23-Java-Spring框架(一)
SpringwebMVC的了解、请求流程、运用等请阅读24-Java-Spring框架(二)
SpringAOP的了解、运用及原理等部分内容请阅读25-Java-Spring框架(三)
一、Spring框架了解
Spring框架是一个开源的框架,为JavaEE应用提供多方面的解决方案,用于简化企业级应用的开发,相当于是一种容器,可以集成其他框架(结构图如下)。
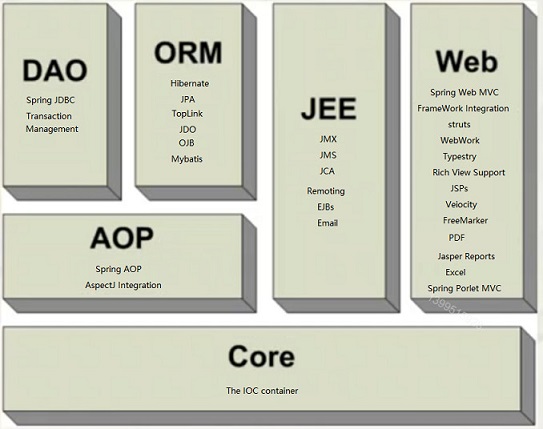
上图反映了框架引包的依赖关系(例如:DAO的jar包依赖AOP的jar包,AOP的jar包依赖Core的jar包)
上图也反映了Spring功能有:
IOC:控制反转,Spring的核心功能
AOP:面向切面编程
Web:MVC结构实现、与其他Web技术融合
DAO:与JDBC整合和事务管理
ORM:与ORM对象映射实现的框架整合
JEE:与JavaEE服务整合
二、SpringIOC(Inversion Of Control)
SpringIOC控制反转,是指程序中对象的获取方式发生反转,由最初的new方式创建,转为由框架创建注入,这样可以降低对象之间的耦合度。
IOC的主要作用是管理程序的组件,创建组件对象和维护对象之间的关系。
Spring容器:在Spring中,任何的Java类都被当成Bean组件,通过容器管理和使用,Spring容器实现了IOC和AOP机制,
Spring容器有ApplicationContext和BeanFactory两种类型。
ApplicationContext继承自BeanFactory,提供了更多的方法,建议使用ApplicationContext。
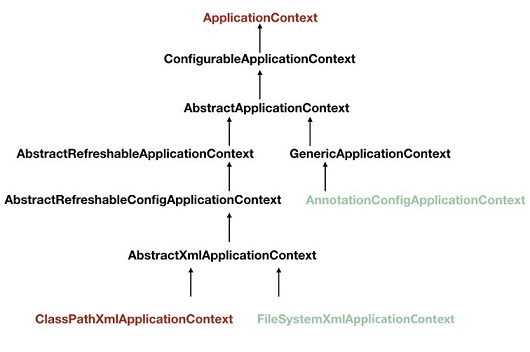
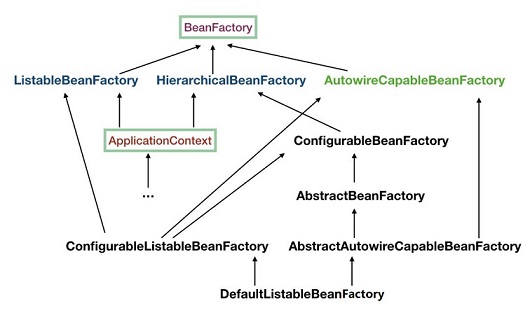
ApplicationContext实例化途径:
1.从classpath下加载配置文件实例化:ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
2.从文件系统中加载配置文件实例化:ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:\\applicationContext.xml");
Bean对象的创建:
Spring容器创建Bean对象有三种方法:
1.使用构造器来实例化
2.使用静态工厂方法来实例化
3.使用动态(实例)工厂方法来实例化
Spring容器创建Bean对象的步骤:
第一步:导入SpringIOC相关包到WebRoot/WBE-INF/lib下(想要相关包的网友请留言私聊)
commons-logging-1.2.jar
spring-beans-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-support-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
第二步:编写实体类和实体工厂类
实体类:
1 package com.springioc.entity;
2
3 public class User {
4 private Integer id;
5 private String username;
6 private String password;
7 public User() {
8 super();
9 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
10 }
11 public User(Integer id, String username, String password) {
12 super();
13 this.id = id;
14 this.username = username;
15 this.password = password;
16 }
17 public Integer getId() {
18 return id;
19 }
20 public void setId(Integer id) {
21 this.id = id;
22 }
23 public String getUsername() {
24 return username;
25 }
26 public void setUsername(String username) {
27 this.username = username;
28 }
29 public String getPassword() {
30 return password;
31 }
32 public void setPassword(String password) {
33 this.password = password;
34 }
35 @Override
36 public int hashCode() {
37 final int prime = 31;
38 int result = 1;
39 result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
40 result = prime * result
41 + ((password == null) ? 0 : password.hashCode());
42 result = prime * result
43 + ((username == null) ? 0 : username.hashCode());
44 return result;
45 }
46 @Override
47 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
48 if (this == obj)
49 return true;
50 if (obj == null)
51 return false;
52 if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
53 return false;
54 User other = (User) obj;
55 if (id == null) {
56 if (other.id != null)
57 return false;
58 } else if (!id.equals(other.id))
59 return false;
60 if (password == null) {
