MySQL数据库之单双表查询
单表查询
先创建表
#创建表
create table employee(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,
hire_date date not null,
post varchar(50),
post_comment varchar(100),
salary double(15,2),
office int, #一个部门一个屋子
depart_id int
); #查看表结构
mysql> desc employee;
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | |
| age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 28 | |
| hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | |
| post | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| post_comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
| salary | double(15,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| office | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| depart_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ #插入记录
#三个部门:教学,销售,运营
insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values
('egon','male',18,'','teacher',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部
('alex','male',78,'','teacher',1000000.31,401,1),
('wupeiqi','male',81,'','teacher',8300,401,1),
('yuanhao','male',73,'','teacher',3500,401,1),
('liwenzhou','male',28,'','teacher',2100,401,1),
('jingliyang','female',18,'','teacher',9000,401,1),
('jinxin','male',18,'','teacher',30000,401,1),
('成龙','male',48,'','teacher',10000,401,1), ('歪歪','female',48,'','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门
('丫丫','female',38,'','sale',2000.35,402,2),
('丁丁','female',18,'','sale',1000.37,402,2),
('星星','female',18,'','sale',3000.29,402,2),
('格格','female',28,'','sale',4000.33,402,2), ('张野','male',28,'','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门
('程咬金','male',18,'','operation',20000,403,3),
('程咬银','female',18,'','operation',19000,403,3),
('程咬铜','male',18,'','operation',18000,403,3),
('程咬铁','female',18,'','operation',17000,403,3)
;
1.注意:
select * from t1 where 条件 group by 分组字段
1.分组只能查询分组字段,要想查看其余的利用聚合函数
2.聚合函数的分类:count,min,max,avg,group_concat,sum等。
3.模糊匹配:用like关键字。
select * from t1 where name like '%eg%'; #%表示任意字符
select * from t1 where name like 'd__l'; #一个下划线表示一个字符,两个下划线就表示两个字符
4.拷贝表 :create table t2 select * from t1;
create table t2 select * from t1 where 1=2 ;
小知识
一.查询语法
SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名
WHERE 条件
GROUP BY field
HAVING 筛选
ORDER BY field
LIMIT 限制条数
二.简单查询
#简单查询
SELECT id,name,sex,age,hire_date,post,post_comment,salary,office,depart_id
FROM employee; SELECT * FROM employee; SELECT name,salary FROM employee; #避免重复DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT post FROM employee; #通过四则运算查询
SELECT name, salary*12 FROM employee;
SELECT name, salary*12 AS Annual_salary FROM employee;
SELECT name, salary*12 Annual_salary FROM employee; #定义显示格式
CONCAT() 函数用于连接字符串
SELECT CONCAT('姓名: ',name,' 年薪: ', salary*12) AS Annual_salary
FROM employee; CONCAT_WS() 第一个参数为分隔符
SELECT CONCAT_WS(':',name,salary*12) AS Annual_salary
FROM employee;
小练习:
1 查出所有员工的名字,薪资,格式为
<名字:egon> <薪资:3000>
select concat('<名字:',name,'> ' ,'<薪资:',salary,'>' ) from employee;
2 查出所有的岗位(去掉重复)
select distinct depart_id from employee;
3 查出所有员工名字,以及他们的年薪,年薪的字段名为年薪
select name,salary*12 年薪 from employee;
三.where约束
where字句中可以使用:
1. 比较运算符:> < >= <= <> !=
2. between 80 and 100 值在10到20之间
3. in(80,90,100) 值是80或90或100
4. like 'eg%'
可以是%或_,
%表示任意多字符
_表示一个字符
like 'e__n' :
5. 逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not
#1:单条件查询
SELECT name FROM employee
WHERE post='sale'; #2:多条件查询
SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE post='teacher' AND salary>10000; #3:关键字BETWEEN AND
SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE salary BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; #4:关键字IS NULL(判断某个字段是否为NULL不能用等号,需要用IS)
SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
WHERE post_comment IS NULL; SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
WHERE post_comment IS NOT NULL; SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee
WHERE post_comment=''; 注意''是空字符串,不是null
ps:
执行
update employee set post_comment='' where id=2;
再用上条查看,就会有结果了 #5:关键字IN集合查询
SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE salary=3000 OR salary=3500 OR salary=4000 OR salary=9000 ; SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE salary IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; SELECT name,salary FROM employee
WHERE salary NOT IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; #6:关键字LIKE模糊查询
通配符’%’
SELECT * FROM employee
WHERE name LIKE 'eg%'; 通配符’_’
SELECT * FROM employee
WHERE name LIKE 'al__';
四.having过滤
having和where语法上是一样的。
select * from employee where id>15;
select * from employee having id>15;
不同点:
#!!!执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > 聚合函数 > having >order by
1.where和having的区别
1. Where 是一个约束声明,使用Where约束来自数据库的数据,Where是在结果返回之前起作用的
(先找到表,按照where的约束条件,从表(文件)中取出数据),Where中不能使用聚合函数
2.Having是一个过滤声明,是在查询返回结果集以后对查询结果进行的过滤操作
(先找到表,按照where的约束条件,从表(文件)中取出数据,然后group by分组,
如果没有group by则所有记录整体为一组,然后执行聚合函数,然后使用having对聚合的结果进行过滤),
在Having中可以使用聚合函数。
3.where的优先级比having的优先级高
4.having可以放到group by之后,而where只能放到group by 之前。
验证:
1.查看员工的id>15的有多少个
select count(id) from employee where id>15;#正确,分析:where先执行,后执行聚合count(id),
然后select出结果
select count(id) from employee having id>15; #报错,分析:先执行聚合count(id),后执行having过滤,
#无法对id进行id>15的过滤
#以上两条sql的顺序是
1:找到表employee--->用where过滤---->没有分组则默认一组执行聚合count(id)--->select执行查看组内id数目
2:找到表employee--->没有分组则默认一组执行聚合count(id)---->having 基于上一步聚合的结果(此时只有count(id)字段了)
进行id>15的过滤,很明显,根本无法获取到id字段
小练习
1. 查询各岗位内包含的员工个数小于2的岗位名、岗位内包含员工名字、个数
select post,group_concat(name) 员工姓名,count(id) 个数 from employee group by post having count(id)<2;
2. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资
select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000;
3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000且小于20000的岗位名、平均工资
select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) between 10000 and 20000;
五、分组查询 group by
大前提:可以按照任意字段分组,但分完组后,只能查看分组的那个字段,要想取的组内的其他字段信息,需要借助函数
单独使用GROUP BY关键字分组
select post from employee group by post;
注意:我们按照post字段分组,那么select查询的字段只能是post,想要获取组内的其他相关信息,需要借助函数 GROUP BY关键字和group_concat()函数一起使用
select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post;#按照岗位分组,并查看组内成员名
select post,group_concat(name) as emp_members FROM employee group by post; GROUP BY与聚合函数一起使用
select post,count(id) as count from employee group by post;#按照岗位分组,并查看每个组有多少人
强调:
分组:一般相同的多的话就可以分成一组(一定是有重复的字段)
小练习:
1. 查询岗位名以及岗位包含的所有员工名字
select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; 2. 查询岗位名以及各岗位内包含的员工个数
select post,count(id) from employee group by post; 3. 查询公司内男员工和女员工的个数
select sex,count(id) from employee group by sex; 4. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的平均薪资
select post,max(salary) from employee group by post; 5. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的最高薪资
select post,max(salary) from employee group by post; 6. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的最低薪资
select post,min(salary) from employee group by post; 7. 查询男员工与男员工的平均薪资,女员工与女员工的平均薪资
select sex,avg(salary) from employee group by sex;
六、关键字的执行优先级(重点)
重点中的重点:关键字的执行优先级
