一步一步详解ID3和C4.5的C++实现
1. 关于ID3和C4.5的原理介绍这里不赘述,网上到处都是,可以下载讲义c9641_c001.pdf或者参考李航的《统计学习方法》.
2. 数据与数据处理
- 本文采用下面的训练数据:

- 数据处理:本文只采用了"Outlook", "Humidity", "Windy"三个属性,然后根据Humidity的值是否大于75,将Humidity的值归为两类,Play Golf 的值就是类别标签,只有yes 和 no两类
- 训练集是字符和数字的混合,这会给编程带来麻烦,所以首先把训练集用数字表示出来:
- const unsigned att_num = ;
- const unsigned rule_num = ;
- string decision_tree_name("Play Golf ?");
- string attribute_names[] = {"Outlook", "Humidity", "Windy"};
- string attribute_values[] = {"Sunny", "Overcast", "Rainy", "> 75", "<= 75", "True", "False", "Yes", "No"};
- //训练集最后一列为分类标签,所以总列数为属性数加1
- unsigned train_data[rule_num][att_num + ] = {
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , }
- };
以train_data的第一行{0, 3, 6, 8}为例解释:前三列值对应的属性与attribute_names中的元素分别对应,最后一列是类别标签的值,0 表示 attribute_values的第1个元素,即”Sunny“,类似3便是attribute_values的第4个元素"> 75",6 是 "False",8 是"No",所以{0, 3, 6, 8} 代表的实例就是:
- const unsigned att_num = ;

其他实例都是以这样的方式数字化,方便编程.
3. 编写必要函数
因为ID3和C4.5都需要计算属性的信息增益,C4.5还需要计算属性的信息增益比,所正确编写这两个函数很重要,对比着讲义c9641_c001.pdf或者其他参考资料,编写出这两个函数.(代码最后附上)
4. 确定数据结构
这是最重要的一环,明确目的:构造一个决策树!这就直接决定了编程的正确或者难易,网上有很多例子,但是我觉得不够简洁,这里我采用一种简单且容易理解的方式:
- struct Tree{
- unsigned root;//节点属性值
- vector<unsigned> branches;//节点可能取值
- vector<Tree> children; //孩子节点
- };
每一个决策树都是由根节点开始,然后有很多分支,分支连接着孩子节点,而每一个孩子节点以及这个孩子节点对应的所有子孙又可以组成一棵树,这是一个不断递归的过程,所以采用了上面的数据结构.
5. 构造决策树
有了上面的基础,开始着手构造决策树,根据规则选出某一属性作为根节点,根据根节点的取值确定分支,然后构造孩子节点,根据上面的陈述可以知道,每一个孩子节点及其后面的子孙又是一棵树,所以这是一个递归操作,即采用前面同样的方式来构造这个子树,以此类推。
6. 打印决策树
因为树的结构是递归的,所以打印决策树同样是一个递归的过程。
7. 代码实现
- /*************************************************
- Copyright:1.0
- Author:90Zeng
- Date:2014-11-25
- Description:ID3/C4.5 algorithm
- **************************************************/
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cmath>
- #include <vector>
- #include <string>
- #include <algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- const unsigned att_num = ;
- const unsigned rule_num = ;
- string decision_tree_name("Play Golf ?");
- string attribute_names[] = {"Outlook", "Humidity", "Windy"};
- string attribute_values[] = {"Sunny", "Overcast", "Rainy", "> 75", "<= 75", "True", "False", "Yes", "No"};
- //训练集最后一列为分类标签,所以总列数为属性数加1
- unsigned train_data[rule_num][att_num + ] = {
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , },{, , , },
- {, , , },{, , , }
- };
- /*************************************************
- Function: unique()
- Description: 将vector中重复元素合并,只保留一个
- Calls: 无
- Input: vector
- Output: vector
- *************************************************/
- template <typename T>
- vector<T> unique(vector<T> vals)
- {
- vector<T> unique_vals;
- vector<T>::iterator itr;
- vector<T>::iterator subitr;
- int flag = ;
- while( !vals.empty() )
- {
- unique_vals.push_back(vals[]);
- itr = vals.begin();
- subitr = unique_vals.begin() + flag;
- while ( itr != vals.end())
- {
- if (*subitr == *itr)
- itr = vals.erase(itr);
- else
- itr++;
- }
- flag++;
- }
- return unique_vals;
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: log2()
- Description: 计算一个数值得以2为底的对数
- Calls: 无
- Input: double
- Output: double
- *************************************************/
- double log2(double n)
- {
- return log10(n) / log10(2.0);
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: compute_entropy()
- Description: 根据属性的取值,计算该属性的熵
- Calls: unique(),log2(),count(),其中count()
- 在STL的algorithm库中
- Input: vector<unsigned>
- Output: double
- *************************************************/
- double compute_entropy(vector<unsigned> v)
- {
- vector<unsigned> unique_v;
- unique_v = unique(v);
- vector<unsigned>::iterator itr;
- itr = unique_v.begin();
- double entropy = 0.0;
- auto total = v.size();
- while(itr != unique_v.end())
- {
