python xmind转Excel(puppet洛洛原创)
需求:将xmind文件转为Excel文件,并添加UI界面操作以降低操作难度。
这个需求一句话就讲清楚了,但实际上还需要做很多工作:
1,了解Xmind文件结构
2,提取Xmind文件分支内容(重点)
3,UI界面(非必要)
一,了解Xmind文件结构
1,xmind文件形式:树形分支结构(可以先思考如何提取各分支内容)。
Excel提取为何种形式:主干与分支连接,用“\”号连接。(了解原理后也可以写成其他你想要的形式)
举例:
https\Tunnel to含义\Tunnel(隧道),中间实体
https\Tunnel to含义\隐藏:规则-隐藏连接
二,提取Xmind文件分支内容(重点)
那么如何解析上述为具体的数据结构呢?用“from xmindparser import xmind_to_dict”,用xmindparser包将其转化为字典格式再做处理。
再举个例子:
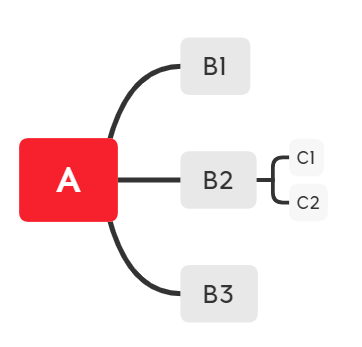
这个xmind文件通过xmind_to_dict可以转换为什么样呢?
{'title': 'A', 'topics': [{'title': 'B1'}, {'title': 'B2', 'topics': [{'title': 'C1'}, {'title': 'C2'}]}, {'title': 'B3'}]}
还是不够直观,用json分析器展开再看:
[
{
'title': '画布 1',
'topic': {
'title': 'A',
'topics': [
{
'title': 'B1'
},
{
'title': 'B2',
'topics': [
{
'title': 'C1'
},
{
'title': 'C2'
}
]
},
{
'title': 'B3'
}
]
},
'structure': 'org.xmind.ui.map.unbalanced'
}
]
内容装在一个list里,字典最外层title为“画布1”,topic装有我们需要的内容(可以看出其他位置叫topics),这是xmind文件中没有的,经验证这是个固定值,可以忽略。然后通过取list,A是字典中value值,key为title,其子节点装在topics的分支中。处理后是这样,最外层是dict:

那么问题来了,如何将其处理为想要的形式呢?一层层的取key、value吗?
当然不是,那工作量将非常庞大,而且不利于阅读和修改。还记得刚才的思考内容吗?这里我们就需要用到你所想的,没错,递归。
为什么要用递归,我们仔细看看结构:
A的三个子节点分别为B1,B2,B3,B2 的子节点为C1C2,参看上图你想到了什么?
1,标题和子节点放在不同的item里,即topic放根节点,那topics则放其子节点。
2,topics无子节点呢?像C1C2那样的点没有子节点,我们发现,它也没有topics;同时,没有子节点证明它是这条分支的最后一层了;试想,如果A没子节点,就只有它一个呢?正如你所想,它只有一个title,没有topics。
3,A的子节点是一个list,list可以有多个子节点,子节点若还有子节点则有topics,若没有则没有topics。
4,title永远装的是string,而topics可以装list,list里还有dict,也可以没有topics。
看了四点还是觉得很乱?
