dev/sd{b1,c1,d1} -c 256 # -C指定创建, -a yes 自动创建设备 , -l 设定level , -n 设定磁盘个数, -c chunk大小
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md5 started.
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mdadm -Ds # 查看信息
ARRAY /dev/md5 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=2c8ae60d:a799fcb7:9008a046:ae6ea430
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mdadm -Ds >/etc/mdadm.conf # 将软raid信息写入到配置文件中去
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mkdir /mnt/md5 # 创建挂载点目录
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mkfs.ext4 /dev/md5 # 创建文件系统
mke2fs 1.42. (-Dec-)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size= (log=)
Fragment size= (log=)
Stride= blocks, Stripe width= blocks
inodes, blocks
blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=
Maximum filesystem blocks=
block groups
blocks per group, fragments per group
inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
, , , ,
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal ( blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
[root@centos7 Bash]$ mount /dev/md5 /mnt/md5 # 挂载设备
[root@centos7 Bash]$ tail -n /etc/mtab
/dev/md5 /mnt/md5 ext4 rw,seclabel,relatime,stripe=,data=ordered 0 # 查看挂载信息
[root@centos7 Bash]$ tail -n /etc/mtab >>/etc/fstab #添加到fstab文件中,确保开机启动,这里建议使用uuid
5.1.4 验证raid
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm -D /dev/md5 #查看详细raid5详细信息,可以发现有3个都是working状态的
/dev/md5:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Dec ::
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : (2046.00 MiB 2145.39 MB)
Used Dev Size : (1023.00 MiB 1072.69 MB)
Raid Devices :
Total Devices :
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Wed Dec ::
State : clean
Active Devices :
Working Devices :
Failed Devices :
Spare Devices : Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 256K Consistency Policy : resync Name : centos7.magedu.com: (local to host centos7.magedu.com)
UUID : 2c8ae60d:a799fcb7:9008a046:ae6ea430
Events : Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
active sync /dev/sdb1
active sync /dev/sdc1
active sync /dev/sdd1
[root@centos7 md5]$ man mdadm
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm /dev/md5 -f /dev/sdc1 # -f 设定指定设备故障, 将/dev/sdc1 这个盘标记失败, 看是否数据能访问,我这里使用-f标记失败,工作中可以根据硬盘指示灯判断磁盘状态
mdadm: set /dev/sdc1 faulty in /dev/md5
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm -D /dev/md5 #在次查看信息,发现工作的是2个, 一个失败的设备
/dev/md5:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Dec ::
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : (2046.00 MiB 2145.39 MB)
Used Dev Size : (1023.00 MiB 1072.69 MB)
Raid Devices :
Total Devices :
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Wed Dec ::
State : clean, degraded # 这里注意了。 我们的一个盘坏掉了。 raid5状态为降级使用了。
Active Devices :
Working Devices :
Failed Devices :
Spare Devices : Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 256K Consistency Policy : resync Name : centos7.magedu.com: (local to host centos7.magedu.com)
UUID : 2c8ae60d:a799fcb7:9008a046:ae6ea430
Events : Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
active sync /dev/sdb1
- removed
active sync /dev/sdd1 - faulty /dev/sdc1
[root@centos7 md5]$ cat a.txt # 发现我们的数据还是能访问的。没有问题。
5.1.5 替换设备
我这里是磁盘坏掉后的执行替换的, 完全可以多一个备用盘, 坏掉自动替换的。
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm /dev/md5 -a /dev/sde1 # 上面我们的sdc1数据损坏,我们需要更换新的磁盘来顶替他的位置。这里添加一个sde1的磁盘, fdisk操作这里省去了。
mdadm: added /dev/sde1
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm -Ds # 查看详细信息
ARRAY /dev/md5 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=2c8ae60d:a799fcb7:9008a046:ae6ea430
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm -D /dev/md5 # 查看详细信息
/dev/md5:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Dec ::
