spring ioc踏出第一步
spring IOC(容器) AOP(面向切面编程)
IOC容器:他的功能就是可以整合像 Structs2 、Hibernate、Mybatis;
IOC:控制反转;所谓的控制就是控制资源的获取方法,获取资源的方式又分为主动和被动方式;
什么是主动式:
就是要使用什么资源我们就new 出来
BookServlet bs = new BookServlet();
什么是被动式?
例如要使用一个userService, UserService userService; 把他当成变量来声明。
容器:就是管理所有组件(有功能的类);假设,一个servlet受容器管理,service也受容器管理;容器可以自动的探查出那些组件需要另外一些组件;容器帮我们创建service对象,并且将service对象赋值。其实容器就是一个中介,例如现在最大的电商淘宝就是一个巨型容器,以前的卖家有货,买家有需要才能卖,什么时候卖,买什么,中间夹杂着许多因素。使卖家与买家之间的耦合度太高,中间的联系太过紧密,这时淘宝的出现就是一个第三方容器,他将货物与需求都管理着,买家什么时候都可以在淘宝上询问价格和商品信息,卖家也可以不像之前那样看买家什么时候买。直接由淘宝这个平台进行管理,分配,展示,交付。这样耦合度就减少了,也就做到了解耦的操作。IOC其实也是一种解耦思想。
ApplicationContext是IOC容器接口,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 代表当前引用的xml 配置文件在这个classpath路径中。
当所创建的spring配置文件放在当前类路径下;使用new CassPathXMLApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);
当所创建的配置文件没在类路径下,例如放在了D盘,所以要使用
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(“D://ioc.xml”);这个类的构造函数。
spring容器帮我们创建了对象,但具体是什么时候帮我们创建了呢?
其实呀,当这句代码执行完之后,配置文件中的对象已经创建完成,容器启动,构造方法就已经执行了。
默认情况下创建的组件(对象)都是单实例的,
IOC容器创建组件(对象)的时候(property)会利用setter方法为JavaBean的属性进行赋值,而Javabean的属性名是由getter/setter方法名决定的,并不是类中定义的私有属性,例如setLastName(String name); 在配置文件中设置所以建议使用系统自动生成的set/get方法。
如果配置的时候对于同一个类配置了多个对象,然后在获取对应那个的时候通过类型获取就会抛出如下异常:org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'main.java.domain.Student' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: stu3,students
意思就是按照Student.class这个类去找,应该只允许找到一个对象就是但离得,但是出现了两个,stu3和students导致出错,解决方法:
Student stu3 = (Student) context.getBean(“students”,Student.class);//获取student对象
getBean(“bean_id”,bean.class);传入bean的id属性和类型,亦可以通过id获取对象。
当构造方法重载时,我们怎样在spring的配置文件中进行配置?
如果指定了name属性给构造方法那就可以精确匹配我们想要的构造方法并给对象设置值,创建出对象。
但如果没有指定name属性,容器默认是按照构造方法中的参数列表顺序一一对应,当顺序与参数列表的顺序不一致时,我们可以添加index属性值来使参数能够与正确的类型对相应。
<constructor-arg index="0" value="happy"/><constructor-arg index="1" value="19"/>
当构造方法重载后参数类型也发生了变化,例如:
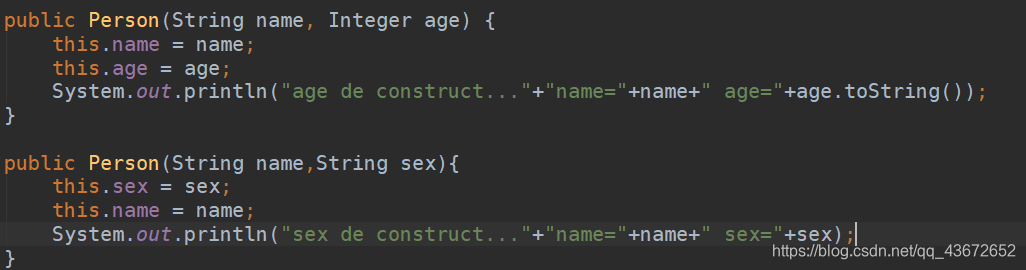
第一个构造方法的第二个参数是integer,第二个构造方法第二个参数是String,如果还像往常一样直接指定value值,运行就会
是的,sex对应的是age的值,我们想要的是使用第一个构造方法创建对象
因此要给这个构造方法加入type属性,指定明确的类型
`<bean id="person_05" class="main.java.domain.Person"><constructor-arg value="小明"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="18" index="1" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg></bean>`
这样就匹配正确的构造方法了。
感觉不指定name属性是真的麻烦。。
P命名空间(就是在xml配置文件中给重复的标签起了个别名,用来放置标签重复)
第一步:导入名称空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"//这一行就是导入了p名称空间>
第二步:使用名称空间给对象赋值
<bean id="person_06" class="main.java.domain.Person" p:age="22" p:name="搜索" scope="singleton"></bean>
person construct…
搜索要开始工作了。。22
正确的为各种数据类型赋值。
测试使用null赋值,默认就是null。
<bean id="person01" class="com.main.java.bean.Person"><property name="name"><null/></property></bean>
对于复杂类型,例如对象,集合等,属性写在标签内部。
