Ubuntu环境下C++使用onnxruntime和Opencv进行YOLOv8模型部署
目录
环境配置
系统环境
Ubuntu18.04
onnxruntime-linux-x64 1.12.1:https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime/releases
opencv 3.4.3
cmake 3.10.2
项目文件路径
1. bin:存放可执行程序和识别结果
2. data:存放数据集
3. src:存放源程序
4. include:存放头文件
5. config.txt:配置文件,内容分别是模型相对路径、图片相对路径、缺陷标识文件相对路径、缺陷识别阈值、缺陷重叠阈值
6. type.names:缺陷标识文件,内容和模型识别的缺陷标识顺序需要一致
文件环境
config.txt
分别表示模型相对路径、图片相对路径、缺陷标识文件相对路径、缺陷识别阈值、缺陷重叠阈值
../models/best.onnx
../data/2.bmp
../type.names
0.4
0.4
CMakeLists.txt
需要更改的地方已经在里面标注好了
# 项目名称,随便写
PROJECT(image_onnx)
# cmake版本,根据自己的写
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
# 编译好的可执行文件放置的位置
set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${image_onnx_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
# find required opencv
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
# directory of opencv headers
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# 根据自己的onnxruntime存放路径编写
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT_PATH /home/ebaina/onnxruntime-linux-x64-1.12.1/)
set(ONNXRUNTIME_INCLUDE_DIRS ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT_PATH}/include/)
set(ONNXRUNTIME_LIB ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT_PATH}lib/libonnxruntime.so)
# 需要编译的cpp文件所在路径,前面是编译好的可执行文件名
add_executable(image_onnx src/main_image.cpp
src/change_image.cpp
src/adjust_result.cpp)
# directory of opencv library
link_directories(${OpenCV_LIBRARY_DIRS})
# opencv libraries
target_link_libraries(image_onnx ${OpenCV_LIBS})
include_directories(${ONNXRUNTIME_INCLUDE_DIRS})
target_link_libraries(image_onnx ${ONNXRUNTIME_LIB})
# include
target_include_directories(image_onnx
PRIVATE
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include
)type.names
缺陷标志文件,内容和模型识别的缺陷标识顺序需要一致,模型识别网站:Netron
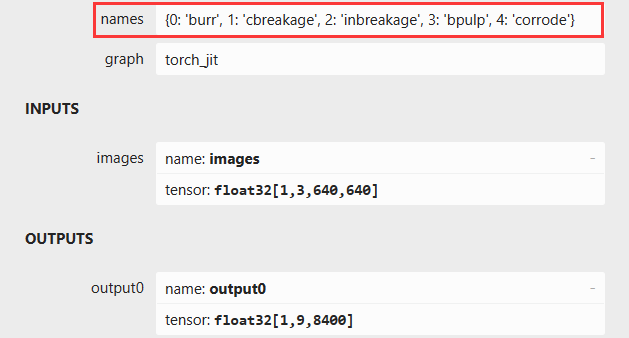
burr
cbreakage
inbreakage
bpulp
corrode
读取config.txt配置文件
// 自动读取模型路径,图片路径,缺陷阈值,重叠阈值
std::string model_path_;
std::string imgPath;
std::string namesPath;
float threshold;
float nms_threshold;
// 打开配置文件并读取配置
std::ifstream configFile("../config.txt");
if (configFile.is_open()) {
configFile >> model_path_ >> imgPath >> namesPath >> threshold >> nms_threshold;
configFile.close();
std::cout << "Model Path: " << model_path_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Image Path: " << imgPath << std::endl;
std::cout << "Names Path: " << namesPath << std::endl;
std::cout << "Threshold: " << threshold << std::endl;
std::cout << "NMS Threshold: " << nms_threshold << std::endl;
} else
std::cerr << "Failed to open config file." << std::endl;
const char* model_path = model_path_.c_str();修改图片尺寸格式
// 图片变换
cv::Mat inputImage = cv::imread(imgPath);
if (inputImage.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to load image." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 获取图片尺寸
int y = inputImage.rows;
int x = inputImage.cols;
// 图片尺寸变换
cv::Mat image0 = resizeImage(inputImage, y, x);
// 图像归一化
std::vector<float> input_image_ = nchwImage(image0);读取缺陷标志文件
// 读取缺陷标志文件
std::ifstream inputFile(namesPath);
if (!inputFile.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open the file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::vector<std::string> typeNames;
std::string line;
while (std::getline(inputFile, line))
