1.2 Data Abstraction(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.2.1
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class Point2DClient { public static void main(String[] args) { int pointnumber;
Point2D[] points; double closestdistance = 0;
int closestpair1;
int closestpair2; //usage
if(args.length < 1)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: Point2DClient N");
StdOut.println("Generate N random points");
return;
} pointnumber = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
points = new Point2D[pointnumber]; //generate pointnumber random points
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.01);
for(int i = 0; i < pointnumber; i++) {
double x = StdRandom.random();
double y = StdRandom.random();
StdOut.printf("Point2D %d (%f %f)\n",i, x,y);
points[i] = new Point2D(x, y);
points[i].draw();
} //find the closet pair of points
closestdistance = points[0].distanceTo(points[1]);
closestpair1 = 0;
closestpair2 = 1;
for(int i = 0; i< pointnumber; i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < pointnumber; j++) {
double distance = points[i].distanceTo(points[j]);
StdOut.printf("distance from %d to %d is %f\n", i,j,distance);
if(distance < closestdistance) {
closestdistance = distance;
closestpair1 = i;
closestpair2 = j;
}
}
} StdOut.printf("closest distance is %f from %d to %d\n", closestdistance, closestpair1, closestpair2);
points[closestpair1].drawTo(points[closestpair2]); } }
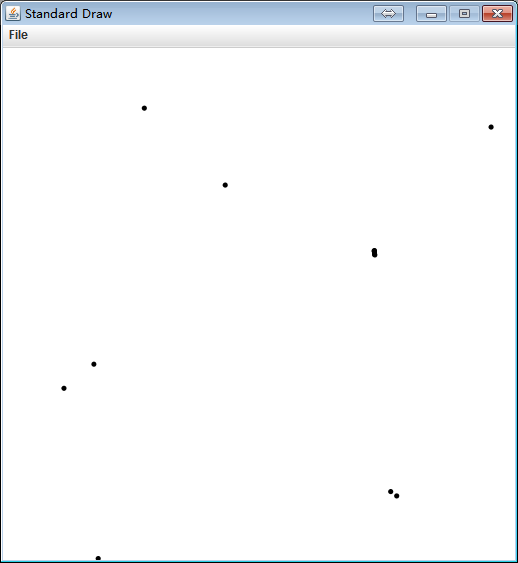
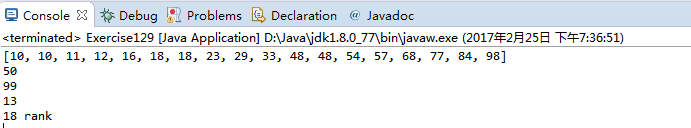
Point2D 0 (0.757256 0.133583)
Point2D 1 (0.276017 0.882527)
Point2D 2 (0.724763 0.603589)
Point2D 3 (0.186021 0.002862)
Point2D 4 (0.768848 0.125174)
Point2D 5 (0.434056 0.732299)
Point2D 6 (0.119133 0.335418)
Point2D 7 (0.177490 0.382443)
Point2D 8 (0.726221 0.595894)
Point2D 9 (0.953359 0.845522)
distance from 0 to 1 is 0.890230
distance from 0 to 2 is 0.471128
distance from 0 to 3 is 0.586001
distance from 0 to 4 is 0.014321
distance from 0 to 5 is 0.680382
distance from 0 to 6 is 0.669282
distance from 0 to 7 is 0.630920
distance from 0 to 8 is 0.463352
distance from 0 to 9 is 0.738453
distance from 1 to 2 is 0.528375
distance from 1 to 3 is 0.884257
distance from 1 to 4 is 0.903585
distance from 1 to 5 is 0.218048
distance from 1 to 6 is 0.569158
distance from 1 to 7 is 0.509697
distance from 1 to 8 is 0.533706
distance from 1 to 9 is 0.678352
distance from 2 to 3 is 0.806918
distance from 2 to 4 is 0.480442
distance from 2 to 5 is 0.317926
distance from 2 to 6 is 0.662347
distance from 2 to 7 is 0.590265
distance from 2 to 8 is 0.007831
distance from 2 to 9 is 0.332847
distance from 3 to 4 is 0.595523
distance from 3 to 5 is 0.770454
distance from 3 to 6 is 0.339217
distance from 3 to 7 is 0.379678
distance from 3 to 8 is 0.802187
distance from 3 to 9 is 1.139685
distance from 4 to 5 is 0.693316
distance from 4 to 6 is 0.682885
distance from 4 to 7 is 0.644896
distance from 4 to 8 is 0.472647
distance from 4 to 9 is 0.743603
distance from 5 to 6 is 0.506647
distance from 5 to 7 is 0.433849
distance from 5 to 8 is 0.322439
distance from 5 to 9 is 0.531503
distance from 6 to 7 is 0.074946
distance from 6 to 8 is 0.660609
distance from 6 to 9 is 0.977823
distance from 7 to 8 is 0.588784
distance from 7 to 9 is 0.903556
distance from 8 to 9 is 0.337499
closest distance is 0.007831 from 2 to 8
1.2.2和1.2.3解法跟1.2.1类似,略
1.2.4
输出结果为:
world
hello
因为最后string1是“world”的引用
string2是“hello”的引用
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Exercise124 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string1 = "hell0";
String string2 = string1;
string1 = "world";
StdOut.println(string1);
StdOut.println(string2);
}
}
结果:

1.2.5
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Exercise125 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "Hello World";