61 if (other.password != null)
62 return false;
63 } else if (!password.equals(other.password))
64 return false;
65 if (username == null) {
66 if (other.username != null)
67 return false;
68 } else if (!username.equals(other.username))
69 return false;
70 return true;
71 }
72 @Override
73 public String toString() {
74 return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password="
75 + password + "]";
76 }
77
78 }
实体工厂类:
1 package com.springioc.entity;
2
3 public class UserFactory {
4 public static User CreateUser(){
5 return new User();
6 }
7
8 public User DynamicCreateUser(){
9 return new User();
10 }
11 }
第三步:编写实例化配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- ************************************************************************************************************************ -->
<!-- 在容器配置文件applicationContext中添加bean的定义,等价于将Bean组件放入Spring容器,后续由Spring负责创建对象 -->
<!-- 在容器中最基本的单位就是bean标签,一个bean标签代表一个对象 -->
<!-- 默认情况下,每一个bean都是单例的,在单例(singleton)情况下,随容器的创建而创建,随着容器的销毁而销毁 -->
<!-- Bean创建对象的三种方式 -->
<!-- 1.构造器
语法格式:
<bean id="对象标识符" class="对象权限定名"></bean>
举例:
<bean id="user" class="com.springioc.entity.User"></bean>
-->
<!-- 2.静态工厂
语法格式:
<bean id="静态工厂标识符" class="工厂权限定名" factory-method="静态方法名"></bean>
举例:
<bean id="staticFactory" class="com.springioc.entity.UserFactory" factory-method="CreateUser"></bean>
-->
<!-- 3.动态(实例)工厂
语法格式:
<bean id="工厂标识符" class="工厂权限定名"></bean>
<bean id="动态工厂标识符" factory-bean="工厂标识符" factory-method="动态方法名"></bean>
举例:
<bean id="userFactory" class="com.springioc.entity.UserFactory"></bean>
<bean id="dynamicCreateUser" factory-bean="userFactory" factory-method="DynamicCreateUser"></bean>
-->
<bean id="userFactory" class="com.springioc.entity.UserFactory"></bean>
<bean id="dynamicCreateUser" factory-bean="userFactory" factory-method="DynamicCreateUser"></bean>
<!-- ************************************************************************************************************* -->
<!-- Bean便签常用属性:
id:bean对象标识符
factory-bean:bean对象创建工厂标识符
class:权限定名
factory-method:对象创建工厂函数
init-method:bean对象初始化方法名
destory-method:bean对象销毁方法名
lazy-init:延迟bean对象实例化,当设置为true的时候,不管是不是单例(singleton),当调用getBean()的时候才会创建对象 Beans标签常用属性:(作用于beans标签中的所有bean标签)
default-init-method:默认bean对象初始化方法名
default-destory-method:默认bean对象销毁方法名
default-lazy-init:默认延迟bean对象实例化
-->
<!-- ************************************************************************************************************** -->
<!-- Bean对象的参数注入
注入类型可以为字符串、集合、Bean对象
1.setter注入
name:实体类属性名
value:注入参数的值
ref:注入bean对象的值
举例:
<bean id = "user" class = "com.springioc.entity.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="username" value="admin"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
</bean>
相当于之前 User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("admin");
user.setPassword("123"); 2.构造器注入
index:实体类构造函数的形参顺序,0表示第一个参数,1表示第二参数,2表示第三个参数...
