本文介绍如何使用 Docker Swarm 来部署 Nebula Graph 集群,并部署客户端负载均衡和高可用
本文作者系:视野金服工程师 | 吴海胜
首发于 Nebula Graph 论坛:https://discuss.nebula-graph.com.cn/t/topic/1388
一、前言
本文介绍如何使用 Docker Swarm 来部署 Nebula Graph 集群,并部署客户端负载均衡和高可用。

二、nebula 集群搭建
2.1 环境准备
机器准备
| ip | 内存(Gb) | cpu(核数) |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.166 | 16 | 4 |
| 192.168.1.167 | 16 | 4 |
| 192.168.1.168 | 16 | 4 |
在安装前确保所有机器已安装 Docker
2.2 初始化 swarm 集群
在 192.168.1.166 机器上执行
$ docker swarm init --advertise-addr 192.168.1.166
Swarm initialized: current node (dxn1zf6l61qsb1josjja83ngz) is now a manager.
To add a worker to this swarm, run the following command:
docker swarm join \
--token SWMTKN-1-49nj1cmql0jkz5s954yi3oex3nedyz0fb0xx14ie39trti4wxv-8vxv8rssmk743ojnwacrr2e7c \
192.168.1.166:2377
To add a manager to this swarm, run 'docker swarm join-token manager' and follow the instructions.
2.3 加入 worker 节点
根据 init 命令提示内容,加入 swarm worker 节点,在 192.168.1.167 192.168.1.168 分别执行
docker swarm join \
--token SWMTKN-1-49nj1cmql0jkz5s954yi3oex3nedyz0fb0xx14ie39trti4wxv-8vxv8rssmk743ojnwacrr2e7c \
192.168.1.166:2377
2.4 验证集群
docker node ls
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION
h0az2wzqetpwhl9ybu76yxaen * KF2-DATA-166 Ready Active Reachable 18.06.1-ce
q6jripaolxsl7xqv3cmv5pxji KF2-DATA-167 Ready Active Leader 18.06.1-ce
h1iql1uvm7123h3gon9so69dy KF2-DATA-168 Ready Active 18.06.1-ce
2.5 配置 docker stack
vi docker-stack.yml
配置如下内容
version: '3.6'
services:
metad0:
image: vesoft/nebula-metad:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.166
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.166
- --port=45500
- --data_path=/data/meta
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-166
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.166:11000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 11000
published: 11000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 11002
published: 11002
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 45500
published: 45500
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-metad0:/data/meta
- logs-metad0:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
metad1:
image: vesoft/nebula-metad:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.167
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.167
- --port=45500
- --data_path=/data/meta
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-167
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.167:11000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 11000
published: 11000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 11002
published: 11002
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 45500
published: 45500
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-metad1:/data/meta
- logs-metad1:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
metad2:
image: vesoft/nebula-metad:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.168
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.168
- --port=45500
- --data_path=/data/meta
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-168
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.168:11000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 11000
published: 11000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 11002
published: 11002
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 45500
published: 45500
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-metad2:/data/meta
- logs-metad2:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
storaged0:
image: vesoft/nebula-storaged:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.166
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.166
- --port=44500
- --data_path=/data/storage
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-166
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.166:12000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 12000
published: 12000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 12002
published: 12002
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-storaged0:/data/storage
- logs-storaged0:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
storaged1:
image: vesoft/nebula-storaged:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.167