s.toUpperCase();
s.substring(6, 11);
StdOut.println(s);
}
}
程序从头到尾s指向的对象都没有改变过,所以最后输出“Hello World”

1.2.6
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Exercise126 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
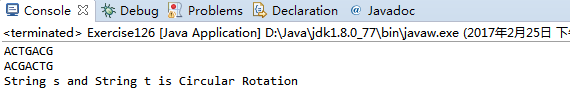
String s = "ACTGACG";
String t = "ACGACTG";
StdOut.println(s);
StdOut.println(t);
if(isCircularRotation(s,t))
StdOut.println("String s and String t is Circular Rotation");
else
StdOut.println("String s and String t isn't Circular Rotation");
}
public static boolean isCircularRotation(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() == t.length() && s.concat(s).indexOf(t) >= 0)
return true;
return false;
}
}
1.2.7
起到反转String的作用,以下是程序测试。
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Exercise127 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
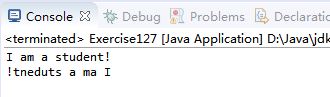
String test = "I am a student!";
StdOut.println(test);
StdOut.println(mystery(test));
}
public static String mystery(String s) {
int N = s.length();
if(N <= 1) return s;
String a = s.substring(0, N/2);
String b = s.substring(N/2, N);
return mystery(b) + mystery(a);
}
}
1.2.8
书中有答案
1.2.9
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Counter;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise129 { public static int rank(int key, int[] a, Counter counter) { counter.increment(); //array must be sorted
int lo = 0;
int hi = a.length - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; if(key < a[mid])
hi = mid -1;
else if(key > a[mid])
lo = mid + 1;
else
return mid; } return -1;
} public static void main(String[] args) { Counter counter = new Counter("rank");
int[] whitelist = In.readInts(args[0]); Arrays.sort(whitelist);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(whitelist)); while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int key = StdIn.readInt();
if(rank(key, whitelist, counter) < 0)
StdOut.println(key);
} StdOut.println(counter);
}
}
1.2.10
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class VisualCounter { private int maxx;
private int maxabsy; private int count = 0;
private int times = 0; public VisualCounter(int N, int max) {
StdDraw.setXscale(0, N);
StdDraw.setYscale(-max, max);
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.005);
StdDraw.line(0, 0, N, 0);
maxx = N;
maxabsy = max;
} public void increment() {
times++;
count++;
StdDraw.point(times, count);
} public void decrement() {
times++;
count--;
StdDraw.point(times, count);
} public static void main(String[] args) { VisualCounter counter = new VisualCounter(100, 100); for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if(StdRandom.bernoulli()) {
counter.increment();
}
else {
counter.decrement();
}
} } }
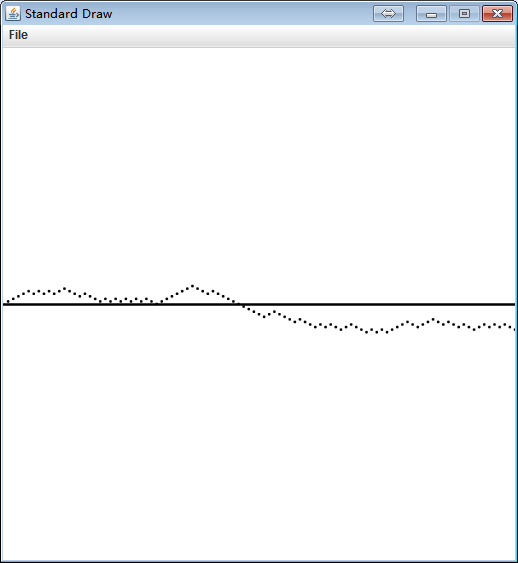
1.2.11
package com.qiusongde;
public class SmartDate {
private final int month;
private final int day;
private final int year;
private final int[] MAXDAY = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
public SmartDate(int m, int d, int y) {
if(!isValid(m, d, y))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y);
month = m;
day = d;
year = y;
}
private boolean isValid(int m, int d, int y) {
if(m < 1 || m > 12)
return false;
if(d < 1 || d > MAXDAY[m-1])
return false;
if(m == 2 && d == 29 && !isLeapYear(y))
return false;
return true;
}
private boolean isLeapYear(int y) {
if(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
public int month() {
return month;
}
public int day() {
return day;
}
public int year() {
return year;
}
public String toString() {
