linux内核情景分析之信号实现
信号在进程间通信是异步的,每个进程的task_struct结构有一个sig指针,指向一个signal_struct结构
struct signal_struct {atomic_t count;struct k_sigaction action[_NSIG];//类似一个信号向量表,每个元素就是一个函数指针spinlock_t siglock;};
struct k_sigaction {struct sigaction sa;};
struct sigaction {unsigned int sa_flags;__sighandler_t sa_handler;sigset_t sa_mask;void (*sa_restorer)(void);int sa_resv[1]; /* reserved */};
/* Fake signal functions */#define SIG_DFL ((__sighandler_t)0) /* default signal handling */#define SIG_IGN ((__sighandler_t)1) /* ignore signal */#define SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t)-1) /* error return from signal */
struct sigaction {unsigned int sa_flags;__sighandler_t sa_handler;sigset_t sa_mask;//屏蔽,一个64位的类型void (*sa_restorer)(void);int sa_resv[1]; /* reserved */};
struct sigqueue {struct sigqueue *next;siginfo_t info;//挂载信号相关信息};
struct sigpending {struct sigqueue *head, **tail;//挂载队列sigset_t signal;//位图,信号要处理时,设置为1};
struct task_struct {int sigpending; //表示该进程是否有信号需要处理int exit_code, exit_signal;/* Protects signal and blocked */struct signal_struct *sig; //指向具体的信号处理动作sigset_t blocked; //阻塞struct sigpending pending;//位图+信号队列}
intdo_sigaction(int sig, const struct k_sigaction *act, struct k_sigaction *oact){struct k_sigaction *k;if (sig < 1 || sig > _NSIG ||(act && (sig == SIGKILL || sig == SIGSTOP)))//不允许对此信号安装信号处理函数return -EINVAL;k = ¤t->sig->action[sig-1];//获取该信号的旧信号处理函数spin_lock(¤t->sig->siglock);if (oact)*oact = *k;//获取老的信号具体操作if (act) {*k = *act;//获取新的信号处理操作,将阻塞位sigkill跟sigstop删除(不允许屏蔽)sigdelsetmask(&k->sa.sa_mask, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));/** POSIX 3.3.1.3:* "Setting a signal action to SIG_IGN for a signal that is* pending shall cause the pending signal to be discarded,* whether or not it is blocked."** "Setting a signal action to SIG_DFL for a signal that is* pending and whose default action is to ignore the signal* (for example, SIGCHLD), shall cause the pending signal to* be discarded, whether or not it is blocked"** Note the silly behaviour of SIGCHLD: SIG_IGN means that the* signal isn't actually ignored, but does automatic child* reaping, while SIG_DFL is explicitly said by POSIX to force* the signal to be ignored.*/if (k->sa.sa_handler == SIG_IGN|| (k->sa.sa_handler == SIG_DFL&& (sig == SIGCONT ||sig == SIGCHLD ||sig == SIGWINCH))) {spin_lock_irq(¤t->sigmask_lock);if (rm_sig_from_queue(sig, current))//如果设置的处理模式是sig_ign或者sig_del//而涉及的信号是上面3个,那就直接丢弃已到达信号recalc_sigpending(current);//是否有信号等待处理总标志位也需要再计算spin_unlock_irq(¤t->sigmask_lock);}}spin_unlock(¤t->sig->siglock);return 0;}
/** Remove signal sig from t->pending.* Returns 1 if sig was found.** All callers must be holding t->sigmask_lock.*/static int rm_sig_from_queue(int sig, struct task_struct *t){return rm_from_queue(sig, &t->pending);}
static int rm_from_queue(int sig, struct sigpending *s){struct sigqueue *q, **pp;if (!sigismember(&s->signal, sig))//表示该位是否已经置1,一般是已经,否则直接returnreturn 0;sigdelset(&s->signal, sig);//清除该标志位pp = &s->head;while ((q = *pp) != NULL) {if (q->info.si_signo == sig) {//如果队列中的信号等于sig(针对新类型信号)if ((*pp = q->next) == NULL)s->tail = pp;kmem_cache_free(sigqueue_cachep,q);//删除atomic_dec(&nr_queued_signals);//-1continue;}pp = &q->next;}return 1;}
asmlinkage longsys_kill(int pid, int sig){struct siginfo info;//收集相关信息info.si_signo = sig;//信号类型info.si_errno = 0;info.si_code = SI_USER;//用户信号info.si_pid = current->pid;//进程号info.si_uid = current->uid;//uidreturn kill_something_info(sig, &info, pid);}
