SpringMVC请求映射handler源码解读
请求映射源码
首先看一张请求完整流转图(这里感谢博客园上这位大神的图,博客地址我忘记了):

前台发送给后台的访问请求是如何找到对应的控制器映射并执行后续的后台操作呢,其核心为DispatcherServlet.java与HandlerMapper。在spring boot初始化的时候,将会加载所有的请求与对应的处理器映射为HandlerMapper组件。我们可以在springMVC的自动配置类中找到对应的Bean。
@Bean@Primary@Overridepublic RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping(@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager,@Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService,@Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) {// Must be @Primary for MvcUriComponentsBuilder to workreturn super.requestMappingHandlerMapping(contentNegotiationManager, conversionService,resourceUrlProvider);}@Beanpublic WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());return welcomePageHandlerMapping;}
请求将首先执行FrameworkServlet下的service方法根据request请求的method找到对应的do**方法。
@Overrideprotected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {processRequest(request, response);}else {//父类根据method参数执行doGet,doPost,doDelete等super.service(request, response);}}
而这些do**其都会进入核心方法,以doGet为例。
@Overrideprotectedfinal void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//核心方法processRequest(request, response);}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {try {//进入此核心方法doService(request, response);}catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {failureCause = ex;throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {failureCause = ex;throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);}finally {resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);if (requestAttributes != null) {requestAttributes.requestCompleted();}logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);}
processRequest()方法中重点在doService(request, response);,而其核心处理逻辑位于DispatchServletl类重写的方法,如下。
@Overrideprotected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {····try {//这里为实际分发控制器的逻辑,其内部是找到对应的handlerMapperdoDispatch(request, response);}finally {if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.if (attributesSnapshot != null) {restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);}}if (requestPath != null) {ServletRequestPathUtils.clearParsedRequestPath(request);}}}
接下来看分发处理逻辑方法,其中重要的方法都使用了原生的注释。接下来分别分析核心源码。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {dispatchException = ex;}catch (Throwable err) {// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);}processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);}catch (Exception ex) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);}catch (Throwable err) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));}finally {if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletionif (mappedHandler != null) {mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);}}else {// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.if (multipartRequestParsed) {cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);}}}}
首先是分析getHandler(),找到对应的处理器映射逻辑。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {if (this.handlerMappings != null) {for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);if (handler != null) {return handler;}}}return null;}
我们将断点标记在getHandler方法上时,可以清除看到handlerMappings,如图。