return month() +"/" + day() + "/" + year();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(13, 31, 2009);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(6, 32, 2009);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2017);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2016);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2000);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2100);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate(6, 31, 2009);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2009);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:13/31/2009
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13)
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:54)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:6/32/2009
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13)
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:60)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:2/29/2017
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13)
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:66)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:2/29/2100
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13)
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:84)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:6/31/2009
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13)
at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:90)
1.2.12
public String dayOfTheWeek() {
//assume that the date is in the 21st century
//in 1/1/2000 is Saturday
int offsetday = 0;//the offset of day from 1/1/2000
final String[] WEEKDAY = {"Saturday", "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday"};
//year
offsetday += 365 * (year - 2000);//ignore leap year first
//month
for(int i = 0; i < month - 1; i++) {
offsetday += MAXDAY[i];//add according to the max day
}
if(month > 2) {
if(!isLeapYear(year))
offsetday--;
}
//day
offsetday += day - 1;
//add leapyear day in February
offsetday += Leapyears(year);
return WEEKDAY[offsetday % 7];
}
//return the number of leap year since 2000
private int Leapyears(int year) {
if(year == 2000)
return 0;
int number = 0;
int offset = year - 2001;
number += offset/4;//how many 4 years since 2001
number -= offset/100 ;//how many 100 years since 2001
number += offset/400;//how many 400 years since 2001
number++;//2000 year is leap year
return number;
}
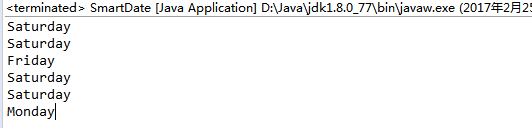
SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2017);
StdOut.println(date1.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2000);
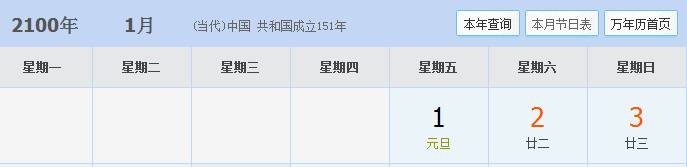
StdOut.println(date2.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2100);
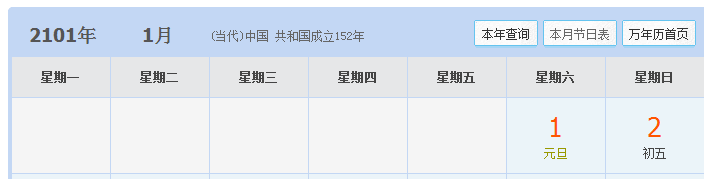
StdOut.println(date3.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2101);
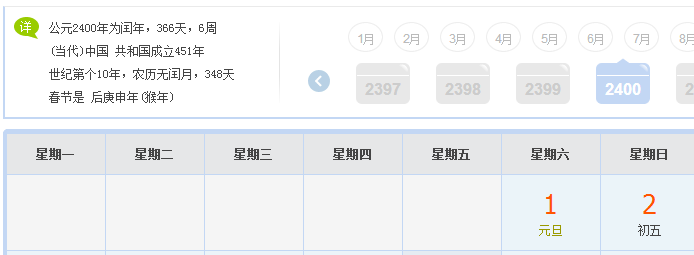
StdOut.println(date4.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2400);
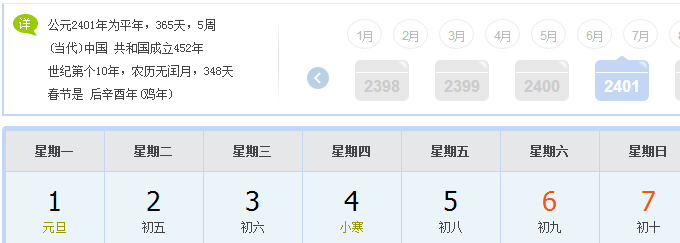
StdOut.println(date5.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2401);
StdOut.println(date6.dayOfTheWeek());

1.2.13
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private String name;
private Date date;
private double amount; public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) {
//should check the argument
name = who;
date = when;
this.amount = amount;
} public String who() {
return name;
} public Date when() {
return date;
} public double amount() {
return amount;
} public String toString() {
return date + " " + name + " " + amount;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017);
Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500);
StdOut.println(transaction);
} }

1.2.14
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private String name;
private Date date;
private double amount; public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) {
//should check the argument
name = who;
date = when;
this.amount = amount;