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.167
- --port=44500
- --data_path=/data/storage
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-167
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.167:12000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 12000
published: 12000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 12002
published: 12004
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-storaged1:/data/storage
- logs-storaged1:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
storaged2:
image: vesoft/nebula-storaged:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --local_ip=192.168.1.168
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.168
- --port=44500
- --data_path=/data/storage
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-168
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.168:12000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 12000
published: 12000
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 12002
published: 12006
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- data-storaged2:/data/storage
- logs-storaged2:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
graphd1:
image: vesoft/nebula-graphd:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --port=3699
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.166
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-166
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.166:13000/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 3699
published: 3699
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 13000
published: 13000
protocol: tcp
# mode: host
- target: 13002
published: 13002
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- logs-graphd:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
graphd2:
image: vesoft/nebula-graphd:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --port=3699
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.167
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=2
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-167
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.167:13001/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 3699
published: 3640
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 13000
published: 13001
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 13002
published: 13003
protocol: tcp
# mode: host
volumes:
- logs-graphd2:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
graphd3:
image: vesoft/nebula-graphd:nightly
env_file:
- ./nebula.env
command:
- --meta_server_addrs=192.168.1.166:45500,192.168.1.167:45500,192.168.1.168:45500
- --port=3699
- --ws_ip=192.168.1.168
- --log_dir=/logs
- --v=0
- --minloglevel=2
deploy:
replicas: 1
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
placement:
constraints:
- node.hostname == KF2-DATA-168
depends_on:
- metad0
- metad1
- metad2
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://192.168.1.168:13002/status"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 20s
ports:
- target: 3699
published: 3641
protocol: tcp
mode: host
- target: 13000
published: 13002
protocol: tcp
# mode: host
- target: 13002
published: 13004
protocol: tcp
mode: host
volumes:
- logs-graphd3:/logs
networks:
- nebula-net
networks:
nebula-net:
external: true
attachable: true
name: host
volumes:
data-metad0:
logs-metad0:
data-metad1:
logs-metad1:
data-metad2:
logs-metad2:
data-storaged0:
logs-storaged0:
data-storaged1:
logs-storaged1:
data-storaged2:
logs-storaged2:
logs-graphd:
logs-graphd2:
logs-graphd3:
编辑 nebula.env,加入如下内容
TZ=UTC
USER=root
2.6 启动 nebula 集群
docker stack deploy nebula -c docker-stack.yml
三、集群负载均衡及高可用配置
Nebula Graph 的客户端目前(1.X)没有提供负载均衡的能力,只是随机选一个 graphd 去连接。所以生产使用的时候要自己做个负载均衡和高可用。
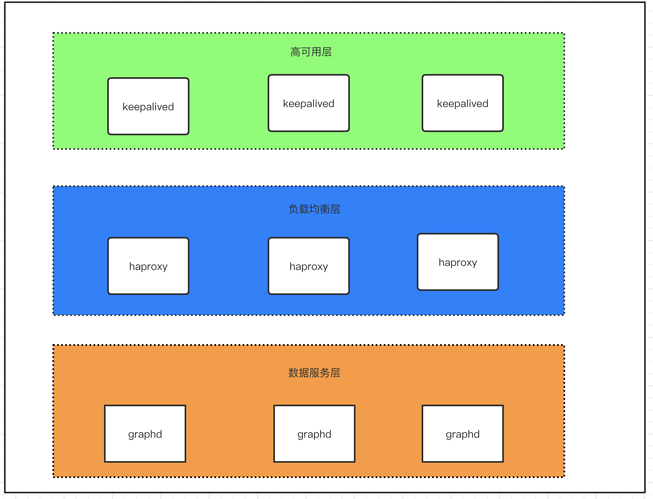
图 3.1
将整个部署架构分为三层,数据服务层,负载均衡层及高可用层。如图 3.1 所示
负载均衡层:对 client 请求做负载均衡,将请求分发至下方数据服务层
高可用层: 这里实现的是 haproxy 的高可用,保证负载均衡层的服务从而保证整个集群的正常服务
3.1 负载均衡配置
haproxy 使用 docker-compose 配置。分别编辑以下三个文件
Dockerfile 加入以下内容
FROM haproxy:1.7
COPY haproxy.cfg /usr/local/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
EXPOSE 3640
docker-compose.yml 加入以下内容
version: "3.2"
services:
haproxy:
container_name: haproxy
build: .
