动手学Transformer
动手实现Transformer,所有代码基于tensorflow2.0,配合illustrated-transformer更香。
- 模型架构
- Encoder+Decoder
- Encoder
- Decoder
- Attention
- Add&Norm
- FeedForward
- Embedding
- Position Encoding
- Encoder+Decoder
模型架构
transformer使用经典的编码器-解码器框架,编码器接受一个输入序列 \((x_1,…,x_n)\),经过Embedding转化为词向量,和位置编码相加作为Encoder的输入,在一顿操作后输入被映射到\(z=(z_1,…,z_n)\),Decoder基于\(z\)在一顿操作后生成输出序列\((y_1,…,y_m)\)。
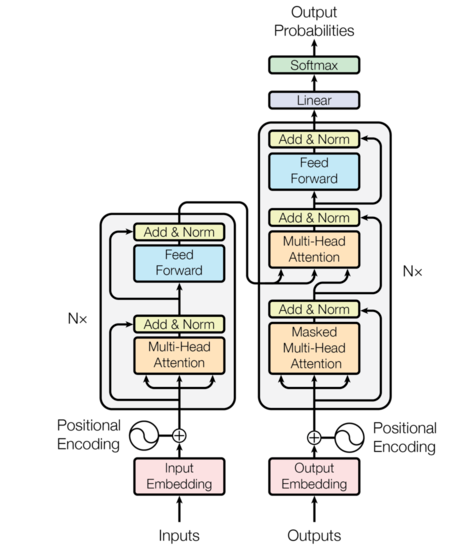
看图说话
- 左边是Encoder,输入为词ID序列,对应形状\([batch\ size,max\ input\ sentense\ length]\),如果embedding维度设置为512,输出形状为\([batch\ size, max\ input\ sentence\ length, 512]\),\(Nx\)表示将Encoder模块堆叠\(N\)次(论文中\(N=6\))
- 右边是Decoder,训练阶段,Decoder输入包括目标句子的词ID序列和最后一个Encoder部分的输出,测试阶段,Decoder的输入为上一次输出的词。Decoder同样被堆叠\(N\)次,最后一个Encoder的输出被接到每一个Decoder块的输入。Decoder输出下一个词的概率,输出形状为\([batch\ size, max\ output\ sentence\ length, \ vocabulary\ length])\) 。
我们先盖房子在装修
class Transformer(tf.keras.Model):
'''
Transformer架构,Encoder-Decoder;softmax
params:
num_layers:堆叠层数
dim_model:embedding 维度
num_heads:multihead attention
dim_ff:FeedForWard 维度
input_vocab_size:输入词典大小
target_vocab_size:输出词典大小
rate:dropout rate
'''
def __init__(self,num_layers, dim_model, num_heads, dim_ff, input_vocab_size,target_vocab_size, rate=0.1):
super(Transformer, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(num_layers, dim_model, num_heads,dim_ff, input_vocab_size, rate)#Encoder
self.decoder = Decoder(num_layers, dim_model, num_heads,dim_ff, target_vocab_size, rate)#Decoder
self.output_layer = tf.keras.layers.Dense(target_vocab_size)
def call(self, inputs, targets, training, enc_padding_mask, look_ahead_mask, dec_padding_mask):
encoder_output = self.encoder(inputs, training, enc_padding_mask) # (batch_size, inputs_seq_len, d_model)
decoder_output, attention_weights = self.decoder(targets, encoder_output, training, look_ahead_mask, dec_padding_mask)
output = self.output_layer(decoder_output) # (batch_size, tar_seq_len, target_vocab_size)
return output, attention_weights
- Encoder

Encoder接受输入token的embedding和位置编码,经过N次Encoder layer 堆叠,代码如下所示
class Encoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Encoder 部分,input embedding ;Encoder layer stack
'''
def __init__(self, num_layers, dim_model, num_heads,dim_ff, input_vocab_size, rate=0.1):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.dim_model = dim_model
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(input_vocab_size, self.dim_model)#输入Embedding
self.pos_encoding = positional_encoding(input_vocab_size, self.dim_model)#位置编码
self.enc_layers = [EncoderLayer(dim_model, num_heads, dim_ff, rate) for _ in range(num_layers)]#创建Encoder layer
self.dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
def call(self, x, training, mask):
seq_len = tf.shape(x)[1]