} public String who() {
return name;
} public Date when() {
return date;
} public double amount() {
return amount;
} public String toString() {
return date + " " + name + " " + amount;
} public boolean equals(Object x) { if(this == x)
return true;
if(x == null)
return false;
if(this.getClass() != x.getClass())
return false; Transaction that = (Transaction) x;
if(!name.equals(that.name))
return false;
if(!date.equals(that.date))
return false;
if(amount != that.amount)
return false; return true;
} public static void main(String[] args) { Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017);
Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); Date date1 = new Date(2, 27, 2017);
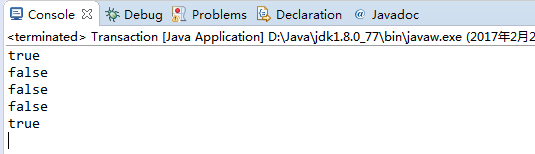
Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date1, 500); Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction));
StdOut.println(transaction.equals(null));
StdOut.println(transaction.equals(date));
StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction1));
StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction2)); } }
1.2.15
书中已经由答案
public static int[] readInts(String name) {
In in = new In(name);
String input = in.readAll();
String[] words = input.split("\\s+");
int[] ints = new int[words.length];
for(int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
ints[i] = Integer.parseInt(words[i]);
}
return ints;
}
其中"\\s+" \\s表示空格、回车、换行符等空白符,+表示多个的意思。
1.2.16
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Rational {
private final long numerator;
private final long denominator;
public Rational(long numerator, long denominator) {
if(denominator == 0)
throw new ArithmeticException("denominator is zero");
//find the greatest common divisor
//to reduce the result to the simplest fraction
long gcd = gcd(numerator, denominator);
//assure denominator is positive
if(denominator < 0) {
this.numerator = -numerator/gcd;
this.denominator = -denominator/gcd;
} else {
this.numerator = numerator/gcd;
this.denominator = denominator/gcd;
}
}
//the greatest commom divisor of |p| and |q|
private long gcd(long p, long q) {
if(p < 0)
p = -p;
if(q < 0)
q = -q;
if(q == 0)
return p;
long r = p % q;
return gcd(q, r);
}
public Rational plus(Rational b) {
return new Rational((this.numerator * b.denominator + this.denominator * b.numerator), this.denominator * b.denominator);
}
public Rational minus(Rational b) {
return this.plus(new Rational(-b.numerator, b.denominator));
}
public Rational times(Rational b) {
return new Rational(this.numerator * b.numerator, this.denominator * b.denominator);
}
public Rational divides(Rational b) {
return new Rational(this.numerator * b.denominator, this.denominator * b.numerator);
}
public boolean equals(Object that) {
if(this == that)
return true;
if(that == null)
return false;
if(this.getClass() != that.getClass())
return false;
Rational other = (Rational) that;
return (this.numerator == other.numerator) && (this.denominator == other.denominator);
}
public String toString() {
return numerator + "/" + denominator;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rational a = new Rational(3, 9);
Rational b = new Rational(-2, 8);
Rational c = new Rational(1, -7);
Rational d = new Rational(-1, -3);
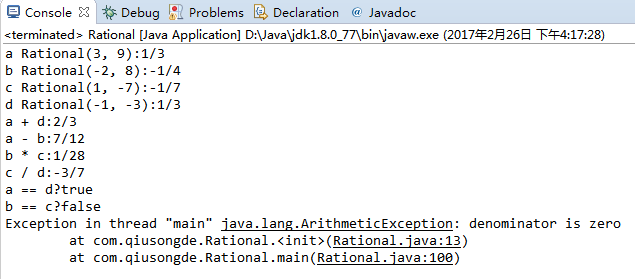
StdOut.println("a Rational(3, 9):" + a.toString());
StdOut.println("b Rational(-2, 8):" + b.toString());
StdOut.println("c Rational(1, -7):" + c.toString());
StdOut.println("d Rational(-1, -3):" + d.toString());
StdOut.println("a + d:" + a.plus(d).toString());
StdOut.println("a - b:" + a.minus(b).toString());
StdOut.println("b * c:" + b.times(c).toString());
StdOut.println("c / d:" + c.divides(d).toString());
StdOut.println("a == d?" + a.equals(d));
StdOut.println("b == c?" + b.equals(c));
new Rational(1, 0);
}
}
1.2.17