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : (2046.00 MiB 2145.39 MB)
Used Dev Size : (1023.00 MiB 1072.69 MB)
Raid Devices :
Total Devices :
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Wed Dec ::
State : clean # 状态恢复正常了。没有问题
Active Devices :
Working Devices :
Failed Devices :
Spare Devices : Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 256K Consistency Policy : resync Name : centos7.magedu.com: (local to host centos7.magedu.com)
UUID : 2c8ae60d:a799fcb7:9008a046:ae6ea430
Events : Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
active sync /dev/sdb1
active sync /dev/sde1
active sync /dev/sdd1 - faulty /dev/sdc1 # 这个盘是坏掉的,我们已经加入了新的磁盘, 这个盘可以干掉了
[root@centos7 md5]$ man mdadm
[root@centos7 md5]$ mdadm /dev/md5 --remove /dev/sdc1 # 这个盘我们从raid5中移除去。
mdadm: hot removed /dev/sdc1 from /dev/md5
5.1.6扩展raid
我们上面使用的是2+1构成的raid5,磁盘利用率为66%,如果我们想改成3+1 可以执行类似如下命令
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mkadm -G -r /dev/md5 -n -a /dev/sdxx # 这里我就不测试了。使用/dev/sdxx代替一个设备。-G 是Grown增长的意思,-r 是resizefs的意思,
5.1.7 清空raid信息
[root@centos7 mnt]$ umount /dev/md5 # 卸载设备
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -S /dev/md5 # 停止raid5
mdadm: stopped /dev/md5
[root@centos7 mnt]$ sed -i '$d' /etc/fstab # 删除fstab中关于raid5挂载的行
[root@centos7 mnt]$ cat /etc/fstab # 确保fstab没有大问题 #
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Tue Nov ::
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(), findfs(), mount() and/or blkid() for more info
# UUID=59ccea87-3c4e-4bbc-9e2f-3fadb1dcf2e6 / ext4 defaults
UUID=f4e867e8-bcde-43a2-adc7-c80b0948e85f /app ext4 noatime,usrquota,grpquota
UUID=1d6cbe88-ffb4-4adf-bacf-76be1fa75708 /boot ext4 defaults
#UUID=b2c064f5-1ee5-4b5c-9e75-ed41cb99c5aa swap swap defaults
#UUID=a0516c4f-40e6--905a-8b44db12ff7b swap swap defaults,pri=
#/dev/sdb2 /test ext4 rw,seclabel,relatime,data=ordered
#/dev/sdb1 /home xfs rw,seclabel,relatime,attr2,inode64,usrquota,grpquota
[root@centos7 mnt]$ rm -rf /etc/mdadm.conf # 删除raid默认配置文件
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm --zero-superblock /dev/sd{b1,e1,d1,c1} # 清空设置上的超级块信息
5.2 RAID10的实现
raid10 ,6个分区,2个一组raid1,3组raid0
5.2.1 案例分析
分析下,我们创建一个raid10设置,2个设备组成一个raid1,6个设备2个一组可以组成3个raid1, 然后把3个raid1组成一个raid0即可
5.2.2 先创建6个设备
[root@centos7 mnt]$ lsblk # 就是使用fdisk 创建的设备, 具体这里就不写了。 最终使用lsblk显示,我们可以看到sdb1,sdb2,sdd1,sde1一共6个磁盘
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda : 200G disk
├─sda1 : 1G part /boot
├─sda2 : 128G part
├─sda3 : .8G part /
├─sda4 : 512B part
└─sda5 : .5G part /app
sdb : 100G disk
├─sdb1 : 1G part
└─sdb2 : 1G part
sdc : 20G disk
├─sdc1 : 1G part
└─sdc2 : 1G part
sdd : 20G disk
└─sdd1 : 1G part
sde : 20G disk
└─sde1 : 1G part
sdf : 20G disk
sr0 : .1G rom /run/media/root/CentOS x86_64
5.2.3 创建raid
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -C /dev/md11 -a yes -l -n /dev/sd{b1,c1} # 创建第一个raid1
mdadm: /dev/sdb1 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices= ctime=Wed Dec ::
mdadm: Note: this array has metadata at the start and
may not be suitable as a boot device. If you plan to
store '/boot' on this device please ensure that
your boot-loader understands md/v1.x metadata, or use
--metadata=0.90
mdadm: /dev/sdc1 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices= ctime=Wed Dec ::
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md11 started.
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -C /dev/md12 -a yes -l -n /dev/sd{b2,c2} #创建第二个raid1
mdadm: Note: this array has metadata at the start and
may not be suitable as a boot device. If you plan to
store '/boot' on this device please ensure that
your boot-loader understands md/v1.x metadata, or use
--metadata=0.90
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md12 started.