# adding embedding and position encoding.
x = self.embedding(x) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, dim_model)
# x *= tf.math.sqrt(tf.cast(self.dim_model, tf.float32))
x += self.pos_encoding[:, :seq_len, :]
x = self.dropout(x, training=training)
for layer in self.enc_layers:
x = layer(x, training, mask)
return x # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
单个Encoder layer 有两个子层: attention层和point wise feed forward network.
class EncoderLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Encoder layer:
multihead attention;add&layer norm;FeedForward;add&layer norm
'''
def __init__(self, dim_model, num_heads, dim_ff, rate=0.1):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.mha = MultiHeadAttention(dim_model, num_heads)
self.ffn = point_wise_feed_forward_network(dim_model, dim_ff)
self.layernorm1 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.layernorm2 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.dropout1 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
self.dropout2 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
def call(self, x, training, mask):
attn_output, _ = self.mha(x, x, x, mask) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
attn_output = self.dropout1(attn_output, training=training)
out1 = self.layernorm1(x + attn_output) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
ffn_output = self.ffn(out1) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
ffn_output = self.dropout2(ffn_output, training=training)
out2 = self.layernorm2(out1 + ffn_output) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
return out2
- Decoder
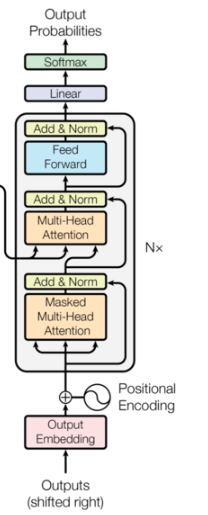
Decoder和Encoder类似,由N个Decoder layer 堆叠而成, 接受输入有三部分:token embedding、位置编码、 最后一个Encoder的输出
class Decoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Decoder 部分:
input embedding;Decoder layer stack;
'''
def __init__(self,num_layers,dim_model, num_heads, dim_ff, target_vocab_size, rate=0.1):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.dim_model = dim_model
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(target_vocab_size, self.dim_model)
self.pos_encoding = positional_encoding(target_vocab_size, self.dim_model)
self.dec_layers = [DecoderLayer(dim_model, num_heads, dim_ff, rate) for _ in range(num_layers)]#创建Decoder layer
self.dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
def call(self,x,enc_output,training,look_ahead_mask,padding_mask):
seq_len = tf.shape(x)[1]
attention_weights = {}
x = self.embedding(x)# (batch_size, target_seq_len, d_model)
x += self.pos_encoding[:,:seq_len,:]
for i,layer in enumerate(self.dec_layers):
x,block1,block2 = layer(x,enc_output,training,look_ahead_mask, padding_mask)
attention_weights['decoder_layer{}_block1'.format(i+1)] = block1
attention_weights['decoder_layer{}_block2'.format(i+1)] = block2
# x.shape == (batch_size, target_seq_len, d_model)
return x, attention_weights
单个Decoder层有三个子层:masked attention层、attention层和point wise feed forward network. masked attention层会掩盖掉序列中还没看到的位置,attention层以target token 为query,Encoder输出为 key和value
class DecoderLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Decoder layer:
masked multihead attention;add&norm;multihead attention;add&norm;FeedForward;add&norm
'''
def __init__(self, dim_model, num_heads,dim_ff,rate=0.1):
super(DecoderLayer,self).__init__()
self.mask_mha = MultiHeadAttention(dim_model, num_heads)
self.mha = MultiHeadAttention(dim_model, num_heads)
self.ffn = point_wise_feed_forward_network(dim_model, dim_ff)