typeNames.push_back(line);
inputFile.close();生成缺陷随机颜色标识
// 缺陷颜色标识随机
int numColors = typeNames.size();
std::vector<std::vector<int>> colors;
for (int i = 0; i < numColors; ++i)
colors.push_back(generateRandomColor());
// // 打印颜色种类
// for (const auto &color : colors)
// std::cout << "R: " << color[0] << ", G: " << color[1] << ", B: " << color[2] << std::endl;模型推理
// 模型设置和推理结果
Ort::Env env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "Default");
// CPU
Ort::Session session_{env, model_path, Ort::SessionOptions{nullptr}};
// 模型输入尺寸
static constexpr const int height_ = 640; //model input height
static constexpr const int width_ = 640; //model input width
Ort::Value input_tensor_{nullptr};
std::array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_{1, 3, height_, width_}; //mode input shape NCHW = 1x3xHxW
// 模型输出尺寸
Ort::Value output_tensor_{nullptr};
std::array<int64_t, 3> output_shape_{1, 9, 8400}; //model output shape,
std::array<_Float32, 9*8400> results_{};
// 模型输入输出张量设置
auto memory_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeDefault);
input_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, input_image_.data(), input_image_.size(), input_shape_.data(), input_shape_.size());
output_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, results_.data(), results_.size(), output_shape_.data(), output_shape_.size());
// 查看模型输入输出的名称
const char* input_names[] = {"images"};
const char* output_names[] = {"output0"};
// 推理
session_.Run(Ort::RunOptions{nullptr}, input_names, &input_tensor_, 1, output_names, &output_tensor_, 1);
float* out = output_tensor_.GetTensorMutableData<float>();推理结果获取
// 推理结果获取
int rows = 9; // 第二维度大小,即行数
int cols = 8400; // 第三维度大小,即列数
std::vector<std::vector<float>> matrix(rows, std::vector<float>(cols));
for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row)
for (int col = 0; col < cols; ++col)
matrix[row][col] = out[row * cols + col];
// 9,8400数组转置为8400,9
std::vector<std::vector<float>> tran_matrix = transpose(matrix);
// // 显示缺陷筛选结果
// std::vector<std::vector<float>> num = tran_matrix;
// for (size_t n = 0; n < num.size(); ++n) {
// bool aboveThreshold = false;
// for (size_t col = 4; col <= 8; ++col)
// if (num[n][col] > threshold) {
// aboveThreshold = true;
// break;
// }
// if (aboveThreshold) {
// std::cout << "Row " << n << ": ";
// for (const auto& val : num[n])
// std::cout << val << " ";
// std::cout << std::endl;
// }
// }缺陷信息还原并显示
// 缺陷还原
std::vector<std::vector<double>> select_matrix;
select_matrix = select(tran_matrix, threshold, cols,rows);
// 缺陷位置信息还原
select_matrix = return_(select_matrix, y, x);
// 缺陷位置信息筛选
select_matrix = nms_(select_matrix, nms_threshold);
// // 打印数组的内容
// for (const auto& row : select_matrix){
// for (const auto& value : row) {
// std::cout << value << " ";
// }
// std::cout << std::endl;
// }
// 绘制识别框
cv::Mat outputImage = draw_image(select_matrix, inputImage, typeNames, colors);
// 自定义窗口大小
int windowWidth = 1200;
int windowHeight = 900;
// 调整窗口大小
cv::namedWindow("Image with Bounding Boxes", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::resizeWindow("Image with Bounding Boxes", windowWidth, windowHeight);
cv::imshow("Image with Bounding Boxes", outputImage);
cv::imwrite("marked_image.jpg", outputImage);
cv::waitKey(0);main代码(关注取源码!)
