Java 常见对象 04
常见对象·Arrays 类和 包装类
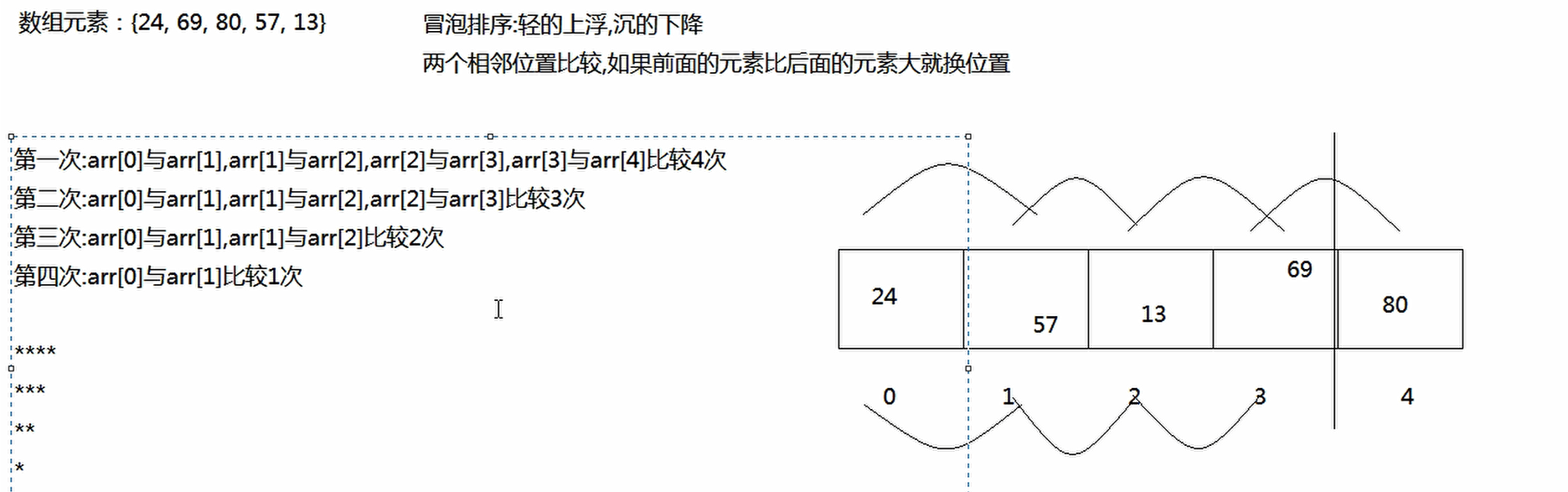
数组高级冒泡排序原理图解
* A:画图演示
* 需求:
数组元素:{24, 69, 80, 57, 13}
请对数组元素进行排序
* 冒泡排序:
相邻元素两两比较,较大的往后放,第一次完毕,最大值出现在了最大索引处
数组高级冒泡排序代码实现
* A:案例演示
* 数组高级冒泡排序代码
package com.heima.array;
public class Demo1_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 24, 69, 80, 57, 13 };
bubbleSort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
/*
* 冒泡排序:
* 1、返回值类型,void
* 2、参数列表,int[] arr
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { // 外循环:只需要比较arr.lenth-1次就行了
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) { // 减一防止索引越界,-i并且提高效率
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
BubbleSort
数组高级选择排序原理图解
* A:画图演示
* 需求:
* 数组元素:{24, 68, 80, 57, 13}
* 请对数组元素进行排序
*选择排序
* 从0索引开始,依次和后面元素比较,小的往前放,第一次完毕时,最小值出现在了最小索引处

数组高级选择排序代码实现
* A:案例演示
* 数组高级选择排序代码
package com.heima.array;
public class Demo2_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 13, 69, 80, 57, 24 };
selectSort(arr);
print(arr);
}
/*
* 如果某个方法只针对本类使用,不想让其他类试图用就可以定义成私有的
*/
public static void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
/*
* 选择排序: 1、返回值void 2、参数列表int[] arr
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { // 只需要比较arr.length-1次
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
swap(arr, i, j);
}
}
}
}
/*
* 换位操作: 1、返回值类型,void 2、参数列表int[] arr, int i, int j
*/
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
Arrays
数组高级二分查找原理图解
* A:画图演示
* 二分查找,查找元素所对应的索引
* 前提,数组元素有序

数组高级二分查找代码实现及注意事项
* A:案例演示
* 数组高级二分查找代码
* B:注意事项
* 如果数组无序,就不能使用二分查找
* 原因:因为如果你排序了,但是你排序的时候就已经改变了数组的原始索引
package com.heima.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo3_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77 };
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = sc.nextInt();
int p = binarySearch(arr, i);
System.out.println(p);
}
/*
* 二分查找: 1、返回值类型,int
* 2、参数列表 int[] arr, int value
*/
private static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int value) {
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length - 1;
int mid = (min + max) / 2;
while (arr[mid] != value) { // 当中间值不等于要找的值,就开始循环查找
if (arr[mid] > value) { // 当中间值大于要找的值,改变最大值
max = mid - 1;
} else if (arr[mid] < value) { // 当中间值小于要找的值,就改变最小值
min = mid + 1;
}
mid = (min + max) / 2; // 无论最大还是最小,中间索引都会随之改变
if (min > max) { // 如果最小索引大于最大索引,则表面要找的值不存在
return -1;
}
}
return -(min + 1);
}
}
Arrays
Arrays类的概述和方法使用
* A:Arrays类概述
* 针对数组进行操作的工具类
* 提供了排序、查找等功能
* B:成员方法
* public static String toString(int[ ] arr)
* public static void sort(int[] arr)
* public static int binarySearch(int[ ] a, int key)

public static String toString(int[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