我们需要一层层取子节点才可以得到我们想要的A\B2\C1、A\B2\C2,节点值永远在title里,而子节点却在dict、list里的dict里,而且子节点里有的只有一个title,有的有一个title加一个topics,前文已经说过,有topics的是还有其子节点的。
那么现在应该清晰点了吧?还不清楚?那伪代码再来一遍:
如果 输入字典:
当字典只有有title时:
操作1
当字典有title和topics时:
操作2
如果 输入list:
遍历list里的字典:
对每个字典进行操作3
如果 输入的既不是字典也不是list:
输出值
思路框架已经搭建了,那操作1、2、3是什么呢?其实就是本框架的重复操作,调用下自己就可以了,不严谨的说这就是递归的通俗解释。
我们贴下代码:
1 def TraversalXmind(root,rootstring):
2 if isinstance(root, dict):
3 if len(root) == 2:
4 TraversalXmind(root['topics'], str(rootstring) )
5 if len(root) == 1:
6 TraversalXmind(root['title'],str(rootstring) )
7
8 elif isinstance(root, list):
9 for sonroot in root:
10 TraversalXmind(sonroot, str(rootstring) + "\\" + sonroot['title'])
11
12 elif isinstance(root,str):
13 print(str(rootstring) )
14
15 # TraversalXmind(root, "\\AA")
完整代码是什么呢?
将上述转换过程卸载model.py中:
1 # -*-coding:utf-8 -*-
2 # Author : zhengyong
3 # Time : 2020/11/5 23:06
4 # FileName: model.py
5
6 from xmindparser import xmind_to_dict
7 import os,csv
8 # filepath1 = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
9 # print(filepath1)
10
11 # filepath = "D:\\test.xmind"
12 # inputedXmind = xmind_to_dict(filepath)
13 # root = inputedXmind[0]['topic']
14
15 def traversalXmind(root, rootstring,lisitcontainer):
16 """
17 功能:递归dictionary文件得到容易写入Excel形式的格式。
18 注意:rootstring都用str来处理中文字符
19 @param root: 将xmind处理后的dictionary文件
20 @param rootstring: xmind根标题
21 """
22 if isinstance(root, dict):
23 if len(root) == 2:
24 traversalXmind(root['topics'], str(rootstring),lisitcontainer)
25 if len(root) == 1:
26 traversalXmind(root['title'], str(rootstring),lisitcontainer)
27
28 elif isinstance(root, list):
29 for sonroot in root:
30 traversalXmind(sonroot, str(rootstring) + "\\" + sonroot['title'],lisitcontainer)
31
32 elif isinstance(root, str):
33 lisitcontainer.append(str(rootstring))
34
35 def getCase(root):
36 rootstring = root['title']
37 lisitcontainer = []
38 traversalXmind(root, rootstring,lisitcontainer)
39 # print(lisitcontainer)
40 return lisitcontainer
41
42 # def getTestCase(filename,lisitcontainer,directory,group,runType,testcaseType,testType):
43 # header = [
44 # '测试案例路径',
45 # '测试案例名称',
46 # '测试案例描述',
47 # '计划执行时长(分钟)',
48 # '步骤描述',
49 # '预期结果',
50 # '优先级',
51 # '小组',
52 # '执行方式',
53 # '测试模块',
54 # '版本号',
55 # '用例类型',
56 # '测试类型',
57 # '关联故事卡片ID',
58 # ]
59 #
60 # with open(filename,'w',newline='') as f:
61 # writer = csv.DictWriter(f,fieldnames=header),
62 # writer.writeheader()
63 # for row in lisitcontainer:
64 # writer.writerow({
65 # '测试案例路径': directory,
66 # '测试案例名称': row,
67 # '小组': group,
68 # '执行方式': runType,
69 # '用例类型':testcaseType,
70 # '测试类型': testType,
71 # })
三,UI界面
UI界面用tkinter写的,直接上代码:
1 #-*-coding:utf-8 -*-
2 # Author : zhengyong
3 # Time : 2020/11/14 23:54
4 # FileName: main1.py
5 # https://github.com/ndnmonkey/transXmindToCSV.git
6
7 import model
8 from xmindparser import xmind_to_dict
9 import tkinter
10 from tkinter import filedialog
11 from tkinter import *
12 import os,csv