#include <assert.h>
#include <random>
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>
#include "cpu_provider_factory.h"
#include <adjust_result.h>
// 随机生成颜色
std::vector<int> generateRandomColor() {
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> dis(0.0, 1.0);
std::vector<int> color(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
color[i] = static_cast<int>(dis(gen) * 255);
}
return color;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// // 模型路径,图片路径,缺陷阈值,重叠阈值
// const char* model_path = "../models/best.onnx";
// std::string imgPath = "../data/3.bmp";
// std::string namesPath = "../type.names";
// float threshold = 0.4;
// float nms_threshold = 0.4;
// 自动读取模型路径,图片路径,缺陷阈值,重叠阈值
std::string model_path_;
std::string imgPath;
std::string namesPath;
float threshold;
float nms_threshold;
// 打开配置文件并读取配置
std::ifstream configFile("../config.txt");
if (configFile.is_open()) {
configFile >> model_path_ >> imgPath >> namesPath >> threshold >> nms_threshold;
configFile.close();
std::cout << "Model Path: " << model_path_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Image Path: " << imgPath << std::endl;
std::cout << "Names Path: " << namesPath << std::endl;
std::cout << "Threshold: " << threshold << std::endl;
std::cout << "NMS Threshold: " << nms_threshold << std::endl;
} else
std::cerr << "Failed to open config file." << std::endl;
const char* model_path = model_path_.c_str();
// 图片变换
cv::Mat inputImage = cv::imread(imgPath);
if (inputImage.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to load image." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 获取图片尺寸
int y = inputImage.rows;
int x = inputImage.cols;
// 图片尺寸变换
cv::Mat image0 = resizeImage(inputImage, y, x);
// 图像归一化
std::vector<float> input_image_ = nchwImage(image0);
// 读取缺陷标志文件
std::ifstream inputFile(namesPath);
if (!inputFile.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open the file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::vector<std::string> typeNames;
std::string line;
while (std::getline(inputFile, line))
typeNames.push_back(line);
inputFile.close();
// // 打印缺陷标志文件内容
// std::cout << "Number of elements: " << typeNames.size() << std::endl;
// for (const std::string &typeName : typeNames)
// std::cout << typeName << std::endl;
// 缺陷颜色标识随机
int numColors = typeNames.size();
std::vector<std::vector<int>> colors;
for (int i = 0; i < numColors; ++i)
colors.push_back(generateRandomColor());
// // 打印颜色种类
// for (const auto &color : colors)
// std::cout << "R: " << color[0] << ", G: " << color[1] << ", B: " << color[2] << std::endl;
// 模型设置和推理结果
Ort::Env env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "Default");
// CPU
Ort::Session session_{env, model_path, Ort::SessionOptions{nullptr}};
// 模型输入尺寸
static constexpr const int height_ = 640; //model input height
static constexpr const int width_ = 640; //model input width
Ort::Value input_tensor_{nullptr};
std::array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_{1, 3, height_, width_}; //mode input shape NCHW = 1x3xHxW
// 模型输出尺寸
Ort::Value output_tensor_{nullptr};
std::array<int64_t, 3> output_shape_{1, 9, 8400}; //model output shape,