toString源码
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1; while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid]; if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
binarySearch源码
package com.heima.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo4_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 33, 22, 11, 44, 66, 55 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // 将数组变成字符串
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // 对数组进行排序
int[] arr2 = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77 }; // 二分查找的对象必须是有序的数组,如果数组中包含多个重复的值,则无法保证找到的是哪一个
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr2, 12)); // 如果要找的值包含在数组中,则返回其索引;否则返回(-(插入点)-1)
}
}
Arrays
基本数据类型包装类的概述
* A:为什么会有基本类型的包装类
* 好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法来操作该数据
* B:常用操作
* 用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换
* C:基本类型和包装类的对应关系
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
package com.heima.wrapclass;
public class Demo1_Integer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(60)); // 二进制输出
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(60)); // 八进制输出
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(60)); // 十六进制输出
}
}
Integer
Integer类的概述和构造方法
* A:Integer类的概述
* 通过JDK提供的API,查看Integer类 的说明
* Integer类 在对象中包装了一个基本类型 int 的值
* 该类提供了多个方法,能在 int 类型和 String 类型之间相互转换
* 还提供了处理 int 类型时非常有用的其他一些常量和方法
* B:构造方法
* public Integer(int value)
* public Integer(String str)
* C:案例演示
* 使用构造方法创建对象


package com.heima.wrapclass;
public class Demo2_Integer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); // Integer能表示的最大数
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); // Integer能表示的最小数
// Integer构造方法
Integer i1 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(i1);
// Integer i2 = new Integer("abc"); // 数字格式异常: java.lang.NumberFormatException
Integer i2 = new Integer("100");
System.out.println(i2);
}
}
Integer
String 和 int 类型的相互转换
* A:int -> String
* a:和 "" 进行拼接
* b:public static String valueOf(int i)
* c:int -> Integer -> String (调用 Integer类 的 toString方法)
* d:public static String toString(int i) (Integer类的静态方法)
* B:String -> int
* a:String -> Integer -> int
* public staticint parseInt(String s)
package com.heima.wrapclass;
public class Demo3_Integer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1(); // int -> String
// demo2(); // String -> int
String s1 = "true";
boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean(s1);
System.out.println(b);
//String s2 = "abc";
//char c = Character.parse // char的包装类Character中没有parseXxx的方法
// 字符串到字符的转换通过toCharArray() 就可以把字符串转换为字符数组