value:注入参数的值
ref:注入bean对象的值
举例:
<bean id = "user" class = "com.springioc.entity.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="2"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="username"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="password"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
注意:(以上两种注入方式都是以字符串的注入类型来举例的,下面是Bean对象注入和集合注入)
Bean对象的注入:如果一个实体类中的属性是另一个实体类时,注入时需将property标签的value属性改为ref属性
集合注入:(集合有set,list,map,props)
概述:假设一个实体类的属性中有集合,那么参数注入集合应该采用集合注入
举例:
<bean id = "girl" class = "com.springioc.entity.Girl">
<property name="glist">
<list>
<value>范冰冰</value>
<value>杨幂</value>
<value>王祖贤</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="gset">
<set>
<ref bean = "user1"/>
<ref bean = "user2"/>
</set>
</property>
<property name="gmap">
<map>
<entry key="美女" value="杨幂"></entry>
<entry key="美人">
<value>范冰冰</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="gprops">
<props>
<prop key="美女">杨幂</prop>
<prop key="美人">范冰冰</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- *************************************************************************************************************** -->
<!-- 一个Bean对象参数注入的实例:加载JDBC驱动-->
<!-- 加载资源文件 -->
<!-- 第一步:先建一个文件,文件名为jdbc.properties,放在src/下,文件中写 admin=root
password=root
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
JDBCdriver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
第二步:在applicationContext.xml中写
<util:properties id="jdbc" location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></util:properties>
-->
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<!-- Spring引入一种表达式语言,它和EL的语法相似,可以读取一个Bean对象/集合中的数据 -->
<!-- 第一步:编写一个和jdbc.properties文件相对应的实体类JDBCTest,属性名需要相等
第二步:在applicationContext.xml中写
<bean id="jdbc" class="com.springioc.test.JDBCTest">
<property name="admin" value="#{db.admin}"></property>
<property name="root" value="#{db.password}"></property>
<property name="url" value="#{db.url}"></property>
<property name="JDBCdriver" value="#{db.JDBCdriver}"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- ************************************************************************************************************** -->
</beans>
第四步:编写实例化测试类
1 package com.springioc.test;
2
3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;//spring-context.jar包中的
4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;//spring-context-support.jar包中的
5
6 import com.springioc.entity.User;
7
8 public class ApplicationContextBuildUserTest {
9 public static void main(String[] args) {
10 //以前的方式创建对象
11 // User user = new User();
12 // System.out.println(user);
13
14 //现在使用Spring框架的容器来创建对象
15 //第一步:创建Spring容器
16 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
17
18 /*第二步:从ApplicationContext容器获取Bean对象
19 * 1.构造器获取对象
20 * 语法格式:
21 * 类型名 变量名 = 容器对象.getBean("对象标识符",组件类型);
22 * 举例:
23 * User user = ac.getBean("user", User.class);
24 * 2.静态工厂获取对象
25 * 语法格式:
26 * 类型名 变量名 = 容器对象.getBean("静态工厂标识符",组件类型);
27 * 举例:
28 * User user = ac.getBean("staticFactory", User.class);
29 * */
30 User user = ac.getBean("dynamicCreateUser", User.class);
31 System.out.println(user);
32 }
33 }
第五步:运行结果
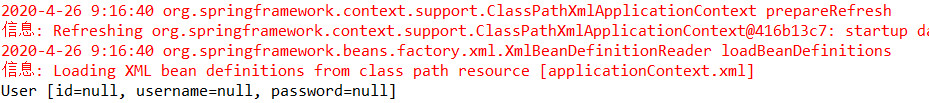
Bean对象的作用域:
指定Spring容器创建Bean对象的作用域:
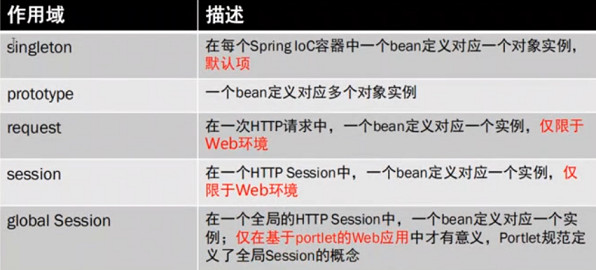
注意:singleton单例模式,通过getBean获取的对象HashCode是相同的,即user1 = user2返回true
prototype多例模式,通过getBean获取的对象HashCode是不同的,即user1 = user2返回false
Bean对象的参数注入:(看上面的applicationContext.xml中注释写的知识点)
容器可以建立Bean对象之间的关系,实现技术途径就是DI注入,Spring DI注入setter注入和构造器注入两种
组件扫描:Spring提供了一套基于注解配置的的使用方法,使用该方法可以大大简化XML的配置信息。
开启组件扫描,可以利用注解方式应用IOC,使用方法如下:
第一步:除了需要引入springIOC相关jar包之外还需要引入SpringAOP相关jar包(需要相关jar包的网友请留言私聊)
aopalliance-1.0.jar
aspectjweaver-1.5.3.jar
spring-aop-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.1.6.RELEASE.jar
第二步:在applicationContext.xml中添加启用标记(用了组件扫描就可以不用bean标签了)
<context:component-scan base-package="包路径(用最大的,例如:com.springioc)"/>
第三步:在组件类中追加以下标记
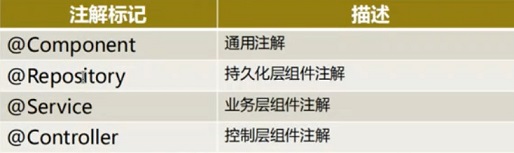
注意:1.扫描组件后,默认id值为组件类名首字母小写,也可以自定义id。例如:@Component("stu")
2.扫描组件后,默认scope为singleton单例,也可以进行指定。例如:@Scope("prototyppe")
3.也可以指定初始化和销毁的方法,例如,在组件类的方法前追加@PostConstruct来指定初始化方法,追加@PreDestory来指定销毁方法
4.将所有bean组件扫描到Spring容器后,可以使用以下注解指定注入关系
@Autowired/@Qulifier:可以处理构造器注入和setter注入
@Resource:只能处理Setter注入,但大部分情况都是setter注入
5.@Value注解可以注入Spring表达式值
首先读取db.properties文件,封装成Properties对象,在applicationContext.xml中添加
<util:properties id="jdbc" location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></util:properties>
然后在组件类属性变量或Setter方法前使用@Value注解
@Value("#{db.url}")
private String url;
追加标记举例:
@Component//默认实体类id名称是实体类名称(首字母小写)
2 @Scope("prototype")//默认为单例模式,此处修改为多例模式
public class User {
}
第四步:测试获取bean对象:
package com.springioc.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;//spring-context.jar包中的
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;//spring-context-support.jar包中的 import com.springioc.entity.User; public class ApplicationContextBuildUserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = ac.getBean("user", User.class);//此处的id:user是从@Component默认实体类id中得出来的
System.out.println(user);
}
}
运行结果:
SpringIOC实现解耦(重点理解)
解耦主题:通过hibernate和JDBC两种技术实现一个用户的删除操作
1.XML配置文件版的解耦
第一步:编写用户实体类和用户DAO接口
//用户DAO实现接口
package com.springiocDecoupling.usedao; public interface UserDAO {
public void delete();
}
第二步:编写Hibernate技术和JDBC技术分别实现删除操作的类
//JDBC实现DAO删除操作
package com.springiocDecoupling.usedao; public class JDBCDAO implements UserDAO{
public void delete(){
System.out.println("通过JDBC实现User删除");
}
}
//Hibernate实现DAO删除操作
package com.springiocDecoupling.usedao; public class HibernateDAO implements UserDAO{
public void delete(){
System.out.println("通过Hibernate实现User删除");
}
}
第三步:编写一个控制用户删除操作的控制类
//控制类,控制删除操作
package com.springiocDecoupling.entity.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.UserDAO; @Controller//用于Spring框架管理
public class UserController { private UserDAO dao;
public UserDAO getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(UserDAO dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public void delete(){