- double cnt = count(v.begin(), v.end(), *itr);
- entropy -= cnt / total * log2(cnt / total);
- itr++;
- }
- return entropy;
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: compute_gain()
- Description: 计算数据集中所有属性的信息增益
- Calls: compute_entropy(),unique()
- Input: vector<vector<unsigned> >
- 相当于一个二维数组,存储着训练数据集
- Output: vector<double> 存储着所有属性的信息
- 增益
- *************************************************/
- vector<double> compute_gain(vector<vector<unsigned> > truths)
- {
- vector<double> gain(truths[].size() - , );
- vector<unsigned> attribute_vals;
- vector<unsigned> labels;
- for(unsigned j = ; j < truths.size(); j++)
- {
- labels.push_back(truths[j].back());
- }
- for(unsigned i = ; i < truths[].size() - ; i++)//最后一列是类别标签,没必要计算信息增益
- {
- for(unsigned j = ; j < truths.size(); j++)
- attribute_vals.push_back(truths[j][i]);
- vector<unsigned> unique_vals = unique(attribute_vals);
- vector<unsigned>::iterator itr = unique_vals.begin();
- vector<unsigned> subset;
- while(itr != unique_vals.end())
- {
- for(unsigned k = ; k < truths.size(); k++)
- {
- if (*itr == attribute_vals[k])
- {
- subset.push_back(truths[k].back());
- }
- }
- double A = (double)subset.size();
- gain[i] += A / truths.size() * compute_entropy(subset);
- itr++;
- subset.clear();
- }
- gain[i] = compute_entropy(labels) - gain[i];
- attribute_vals.clear();
- }
- return gain;
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: compute_gain_ratio()
- Description: 计算数据集中所有属性的信息增益比
- C4.5算法中用到
- Calls: compute_gain();compute_entropy()
- Input: 训练数据集
- Output: 信息增益比
- *************************************************/
- vector<double> compute_gain_ratio(vector<vector<unsigned> > truths)
- {
- vector<double> gain = compute_gain(truths);
- vector<double> entropies;
- vector<double> gain_ratio;
- for(unsigned i = ; i < truths[].size() - ; i++)//最后一列是类别标签,没必要计算信息增益比
- {
- vector<unsigned> attribute_vals(truths.size(), );
- for(unsigned j = ; j < truths.size(); j++)
- {
- attribute_vals[j] = truths[j][i];
- }
- double current_entropy = compute_entropy(attribute_vals);
- if (current_entropy)
- {
- gain_ratio.push_back(gain[i] / current_entropy);
- }
- else
- gain_ratio.push_back(0.0);
- }
- return gain_ratio;
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: find_most_common_label()
- Description: 找出数据集中最多的类别标签
- Calls: count();
- Input: 数据集
- Output: 类别标签
- *************************************************/
- template <typename T>
- T find_most_common_label(vector<vector<T> > data)
- {
- vector<T> labels;
- for (unsigned i = ; i < data.size(); i++)
- {
- labels.push_back(data[i].back());
- }
- vector<T>:: iterator itr = labels.begin();
- T most_common_label;
- unsigned most_counter = ;
- while (itr != labels.end())
- {
- unsigned current_counter = count(labels.begin(), labels.end(), *itr);
- if (current_counter > most_counter)
- {
- most_common_label = *itr;
- most_counter = current_counter;
- }
- itr++;
- }
- return most_common_label;
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: find_attribute_values()
- Description: 根据属性,找出该属性可能的取值
- Calls: unique();
- Input: 属性,数据集
- Output: 属性所有可能的取值(不重复)
- *************************************************/
- template <typename T>
- vector<T> find_attribute_values(T attribute, vector<vector<T> > data)
- {
- vector<T> values;
- for (unsigned i = ; i < data.size(); i++)
- {
- values.push_back(data[i][attribute]);
- }
- return unique(values);
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: drop_one_attribute()
- Description: 在构建决策树的过程中,如果某一属性已经考察过了
- 那么就从数据集中去掉这一属性,此处不是真正意义
- 上的去掉,而是将考虑过的属性全部标记为110,当
- 然可以是其他数字,只要能和原来训练集中的任意数
- 字区别开来即可
- Calls: unique();
- Input: 属性,数据集
- Output: 属性所有可能的取值(不重复)
- *************************************************/