/** kill_something_info() interprets pid in interesting ways just like kill(2).** POSIX specifies that kill(-1,sig) is unspecified, but what we have* is probably wrong. Should make it like BSD or SYSV.*/static int kill_something_info(int sig, struct siginfo *info, int pid){if (!pid) {//pid==0发送给当前进程的所有进程return kill_pg_info(sig, info, current->pgrp);} else if (pid == -1) { //发送到除当前进程以外的进程int retval = 0, count = 0;struct task_struct * p;read_lock(&tasklist_lock);for_each_task(p) {if (p->pid > 1 && p != current) {int err = send_sig_info(sig, info, p);++count;if (err != -EPERM)retval = err;}}read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);return count ? retval : -ESRCH;} else if (pid < 0) {//小于值,则发送给-pid的进程组return kill_pg_info(sig, info, -pid);} else {return kill_proc_info(sig, info, pid);//发送给具体的进程}}
inline intkill_proc_info(int sig, struct siginfo *info, pid_t pid){int error;struct task_struct *p;read_lock(&tasklist_lock);p = find_task_by_pid(pid);//找到pid对应的task_struct结构error = -ESRCH;if (p)error = send_sig_info(sig, info, p);//发送信号read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);return error;}
int //信号 信号相关信息 接收信号进程的pcbsend_sig_info(int sig, struct siginfo *info, struct task_struct *t){unsigned long flags;int ret;#if DEBUG_SIGprintk("SIG queue (%s:%d): %d ", t->comm, t->pid, sig);#endifret = -EINVAL;if (sig < 0 || sig > _NSIG)//不在信号范围出错goto out_nolock;/* The somewhat baroque permissions check... */ret = -EPERM;if (bad_signal(sig, info, t))//进行错误检查goto out_nolock;/* The null signal is a permissions and process existance probe.No signal is actually delivered. Same goes for zombies. */ret = 0;if (!sig || !t->sig)//如果信号为0或者,不存在对应操作goto out_nolock;spin_lock_irqsave(&t->sigmask_lock, flags);handle_stop_signal(sig, t);//收到某些特定的信号,不可屏蔽一些其他后续信号,这个负责处理/* Optimize away the signal, if it's a signal that can behandled immediately (ie non-blocked and untraced) andthat is ignored (either explicitly or by default). */if (ignored_signal(sig, t))//如果响应是忽略,而且不用跟踪,没有屏蔽,那就不用投递信号goto out;/* Support queueing exactly one non-rt signal, so that wecan get more detailed information about the cause ofthe signal. */if (sig < SIGRTMIN && sigismember(&t->pending.signal, sig))goto out;//老编制的信号,投递,就是把接收信号位图设置为1,不用将信号挂到队列ret = deliver_signal(sig, info, t);out:spin_unlock_irqrestore(&t->sigmask_lock, flags);if ((t->state & TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE) && signal_pending(t))//如果接收的进程处于这个状态,//而且有信号要处理,则唤醒进程wake_up_process(t);out_nolock:#if DEBUG_SIGprintk(" %d -> %d\n", signal_pending(t), ret);#endifreturn ret;}
static int deliver_signal(int sig, struct siginfo *info, struct task_struct *t){int retval = send_signal(sig, info, &t->pending);if (!retval && !sigismember(&t->blocked, sig))signal_wake_up(t);return retval;}
static int send_signal(int sig, struct siginfo *info, struct sigpending *signals){struct sigqueue * q = NULL;//创建一个相关嘟列/* Real-time signals must be queued if sent by sigqueue, orsome other real-time mechanism. It is implementationdefined whether kill() does so. We attempt to do so, onthe principle of least surprise, but since kill is notallowed to fail with EAGAIN when low on memory we justmake sure at least one signal gets delivered and don'tpass on the info struct. */if (atomic_read(&nr_queued_signals) < max_queued_signals) {q = kmem_cache_alloc(sigqueue_cachep, GFP_ATOMIC);}if (q) {atomic_inc(&nr_queued_signals);q->next = NULL;//新创建的,设置为null*signals->tail = q;//指向尾部signals->tail = &q->next;//switch ((unsigned long) info) {case 0:q->info.si_signo = sig;q->info.si_errno = 0;q->info.si_code = SI_USER;q->info.si_pid = current->pid;q->info.si_uid = current->uid;break;case 1:q->info.si_signo = sig;q->info.si_errno = 0;q->info.si_code = SI_KERNEL;q->info.si_pid = 0;q->info.si_uid = 0;break;default:copy_siginfo(&q->info, info);//拷贝相关信息,到队列break;}} else if (sig >= SIGRTMIN && info && (unsigned long)info != 1&& info->si_code != SI_USER) {/** Queue overflow, abort. We may abort if the signal was rt* and sent by user using something other than kill().*/return -EAGAIN;}sigaddset(&signals->signal, sig);//将接收信号,相应位图设置为1return 0;}
