Data Flow Diagram with Examples - Customer Service System
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) provides a visual representation of the flow of information (i.e. data) within a system. By creating a Data Flow Diagram, you can tell the information provided by and delivered to someone who takes part in system processes, the information needed in order to complete the processes and the information needed to be stored and accessed. Data Flow Diagram is widely-used in software engineering. You can use DFD in modeling information systems. This article describes and explain Data Flow Diagram (DFD) by using a customer service system as an example.
The CS System Example
The data flow diagram is a hierarchy of diagram consist of:
- Context Diagram (conceptually level zero)
- The Level-1 DFD
- And possible Level-2 DFD and further levels of functional decomposition depending on the complexity of your system
Context DFD
The figure below shows a context Data Flow Diagram that is drawn for a railway company's Customer Service System. It contains a process (shape) that represents the system to model, in this case, the "CS System". It also shows the participants who will interact with the system, called the external entities. In this example, CS Assistant and Passenger are the two entities who will interact with the system. In between the process and the external entities, there are data flow (connectors) that indicate the existence of information exchange between the entities and the system.
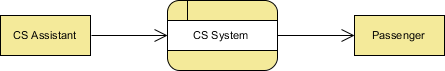
Context DFD is the entrance of a data flow model. It contains one and only one process and does not show any data store.
Level 1 DFD
The figure below shows the level 1 DFD, which is the decomposition (i.e. break down) of the CS System process shown in the context DFD. Read through the diagram and then we will introduce some of the key concepts based
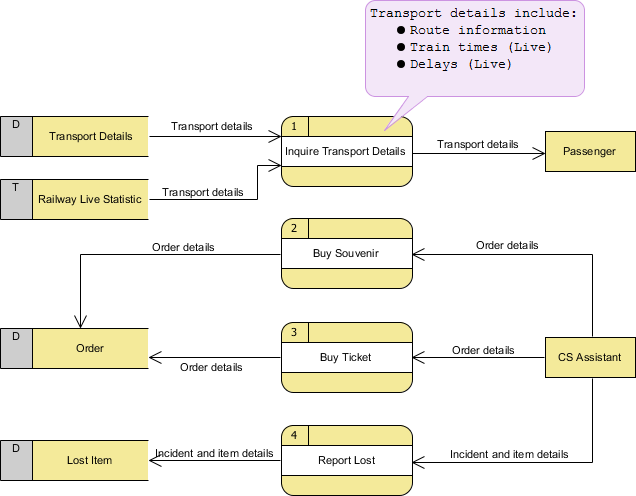
The CS System Data Flow Diagram example contains four processes, two external entities and four data stores. Although there is no design guidelines that governs the positioning of shapes in a Data Flow Diagram, we tend to put the processes in the middle and data stores and external entities on the sides to make it easier to comprehend.
Based on the diagram, we know that a Passenger can receive Transport details from the Inquiry Transport Details process, and the details are provided by the data stores Transport Details and Railway Live Statistic. While data stored in Transport Details are persistent data (indicated by the label "D"), data stored in Railway Live Statistic are transient data that are held for a short time (indicated by the label "T"). A callout shape is used to list out the kind of details that can be inquired by passenger.
CS Assistant can initiate the Buy Souvenir process, which will result in having the Order details stored in the Order data store. Although customer is the real person who buy souvenir, it is the CS Assistant who accesses the system for storing the order details. Therefore, we make the data flow from CS Assistant to the Buy Souvenir process.
CS Assistant can also initiate the Buy Ticket process by providing Order details and the details will be stored again in the Order data store. Data Flow Diagram is a high level diagram that is drawn with a high degree of abstraction. The data store Order which is drawn here does not necessarily imply a real order database or order table in a database. The way how order details are stored physically is to be decided later on when implementing the system.
Finally, CS Assistant can initiate the Report Lost process by providing the Incident and item details and the information will be stored in the Lost Item database.
Data Flow Diagram Tips and Cautions
Stating the type of data with D, M and T
Each data store which is drawn in a Data Flow Diagram are prefixed by a letter, which is 'D' by default. The letter indicates the kind of data the data store holds. The letter 'D' is used to represent a persistent computerized data, which is probably the most common kind of data type in a typical information system. Besides computerized data, data can also be held for a short time in temporary. We call this kind of data transient data and is represented by letter 'T'. Sometimes, data is stored without the use of a computer. We call this kind of data manual data and is represented by letter 'M'. Finally, if the data is stored without using computer and also is held for a short time, this is known as manual transient data and is represented by T(M).
Be aware of the level of details
In this Data Flow Diagram example, the word "details" is used many times when labeling data. We have "transport details" and "order details". What if we write them explicitly as "route information, train times and delays", "souvenir name, quantity and amount" and "ticket type and amount"? Is this correct? Well, there is no definite answer to this question but try to ask yourself a question when making a decision. Why are you drawing a DFD?
In most cases, Data Flow Diagram is drawn in the early phase of system development, where many details are yet to be confirmed. The use of general terminologies like "details", "information", "credential" certainly leave room for discussion. However, using general terms can be kind of lacking details and make the design lost its usefulness. So it really depends on the purpose of your design.
Don't overdrawn
In a Data Flow Diagram, we focus on the interactions between the system and external parties, rather than the internal communications among interfaces. Therefore, data flows between interfaces and the data stores used are considered to be out of scope and should not be shown in the diagram.