//1.2.16
//1.2.17
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Rational { private final long numerator;
private final long denominator; private final long MAX = Long.MAX_VALUE;
private final long MIN = Long.MIN_VALUE; public Rational(long numerator, long denominator) { if(denominator == 0)
throw new ArithmeticException("denominator is zero"); //find the greatest common divisor
//to reduce the result to the simplest fraction
long gcd = gcd(numerator, denominator); //assure denominator is positive
if(denominator < 0) {
this.numerator = -numerator/gcd;
this.denominator = -denominator/gcd;
} else {
this.numerator = numerator/gcd;
this.denominator = denominator/gcd;
} } //the greatest commom divisor of |p| and |q|
private long gcd(long p, long q) { if(p < 0)
p = -p; if(q < 0)
q = -q; if(q == 0)
return p; long r = p % q;
return gcd(q, r);
} //true --> will overflow
//false --> will not overflow
private boolean is_overflow_plus(long a, long b) {
return a >= 0 ? MAX - a < b : MIN - a > b;
} //true --> will overflow
//false --> will not overflow
private boolean is_overflow_times(long a, long b) { if(a == 0 || b == 0) {
return false;
} if( a >= 0 && b >=0 ) {
return MAX / a < b;
}
else if( a < 0 && b < 0 ) {
return MAX / a > b;
}
else {
return a < 0 ? MIN / a < b: MIN / a > b ;
} } public Rational plus(Rational b) { assert is_overflow_times(this.numerator, b.denominator) : "plus overflows";
assert is_overflow_times(this.denominator, b.numerator) : "plus overflows";
assert is_overflow_plus(this.numerator * b.denominator, this.denominator * b.numerator) : "plus overflows"; return new Rational((this.numerator * b.denominator + this.denominator * b.numerator), this.denominator * b.denominator);
} public Rational minus(Rational b) {
return this.plus(new Rational(-b.numerator, b.denominator));
} public Rational times(Rational b) { assert is_overflow_times(this.numerator, b.numerator) : "times overflows";
assert is_overflow_times(this.denominator, b.denominator) : "times overflows"; return new Rational(this.numerator * b.numerator, this.denominator * b.denominator);
} public Rational divides(Rational b) {
return this.times(new Rational(b.denominator, b.numerator));
} public boolean equals(Object that) { if(this == that)
return true; if(that == null)
return false; if(this.getClass() != that.getClass())
return false; Rational other = (Rational) that;
return (this.numerator == other.numerator) && (this.denominator == other.denominator);
} public String toString() {
return numerator + "/" + denominator;
} public static void main(String[] args) { // Rational a = new Rational(3, 9);
// Rational b = new Rational(-2, 8);
// Rational c = new Rational(1, -7);
// Rational d = new Rational(-1, -3);
//
// StdOut.println("a Rational(3, 9):" + a.toString());
// StdOut.println("b Rational(-2, 8):" + b.toString());
// StdOut.println("c Rational(1, -7):" + c.toString());
// StdOut.println("d Rational(-1, -3):" + d.toString());
//
// StdOut.println("a + d:" + a.plus(d).toString());
// StdOut.println("a - b:" + a.minus(b).toString());
// StdOut.println("b * c:" + b.times(c).toString());
// StdOut.println("c / d:" + c.divides(d).toString());
// StdOut.println("a == d?" + a.equals(d));
// StdOut.println("b == c?" + b.equals(c));
//
// new Rational(1, 0); Rational a = new Rational(Long.MAX_VALUE, 2);
Rational b = new Rational(2, Long.MAX_VALUE);
