《机器学习Python实现_10_06_集成学习_boosting_gbdt分类实现》
一.利用回归树实现分类
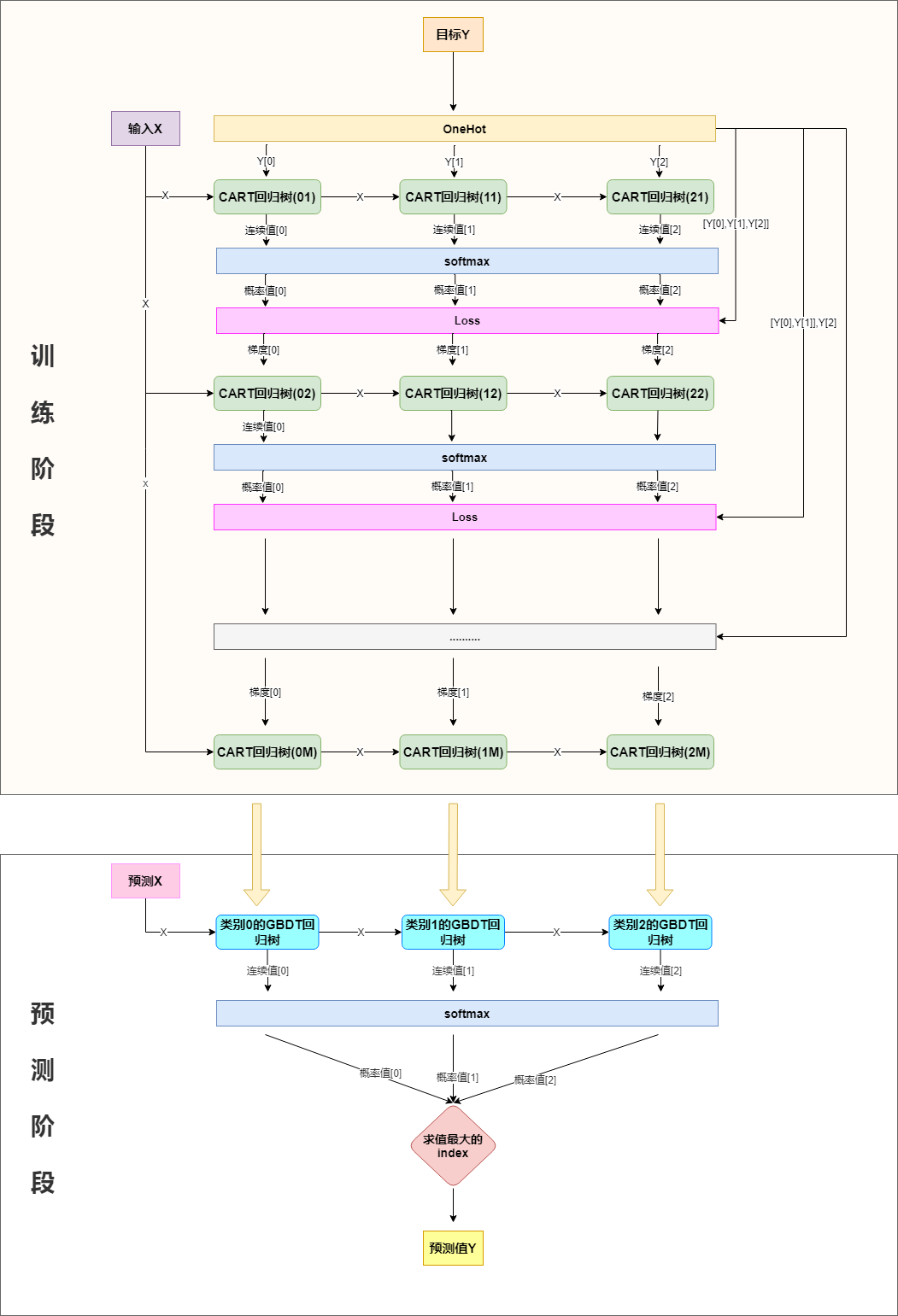
分类也可以用回归树来做,简单说来就是训练与类别数相同的几组回归树,每一组代表一个类别,然后对所有组的输出进行softmax操作将其转换为概率分布,然后再通过交叉熵或者KL一类的损失函数求每颗树相应的负梯度,指导下一轮的训练,以三分类为例,流程如下:
二.softmax+交叉熵损失,及其梯度求解
分类问题,一般会选择用交叉熵作为损失函数,下面对softmax+交叉熵损失函数的梯度做推导:
softmax函数在最大熵那一节已有使用,再回顾一下:
\]
交叉熵在logistic回归有介绍:
\]
将\(p_i\)替换为\(\frac{e^{y_i^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\)即是我们的损失函数:
=-\sum_{i=1}^n y_i(y_i^{hat}-log\sum_{j=1}^n e^{y_j^{hat}})\\
=log\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}-\sum_{i=1}^ny_iy_i^{hat}(由于是onehot展开,所以\sum_{i=1}^n y_i=1)
\]
计算梯度:
\]
所以,第一组回归树的拟合目标为\(y_1-\frac{e^{y_1^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\),第二组回归树学习的拟合目标为\(y_2-\frac{e^{y_2^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\),....,第\(n\)组回归树的拟合目标为\(y_n-\frac{e^{y_n^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\)
三.代码实现
import os
os.chdir('../')
from ml_models.tree import CARTRegressor
from ml_models import utils
import copy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
class GradientBoostingClassifier(object):
def __init__(self, base_estimator=None, n_estimators=10, learning_rate=1.0):
"""
:param base_estimator: 基学习器,允许异质;异质的情况下使用列表传入比如[estimator1,estimator2,...,estimator10],这时n_estimators会失效;
同质的情况,单个estimator会被copy成n_estimators份
:param n_estimators: 基学习器迭代数量
:param learning_rate: 学习率,降低后续基学习器的权重,避免过拟合
"""
self.base_estimator = base_estimator
self.n_estimators = n_estimators
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
if self.base_estimator is None:
# 默认使用决策树桩
self.base_estimator = CARTRegressor(max_depth=2)
# 同质分类器
if type(base_estimator) != list:
estimator = self.base_estimator
self.base_estimator = [copy.deepcopy(estimator) for _ in range(0, self.n_estimators)]
# 异质分类器
else:
self.n_estimators = len(self.base_estimator)
# 扩展class_num组分类器
self.expand_base_estimators = []
def fit(self, x, y):
# 将y转one-hot编码
class_num = np.amax(y) + 1
y_cate = np.zeros(shape=(len(y), class_num))
y_cate[np.arange(len(y)), y] = 1
# 扩展分类器
self.expand_base_estimators = [copy.deepcopy(self.base_estimator) for _ in range(class_num)]
# 拟合第一个模型
y_pred_score_ = []
# TODO:并行优化
for class_index in range(0, class_num):
self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][0].fit(x, y_cate[:, class_index])
y_pred_score_.append(self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][0].predict(x))
y_pred_score_ = np.c_[y_pred_score_].T
# 计算负梯度
new_y = y_cate - utils.softmax(y_pred_score_)
# 训练后续模型
for index in range(1, self.n_estimators):
y_pred_score = []
for class_index in range(0, class_num):
self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][index].fit(x, new_y[:, class_index])