from
where
group by
having
select
distinct
order by
limit
1.找到表:from
2.拿着where指定的约束条件,去文件/表中取出一条条记录
3.将取出的一条条记录进行分组group by,如果没有group by,则整体作为一组
4.如果有聚合函数,则将组进行聚合
5.将4的结果过滤:having
6.查出结果:select
7.去重
8.将6的结果按条件排序:order by
9.将7的结果限制显示条数
七、查询排序order by
按单列排序
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC; 按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序
SELECT * from employee
ORDER BY age,
salary DESC; ===========order by==========
1.select * from employee order by salary;#如果不指定,默认就是升序
2.select * from employee order by salary asc;
3.select * from employee order by salary desc; #先按照年龄升序,当年龄相同的太多,分不清大小时,在按照工资降序
4.select * from employee order by age asc, salary desc;
多表查询
一.介绍
首先先准备表
员工表和部门表
#建表
create table department(
id int,
name varchar(20)
); create table employee1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
); #插入数据
insert into department values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营'); insert into employee1(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('egon','male',18,200),
('alex','female',48,201),
('wupeiqi','male',38,201),
('yuanhao','female',28,202),
('liwenzhou','male',18,200),
('jingliyang','female',18,204)
;
查看
二、多表连接查询
1.交叉连接:不适用任何匹配条件。生成笛卡尔积、
select * from employee1 ,department;
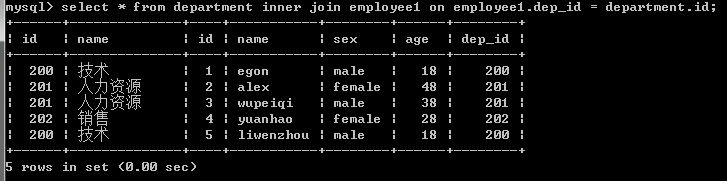
2.内连接:找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果。(只连接匹配的行)
#找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果
#department没有204这个部门,因而employee表中关于204这条员工信息没有匹配出来
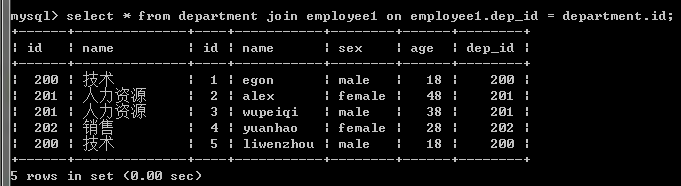
select * from employee1,department where employee1.dep_id=department.id; #上面用where表示的可以用下面的内连接表示,建议使用下面的那种方法
select * from employee1 inner join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id; #也可以这样表示哈
select employee1.id,employee1.name,employee1.age,employee1.sex,department.name from
employee1,department where employee1.dep_id=department.id;
注意:内连接的join可以忽略不写,但是还是加上看起来清楚点
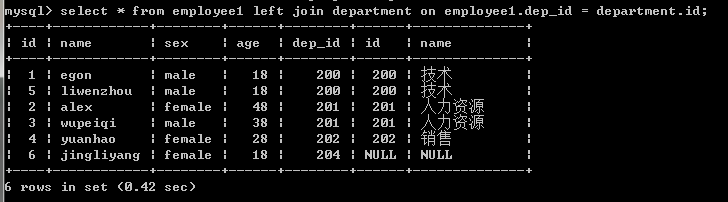
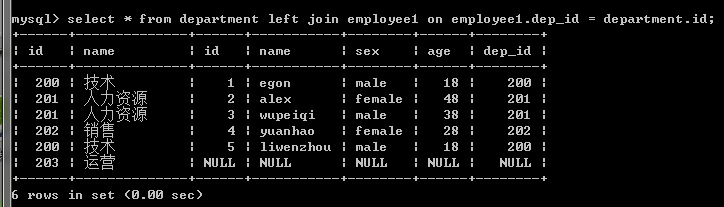
3.左连接:优先显示左表全部记录。
#左链接:在按照on的条件取到两张表共同部分的基础上,保留左表的记录
select * from employee1 left join department on department.id=employee1.dep_id;
select * from department left join employee1 on department.id=employee1.dep_id;
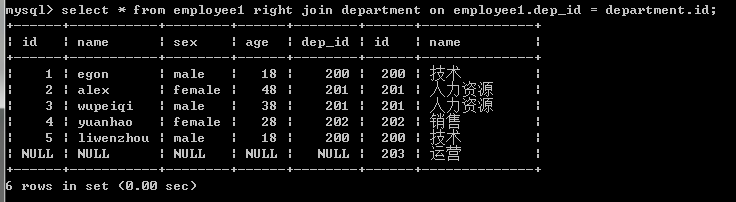
4.右链接:优先显示右表全部记录。
#右链接:在按照on的条件取到两张表共同部分的基础上,保留右表的记录
select * from employee1 right join department on department.id=employee1.dep_id;
select * from department right join employee1 on department.id=employee1.dep_id;

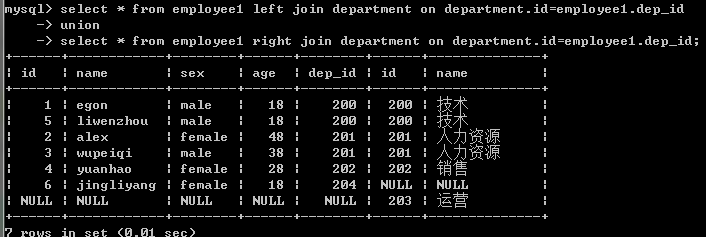
5.全外连接:显示左右两个表的全部记录。
注意:mysql不支持全外连接 full join
强调:mysql可以使用union间接实现全外连接
select * from employee1 left join department on department.id=employee1.dep_id
union
select * from employee1 right join department on department.id=employee1.dep_id;
三、符合条件连接查询
示例1:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25,
即找出公司所有部门中年龄大于25岁的员工
select * from employee1 inner join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id and age>25;
示例2:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示
select * from employee1 inner join department on employee1.dep_id=department.id
= and age>25 and age>25 order by age asc;
四、子查询
#1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
#2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
#3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
#4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
MySQL数据库之单双表查询的更多相关文章
- MySQL数据库之单表查询中关键字的执行顺序
目录 MySQL数据库之单表查询中关键字的执行顺序 1 语法顺序 2 执行顺序 3 关键字使用语法 MySQL数据库之单表查询中关键字的执行顺序 1 语法顺序 select distinct from ...