self.layernorm1 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.layernorm2 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.layernorm3 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.dropout1 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
self.dropout2 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
self.dropout3 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate)
def call(self,x,enc_output, training, look_ahead_mask, padding_mask):
#masked multi-head attention
mask_attn_output, attn_weights_block1 = self.mask_mha(x,x,x,look_ahead_mask)
mask_attn_output = self.dropout1(mask_attn_output,training)
out1 = self.layernorm1(x + mask_attn_output)
#multi-head attention
attn_output,attn_weights_block2 = self.mha(out1,enc_output,enc_output,padding_mask)
attn_ouput = self.dropout2(attn_output, training=training)
out2 = self.layernorm2(attn_output + out1) # (batch_size, target_seq_len, d_model)
# feed-forward
ffn_output = self.ffn(out2) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
ffn_output = self.dropout2(ffn_output, training=training)
out3 = self.layernorm3(out1 + ffn_output) # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
return out3, attn_weights_block1, attn_weights_block2
- Attention
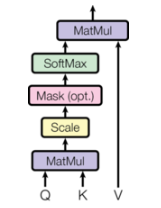
点积attention
\]
def Attention(query,key,value,mask=None):
qk = tf.matmul(query,key,transpose_b=True)#对key进行转置
dk = tf.cast(tf.shape(key)[-1],tf.float32)
scale = qk / tf.math.sqrt(dk)
if mask is not None:
scale = scale + (mask*1e-9)#le-9接近于负无穷,对应softmax输出就为0
score = tf.nn.softmax(scale,axis=-1)
output = tf.matmul(score,value)
return output,score
- Multihead attention
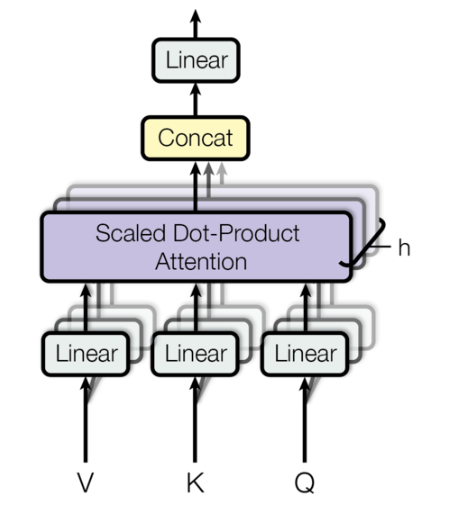
将输入划分为多个head,对应维度变化\((batch\_size,seq\_len,dim\_model) \rightarrow (batch\_size,head,seq\_len,d_k)\), 每个head操作不变,将多个head结果拼接经过权重矩阵\(W^O\)输出
where ~~~~~~ head_i=Attention(QW^Q_i,KW^K_i,VW^V_i)
\]
class MultiHeadAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Multihead attention
'''
def __init__(self,dim_model,num_heads):
super(MultiHeadAttention,self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.dim_model = dim_model
assert dim_model%self.num_heads == 0
self.d_k = dim_model//num_heads
self.wq = tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_model)
self.wk = tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_model)
self.wv = tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_model)
self.wo = tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_model)
def split_heads(self,x,batch_size):
#split 输入到多个head,(batch_size,seq_len,dim_model)->(batch_size,head,seq_len,self.d_k)
x = tf.reshape(x,(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.d_k))
return tf.transpose(x,perm=[0,2,1,3])#重排输出维度
def call(self,q,k,v,mask):
batch_size = tf.shape(q)[0]
q = self.wq(q) # (batch_size, seq_len, dim_model)
k = self.wk(k)
v = self.wv(v)
q = self.split_heads(q, batch_size) # (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len_q, d_k)
k = self.split_heads(k, batch_size)
v = self.split_heads(v, batch_size)
attention,attention_weights = Attention(q,k,v,mask)
attention = tf.transpose(attention,perm=[0,2,1,3])
concat_attention = tf.reshape(attention,(batch_size,-1,self.dim_model))
return self.wo(concat_attention),attention_weights
- Masking
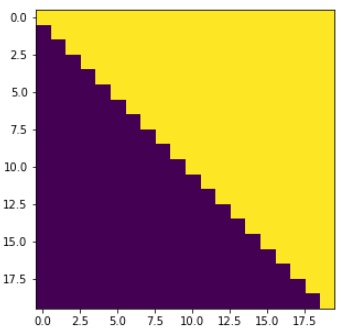
在解码时,为了保证预测当前词不会看到后面的词,需要将后面的词掩码掉。如下图所示,上三角元素为1,表示该位置需要被mask
#mask掉后面的词,保证预测前面词时看不到后面的
def look_ahead_mask(size):
"Mask out subsequent positions."