13
14
15 window = tkinter.Tk()
16 window.title("用例导出工具")
17 # 设置窗口图标
18 # window.iconbitmap("D:\Code\Python\XmindToExcel\image\icon.ico")
19 # window.iconbitmap("image\ifavicon.ico")
20 window.geometry("400x370+200+50")
21
22 # 标题
23 labeltitle = tkinter.Label(window,text = "用例导出工具",font = ('幼圆',20)).pack()
24
25 # 创建菜单栏
26 MenuBar = tkinter.Menu(window)
27 # 将菜单栏放到主窗口
28 window.config(menu=MenuBar)
29 # 创建文件菜单,不显示分窗
30 fileBar = tkinter.Menu(MenuBar, tearoff=0)
31 # 添加文件菜单项
32 fileBar.add_command(label="用法说明")
33 # fileBar.add_command(label="联系作者")
34 # 创建分割线
35 # fileBar.add_separator()
36 fileBar.add_command(label="退出", command=window.destroy)
37 # 将文件菜单添加到菜单栏
38 MenuBar.add_cascade(label="菜单", menu=fileBar)
39
40 xlabe = 20
41 xtext = 80
42 y =10
43 step = 30
44 textwidth = 250
45
46 inputtext1 = tkinter.StringVar(value='\常规版本用例\当前版本名\姓名\需求名')
47 labe1 = tkinter.Label(window, text='用例路径:').place(x=xlabe,y = y + step)
48 text1 = tkinter.Entry(window, show=None, textvariable=inputtext1)
49 text1.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + step)
50
51 inputtext2 = tkinter.StringVar(value='小组长姓名')
52 labe2 = tkinter.Label(window, text='组长姓名:').place(x=xlabe,y=y + 2*step)
53 text2 = tkinter.Entry(window, show=None, textvariable=inputtext2)
54 text2.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + 2*step)
55
56 inputtext3 = tkinter.StringVar(value='手工测试')
57 labe3 = tkinter.Label(window, text='执行方式:').place(x=xlabe,y=y + 3*step)
58 text3 = tkinter.Entry(window, show=None, textvariable=inputtext3)
59 text3.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + 3*step)
60
61 inputtext4 = tkinter.StringVar(value='系统用例')
62 labe4 = tkinter.Label(window, text='用例类型:').place(x=xlabe,y=y + 4*step)
63 text4 = tkinter.Entry(window, show=None, textvariable=inputtext4)
64 text4.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + 4*step)
65
66 inputtext5 = tkinter.StringVar(value='手工测试')
67 labe5 = tkinter.Label(window, text='测试类型:').place(x=xlabe,y=y + 5*step)
68 text5 = tkinter.Entry(window, show=None, textvariable=inputtext5)
69 text5.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + 5*step)
70
71 def getTextValues():
72 templist = []
73 var1 = text1.get();templist.append(var1)
74 var2 = text2.get();templist.append(var2)
75 var3 = text3.get();templist.append(var3)
76 var4 = text4.get();templist.append(var4)
77 var5 = text5.get();templist.append(var5)
78 # print("1",templist)
79 return templist
80
81 casebutton1 = tkinter.Button(window,text = '1,提交用例信息',width=5,height=1,command=getTextValues)
82 casebutton1.place(x=110,y=y + 6*step)
83 casebutton1.configure(width = 34, height = 2)
84
85 def open_file():
86 templist = getTextValues()
87 # print("2",templist)
88 filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(title='打开Xmind文件', filetypes=[('xmind', '*.xmind')])
89
90 entry_filename.delete(0, END)
91 entry_filename.insert('insert', filename)