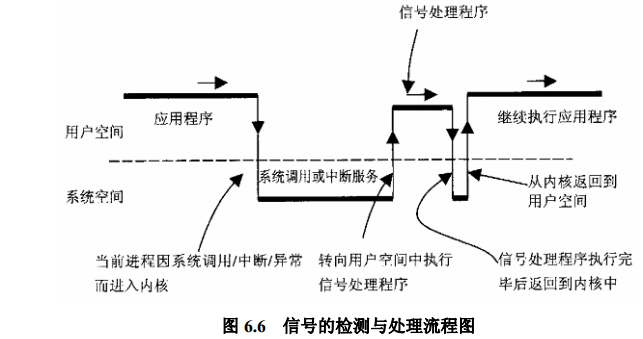
/** Note that 'init' is a special process: it doesn't get signals it doesn't* want to handle. Thus you cannot kill init even with a SIGKILL even by* mistake.*/int do_signal(struct pt_regs *regs, sigset_t *oldset){siginfo_t info;struct k_sigaction *ka;/** We want the common case to go fast, which* is why we may in certain cases get here from* kernel mode. Just return without doing anything* if so.*/if ((regs->xcs & 3) != 3)return 1;if (!oldset)//如果为0oldset = ¤t->blocked;//获取其屏蔽信号for (;;) {unsigned long signr;spin_lock_irq(¤t->sigmask_lock);signr = dequeue_signal(¤t->blocked, &info);//取出一个没屏蔽的信号spin_unlock_irq(¤t->sigmask_lock);if (!signr)//如果为0则跳出(因为表示当前没有这样的信号了)break;//如果当前if ((current->ptrace & PT_PTRACED) && signr != SIGKILL) {/* Let the debugger run. */current->exit_code = signr;current->state = TASK_STOPPED;notify_parent(current, SIGCHLD);schedule();/* We're back. Did the debugger cancel the sig? */if (!(signr = current->exit_code))continue;current->exit_code = 0;/* The debugger continued. Ignore SIGSTOP. */if (signr == SIGSTOP)continue;/* Update the siginfo structure. Is this good? */if (signr != info.si_signo) {info.si_signo = signr;info.si_errno = 0;info.si_code = SI_USER;info.si_pid = current->p_pptr->pid;info.si_uid = current->p_pptr->uid;}/* If the (new) signal is now blocked, requeue it. */if (sigismember(¤t->blocked, signr)) {send_sig_info(signr, &info, current);continue;}}ka = ¤t->sig->action[signr-1];//获取信号向量if (ka->sa.sa_handler == SIG_IGN) {//如果对应的处理是SIG_IGNif (signr != SIGCHLD)//忽略则继续取没屏蔽信号,处理continue;//是儿子信号则等待所有子进程退出/* Check for SIGCHLD: it's special. */while (sys_wait4(-1, NULL, WNOHANG, NULL) > 0)/* nothing */;continue;}//信号向量设置为SIG_DFLif (ka->sa.sa_handler == SIG_DFL) {int exit_code = signr;/* Init gets no signals it doesn't want. */if (current->pid == 1)//不可以对init进程发送相关信号continue;switch (signr) {case SIGCONT: case SIGCHLD: case SIGWINCH:continue;//如果是SIGCONT之类,continue继续处理信号case SIGTSTP: case SIGTTIN: case SIGTTOU:if (is_orphaned_pgrp(current->pgrp))continue;/* FALLTHRU */case SIGSTOP://如果是sigstop信号current->state = TASK_STOPPED;//设置标志位current->exit_code = signr;if (!(current->p_pptr->sig->action[SIGCHLD-1].sa.sa_flags & SA_NOCLDSTOP))notify_parent(current, SIGCHLD);schedule();continue;case SIGQUIT: case SIGILL: case SIGTRAP:case SIGABRT: case SIGFPE: case SIGSEGV:case SIGBUS: case SIGSYS: case SIGXCPU: case SIGXFSZ:if (do_coredump(signr, regs))//这类信号默认处理exit_code |= 0x80;/* FALLTHRU */default://多数信号的默认处理sigaddset(¤t->pending.signal, signr);//猜想设置此位表示默认处理,留给父进程查看信息recalc_sigpending(current);//检查进程是否有非阻塞的挂起信号current->flags |= PF_SIGNALED;do_exit(exit_code);//结束接收信号的进程/* NOTREACHED */}}/* Reenable any watchpoints before delivering the* signal to user space. The processor register will* have been cleared if the watchpoint triggered* inside the kernel.*/__asm__("movl %0,%%db7" : : "r" (current->thread.debugreg[7]));/* Whee! Actually deliver the signal. */handle_signal(signr, ka, &info, oldset, regs);return 1;}/* Did we come from a system call? */if (regs->orig_eax >= 0) {/* Restart the system call - no handlers present */if (regs->eax == -ERESTARTNOHAND ||regs->eax == -ERESTARTSYS ||regs->eax == -ERESTARTNOINTR) {regs->eax = regs->orig_eax;regs->eip -= 2;}}return 0;}

linux内核情景分析之信号实现的更多相关文章
- linux内核情景分析之execve()
用来描述用户态的cpu寄存器在内核栈中保存情况.可以获取用户空间的信息 struct pt_regs { long ebx; //可执行文件路径的指针(regs.ebx中 long ecx; //命令 ...