dao.delete();
}
}
第四步:配置applicationContext.xml信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id = "jdao" class = "com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.JDBCDAO"></bean>
<bean id = "hdao" class = "com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.HibernateDAO"></bean> <bean id = "ucontroller" class="com.springiocDecoupling.entity.Controller.UserController">
<property name="dao" ref="jdao"></property><!--解耦操作就体现在此处,要用jdbc,ref属性修改为jdao就行了,要用hibernate,ref属性修改为hdao就行了-->
</bean>
</beans>
第五步:编写测试类
package com.springiocDecoupling.entity.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;//spring-context.jar包中的
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;//spring-context-support.jar包中的 import com.springiocDecoupling.entity.Controller.UserController; public class ApplicationContextBuildUserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserController ucon = ac.getBean("ucontroller", UserController.class);
ucon.delete();
}
}
测试结果:

2.通过注解的方式进行解耦
第一步:编写用户实体类和用户DAO接口
第二步:第二步:编写Hibernate技术和JDBC技术分别实现删除操作的类
package com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("jdao")
public class JDBCDAO implements UserDAO{
public void delete(){
System.out.println("通过JDBC实现User删除");
}
}
package com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("hdao")
public class HibernateDAO implements UserDAO{
public void delete(){
System.out.println("通过Hibernate实现User删除");
}
}
第三步:编写一个控制用户删除操作的控制类
package com.springiocDecoupling.entity.Controller;
import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.UserDAO; @Controller("ucontroller")
public class UserController {
//如果使用Autowired的话需要Qualifier搭配,例如:
11 //@Autowired
11 //@Qualifier("jdao")
@Resource(name="jdao")//解耦操作就体现在此处,要用jdbc修改为jdao就行了,要用hibernate修改为hdao就行了
private UserDAO dao;
public UserDAO getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(UserDAO dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public void delete(){
dao.delete();
}
}
第四步:配置applicationContext.xml信息,启动组件扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--
<bean id = "jdao" class = "com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.JDBCDAO"></bean>
<bean id = "hdao" class = "com.springioc_Decoupling.usedao.HibernateDAO"></bean> <bean id = "ucontroller" class="com.springiocDecoupling.entity.Controller.UserController">
<property name="dao" ref="hdao"></property>
</bean>
--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.springiocDecoupling"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
第五步:编写测试类
测试结果:


23-Java-Spring框架(一)的更多相关文章
- [Java]Spring框架
在这里学习Spring框架: >>spring&struts框架学习 >>spring >>Java回顾之Spring基础 >>IBM Java ...
- 基于java spring框架开发部标1078视频监控平台精华文章索引
部标1078视频监控平台,是一个庞杂的工程,涵盖了多层协议,部标jt808,jt809,jt1078,苏标Adas协议等,多个平台功能标准,部标796标准,部标1077标准和苏标主动安全标准,视频方面 ...
- 《Java Spring框架》SpringXML配置详解
Spring框架作为Bean的管理容器,其最经典最基础的Bean配置方式就是纯XML配置,这样做使得结构清晰明了,适合大型项目使用.Spring的XML配置虽然很繁琐,而且存在简洁的注解方式,但读懂X ...