}
public static void demo2() {
String s = "200";
Integer i3 = new Integer(s);
int i4 = i3.intValue();// string转换成integer 再转换成int
System.out.println(i4);
int i5 = Integer.parseInt(s);// 直接将string转换成int,推荐使用
System.out.println(i5);
/*
* 基本数据类型的包装类又八种
* 其中七种都有parseXxx的方法,可以将七种类型转换成基本数据类型,char类型没有
* 字符串到字符的转换通过toCharArray方法就行
*/
}
public static void demo1() {
int i = 100;
String s1 = i + "";
System.out.println(s1); // 将数字和""相加,推荐使用
String s2 = String.valueOf(i);
System.out.println(s2); // 调用valueof方法
Integer i2 = new Integer(i);
String s3 = i2.toString();
System.out.println(s3); // 将int转换为integer再调用toString方法
String s4 = Integer.toString(i);
System.out.println(s4); // 直接调用integer类
}
}
Integer
JDk5新特性自动装箱和自动拆箱
* A:JDK5的新特性
* 自动装箱:把基本类型转换为包装类类型
* 自动拆箱:把包装类类型转换为基本类型
* B:案例演示
* JDK5的新特性自动装箱和拆箱
* Integer i = 100;
* i += 100;
* C:注意事项
* 在使用时,Integer x = null; 代码就会出现NullPointerException
* 建议先判断为否为null,然后再使用
package com.heima.wrapclass;
public class Demo4_JDK5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 100;
Integer i1 = new Integer(x);// 将基本数据类型包装成对象,手动装箱
int y = i1.intValue(); // 将对象转换成基本数据类型,手动拆箱
Integer i2 = 100;// 自动装箱,把基本数据类型 转换成 引用数据类型
int z = i2 + 200;// 自动拆箱,把引用数据类型 转换为 基本数据类型
System.out.println(z);
// Integer i3 = null;
// int a = i3 + 100; // 底层调用intValue,但是i3是null,会出现空指针异常:java.lang.NullPointerException
// System.out.println(a);
}
}
JDk5
Integer 的面试题
* A:Integer 的面试题
* 看程序写结果
package com.heima.wrapclass;
public class Demo5_Integer {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = new Integer(97);
Integer i2 = new Integer(97);
System.out.println(i1 == i2); // 判断地址值,false
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2)); // Integer类以重写equals方法,true
System.out.println("---------------------");
Integer i3 = new Integer(197);
Integer i4 = new Integer(197);
System.out.println(i3 == i4); // false
System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); // true
System.out.println("----------------------");
Integer i5 = 127;
Integer i6 = 127;
System.out.println(i5 == i6); // true,i5和i6指向了同一对象
System.out.println(i5.equals(i6)); //true
System.out.println("----------------------");
Integer i7 = 128;
Integer i8 = 128;
System.out.println(i7 == i8); // false
System.out.println(i7.equals(i8)); // true
/*
* -128到127是byte的取值范围,
* 如果在这个取值范围内,自动装箱就不会创建新对象,而是从常量池中获取
* 如果超过了byte的取值范围,就会再新创建对象
*/
}
}
Java 常见对象 04的更多相关文章
- Java常见对象Object类中的个别方法
Java常见对象Object类 public int hashCode() : 返回该对象的哈希码值. 注意:哈希值是根据哈希算法计算出来的一个值,这个值和地址值有关,但是不是实际地址值.你可以理解成 ...
- Java 常见对象 05
常见对象·正则表达式 和 其他类 正则表达式的概述和简单使用 * A:正则表达式 * 是指一个用来描述或者匹配一系列符合某个语法规则的字符串的单个字符串.其实就是一种规则,有自己的特殊应用 * 作用: ...