Don't mix up data flow and process flow
Some designers may feel uncomfortable when coming across a connector connecting from a data store to a process, without showing the step of data request being specified on the diagram. Some designers will attempt to put a request attached to the connector between a process and a data store, labeling it "a request" or "request for something", which is surely unnecessary.
Keep in mind that Data Flow Diagram was designed for representing the exchange of information. Connectors in a Data Flow Diagram are for representing data, not for representing process flow, step or anything else. When we label a data flow that ends at a data store "a request", this literally means we are passing a request as data into a data store. Although this may be the case in implementation level as some of the DBMS do support the use of functions, which intake some values as parameters and return a result, however, in data flow diagram, we tend to treat data store as a sole data holder that does not possess any processing capability. If you want to model the system flow or process flow, you could use either Activity Diagram or BPMN Business Process Diagram instead. If you want to model the internal structure of data store, you may use Entity Relationship Diagram.
Data Flow Diagram with Examples - Customer Service System的更多相关文章
- 数据可视化 —— 数据流图(Data Flow Diagram)
数据流图(Data Flow Diagram):简称 DFD,它从数据传递和加工角度,以图形方式来表达系统的逻辑功能.数据在系统内部的逻辑流向和逻辑变换过程,是结构化系统分析方法的主要表达工具及用于表 ...
- react & redux data flow diagram
react & redux data flow diagram Redux 数据流程图
- SSIS Data Flow 的 Execution Tree 和 Data Pipeline
一,Execution Tree 执行树是数据流组件(转换和适配器)基于同步关系所建立的逻辑分组,每一个分组都是一个执行树的开始和结束,也可以将执行树理解为一个缓冲区的开始和结束,即缓冲区的整个生命周 ...
- Intel® Threading Building Blocks (Intel® TBB) Developer Guide 中文 Parallelizing Data Flow and Dependence Graphs并行化data flow和依赖图
https://www.threadingbuildingblocks.org/docs/help/index.htm Parallelizing Data Flow and Dependency G ...
- Data Flow ->> Script Component
和Control Flow中的Script Task非常类似,不同的是Script Component是Per-Row的执行类型.打个比方,在Script Component中加入两个Output的字 ...
- Spring Cloud Data Flow 中的 ETL
Spring Cloud Data Flow 中的 ETL 影宸风洛 程序猿DD 今天 来源:SpringForAll社区 1 概述 Spring Cloud Data Flow是一个用于构建实时数据 ...
- 【SFA官方译文】:Spring Cloud Data Flow中的ETL
原创: 影宸风洛 SpringForAll社区 昨天 原文链接:https://www.baeldung.com/spring-cloud-data-flow-etl 作者:Norberto Ritz ...
- (转)CAS (4) —— CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example)
CAS (4) —— CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example) tomcat版本: tomcat-8.0.29 jdk版本: jdk1.8.0 ...
- SSIS ->> Data Flow Design And Tuning
Requirements: Source and destination system impact Processing time windows and performance Destinati ...
随机推荐
- JQuery主要内容
一.什么是JQuery jquery全称javaScript Query,是js的一个框架,本质上仍然是js 二.jQuery的特点 支持各种主流浏览器 使用特别简单 拥有丰富的插件和边界的插件扩展机 ...
- ovirt 重新安装主机失败
重新安装主机引擎事件报错 Host engine installation failed. Failed to execute Ansible host-deploy role. Please che ...
- C 电压
时间限制 : 10000 MS 空间限制 : - KB 评测说明 : 1s,256m 问题描述 JOI社的某个实验室中有着复杂的电路.电路由n个节点和m根细长的电阻组成.节点被标号为1~N ...
- Java 添加、读取和删除 Excel 批注
批注是一种富文本注释,常用于为指定的Excel单元格添加提示或附加信息. Free Spire.XLS for Java 为开发人员免费提供了在Java应用程序中对Excel文件添加和操作批注的功能. ...
- IDEA运行报错 Error:java: 错误: 不支持发行版本 xx
解决方案 修改项目配置,进入Project Setting,截图可参考下面的截图 1.修改全局设置 修改Project->Project Language Level->选择版本比当前jd ...
- App 性能测试分享
在本文内,主要以Android性能测试为主进行分析 一.性能测试包含 1.启动时间测试 测试场景包括 - - - 首次安装启动时间.冷启动.热启动测试 2.页面响应时间: 用户从点击一个控件, ...
- MariaDB使用数据库查询《三》
MariaDB使用数据库查询 案例5:使用数据库查询 5.1 问题 本例要求配 ...
- 面试刷题37:微服务是什么?springcloud,springboot是什么?
面试中被问到为什么要使用微服务架构?springcloud的核心组件有哪些? 拿我们国家的兵种来说,如何把战争这个单体架构微服务化,就是根据适用的场景,拆分出不同的兵种(微服务) 然后每个兵种之间通过 ...
- Java通过Http请求服务器
Java通过Http请求服务器图片输出.下载.转换 Java开发过程中总会遇到从服务器中请求文件(图片.text文档等).此处详情记录从服务器下载图片的方法,以及以多种方式输出. 1.整体流程: 建立 ...
- 【php】面向对象(三)
知识点关键词:FSCICATS一. f => final: a) 是一个修饰符,用来修饰类和成员方法 b) 使用final修饰符修饰的类不能被继承,使用final修饰符修饰的成员方法,不能被重写 ...