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MAX_VALUE - 1, 1));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MAX_VALUE - 1, 2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MIN_VALUE + 2, -2));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MIN_VALUE + 2, -3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(Long.MAX_VALUE/2, 3));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(Long.MAX_VALUE/2, 2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MAX_VALUE/2), -3));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MAX_VALUE/2), -2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MIN_VALUE/2), -3));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MIN_VALUE/2), -2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times((Long.MIN_VALUE/2), 3));
StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times((Long.MIN_VALUE/2), 2)); StdOut.println(a.plus(b));
StdOut.println(a.times(b));
} }
开启assert之前的运行结果:

开始之后的运行结果:

1.2.18
https://www.johndcook.com/blog/standard_deviation/
Accurately computing running variance
1.2.19
//1.2.11
//1.2.12
//1.2.19
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class SmartDate { private final int month;
private final int day;
private final int year; private final int[] MAXDAY = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; public SmartDate(String date) { String[] fields = date.split("/"); if(fields.length < 3) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("should more than 3 arguments");
} int m = Integer.parseInt(fields[0]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(fields[1]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(fields[2]); if(!isValid(m, d, y))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y); month = m;
day = d;
year = y;
} public SmartDate(int m, int d, int y) {
if(!isValid(m, d, y))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y);
month = m;
day = d;
year = y;
} private boolean isValid(int m, int d, int y) {
if(m < 1 || m > 12)
return false;
if(d < 1 || d > MAXDAY[m-1])
return false;
if(m == 2 && d == 29 && !isLeapYear(y))
return false;
return true;
} private boolean isLeapYear(int y) {
if(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0)
return true;
return false;
} public int month() {
return month;
} public int day() {
return day;
} public int year() {
return year;
} public String dayOfTheWeek() {
//assume that the date is in the 21st century
//in 1/1/2000 is Saturday int offsetday = 0;//the offset of day from 1/1/2000
final String[] WEEKDAY = {"Saturday", "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday"}; //year
offsetday += 365 * (year - 2000);//ignore leap year first //month
for(int i = 0; i < month - 1; i++) {
offsetday += MAXDAY[i];//add according to the max day
}
if(month > 2) {
if(!isLeapYear(year))
offsetday--;
} //day
offsetday += day - 1; //add leapyear day in February
offsetday += Leapyears(year); return WEEKDAY[offsetday % 7];
} //return the number of leap year since 2000
private int Leapyears(int year) { if(year == 2000)
return 0; int number = 0;
int offset = year - 2001; number += offset/4;//how many 4 years since 2001
number -= offset/100 ;//how many 100 years since 2001
number += offset/400;//how many 400 years since 2001
number++;//2000 year is leap year return number;
} public String toString() {
return month +"/" + day + "/" + year;
} public static void main(String[] args) { // try {
// SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(13, 31, 2009);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(6, 32, 2009);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2017);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2016);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2000);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2100);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate(6, 31, 2009);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//
// try {
// SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2009);
// } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// } // SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2017);
// StdOut.println(date1.dayOfTheWeek());
//
// SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2000);
// StdOut.println(date2.dayOfTheWeek());
//
// SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2100);
// StdOut.println(date3.dayOfTheWeek());
//
// SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2101);
// StdOut.println(date4.dayOfTheWeek());
//
//
// SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2400);
// StdOut.println(date5.dayOfTheWeek());
//
// SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2401);
// StdOut.println(date6.dayOfTheWeek()); try {
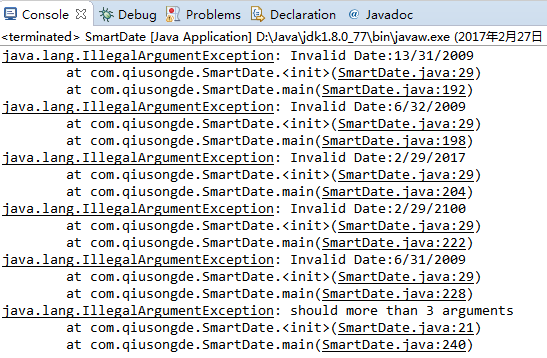
SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate("13/31/2009");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate("6/32/2009");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate("2/29/2017");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate("2/29/2016");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate("2/29/2000");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate("2/29/2100");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate("6/31/2009");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate("2/25/2009");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} try {
SmartDate date9 = new SmartDate("2/25");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} } }
//1.2.13
//1.2.14
//1.2.19
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private final String name;
private final Date date;
private final double amount; public Transaction(String transaction) { String[] fields = transaction.split("\\s+"); if(fields.length < 3) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("should more than 3 arguments");
} name = fields[0];
date = new Date(fields[1]);
amount = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]); } public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) {
//should check the argument
name = who;
date = when;
this.amount = amount;
} public String who() {
return name;
} public Date when() {
return date;
} public double amount() {
return amount;
} public String toString() {
return date + " " + name + " " + amount;
} public boolean equals(Object x) { if(this == x)
return true;
if(x == null)
return false;
if(this.getClass() != x.getClass())
return false; Transaction that = (Transaction) x;
return (this.amount == that.amount) && (this.name.equals(that.name))
&& (this.date.equals(that.date));
} public static void main(String[] args) { // Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017);
// Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500);
//
// Date date1 = new Date(2, 27, 2017);
// Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date1, 500);
//
// Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500);
//
// StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction));
// StdOut.println(transaction.equals(null));
// StdOut.println(transaction.equals(date));
// StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction1));
// StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction2));
Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde 2/26/2017 500");
StdOut.println(transaction1);
Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde 2/27/2017 500");
StdOut.println(transaction2); try {
Transaction transaction3 = new Transaction("Songde 2/27/2017");
StdOut.println(transaction3);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} } }

1.2 Data Abstraction(算法 Algorithms 第4版)的更多相关文章
- 1.1 BASIC PROGRAMMING MODEL(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.1.1 private static void exercise111() { StdOut.println("1.1.1:"); StdOut.println((0+15)/ ...
- CSIS 1119B/C Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms
CSIS 1119B/C Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Programming Assignment TwoDue Date: 18 A ...