92 # print(entry_filename,type(entry_filename))
93
94 # print(filename)
95 fname = entry_filename.get() #用get提取entry中的内容
96 fname = str(fname).replace('/','\\\\')
97 # print("fname",fname)
98
99 # filepath = "D:\\test.xmind"
100 # inputedXmind = xmind_to_dict(filepath)
101 # root = inputedXmind[0]['topic']
102 #
103 inputedXmind = xmind_to_dict(fname)
104 root = inputedXmind[0]['topic']
105 lisitcontainer = model.getCase(root)
106 # print(lisitcontainer)
107
108 # templist
109 directory = templist[0]
110 group = templist[1]
111 runType = templist[2]
112 testcaseType = templist[3]
113 testType = templist[4]
114 # filename = 'testcase.csv'
115 header = [
116 '测试案例路径',
117 '测试案例名称',
118 '测试案例描述',
119 '计划执行时长(分钟)',
120 '步骤描述',
121 '预期结果',
122 '优先级',
123 '小组',
124 '执行方式',
125 '测试模块',
126 '版本号',
127 '用例类型',
128 '测试类型',
129 '关联故事卡片ID',
130 ]
131 # print(filename) #D:\\test.xmind
132 savepath = fname.split('.')[0] + ".csv"
133 # print("savepath:",savepath)
134
135 with open(savepath, 'w', newline='') as f:
136 writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=header)
137 writer.writeheader()
138 for row in lisitcontainer:
139 writer.writerow({
140 '测试案例路径': directory,
141 '测试案例名称': row,
142 '小组': group,
143 '执行方式': runType,
144 '用例类型': testcaseType,
145 '测试类型': testType,
146 })
147
148 # 设置button按钮接受功能
149 importbutton = tkinter.Button(window, text="2,导入Xmind文件", command=open_file)
150 importbutton.place(x=110,y=y + 9*step)
151 importbutton.configure(width =34,height=2)
152
153 # 设置entry
154 entry_filename = tkinter.Entry(window, width=30, font=("宋体", 10, 'bold'))
155 entry_filename.place(width=textwidth,x=xtext+ 1*step,y=y + 8*step)
156
157 # 版权页
158 labelright = tkinter.Label(window,text = "version 0.3 bug修复:zhengyong731@pingan.com.cn",font = ('宋体',8)).place(x=60,y=350)
159 # Tk().iconbitmap('D:\Code\Python\XmindToExcel\image\icon.ico')
160 window.mainloop()
那么这时候还有一个问题,运行之后的结果是什么?
用pyinstaller就可以打包代码文件变成可执行文件:
方法:
1,安装pyinstaller(不具体介绍)
2,使用:
命令行:
pyinstaller -F 主文件名.py
运行可执行文件有黑框怎么办?
pyinstaller -F -w mycode.py (-w就是取消窗口)
3,生成的可执行文件在哪?
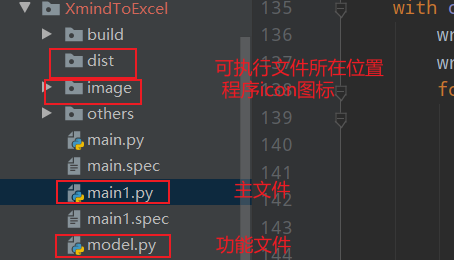
在主文件同级文件夹dist中,
4,具体文件结构:
四,声明
所有代码均为原创,因为实在找不到可用的教程,了解到找教程的艰辛,所以抛砖引玉,本人水平有限,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教,可以交流讨论。
欢迎转载,请注明以下内容:
本人在cnblogs上的ID为puppet洛洛,博客地址为https://www.cnblogs.com/two-peanuts/所有包含原创声明的博客均为本人原创作品。博客的内容除已注明的引用文献外均为本人独立研究成果。除特殊注明外均采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 3.0 中国大陆 许可协议进行许可。
五,github地址
具体的文件结构已传至github,欢迎star。
python xmind转Excel(puppet洛洛原创)的更多相关文章
- Delphi中使用python脚本读取Excel数据
Delphi中使用python脚本读取Excel数据2007-10-18 17:28:22标签:Delphi Excel python原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 . ...
- python批量处理excel文件数据
https://www.zhihu.com/question/39299070?sort=created 作者:水中柳影链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/392990 ...
- python下读取excel文件
项目中要用到这个,所以记录一下. python下读取excel文件方法多种,用的是普通的xlrd插件,因为它各种版本的excel文件都可读. 首先在https://pypi.python.org/py ...