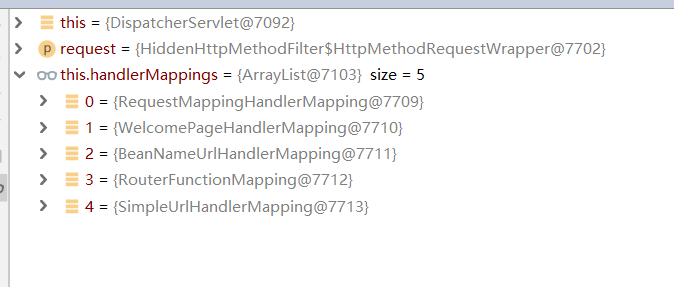
这里,用户请求与处理器的映射关系都在RequestMapperHandlerMapping中,而欢迎页处理请求则在WelcomePageHanderMapping中进行映射。
以下为RequestMapperHandlerMapping中映射部分截图,可以看到用户的所有请求映射这里面都有:
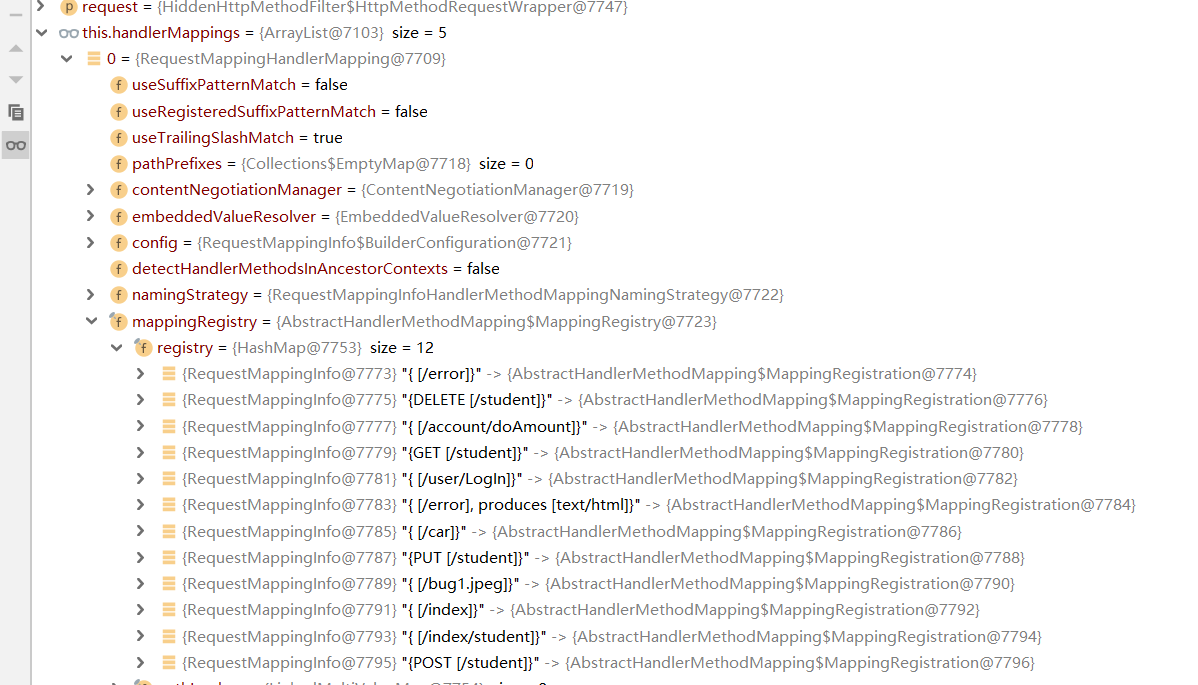
getHandler()后的方法是通过比较request请求中method与HandlerMapper中相同url下的method,再进行唯一性校验,不通过异常,通过找到唯一的handler。
后续,通过handler找到处理的设配器,通过适配器得到一个ModelAndView对象,这个对象就是最后返回给前端页面的对象。
至此,一个请求完整映射到返回前端结束。
说明:这是实现了FramworkServlet的doService方法,FramworkServlet继承自HttpServlet,并且重写了父类中的doGet(),doPost(),doPut(),doDelete 等方法,在这些重写的方法里都调用了 processRquest() 方法做请求处理,进入processRquest()可以看到里面调用了FramworkServlet中定义的doService() 方法。
SpringMVC请求映射handler源码解读的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解读 - HandlerMapping
SpringMVC在请求到handler处理器的分发这步是通过HandlerMapping模块解决的.handlerMapping 还处理拦截器. 先看看HandlerMapping的继承树吧 可以大 ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系
一般我们开发时,使用最多的还是@RequestMapping注解方式. @RequestMapping(value = "/", param = "role=guest& ...
- Flask(4)- flask请求上下文源码解读、http聊天室单聊/群聊(基于gevent-websocket)
一.flask请求上下文源码解读 通过上篇源码分析,我们知道了有请求发来的时候就执行了app(Flask的实例化对象)的__call__方法,而__call__方法返回了app的wsgi_app(en ...
- flask的请求上下文源码解读
一.flask请求上下文源码解读 通过上篇源码分析( ---Flask中的CBV和上下文管理--- ),我们知道了有请求发来的时候就执行了app(Flask的实例化对象)的__call__方法,而__ ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系 https://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/520840 ...
- Alamofire源码解读系列(十二)之请求(Request)
本篇是Alamofire中的请求抽象层的讲解 前言 在Alamofire中,围绕着Request,设计了很多额外的特性,这也恰恰表明,Request是所有请求的基础部分和发起点.这无疑给我们一个Req ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestMappingInfo
使用@RequestMapping注解时,配置的信息最后都设置到了RequestMappingInfo中. RequestMappingInfo封装了PatternsRequestCondition, ...
- CesiumJS 2022^ 源码解读[7] - 3DTiles 的请求、加载处理流程解析
目录 1. 3DTiles 数据集的类型 2. 创建瓦片树 2.1. 请求入口文件 2.2. 创建树结构 2.3. 瓦片缓存机制带来的能力 3. 瓦片树的遍历更新 3.1. 三个大步骤 3.2. 遍历 ...
- Jfinal启动源码解读
本文对Jfinal的启动源码做解释说明. PS:Jfinal启动容器可基于Tomcat/Jetty等web容器启动,本文基于Jetty的启动方式做启动源码的解读和分析,tomcat类似. 入口 JF ...
随机推荐
- 全方位构造免杀 webshell 小结[一]
转载自https://klionsec.github.io/2017/10/11/bypasswaf-for-webshell/ 全方位构造免杀 webshell 小结[一] 前言: 本 ...
- 用python写的一个自动卸载python包的脚本
import osplist=os.popen("pip list") # 执行windows cmd命令,获取所有包package列表,并获取返回结果到plist#跳过第1,2行 ...
- macOS 需要更新软件才能连接到 iOS 设备
macOS 需要更新软件才能连接到 iOS 设备 更新 Mac 上的软件 如果您在 iPhone.iPad 或 iPod touch 上看到"需要更新软件才能连接到 iOS 设备" ...
- WebIDE All In One
WebIDE All In One web IDE Visual Studio Code vscode Code editing Redefined. Free. Built on open sour ...
- 使用 js 实现一个中文自动转换成拼音的工具库
使用 js 实现一个中文自动转换成拼音的工具库 中文 => zhong-wen 应用场景 SEO 友好, URL 自动转换 blogs 发布文章,自动化部署,自动生成 url 的 path (时 ...
- Dart & data type(static / dynamic)
Dart & data type(static / dynamic) Darts 飞镖 标枪 javelin/darts type https://dartpad.dartlang.org/ ...
- Angular Routing
Angular Routing v9.0.7 https://angular.io/start/start-routing
- V8 & ECMAScript & ES-Next
V8 & ECMAScript & ES-Next ES6, ES7, ES8, ES9, ES10, ES11, ES2015, ES2016, ES2017, ES2018, ES ...
- 基本ILS面的评估
一.定义与用途 基本ILS面是ICAO DOC8168飞行程序设计规范中提到的一种限制面. 它相当于附件14中代码为3或4的精密进近跑道所规定的障碍物限制面的子集. 包含:进近面(分为两部分).过渡面 ...
- linux驱动系列之程序反汇编
摘抄网页:http://www.169it.com/article/330129798173630299.html 参考网页:http://www.cppblog.com/liu1061/articl ...