- CSC 172 (Data Structures and Algorithms)
Project #3 (STREET MAPPING)CSC 172 (Data Structures and Algorithms), Spring 2019,University of Roche ...
- Basic Data Structures and Algorithms in the Linux Kernel--reference
http://luisbg.blogalia.com/historias/74062 Thanks to Vijay D'Silva's brilliant answer in cstheory.st ...
- ubuntu命令行下java工程编辑与算法(第四版)环境配置
ubuntu命令行下java工程编辑与算法(第四版)环境配置 java 命令行 javac java 在学习算法(第四版)中的实例时,因需要安装配套的java编译环境,可是在编译java文件的时候总是 ...
- 常见排序算法题(java版)
常见排序算法题(java版) //插入排序: package org.rut.util.algorithm.support; import org.rut.util.algorithm.Sor ...
- 配置算法(第4版)的Java编译环境
1. 下载 1.1 JDK http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html选择“Windows x64 180.5 ...
- 算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.3.49 用 6 个栈实现一个 O(1) 队列
因为这个解法有点复杂,因此单独开一贴介绍. 那么这里就使用六个栈来解决这个问题. 这个算法来自于这篇论文. 原文里用的是 Pure Lisp,不过语法很简单,还是很容易看懂的. 先导知识——用两个栈模 ...
- 在Eclipse下配置算法(第四版)运行环境
第一步:配置Eclipse运行环境 Eclipse运行环境配置过程是很简单的,用过Eclipse进行java开发或学习的同学应该都很熟悉这个过程了. 配置过程: (1)系统环境:Windows7 64 ...
随机推荐
- Mockito图书馆
转载:https://static.javadoc.io/org.mockito/mockito-core/2.12.0/org/mockito/Mockito.html#42 org.mockito ...
- 微信小程序 - 时间戳转时间
获取当前时间:十位unix时间戳 var timestamps = Math.round(new Date().getTime() / 1000).toString(); 时间戳转时间(官方自带) 使 ...
- 【React Native开发】React Native控件之DrawerLayoutAndroid抽屉导航切换组件解说(13)
),请不要反复加群! 欢迎各位大牛,React Native技术爱好者增加交流!同一时候博客左側欢迎微信扫描关注订阅号,移动技术干货,精彩文章技术推送! 该DrawerLayoutAndroid组件封 ...
- 谈 API 的撰写 - 总览
背景 之前团队主要的工作就是做一套 REST API.我接手这个工作时发现那些API写的比较业余,没有考虑几个基础的HTTP/1.1 RFC(2616,7232,5988等等)的实现,于是我花了些时间 ...
- 代理server的概要知识
技术支持请留言:http://www.lcpower.cn 一.什么是代理server? 代理server英文全称是Proxy Server.其功能就是代理网络用户去取得网络信息.形象的说:它是网络信 ...
- jenkins 构建一个前端web项目
Jenkins发布web前端代码 “系统管理”“管理插件”“已安装” 检查是否有“Git plugin”和“Publish Over SSH”两个插件,如果没有,则需点击“可选插件”,找到它并安装 ...
- 深入解析Windows窗体创建和消息分发
Windows GUI採用基于事件驱动的编程模型,其实差点儿全部的界面库都是这样做的.在纯粹的Window32 SDK编程时代.人们还能够搞懂整个Windows窗口创建和消息的流通过程.可是在如今各种 ...
- Hibernate学习四----------Blob
© 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处 实例 1.项目结构 2.pom.xml <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0 ...
- Flex版的2048游戏
近期2048游戏好像挺火.在公交,吃饭,甚至在路上走路都有人拿着手机在玩,之前我看同事玩,认为非常幼稚,移来移去太无聊了吧 到后面自己也下了.发现确实挺无聊的,也就是在无聊的时候打发无聊的时间,后来就 ...
- android 怎样加速./mk snod打包
mm命令高速编译一个模块之后,一般用adb push到手机看效果,假设环境不同意用adb push或模块不常常改.希望直接放到image里,则能够用./mk snod,这个命令只将system文件夹打 ...