<bean id="person_05" class="main.java.domain.Person"><constructor-arg value="小明"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="18" index="1" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg><property ref="stu3" name="s1" ></property></bean>
ref是引用类型,这里引用了一个对象,Student类型。
运行下面这段代码结果是true
Object stu3 = context.getBean("stu3");Person person_05 = (Person) context.getBean("person_05");Student s1 = person_05.getS1();System.out.println(s1==stu3);//true
从IOC容器中取得的对象与利用person对象调用自身student属性获取的对象是同一个,想要给一个对象中设置另个对象当属性还有一种方法
<bean id="person_05" class="main.java.domain.Person"><constructor-arg value="小明"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="18" index="1" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg><!--<property ref="stu3" name="s1" ></property>--><property name="s1"><bean class="main.java.domain.Student"><property name="name" value="小光"></property></bean></property></bean>
作用与使用对象的引用效果一样。不同的是,这个相当于是字节new出来的一个Student对象,上面的输出就是false,属性设置与引用的一样。是内部bean与之前的没有关系,ref引用的是外部的对想。
对于内部的bean即使给他加上id,我们在外部想要获取他,那也是不行的,内部的bean只能定义,不能获取到,通过getBean(“InnerId”);是会报错的。
属性是map类型
<property name="map"><map><entry key="1" value="xxx"></entry><entry key="2" value="zzz"></entry><entry key="3" value="ccc"></entry><entry key="5" ><bean class="java.bean.person"><perproty name=""name value="张三"></perproty></bean></entry></map></property>
属性时list类型
<property name="list"><list><value>小武</value><value>小两</value></ref="stu3" name="student"><bean class="java.bean.car"><perproty name="car" value="hongguang"></perproty></bean></list></property>
属性是properties
<property name="properties"><props>//键值对都是字符类型,如果props标签体中没有<prop>就相当于只new properties();<prop key="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.driver</prop><prop key="username">root</prop><prop key="password">root</prop></props></property>
使用util命名空间,
需要引入命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.1.xsd"xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"><bean><!-- 相当于new LinkHashMap(),这个util map在别的对象中可以被引用--><!-- 使用util的集合必须要加上id属性才可以被其他对象共享--><util:map id="myMap"><entry key="k1" value="reset"></entry><entry key="k2" value="123"></entry><entry key="k1" ><bean class="main.java.domain.Student"></bean></entry></util:map><util:list id="myList"><value>123</value><list></list><ref bean="myMap"/></util:list><util:set id="mySet"></util:set><util:properties id="myPro"></util:properties></bean></beans>
使用util的集合必须要加上id属性才可以被其他对象共享。
级联属性:就是属性的属性,例如person类中有关于car的对象,car自身又有color这个属性,而color和person就是级联属性。
将person中的car对象的价格price改为360000,
测试代码:
private ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/bean.xml");@Testpublic void test2(){Person person01 = (Person) context.getBean("person01");Car car = person01.getCar();System.out.println("person的car:"+car.toString());Object car01 = context.getBean("car01");System.out.println("容器中的car: "+car01.toString());}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"><bean id="person01" class="main.java.domain.Person"><property name="name" value="憨憨"></property><property name="age" value="36"></property><!--级联属性--><property name="car" ref="car01"></property><property name="car.price" value="360000"></property></bean><bean id="car01" class="main.java.domain.Car"><property name="name" value="宝马"></property><property name="color" value="black"></property><property name="price" value="1000000"></property></bean></beans>
运行结果:
person的car:Car{name=‘宝马’, price=360000, color=‘black’}
容器中的car: Car{name=‘宝马’, price=360000, color=‘black’}
通过继承对象属性来实现bean配置信息的重用。
如果有两个person对象A、B,他们两个除了姓名不一样,其余属性都一样,那么如果A的信息已确定,B的个人属性大部分信息都可以从A身上获得。直接只需要修改直接独特的那部分信息。
<bean class="main.java.domain.Person" id="personA"><property name="name" value="小A"></property><property name="age" value="26"></property></bean><!--属性的重用,通过类似于继承关系 配置parent属性来制定继承那个对象的信息--><bean id="personB" parent="personA"><property name="name" value="小B"></property></bean>
测试:
@Testpublic void test3(){Object personB = context.getBean("personB");Object personA = context.getBean("personA");System.out.println("B: "+personB);System.out.println("A: "+personA);}
结果:
B: Person{name=‘小B’, age=26, sex=‘null’, s1=null}
A: Person{name=‘小A’, age=26, sex=‘null’, s1=null}
现在我想让A永远当成一个类似于父类的东西,只能被继承配置信息,这个只要在加上abstract属性并设置为true就行。这个代表不能被直接获取 。
默认情况下,对象的创建顺序就是在配置文件中bean写的前后顺序,它会一个bean一个bean的逐个创建,但现在要想改变默认的这个顺序,那具体要怎样更改?
例如:
<bean id="car02" class="main.java.domain.Car"></bean><bean id="person06" class="main.java.domain.Person"></bean><bean id="student05" class="main.java.domain.Student"></bean>
上面的对象创建顺序默认就是 car02,person06,student05,但现在要想让person06, student05在car02之前创建就要在car02的bean标签中加入
depends-on属性,
<bean id="car02" class="main.java.domain.Car" depends-on="person_06,student05"></bean><bean id="person06" class="main.java.domain.Person"></bean><bean id="student05" class="main.java.domain.Student"></bean>
这样顺序就变成了我们想要的,同样构造函数的顺序也发生了变化。
bean的作用域:指定bean是否是单实例或多实例
prototype: 多实例;
1.
容器启动时不会主动创建多实例的bean,
2.
获取才创建这个bean
3.
每次获取都会创建一个新的对象。
singleton: 单实例,且默认就是单实例
1.
在容器启动完成之前就已经创建好了对象,保存在了容器中。
2.
任何获取都是之前创建好的那个对象;
request:在web环境中同一次请求创建一个bean
session:在web环境中同义词会话创建一个bean。
spring ioc踏出第一步的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot-开启第一步
Spring Boot开发的目的是为了简化Spring应用的开发,使用Spring Boot可以零配置开启一个Spring应用.这得益于Spring Boot中的自动配置组件,如果开发者觉得默认的配置 ...
- 踏出第一步——安装并跑通python程序
一.首先学会安装python软件 1.在浏览器下输入安装python软件的官方网址. 点击打开链接 2.在界面上点击"Downloads"下的"Windows" ...
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(二):初始化过程---简介
首先我们先来看看如下一段代码 ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml"); DefaultList ...
- 我的自定义框架 || 基于Spring Boot || 第一步
今天在园子里面看到一位大神写的springboot做的框架,感觉挺不错,遂想起来自己还没有一个属于自己的框架,决定先将大神做好的拿过来,然后加入自己觉得需要的模块,不断完善 目前直接复制粘贴过来的,后 ...