- 《Java Spring框架》基于IDEA搭建Spring源码
第一步: IDEA :IntelliJ IDEA 2018.1.4 :JDK安装(必须1.8或者以上),IDEA安装(过程省略). 第二步: Gradle:下载地址:https://servic ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:SSM(Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis)框架整合搭建详细步骤
因为 Spring MVC 是 Spring 框架中的一个子模块,所以 Spring 与 SpringMVC 之间不存在整合的问题.实际上,SSM 框架的整合只涉及 Spring 与 MyBatis ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:SSH框架(Struts2+Spring+Hibernate)搭建整合详细步骤
在实际项目的开发中,为了充分利用各个框架的优点,通常都会把 Spring 与其他框架整合在一起使用. 整合就是将不同的框架放在一个项目中,共同使用它们的技术,发挥它们的优点,并形成互补.一般而言,在进 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring使用AspectJ开发AOP基于XML和基于Annotation
AspectJ 是一个基于 Java 语言的 AOP 框架,它扩展了 Java 语言.Spring 2.0 以后,新增了对 AspectJ 方式的支持,新版本的 Spring 框架,建议使用 Aspe ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring JDK动态代理
JDK 动态代理是通过 JDK 中的 java.lang.reflect.Proxy 类实现的.下面通过具体的案例演示 JDK 动态代理的使用. 1. 创建项目 在 MyEclipse 中创建一个名称 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring DI(依赖注入)的实现方式属性注入和构造注入
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)和控制反转含义相同,它们是从两个角度描述的同一个概念. 当某个 Java 实例需要另一个 Java 实例时,传统的方法是由调用者创建被调用者的 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring IoC容器BeanFactory和ApplicationContext
IoC 是指在程序开发中,实例的创建不再由调用者管理,而是由 Spring 容器创建.Spring 容器会负责控制程序之间的关系,而不是由程序代码直接控制,因此,控制权由程序代码转移到了 Spring ...
随机推荐
- iOS isa 和 Class
一.Runtime 简介 Runtime 又叫运行时,是一套底层的 C 语言 API,是 iOS 系统的核心之一.开发者在编码过程中,可以给任意一个对象发送消息,在编译阶段只是确定了要向接收者发送这条 ...
- iOS 内存管理:从 MRC 到 ARC 实践
对于 iOS 程序员来说,内存管理是入门的必修课.引用计数.自动释放等概念,都是与 C 语言完全不同的. iOS 内存管理的核心是引用计数. 接触 MRC 时遇到最头疼的问题就是:为什么那么多 rel ...
- 15.自动部署web工程
用maven自动部署web工程 在pom.xml中写入以下: <build> <!--最终名称,进入网页时有http://localhost:8080/xxx/--> < ...
- RocketMQ调研
一.发展历程 早期淘宝内部有两套消息中间件系统:Notify和Napoli. 先有的Notify(至今12历史),后来因有序场景需求,且恰好当时Kafka开源(2011年),所以参照Kafka的设计理 ...
- 实际开发中 dao、entity的代码怎样自动生成?一款工具送给你
01 关注"一猿小讲"朋友,都知道以往的文章一直倡导拒绝 CRUD,那到底什么是 CRUD?今天咱们就聊聊 Java 妹子小猿与数据库老头交互的事儿. 产品小汪铿锵有力的说:小猿同 ...
- LVS 集群与存储《路由转发》
LVS 集群与存储<路由转发> 集群简介 u 什么是集群 • 一组通过高 ...
- 怎么用scratch做大鱼吃小鱼
行走代码不说了.出鱼代码大概就是 棋子被点击时 重复执行 移到x:从()到()任意选一个数,y一样 克隆自己 等待你想要的秒数.吃鱼代码就是 当作为克隆体启动是 重复执行 如果碰到()那么 删除克隆体 ...
- 【php】错误日志处理
一. 错误处理: a) 在写程序的过程当中,遇到错误时,你的反应?可能比较急躁,比较烦 b) 遇到错误后:一别哭,二别闹,三别上吊,四别尿……二. 你可能会遇到的错误: a) 语法错误 i. 语法错误 ...
- 微信小程序--分享功能
微信小程序--分享功能 微信小程序前段时间开放了小程序右上角的分享功能, 可以分享任意一个页面到好友或者群聊, 但是不能分享到朋友圈 这里有微信开发文档链接:点击跳转到微信分享功能API 入口方法: ...
- 29 collection 集合体系结构
/*collection:采集 * ArrayList * 集合的体系结构: * 由于不同的数据结构(数据的组织,存储方式),所以Java为我们提供了不同的集合, * 但是不同的集合他们的功能都是相似 ...