- Java 常见对象 03
常见对象·StringBuffer类 StringBuffer类概述 * A:StringBuffer类概述 * 通过 JDk 提供的API,查看StringBuffer类的说明 * 线程安全的可变字 ...
- Java 常见对象 02
常见对象·String类 Scanner 的概述和方法介绍 * A:Scanner 的概述 * B:Scanner 的构造方法原理 * Scanner(InputStream source) * Sy ...
- Java 常见对象 01
常见对象·Object类 Object类的概述 * A:Object 类概述 * 类层次结构的根类 * 所有类都直接或间接地继承自该类 * B:构造方法 * public Object() * 回想为 ...
- Java常见对象之String
String类的概述 String 类代表字符串.Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例实现.字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变. String ...
- Java常见对象内存分析
首先要明确Java内存的个位置上放的是啥 类.对象.实例三者的关系: 1.类:是对象的模板,可以实例化对象.(this不能出现在静态方法中) 2.对象:类的个体. 3.实例:实现的对象. 4.对应的引 ...
- day11<Java开发工具&常见对象>
Java开发工具(常见开发工具介绍) Java开发工具(Eclipse中HelloWorld案例以及汉化) Java开发工具(Eclipse的视窗和视图概述) Java开发工具(Eclipse工作空间 ...
- Java学习笔记 04 类和对象
一.类和对象的概念 类 >>具有相同属性和行为的一类实体 对象 >>实物存在的实体.通常会将对象划分为两个部分,即静态部分和动态部分.静态部分指的是不能动的部分,被称为属性,任 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu中Unable to acquire the dpkg frontend lock (/var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend)问题的解决
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/shimadear/article/details/90598646 问题描述: 解决方法: 第一种情况: 进程中存在与apt相关的正在运行的进程 ...
- Entity Framework (EF) Core学习笔记 1
1. Entity Framework (EF) Core 是轻量化.可扩展.开源和跨平台的数据访问技术,它还是一 种对象关系映射器 (ORM),它使 .NET 开发人员能够使用面向对象的思想处理数据 ...
- XV6学习(16)Lab net: Network stack
最后一个实验了,代码在Github上. 这一个实验其实挺简单的,就是要实现网卡的e1000_transmit和e1000_recv函数.不过看以前的实验好像还要实现上层socket相关的代码,今年就只 ...
- k8s二进制部署 - 总结
镜像仓库: 安装软件:docker.docker-compose.harbor.nginx 1.下载cfssl.cfssljson.cfssl-certinfo,增加执行权限并放在PATH环境变量路径 ...
- MySQL 基础面试题
请写出什么是事务? 事务是一组不可分割的 DML 语句,事务处理可以用来维护数据库的完整性,保证一组 SQL 语句要么全部执行成功,要么全部不执行,只有 InnoDB 存储引擎才支持事务 . 事务的特 ...
- PHP 弱类型 && CODE/COMMADN injection
CODE/COMMAND INJECTION CODE INJECTION https://www.freebuf.com/sectool/168653.html EXAMPLE1 <?php ...
- liunx命令二
声明:以下资料全部摘自实验楼 常用快捷键 按键 作用 Table 补全命令 Ctrl+c 强制结束 Ctrl+d 键盘输入结束或退出终端 Ctrl+s 暂停当前程序,暂停后按下任意键恢复运行 Ctrl ...
- MathJax TeX & LaTeX
MathJax TeX & LaTeX mathcal https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search/solution/er-fen-cha-z ...
- MobX All In One
MobX All In One Simple, scalable state management. https://mobx.js.org/README.html https://github.co ...
- RT-Thread学习笔记3-线程间通信 & 定时器
目录 1. 事件集的使用 1.1 事件集控制块 1.2 事件集操作 2. 邮箱的使用 2.1 邮箱控制块 2.2 邮箱的操作 3. 消息队列 3.1 消息队列控制块 3.2 消息队列的操作 4. 软件 ...