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -C /dev/md13 -a yes -l -n /dev/sd{d1,e1} # 创建第三个raid1
mdadm: /dev/sdd1 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices= ctime=Wed Dec ::
mdadm: Note: this array has metadata at the start and
may not be suitable as a boot device. If you plan to
store '/boot' on this device please ensure that
your boot-loader understands md/v1.x metadata, or use
--metadata=0.90
mdadm: /dev/sde1 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices= ctime=Wed Dec ::
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md13 started.
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -C /dev/md10 -a yes -l -n /dev/md{,,} # 将3个raid1 合并为一个raid0
mdadm: /dev/md11 appears to contain an ext2fs file system
size=2095104K mtime=Wed Dec ::
mdadm: /dev/md13 appears to contain an ext2fs file system
size=2095104K mtime=Wed Dec ::
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md10 started.
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mkfs.ext
mkfs.ext2 mkfs.ext3 mkfs.ext4
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mkfs.ext4 /dev/md10 # 创建文件系统
mke2fs 1.42. (-Dec-)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size= (log=)
Fragment size= (log=)
Stride= blocks, Stripe width= blocks
inodes, blocks
blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=
Maximum filesystem blocks=
block groups
blocks per group, fragments per group
inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
, , , ,
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal ( blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -Ds # 查看配置信息
ARRAY /dev/md11 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=0ce2cd6c:cd21fab6:3e65cfb5:64bd86f3
ARRAY /dev/md12 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=8af31dff:efab06ed:48e2613b:a599c774
ARRAY /dev/md13 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=a8c99d60:2d0c61e7:97a76809:9396c020
ARRAY /dev/md10 metadata=1.2 name=centos7.magedu.com: UUID=50b2fa58:4ce65d67:8c50c853:fa175a28
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -Ds >> /etc/mdadm.conf # 写配置文件到mdadm的配置文件中
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mkdir /mnt/md10 # 创建挂载目录
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mount /dev/md10 /mnt/md10 # 挂载文件系统
[root@centos7 mnt]$ tail -n /etc/mtab # 查看mtab文件中的最后一行, 也就是我们的md10挂载信息
/dev/md10 /mnt/md10 ext4 rw,seclabel,relatime,stripe=,data=ordered
[root@centos7 mnt]$ tail -n /etc/mtab >> /etc/fstab #添加到开机启动
5.2.4 raid 清除工作
[root@centos7 mnt]$ umount /dev/md10 # 取消挂载
[root@centos7 mnt]$ rm -rf /etc/mdadm.conf # 删除mdadm的默认配置
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -S /dev/md10 # 停止raid0设置
mdadm: stopped /dev/md10
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -S /dev/md11 # 停止raid1设置
mdadm: stopped /dev/md11
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -S /dev/md12 # 停止radi1 设置
mdadm: stopped /dev/md12
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -S /dev/md13 # 停止raid 1 设置
mdadm: stopped /dev/md13
[root@centos7 mnt]$ sed -i '$d' /etc/fstab # 删除fstab的挂载
[root@centos7 mnt]$ cat /etc/fstab # 确保正确 #
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Tue Nov ::
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(), findfs(), mount() and/or blkid() for more info
# UUID=59ccea87-3c4e-4bbc-9e2f-3fadb1dcf2e6 / ext4 defaults
UUID=f4e867e8-bcde-43a2-adc7-c80b0948e85f /app ext4 noatime,usrquota,grpquota
UUID=1d6cbe88-ffb4-4adf-bacf-76be1fa75708 /boot ext4 defaults
#UUID=b2c064f5-1ee5-4b5c-9e75-ed41cb99c5aa swap swap defaults
#UUID=a0516c4f-40e6--905a-8b44db12ff7b swap swap defaults,pri=
#/dev/sdb2 /test ext4 rw,seclabel,relatime,data=ordered
#/dev/sdb1 /home xfs rw,seclabel,relatime,attr2,inode64,usrquota,grpquota
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm -D # 再次查看下mdadm信息,确保没有了
mdadm: No devices given.