volumes:
- ./haproxy.cfg:/usr/local/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
ports:
- 3640:3640
restart: always
networks:
- app_net
networks:
app_net:
external: true
haproxy.cfg 加入以下内容
global
daemon
maxconn 30000
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
defaults
log-format %hr\ %ST\ %B\ %Ts
log global
mode http
option http-keep-alive
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 10000ms
timeout server 50000ms
timeout http-request 20000ms
# custom your own frontends && backends && listen conf
# CUSTOM
listen graphd-cluster
bind *:3640
mode tcp
maxconn 300
balance roundrobin
server server1 192.168.1.166:3699 maxconn 300 check
server server2 192.168.1.167:3699 maxconn 300 check
server server3 192.168.1.168:3699 maxconn 300 check
listen stats
bind *:1080
stats refresh 30s
stats uri /stats
3.2 启动 haproxy
docker-compose up -d
3.3 高可用配置
注:配置 keepalive 需预先准备好 vip(虚拟 ip),在以下配置中 192.168.1.99 便为虚拟 ip
在 192.168.1.166 、192.168.1.167、192.168.1.168上 均做以下配置
安装 keepalived
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade && apt-get install keepalived -y
更改 keepalived配置文件 /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf(三台机器中 做如下配置,priority 应设置不同值确定优先级)
192.168.1.166 机器配置
global_defs {
router_id lb01 # 标识信息,一个名字而已;
}
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy" interval 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 52
priority 999
# 设定 MASTER 与 BACKUP 负载均衡器之间同步检查的时间间隔,单位是秒
advert_int 1
# 设置验证类型和密码
authentication {
# 设置验证类型,主要有 PASS 和 AH 两种
auth_type PASS
# 设置验证密码,在同一个 vrrp_instance 下,MASTER 与 BACKUP 必须使用相同的密码才能正常通信
auth_pass amber1
}
virtual_ipaddress {
# 虚拟 IP 为 192.168.1.99/24; 绑定接口为 ens160; 别名 ens169:1,主备相同
192.168.1.99/24 dev ens160 label ens160:1
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
}
167 机器配置
global_defs {
router_id lb01 # 标识信息,一个名字而已;
}
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy" interval 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 52
priority 888
# 设定 MASTER 与 BACKUP 负载均衡器之间同步检查的时间间隔,单位是秒
advert_int 1
# 设置验证类型和密码
authentication {
# 设置验证类型,主要有 PASS 和 AH 两种
auth_type PASS
# 设置验证密码,在同一个 vrrp_instance 下,MASTER 与 BACKUP 必须使用相同的密码才能正常通信
auth_pass amber1
}
virtual_ipaddress {
# 虚拟 IP 为 192.168.1.99/24; 绑定接口为 ens160; 别名 ens160:1,主备相同
192.168.1.99/24 dev ens160 label ens160:1
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
}
168 机器配置
global_defs {
router_id lb01 # 标识信息,一个名字而已;
}
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy" interval 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 52
priority 777
# 设定 MASTER 与 BACKUP 负载均衡器之间同步检查的时间间隔,单位是秒
advert_int 1
# 设置验证类型和密码
authentication {
# 设置验证类型,主要有 PASS 和 AH 两种
auth_type PASS
# 设置验证密码,在同一个 vrrp_instance 下,MASTER 与 BACKUP 必须使用相同的密码才能正常通信
auth_pass amber1
}
virtual_ipaddress {
# 虚拟 IP 为 192.168.1.99/24;绑定接口为 ens160; 别名 ens160:1,主备相同
192.168.1.99/24 dev ens160 label ens160:1
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
}
keepalived 相关命令
# 启动 keepalived
systemctl start keepalived
# 使 keepalived 开机自启
systemctl enable keeplived
# 重启 keepalived
systemctl restart keepalived
四、其他
离线怎么部署?把镜像更改为私有镜像库就成了,有问题欢迎来勾搭啊。

我的小鱼你醒了 还认识早晨吗 昨夜你曾经说 愿夜幕永不开启
如果你对本文有任何疑问,欢迎来论坛和原作者聊聊~~ 原帖地址:https://discuss.nebula-graph.com.cn/t/topic/1388

本文介绍如何使用 Docker Swarm 来部署 Nebula Graph 集群,并部署客户端负载均衡和高可用的更多相关文章
- 用Docker swarm快速部署Nebula Graph集群
用Docker swarm快速部署Nebula Graph集群 一.前言 本文介绍如何使用 Docker Swarm 来部署 Nebula Graph 集群. 二.nebula集群搭建 2.1 环境准 ...
- Docker Swarm和Kubernetes在大规模集群中的性能比较
Contents 这篇文章主要针对Docker Swarm和Kubernetes在大规模部署的条件下的3个问题展开讨论.在大规模部署下,它们的性能如何?它们是否可以被批量操作?需要采取何种措施来支持他 ...
- Linux 集群概念 , wsgi , Nginx负载均衡实验 , 部署CRM(Django+uwsgi+nginx), 部署学城项目(vue+uwsgi+nginx)
Linux 集群概念 , wsgi , Nginx负载均衡实验 , 部署CRM(Django+uwsgi+nginx), 部署学城项目(vue+uwsgi+nginx) 一丶集群和Nginx反向代理 ...