y_pred_score.append(self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][index].predict(x))
y_pred_score_ += np.c_[y_pred_score].T * self.learning_rate
new_y = y_cate - utils.softmax(y_pred_score_)
def predict_proba(self, x):
# TODO:并行优化
y_pred_score = []
for class_index in range(0, len(self.expand_base_estimators)):
estimator_of_index = self.expand_base_estimators[class_index]
y_pred_score.append(
np.sum(
[estimator_of_index[0].predict(x)] +
[self.learning_rate * estimator_of_index[i].predict(x) for i in
range(1, self.n_estimators - 1)] +
[estimator_of_index[self.n_estimators - 1].predict(x)]
, axis=0)
)
return utils.softmax(np.c_[y_pred_score].T)
def predict(self, x):
return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x), axis=1)
#造伪数据
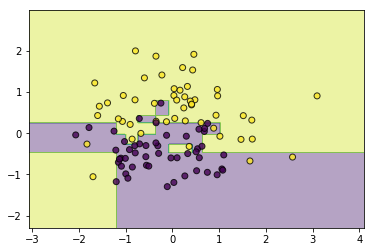
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=.5,random_state=21)
# 同质
classifier = GradientBoostingClassifier(base_estimator=CARTRegressor(),n_estimators=10)
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
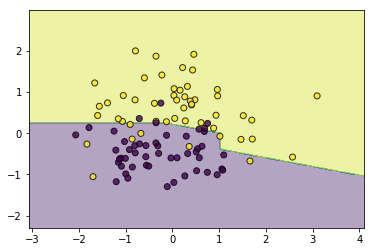
#异质
from ml_models.linear_model import LinearRegression
classifier = GradientBoostingClassifier(base_estimator=[LinearRegression(),LinearRegression(),LinearRegression(),CARTRegressor(max_depth=2)])
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
《机器学习Python实现_10_06_集成学习_boosting_gbdt分类实现》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- 剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 Offer 21 这题的解法其实是考察快慢指针和头尾指针. package com.walegarrett.offer; /** * @Aut ...
- rsyslog日志总结
rsyslog日志总结 一 rsyslog介绍 syslogd被rsyslog取代 将日志写入数据库 可以利用模块和插件控制输入输出 rsyslog程序管理本地和远程日志 安装软件 根据需求修改配置文 ...
- Linux增删改查移文件、文件夹
关于Linux中文件基本处理命令 (1)添加文件.文件夹(图例):touch Demo命令创建文件(Demo)为文件名. 即mkdir Temp命令为创建文件夹(Temp)为文件夹名. 创建文件.文件 ...
- Fedora一键安装NVIDIA显卡驱动Fedora28+
这是一篇以前写的文章,写在CSDN的,现在不想使用CSDN了,就把笔记写在了博客源,后续考虑建立自己的博客,每一个CRUD程序员都想建立自己的博客吧,我猜是的 进入正题 rpm fusion源包含Nv ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 190
A Very Very Primitive Game int main() { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; if(c == 0 ...
- P1725 琪露诺 题解(单调队列)
题目链接 琪露诺 解题思路 单调队列优化的\(dp\). 状态转移方程:\(f[i]=max{f[i-l],f[i-l+1],...,f[i-r-1],f[i-r]}+a[i]\) 考虑单调队列优化. ...
- AES加密--适用于RC2、RC4和Blowfish
package test; import java.security.GeneralSecurityException; import java.security.Key; import javax. ...
- AmazonS3 使用AWS SDK for Java实现跨源资源共享 (CORS)
CORS 配置 创建 CORS 配置并对存储桶设置该配置 通过添加规则来检索并修改配置 向存储桶添加修改过的配置 删除配置 import com.amazonaws.AmazonServiceExce ...
- wget 爬取网站网页
相应的安装命名 yum -y install wget yum -y install setup yum -y install perl wget -r -p -np -k -E http:// ...
- Nodejs学习笔记(3) 创建服务器:Web 模块(http)与 express 框架
目录 参考资料 1. 使用 http 模块创建服务器 1.1 实现思路及代码 1.2 HTTP 结构 1.2.1 Request中的重要字段 1.2.2 Response 头信息:文件类型.状态码.连 ...