std::array<_Float32, 9*8400> results_{};
// 模型输入输出张量设置
auto memory_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeDefault);
input_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, input_image_.data(), input_image_.size(), input_shape_.data(), input_shape_.size());
output_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, results_.data(), results_.size(), output_shape_.data(), output_shape_.size());
// 查看模型输入输出的名称
const char* input_names[] = {"images"};
const char* output_names[] = {"output0"};
// 推理
session_.Run(Ort::RunOptions{nullptr}, input_names, &input_tensor_, 1, output_names, &output_tensor_, 1);
float* out = output_tensor_.GetTensorMutableData<float>();
// 推理结果获取
int rows = 9; // 第二维度大小,即行数
int cols = 8400; // 第三维度大小,即列数
std::vector<std::vector<float>> matrix(rows, std::vector<float>(cols));
for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row)
for (int col = 0; col < cols; ++col)
matrix[row][col] = out[row * cols + col];
// 9,8400数组转置为8400,9
std::vector<std::vector<float>> tran_matrix = transpose(matrix);
// // 显示缺陷筛选结果
// std::vector<std::vector<float>> num = tran_matrix;
// for (size_t n = 0; n < num.size(); ++n) {
// bool aboveThreshold = false;
// for (size_t col = 4; col <= 8; ++col)
// if (num[n][col] > threshold) {
// aboveThreshold = true;
// break;
// }
// if (aboveThreshold) {
// std::cout << "Row " << n << ": ";
// for (const auto& val : num[n])
// std::cout << val << " ";
// std::cout << std::endl;
// }
// }
// 缺陷还原
std::vector<std::vector<double>> select_matrix;
select_matrix = select(tran_matrix, threshold, cols,rows);
// 缺陷位置信息还原
select_matrix = return_(select_matrix, y, x);
// 缺陷位置信息筛选
select_matrix = nms_(select_matrix, nms_threshold);
// // 打印数组的内容
// for (const auto& row : select_matrix){
// for (const auto& value : row) {
// std::cout << value << " ";
// }
// std::cout << std::endl;
// }
// 绘制识别框
cv::Mat outputImage = draw_image(select_matrix, inputImage, typeNames, colors);
// 自定义窗口大小
int windowWidth = 1200;
int windowHeight = 900;
// 调整窗口大小
cv::namedWindow("Image with Bounding Boxes", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::resizeWindow("Image with Bounding Boxes", windowWidth, windowHeight);
cv::imshow("Image with Bounding Boxes", outputImage);
cv::imwrite("marked_image.jpg", outputImage);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}Ubuntu环境下C++使用onnxruntime和Opencv进行YOLOv8模型部署的更多相关文章
- Linux(Ubuntu)环境下使用Fiddler
自己的开发环境是Ubuntu, 对于很多优秀的软件但是又没有Linux版本这件事,还是有点遗憾的.比如最近遇到一个问题,在分析某个网站的请求路径和cookie时就遇到了问题.本来Chome浏览器自带的 ...
- Go学习笔记(一):Ubuntu 环境下Go的安装
本文是根据<Go Web 编程>,逐步学习 Ubuntu 环境下go的安装的笔记. <Go Web 编程>的URL地址如下: https://github.com/astaxi ...
- Ubuntu环境下SSH的安装及使用
Ubuntu环境下SSH的安装及使用 SSH是指Secure Shell,是一种安全的传输协议,Ubuntu客户端可以通过SSH访问远程服务器 .SSH的简介和工作机制可参看上篇文章SSH简介及工作机 ...
- Ubuntu环境下的Redis 配置与C++使用入门
Redis是一个高性能的key-value数据库. Redisedis的出现,非常大程度补偿了memcached这类key/value存储的不足,在部分场合能够对关系数据库起到非常好的补充作用.它 ...
- ubuntu环境下docker安装步骤
本文是根据docker官方文档翻译,原文:https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/linux/ubuntulinux/ Docker 支持以下 Ubun ...
- ubuntu 环境下的QT程序打包
很多的时候 需要将自己写的QT 程序发布一下 所以今天教一下 怎么在ubuntu 环境下将自己的写的Qt 程序打包打包是为了不依赖 开发环境 和开发的库. 1. QtCreate使用Release版 ...