- SaltStack一键部署负载均衡和高可用
一.负载均衡的部署 server1 haproxy (调度器) server2 apache server3 nginx 1)在server1上首先安装salt-minion服务.并 ...
- Docker Swarm(十)Portainer 集群可视化管理
前言 搭建好我们的容器编排集群,那我们总不能日常的时候也在命令行进行操作,所以我们需要使用到一些可视化的工具,Docker图形化管理提供了很多工具,有Portainer.Docker UI.Shipy ...
- 使用容器编排工具docker swarm安装clickhouse多机集群
1.首先需要安装docker最新版,docker 目前自带swarm容器编排工具 2.选中一台机器作为master,执行命令sudo docker swarm init [options] 3,再需 ...
- HBase 1.2.6 完全分布式集群安装部署详细过程
Apache HBase 是一个高可靠性.高性能.面向列.可伸缩的分布式存储系统,是NoSQL数据库,基于Google Bigtable思想的开源实现,可在廉价的PC Server上搭建大规模结构化存 ...
- 使用 Kubeadm+Containerd 部署一个 Kubernetes 集群
本文独立博客阅读地址:https://ryan4yin.space/posts/kubernetes-deployemnt-using-kubeadm/ 本文由个人笔记 ryan4yin/knowle ...
- 简述SQL2008部署多实例集群(学习)
数据库集群 集群的存在意义是为了保证高可用.数据安全.扩展性以及负载均衡. 什么是集群? 由二台或更多物理上独立的服务器共同组成的"虚拟"服务器称之为集群服务器.一项称做M ...
随机推荐
- 6 vue-element.ui 左侧导航栏
<template> <div> <el-menu :default-active="'/'+activeIndex2" mode="ver ...
- JVM学习第三天(JVM的执行子系统)之类加载机制补充
昨晚没看完,今天继续 系统的类加载器 对于任意一个类,都需要由加载它的类加载器和这个类本身一同确立其在Java虚拟机中的唯一性,每一个类加载器,都拥有一个独立的类名称空间.这句话可以表达得更通俗一些: ...
- 基于arm v8搭建区块链环境
服务器信息: cpu:华为鲲鹏 cpu架构:arm v8 系统:CenOS-AltArch 7.6 相关工具安装 yum更新 yum update 安装vim/gcc/git/curl工具软件 yum ...
- DNS 劫持/污染
who is dns 劫持 or 污染? 对 劫持 和 污染 这两个名词的理解一直都很混淆,这里就简单的记录一下他俩到底有哪些本质上的区别吧~ DNS 劫持 DNS劫持 即: DNS Hijackin ...
- 关于json序列化相关代码
自己写的一个 /// <summary> /// 序列化JSON,返回string /// </summary> /// <param name="dt&quo ...
- 谈谈 mysql和oracle的使用感受 -- 差异
之前一直使用mysql作为存储数据库,虽然中间偶尔使用sqlite作为本地数据库存储,但没有感觉多少差别. 后来遇上了oracle,且以其作为主要存储,这下就不得不好好了解其东西了.oracle作为商 ...
- linux系统漏洞扫描工具lynis
lynis 是一款运行在 Unix/Linux 平台上的基于主机的.开源的安全审计软件.Lynis是针对Unix/Linux的安全检查工具,可以发现潜在的安全威胁.这个工具覆盖可疑文件监测.漏洞.恶意 ...
- JVM强引用、软引用、弱引用、虚引用、终结器引用垃圾回收行为总结
JVM引用 我们希望能描述这样一类对象: 当内存空间还足够时,则能保留在内存中:如果内存空间在进行垃圾收集后还是很紧张,则可以抛弃这些对象. -[既偏门又非常高频的面试题]强引用.软引用.弱引用.虚引 ...
- 【JAVA】HashMap源码阅读
目录 1.关键的几个static参数 2.内部类定义Node节点 3.成员变量 4.静态方法 5.HashMap的四个构造方法 6.put方法 7.扩容resize方法 8.get方法 9.remov ...
- Oracle学习(一)SQL基础
一.认识SQL SQL是什么? SQL,结构化查询语言,全称是 Structured Query Language. SQL 是一门 ANSI(American National Standards ...