- Spring的IOC容器第一辑
一.Spring的IOC容器概述 Spring的IOC的过程也被称为依赖注入(DI),那么对象可以通过构造函数参数,工厂方法的参数或在工厂方法构造或返回的对象实例上设置的属性来定义它们的依赖关系,然后 ...
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(三):初始化过程---Resource定位
我们知道Spring的IoC起到了一个容器的作用,其中装得都是各种各样的Bean.同时在我们刚刚开始学习Spring的时候都是通过xml文件来定义Bean,Spring会某种方式加载这些xml文件,然 ...
- Spring IoC源码解析——Bean的创建和初始化
Spring介绍 Spring(http://spring.io/)是一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,同时也是轻量级的IoC和AOP的容器框架,主要是针对JavaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器 ...
- Spring:源码解读Spring IOC原理
Spring IOC设计原理解析:本文乃学习整理参考而来 一. 什么是Ioc/DI? 二. Spring IOC体系结构 (1) BeanFactory (2) BeanDefinition 三. I ...
- 轻松理解spring IOC
spring IOC(Inversion of control)即控制反转 概念:一,spring框架的核心之一 二,控制权由对象本身转向容器:由容器根据配置文件去创建实例并创建各个实例之间的依赖关系 ...
随机推荐
- P5327 [ZJOI2019]语言
一边写草稿一边做题吧.要看题解的往下翻,或者是旁边的导航跳一下. 草稿 因为可以开展贸易活动的条件是存在一种通用语 \(L\) 满足 \(u_i\) 到 \(v_i\) 的最短路径上都会 \(L\) ...
- tomcat中配置jndi数据库源
tomcat添加依赖 lib目录下添加依赖mysql-connector-java-8.0.16 配置数据源 介绍两种方法:tomcat中配置或web应用中配置 tomcat/conf/context ...
- 多任务-python实现-协程(2.1.11)
多任务-python实现-协程(2.1.11) 23/100 发布文章 qq_26624329 @ 目录 1.概念 2.迭代器 1.概念 协程与子例程一样,协程(coroutine)也是一种程序组件. ...
- P2240 【深基12.例1】部分背包问题
P2240 [深基12.例1]部分背包问题 题目描述 阿里巴巴走进了装满宝藏的藏宝洞.藏宝洞里面有 N(N \le 100)N(N≤100) 堆金币,第 ii 堆金币的总重量和总价值分别是 m_i,v ...
- IphoneX适配正确姿势
IphoneX适配正确姿势 写在前面 距离18年9月iphonex发布以来已经快两年了(所以对于iphonex机型的头部刘海(sensor housing)和底部小黑条(Home Indicator) ...
- 探究 | App Startup真的能减少启动耗时吗
前言 之前我们说了启动优化的一些常用方法,但是有的小伙伴就很不屑了: "这些方法很久之前就知道了,不知道说点新东西?比如App Startup?能对启动优化有帮助吗?" ok,既然 ...
- 从源码角度学习Java动态代理
前言 最近,看了一下关于RMI(Remote Method Invocation)相关的知识,遇到了一个动态代理的问题,然后就决定探究一下动态代理. 这里先科普一下RMI. RMI 像我们平时写的程序 ...
- 高德打车对接loader.js文件的实现
const u = navigator.userAgent;const isAndroid = u.indexOf('Android') > -1 || u.indexOf('Adr') > ...
- MES系统介绍
为什么要引入MES系统? 随着ERP在企业应用的深入,ERP系统逐渐显示出其局限性.当ERP下达的工单到生产现场后,产品制造是以产线 "工单"或"批次"(Bat ...
- 如果不空null并且不是空字符串才去修改这个值,但这样写只能针对字符串(String)类型,如果是Integer类型的话就会有问题了。 int i = 0; i!=''。 mybatis中会返回tr
mybatis 参数为Integer型数据并赋值0时,有这样一个问题: mybatis.xml中有if判断条件判断参数不为空时,赋值为0的Integer参数被mybatis判断为空,因此不执行< ...