mask = tf.linalg.band_part(tf.ones((size, size)), 0, -1)#保留上三角,1表示需要被mask
return mask
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5))
plt.imshow(look_ahead_mask(20))
None
#序列填充mask,对padding位置输出1表示被填充
def padding_mask(seq):
seq = tf.cast(tf.math.equal(seq, 0), tf.float32)
# add extra dimensions so that we can add the padding
# to the attention logits.
return seq[:, tf.newaxis, tf.newaxis, :] # (batch_size, 1, 1, seq_len)
- Feed-Forward network
接在attention子层后面,用于增强非线性表示能力
\]
def point_wise_feed_forward_network(dim_model, dim_ff):
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_ff, activation='relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(dim_model))
return model
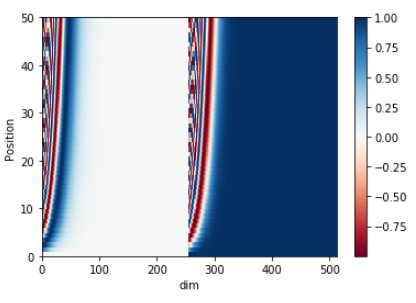
- position encoding
位置编码是影响Transformer长文本建模的主要因素,由于input embedding 中不包含词的位置信息,需要加入位置编码表示词在句子中的位置信息。
为了表示词的绝对位置信息和相对位置信息,本文中使用了正余弦函数
\]
其中 \(pos\) 表示位置,\(i\) 表示维度,关于为什么使用正余弦作为位置编码,可以参考这里。
def positional_encoding(maxlen,dim_model):
position = np.arange(0, maxlen)[:,np.newaxis]
div = np.array([1/np.power(10000.0,((2*i)/dim_model)) for i in range(dim_model)])[np.newaxis,:]
# div = np.exp(np.arange(0, dim_model, 2) * -(np.log(10000.0) / dim_model))
sine = np.sin(position*div[:,0::2])
cons = np.cos(position*div[:,1::2])
pos_encoding = np.concatenate([sine,cons], axis=-1)[np.newaxis, :]
return tf.cast(pos_encoding, dtype=tf.float32)
pos_encoding = positional_encoding(50, 512)
print (pos_encoding.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(pos_encoding[0], cmap='RdBu')
plt.xlabel('dim')
plt.xlim((0, 512))
plt.ylabel('Position')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
transformer的基本概念就先学到这里了
reference:
Illustrated-transformer. https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-transformer/
Transformer_implementation_and_application. https://github.com/yuanxiaosc/Transformer_implementation_and_application
The Annotated Transformer. http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html#full-model
动手学Transformer的更多相关文章
- 对比《动手学深度学习》 PDF代码+《神经网络与深度学习 》PDF
随着AlphaGo与李世石大战的落幕,人工智能成为话题焦点.AlphaGo背后的工作原理"深度学习"也跳入大众的视野.什么是深度学习,什么是神经网络,为何一段程序在精密的围棋大赛中 ...
- 【动手学深度学习】Jupyter notebook中 import mxnet出错
问题描述 打开d2l-zh目录,使用jupyter notebook打开文件运行,import mxnet 出现无法导入mxnet模块的问题, 但是命令行运行是可以导入mxnet模块的. 原因: 激活 ...
- 小白学习之pytorch框架(2)-动手学深度学习(begin-random.shuffle()、torch.index_select()、nn.Module、nn.Sequential())
在这向大家推荐一本书-花书-动手学深度学习pytorch版,原书用的深度学习框架是MXNet,这个框架经过Gluon重新再封装,使用风格非常接近pytorch,但是由于pytorch越来越火,个人又比 ...