- ubuntu环境下eclipse的安装以及hadoop插件的配置
ubuntu环境下eclipse的安装以及hadoop插件的配置 一.eclipse的安装 在ubuntu桌面模式下,点击任务栏中的ubuntu软件中心,在搜索栏搜索eclipse 注意:安装过程需要 ...
- Ubuntu环境下No module named '_tkinter'错误的解决
在Ubuntu环境下运行下面代码: import matplotlib as plt 出现以下错误: No module named '_tkinter' 解决方法: sudo apt-get ins ...
- Ubuntu环境下配置GCC
Ubuntu网络环境下安装GCC及其头文件步骤: 1.Ubuntu环境下配置GCC 刚装好的GCC什么都不能编译,因为没有一些必须的头文件,所以要安装build-essential,安装了这个包会安装 ...
- 在Ubuntu环境下配置NIMH MEG Core Facility之CTF Tools
在Ubuntu环境下配置NIMH MEG Core Facility之CTF Tools 网站有提示: The install script won't work, but you can copy ...
随机推荐
- 是时候丢掉BeanUtils了
前言 为了更好的进行开发和维护,我们都会对程序进行分层设计,例如常见的三层,四层,每层各司其职,相互配合.也随着分层,出现了VO,BO,PO,DTO,每层都会处理自己的数据对象,然后向上传递,这就避免 ...
- Node.js安装中出现的问题及其解决方案
Node.js安装与配置流程,请参考 1.npm -v测试时出现警告 更好的选择是安装一个更完善的版本 问题出现的原因 node更新后是最新版 但是npm的版本没有相应的更新存在版本滞后导致问题出现 ...
- ATtiny88初体验(三):串口
ATtiny88初体验(三):串口 ATtiny88单片机不包含串口模块,因此只能使用软件方式模拟串口时序. 串口通信时序通常由起始位.数据位.校验位和停止位四个部分组成,常见的配置为1位起始位.8位 ...
- embed简介
go embed 是 Go 1.16 中引入的特性,它允许将文件嵌入到 Go 代码中,以便在运行时访问这些文件.这对于将静态资源(如 HTML.CSS.JavaScript 文件)直接嵌入到 Go 二 ...
- Redis的五大数据类型的数据结构
概述 Redis底层有六种数据类型包括:简单动态字符串.双向链表.压缩列表.哈希表.跳表和整数数组.这六种数据结构五大数据类型关系如下: String:简单动态字符串 List:双向链表.压缩列表 ...
- C++ 算法竞赛、02 周赛篇 | AcWing 第2场周赛
AcWing 第2场周赛 竞赛 - AcWing 3626 三元一次方程 AcWing 3626. 三元一次方程 - AcWing 两层循环 #include <iostream> usi ...
- 详细解释一下Spring是如何解决循环依赖问题的
Spring是如何解决循环依赖问题的? 我们都知道,如果在代码中,将两个或多个Bean互相之间持有对方的引用就会发生循环依赖.循环的依赖将会导致注入死循环,这是Spring发生循环依赖的原因 循环依赖 ...
- 2.10 PE结构:重建重定位表结构
Relocation(重定位)是一种将程序中的一些地址修正为运行时可用的实际地址的机制.在程序编译过程中,由于程序中使用了各种全局变量和函数,这些变量和函数的地址还没有确定,因此它们的地址只能暂时使用 ...
- 制作一个内部的 zabbix-agent 快速部署脚本
下载官方的基础 agent 部署包 官方地址:点击到达 curl -O https://cdn.zabbix.com/zabbix/binaries/stable/5.0/5.0.36/zabbix_ ...
- 关于关闭Sublime Text自动更新提示
Sublime Text默认提示自动更新,实在让人烦不胜烦,那么有没有办法解决嘞,那当然是有的,下面就教你如何关闭Sublime Text自动更新提示 首先注册,不注册的话,一切操作都没有用:(注册码 ...