- Linux内核情景分析之消息队列
早期的Unix通信只有管道与信号,管道的缺点: 所载送的信息是无格式的字节流,不知道分界线在哪,也没通信规范,另外缺乏控制手段,比如保温优先级,管道机制的大小只有1页,管道很容易写满而读取没有及时,发 ...
- Linux内核情景分析之异常访问,用户堆栈的扩展
情景假设: 在堆内存中申请了一块内存,然后释放掉该内存,然后再去访问这块内存.也就是所说的野指针访问. 当cpu产生页面错误时,会把失败的线性地址放在cr2寄存器.线性地址缺页异常的4种情况 1.如果 ...
- Linux内核情景分析的alloc_pages
NUMA结构的alloc_pages ==================== mm/numa.c 43 43 ==================== 43 #ifdef CONFIG_DISCON ...
- linux内核情景分析之exit与Wait
//第一层系统调用 asmlinkage long sys_exit(int error_code) { do_exit((error_code&0xff)<<8); } 其主体是 ...
- linux内核情景分析之内核中的互斥操作
信号量机制: struct sempahore是其结构,定义如下 struct semaphore { atomic_t count;//资源数目 int sleepers;//等待进程数目 wait ...
- linux内核情景分析之匿名管道
管道的机制由pipe()创建,由pipe()所建立的管道两端都在同一进程.所以必须在fork的配合下,才可以在具有亲缘关系的进程通信 /* * sys_pipe() is the normal C c ...
- linux内核情景分析之命名管道
管道是一种"无名","无形文件,只可以近亲进程使用,不可以再任意两个进程通信使用,所以只能实现"有名","有形"的文件来实现就可以 ...
- linux内核情景分析之强制性调度
从系统调用返回到用户空间是否调度,从ret_with_reschedule可看出,是否真正调度,取决于当前进程的pcb中的need_resched是否设置为1,那如何设置为1取决于以下几种情况: 时间 ...
随机推荐
- Ansible学习 Inventory文件
Ansible可同时操作属于一个组的多台主机,组与主机之间关系配置在inventory文件中,inventory默认的配置文件是/etc/ansible/hosts 1.在/etc/ansible/h ...
- js操作地址栏
//判断地址里是否有?号,如果没有就从最后一个/截到最后,如果有?就从最后一个/截至?号处 listTable.url = location.href.lastIndexOf("?" ...
- awk速查手册
简介awk是一个强大的文本分析工具,相对于grep的查找,sed的编辑,awk在其对数据分析并生成报告时,显得尤为强大.简单来说awk就是把文件逐行的读入,以空格为默认分隔符将每行切片,切开的部分再进 ...
- python面向对象之反射和内置方法
一.静态方法(staticmethod)和类方法(classmethod) 类方法:有个默认参数cls,并且可以直接用类名去调用,可以与类属性交互(也就是可以使用类属性) 静态方法:让类里的方法直接被 ...
- HDU - 6514 Monitor(二维差分)
题意 给定一个\(n×m\)的矩阵.(\(n×m <= 1e7\)). \(p\)次操作,每次可以在这个矩阵中覆盖一个矩形. \(q\)次询问,每次问一个矩形区域中,是否所有的点都被覆盖. 解析 ...
- 笔记-python-tutorial-8.errors and exceptions
笔记-python-tutorial-8.errors and exceptions 1. errors and exceptions 1.1. syntax errors >& ...
- spark 对hbase 操作
本文将分两部分介绍,第一部分讲解使用 HBase 新版 API 进行 CRUD 基本操作:第二部分讲解如何将 Spark 内的 RDDs 写入 HBase 的表中,反之,HBase 中的表又是如何以 ...
- input框中的必填项之取消当前input框为必填项
html5新增了一个required属性,可以使用这个属性对文本框设置必填项,直接在input文本框上添加required即可 . 效果如图:
- 将FragmentManger事务添加到返回栈中
FragmentManger事务添加或替换的 Fragment 后,这时点击 Back 键,程序并不会返回添加之前的状态. 我们可以使用 Transaction 对象的 addToBackStack( ...
- IOS开发学习笔记019-动态创建控件
动态创建控件 一.按钮 二.文本输入框 三.lable标签 注意: 只是简单的拖拽控件会毁了你,所以最好还是手动通过代码创建控件. 如果要通过代码生成按钮的话,可以在系统自带的函数viewDidLoa ...