- 动手学TCP——CS144实验感想
在Stanford CS144的课程实验Lab0~Lab4中,我们动手实现了一个自己的TCP协议,并且能够真的与互联网通信!此外,感谢Stanford开源本实验并提供了大量的优质测试用例,使得我们仅仅 ...
- 动手学深度学习17-kaggle竞赛实践小项目房价预测
kaggle竞赛 获取和读取数据集 数据预处理 找出所有数值型的特征,然后标准化 处理离散值特征 转化为DNArray后续训练 训练模型 k折交叉验证 预测样本,并提交结果 kaggle竞赛 本节将动 ...
- 动手学深度学习4-线性回归的pytorch简洁实现
导入同样导入之前的包或者模块 生成数据集 通过pytorch读取数据 定义模型 初始化模型 定义损失函数 定义优化算法 训练模型 小结 本节利用pytorch中的模块,生成一个更加简洁的代码来实现同样 ...
- 动手学servlet(六) 过滤器和监听器
过滤器(Filter) 过滤器是在客户端和请求资源之间,起一个过滤的作用,举个例子,比如我们要请求admin文件夹下的index.jsp这个页面,那么我们可以用一个过滤器,判断登录用户是不是管理员 ...
- 动手学servlet(五) 共享变量
1. 无论对象的作用域如何,设置和读取共享变量的方法是一致的 -setAttribute("varName",obj); -getAttribute("varName&q ...
- 动手学servlet(四) cookie和session
Cookie cookie是保存在客户端的一个“键值对”,用来存储用户的一些信息 cookie的应用: -在电子商务会话中标识用户 -对网站进行定制,比如你经常浏览哪些内容,就展示哪些页面给你 - ...
随机推荐
- Java并发编程之CAS二源码追根溯源
Java并发编程之CAS二源码追根溯源 在上一篇文章中,我们知道了什么是CAS以及CAS的执行流程,在本篇文章中,我们将跟着源码一步一步的查看CAS最底层实现原理. 本篇是<凯哥(凯哥Java: ...
- Symantec(赛门铁克)非受管检测
为了查找局域网内没有安装赛门铁克客户端的IP,采用Symantec Endpoint Protect Manager 的非受管检测机制进行网段扫描. 非受管检测机制的原理是:每台电脑开机时都会向同网段 ...
- 洛谷 P5176 公约数 题解
原题链接 我天哪 大大的庆祝一下: 数论黑题 \(T1\) 达成! 激动地不行 记住套路:乱推 \(\gcd\),欧拉筛模板,然后乱换元,乱换式子,完了整除分块,欧拉筛和前缀和就解决了! \[\sum ...
- 「面试指南」JS数组Array常用算法,Array算法的一般解答思路
先看一道面试题 在 LeetCode 中有这么一道简单的数组算法题: // 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target, // 请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那两个整数,并返回他们的数组下 ...
- 原 c++中map与unordered_map的区别
c++中map与unordered_map的区别 头文件 map: #include < map > unordered_map: #include < unordered_map ...
- dyld
一.介绍 在 MacOS 和 iOS 上,可执行程序的启动依赖于 xnu 内核进程运作和动态链接加载器 dyld. dyld 全称 the dynamic link editor,即动态链接器,其本质 ...
- mongodb服务器启动
以配置文件启动服务器: mongod --config /usr/local/mongodata/config/mongodb.conf(配置文件路径) 客户端启动: mango 关闭mongodb的 ...
- 【3D】PoseCNN姿态检测网络复现过程记录
最近在研究室内6D姿态检测相关问题,计划在PoseCNN网络基础上进行改进实现.但是在第一步的复现过程中踩了无数的坑,最终成功运行了demo,但目前数据集train还是遇到了一些问题.有问题欢迎一起交 ...
- python基础学习-字符串常见操作
字符串常见操作 索引 s = "abcdefg" # 字符串数据,切片后取出的数据都是字符串类型 # 从左至右取值:从0开始 # 从右向左取值:从-1开始 print(" ...
- 【cs224w】Lecture 6 - 消息传递 及 节点分类
目录 Node Classification Probabilistic Relational Classifier Iterative Classification Belief Propagati ...