- MySQL数据库语法-单表查询练习
MySQL数据库语法-单表查询练习 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客主要是对聚合函数和分组的练习. 一.数据表和测试数据准备 /* @author :yinz ...
- mysql数据库之单表查询多表查询
单表查询 前期表准备 create table emp( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, sex e ...
- mysql数据库之单表查询
单标查询 单表查询语句 关键字执行的优先级 简单查询 where约束 group by 聚合函数 HAVING过滤 order by 查询排序 LIMIT限制查询的记录数 使用正则表达式查询 单表查询 ...
- mysql 基础入门 单表查询
单表查询 select 表头,表头 as 别名 ,表头(+-*/的运算) from table_a 1.条件查询 where + 条件 <> , != 不等于 = 等于,也可以表示字符串值 ...
- Java对MySQL数据库进行连接、查询和修改(转)
Java对MySQL数据库进行连接.查询和修改 0. 一般过程: (1) 调用Class.forName()方法加载驱动程序. (2) 调用DriverManager对象的getConnection( ...
- mysql 数据操作 单表查询 目录
mysql 数据操作 单表查询 mysql 数据操作 单表查询 简单查询 避免重复DISTINCT mysql 数据操作 单表查询 通过四则运算查询 mysql 数据操作 单表查询 concat()函 ...
- MySQL数据库语法-多表查询练习一
MySQL数据库语法-多表查询练习一 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客主要介绍的多表查询的外键约束,以及如何使用外链接和内连接查询数据信息. 一.数据表和测试 ...
- mysql 数据操作 单表查询 where 约束 目录
mysql 数据操作 单表查询 where约束 between and or mysql 数据操作 单表查询 where约束 is null in mysql 数据操作 单表查询 where约束 li ...
随机推荐
- HTML5本地存储——IndexedDB
在HTML5本地存储——Web SQL Database提到过Web SQL Database实际上已经被废弃,而HTML5的支持的本地存储实际上变成了 Web Storage(Local Stora ...
- Extjs自定义验证介绍
表单验证实例(空验证,密码确认验证,email验证) 我们可以用单独的js写表单验证,但是extjs已经为我们想到了(自己单独写反而不方便). 在验证之前,我不得不提两个小知识点: //大家在很多的e ...
- shell脚本进阶 详解及其实例(一)
v\:* {behavior:url(#default#VML);} o\:* {behavior:url(#default#VML);} w\:* {behavior:url(#default#VM ...
- TCP连接三次握手协议,释放连接四次挥手,以及使用 awl伪造mac地址进行多线程syn洪泛攻击。
这个TCP连接就是一次追女生-谈恋爱-分手,追求比分手简单,但是分手比追求复杂.哥,谈了半年的女朋友,在就快要成功了的时候分了,原因是因为有人在后面该老子背后搞SYN洪泛攻击,最后女朋友丢失了.学会T ...
- 如何使用jquery.qrcode.js插件生成二维码
1.首先需要准备 jquery.qrcode.js 和 jquery.js github地址:https://github.com/lrsjng/jquery-qrcode 官方文档地址:http:/ ...
- Vcenter虚拟化三部曲----Vcenter server 5.5安装部署
配置SQL Server 2008 R2 1.选择启动 SQL Server Management Studio. 2.选择SQL Server 身份验证登录 ---- 输入sa用户及密码. 3.右键 ...
- eclipse的svn插件
SVN插件下载地址及更新地址,你根据需要选择你需要的版本.现在最新是1.8.xLinks for 1.8.x Release:Eclipse update site URL: http://subcl ...
- jquery 增加与删除数组元素
1.数组元素的添加 demoArray.push(value); var demo=new Array(); var key=[4,5]; demo.push(1);//插入数字 demo.push( ...
- linux 命令 uniq
linux命令uniq去重 实例详细说明linux下去除重复行命令uniq 一,uniq干什么用的 文本中的重复行,基本上不是我们所要的,所以就要去除掉.linux下有其他命令可以去除重复行,但是我觉 ...
- AFNetworking 2.x 的SSL身份认证
一般来讲如果app用了web service , 我们需要防止数据嗅探来保证数据安全.通常的做法是用ssl来连接以防止数据抓包和嗅探 其实这么做的话还是不够的.我们还需要防止中间人攻击(不明白的自己去 ...