[root@centos7 mnt]$ mdadm --zero-superblock /dev/sd{b1,b2,c1,c2,d1,e1} # 请求md的元数据信息
6 参考
博客参考:http://blog.jobbole.com/83808/
wiki参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAID
linux磁盘管理系列-软RAID的实现的更多相关文章
- linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- linux磁盘管理系列-LVM的使用
LVM是什么 LVM是Linux操作系统的逻辑卷管理器. 现在有两个Linux版本的LVM,分别是 LVM1,LVM2.LVM1是一种已经被认为稳定了几年的成熟产品,LVM2 是最新最好的LVM版本. ...
- linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- Linux磁盘管理系列 — LVM和RAID
一.逻辑卷管理器(LVM) 1.什么是逻辑卷管理器(LVM) LVM是逻辑盘卷管理(Logical Volume Manager)的简称,它是Linux环境下对卷进行操作的抽象层. LVM是建立在硬盘 ...
- 每天进步一点点——Linux磁盘管理LVM与RAID
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/cywosp/article/details/38965799 1. 传统磁盘管理问题 当分区大小不够用时无法扩展其大小,仅仅能通过加入硬盘. ...
- Linux磁盘管理系列 — 磁盘配额管理
一.磁盘管理的概念 Linux系统是多用户任务操作系统,在使用系统时,会出现多用户共同使用一个磁盘的情况,如果其中少数几个用户占用了大量的磁盘空间,势必压缩其他用户的磁盘的空间和使用权限.因此,系统管 ...
- Linux磁盘管理,vi编辑器以及包管理器
一.Linux磁盘管理 Linux磁盘管理常用的三个命令为df,du,fdisk df:列出文件系统的整体磁盘使用量,利用这个命令来获取磁盘被占用了多少空间,,目前还剩下多少空间用法:df [-ahi ...
- Linux学习之十九-Linux磁盘管理
Linux磁盘管理 1.相关知识 磁盘,是计算机硬件中不可或缺的部分磁盘,是计算机的外部存储器中类似磁带的装置,将圆形的磁性盘片装在一个方的密封盒子里,这样做的目的是为了防止磁盘表面划伤,导致数据丢失 ...
随机推荐
- LINUX 笔记-crontab命令
用户所建立的crontab文件中,每一行都代表一项任务,每行的每个字段代表一项设置,它的格式共分为六个字段,前五段是时间设定段,第六段是要执行的命令段,格式如下: minute hour da ...
- Python连接SQLite数据库
SQLite作为一款轻型数据库,管理工具有很多,比如SQLite Expert Professional,很适合用来存储Python网站,爬虫的相关数据,下面列出基本的增删查改操作 读取操作: con ...
- IDEA-最简单的struts2项目 关于lib项目的默认位置
文件结构 struts.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts ...
- Linux中的各种软件安装
Linux下的软件形式 Linux上的软件有几种常见的方式 二进制发布包 软件包已经针对具体平台完成了编译和打包,解压后即可以使用,最多去改改配置文件,也是Linux上最通用和常见的软件包发布形式 例 ...
- C++流类库(11)
C++的流类库由几个进行I/O操作的基础类和几个支持特定种类的源和目标的I/O操作的类组成. 流类库的基础类 ios类是isrream类和ostream类的虚基类,用来提供对流进行格式化I/O操作和错 ...
- 使用原生php读写excel文件
最近在工作中遇到一个需求,需要将数据库中的数据导出到excel文件中,并下载excel文件.因为以前没做过,所以就百度了一下, 网上说的大多是使用PHPExcel类来操作excel文件,这还要去下载这 ...
- LeetCode 268. Missing Number (缺失的数字)
Given an array containing n distinct numbers taken from 0, 1, 2, ..., n, find the one that is missin ...
- Charles从入门到放弃
Charles版本:4.0.2 一.开始 连接方式 方法一:电脑和手机连接同一个wifi 方法二:电脑使用网线连接网络,手机通过USB连接电脑 二.过滤网络请求 1.简单过滤 在Sequence模式下 ...
- Python迭代
本篇将介绍Python的迭代,更多内容请参考:Python学习指南 简介 在Python中,如果给定一个list或者tuple,我们可以通过for循环来遍历这个list或者tuple,这种遍历我们称为 ...
- Leetcode题解(32)
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II 题目 直接代码: /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct ...