- Python读写操作Excel模块_xlrd_xlwt_xlutils
Python 读写操作Excel -- 安装第三方库(xlrd.xlwt.xlutils.openpyxl) 如果仅仅是要以表单形式保存数据,可以借助 CSV 格式(一种以逗号分隔的表格数据格式)进行 ...
- python制作简单excel统计报表3之将mysql数据库中的数据导入excel模板并生成统计图
python制作简单excel统计报表3之将mysql数据库中的数据导入excel模板并生成统计图 # coding=utf-8 from openpyxl import load_workbook ...
- python制作简单excel统计报表2之操作excel的模块openpyxl简单用法
python制作简单excel统计报表2之操作excel的模块openpyxl简单用法 # coding=utf-8 from openpyxl import Workbook, load_workb ...
- Python“文件操作”Excel篇(上)
大家好,我们今天来一起探索一下用Python怎么操作Excel文件.与word文件的操作库python-docx类似,Python也有专门的库为Excel文件的操作提供支持,这些库包括xlrd.xlw ...
- 用python实现简单EXCEL数据统计的实例
用python实现简单EXCEL数据统计的实例 下面小编就为大家带来一篇用python实现简单EXCEL数据统计的实例.小编觉得挺不错的,现在就分享给大家,也给大家做个参考.一起跟随小编过来看看吧 任 ...
- 数据测试001:利用python连接数据库插入excel数据
数据测试001:利用python连接数据库插入excel数据 最近在做数据测试,主要是做报表系统,需要往数据库插入数据验证服务逻辑,本次介绍如何利用python脚本插入Oracle和Mysql库中: ...
随机推荐
- Centos7安装Java8
centos7 用yum安装java8
- 机器学习算法——kNN(k-近邻算法)
算法概述 通过测量不同特征值之间的距离进行 [分类] 优点:精度高.对异常值不敏感.无数据输入假定. 缺点:计算复杂度高.空间复杂度高. 适用数据范围: 数值型 和 标称型 . 算法流程 数据 样本数 ...
- 第十四周C++学习总结
类模板使用方法:类模板名 <数据类型> 对象名: C++有个标准模板库(STL)(standard template library),编程时使用它会提高程序的可靠性. Stl 包含了(容 ...
- 我要告诉你:java接口中可以定义private私有方法
在传统的Java编程中,被广为人知的一个知识点是:java Interface接口中不能定义private私有方法.只允许我们定义public访问权限的方法.抽象方法或静态方法.但是从Java 9 开 ...
- day19 Pyhton学习 递归函数
# 函数的递归 : 在一个函数的内部调用它自己 # import sys # sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000) # 设置递归的最大深度 # 总结 # 1.递归函数的定义 : ...
- Helium文档7-WebUI自动化-highlight高亮显示元素
前言 highlight方法是通过红框高亮显示元素,在调试中有很大优势,可以清楚看到定位的元素位置 入参介绍 def highlight(element): """ ...
- MySQL备份和恢复[4]-xtrabackup备份工具
xtrabackup工具介绍 Percona 公司 官网:www.percona.com percona-server InnoDB --> XtraDB Xtrabackup备份工具 perc ...
- Java接口的初始化
背景 接口与类真正有所区别的是前面讲述的四种"有且仅有"需要开始初始化场景中的第三种:当一个类在初始化时,要求其父类全部都已经初始化过了,但是一个接口在初始化时,并不要求其父接口全 ...
- 微信小程序分类的实现
微信小程序的分类功能思路 实现思路 1.把屏幕当成一个固定的盒子,然后把盒子分成两边,并让盒子的每一边都能够滚动. 2.通过将左侧边栏元素的id和右边内容的categoryId进行匹配,渲染展示相同i ...
- 一篇文章 图解Python 玩转Python
0 Python 解释器:1.Python数据结构:2.变量与运算符3 Python 流程控制 4 Python 文件处理5 python 输入输出6 Python 异常7 Python 函数和模块8 ...