- template <typename T>
- vector<vector<T> > drop_one_attribute(T attribute, vector<vector<T> > data)
- {
- vector<vector<T> > new_data(data.size(),vector<T>(data[].size() - , ));
- for (unsigned i = ; i < data.size(); i++)
- {
- data[i][attribute] = ;
- }
- return data;
- }
- struct Tree{
- unsigned root;//节点属性值
- vector<unsigned> branches;//节点可能取值
- vector<Tree> children; //孩子节点
- };
- /*************************************************
- Function: build_decision_tree()
- Description: 递归构建决策树
- Calls: unique(),count(),
- find_most_common_label()
- compute_gain()(ID3),
- compute_gain_ratio()(C4.5),
- find_attribute_values(),
- drop_one_attribute(),
- build_decision_tree()(递归,
- 当然要调用函数本身)
- Input: 训练数据集,一个空决策树
- Output: 无
- *************************************************/
- void build_decision_tree(vector<vector<unsigned> > examples, Tree &tree)
- {
- //第一步:判断所有实例是否都属于同一类,如果是,则决策树是单节点
- vector<unsigned> labels(examples.size(), );
- for (unsigned i = ; i < examples.size(); i++)
- {
- labels[i] = examples[i].back();
- }
- if (unique(labels).size() == )
- {
- tree.root = labels[];
- return;
- }
- //第二步:判断是否还有剩余的属性没有考虑,如果所有属性都已经考虑过了,
- //那么此时属性数量为0,将训练集中最多的类别标记作为该节点的类别标记
- if (count(examples[].begin(),examples[].end(),) == examples[].size() - )//只剩下一列类别标记
- {
- tree.root = find_most_common_label(examples);
- return;
- }
- //第三步:在上面两步的条件都判断失败后,计算信息增益,选择信息增益最大
- //的属性作为根节点,并找出该节点的所有取值
- vector<double> standard = compute_gain(examples);
- //要是采用C4.5,将上面一行注释掉,把下面一行的注释去掉即可
- //vector<double> standard = compute_gain_ratio(examples);
- tree.root = ;
- for (unsigned i = ; i < standard.size(); i++)
- {
- if (standard[i] >= standard[tree.root] && examples[][i] != )
- tree.root = i;
- }
- tree.branches = find_attribute_values(tree.root, examples);
- //第四步:根据节点的取值,将examples分成若干子集
- vector<vector<unsigned> > new_examples = drop_one_attribute(tree.root, examples);
- vector<vector<unsigned> > subset;
- for (unsigned i = ; i < tree.branches.size(); i++)
- {
- for (unsigned j = ; j < examples.size(); j++)
- {
- for (unsigned k = ; k < examples[].size(); k++)
- {
- if (tree.branches[i] == examples[j][k])
- subset.push_back(new_examples[j]);
- }
- }
- // 第五步:对每一个子集递归调用build_decision_tree()函数
- Tree new_tree;
- build_decision_tree(subset,new_tree);
- tree.children.push_back(new_tree);
- subset.clear();
- }
- }
- /*************************************************
- Function: print_tree()
- Description: 从第根节点开始,逐层将决策树输出到终
- 端显示
- Calls: print_tree();
- Input: 决策树,层数
- Output: 无
- *************************************************/
- void print_tree(Tree tree,unsigned depth)
- {
- for (unsigned d = ; d < depth; d++) cout << "\t";
- if (!tree.branches.empty()) //不是叶子节点
- {
- cout << attribute_names[tree.root] << endl;
- for (unsigned i = ; i < tree.branches.size(); i++)
- {
- for (unsigned d = ; d < depth + ; d++) cout << "\t";
- cout << attribute_values[tree.branches[i]] << endl;
- print_tree(tree.children[i],depth + );
- }
- }
- else //是叶子节点
- {
- cout << attribute_values[tree.root] << endl;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- vector<vector<unsigned> > rules(rule_num, vector<unsigned>(att_num + , ));
- for(unsigned i = ; i < rule_num; i++)
- {
- for(unsigned j = ; j <= att_num; j++)
- rules[i][j] = train_data[i][j];
- }
- Tree tree;
- build_decision_tree(rules, tree);
- cout << decision_tree_name << endl;
- print_tree(tree,);
- return ;
- }
8.运行结果:

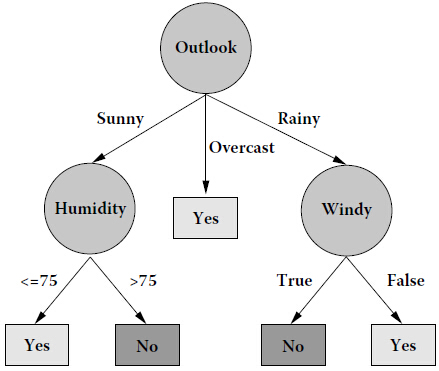
前者是采用ID3运行的结果,后者是讲义c9641_c001.pdf给出的构造的决策树,二者一致,验证了程序的正确性.
9.总结
所谓”百鸟在林,不如一鸟在手“, ID3和C4.5的思想都很简单,容易理解,但是在实现的的过程中由于数据结构的确定和递归调用等问题,还是调试了很久,收获很多,实践出真知!
一步一步详解ID3和C4.5的C++实现的更多相关文章
- JFinal源码详解
JFinal的框架我24号的一篇博文写到过,它优秀的地方在精简代码上,那么有两处源码是我觉得是值得我们要好好解析一下,一处是初始化加载—servlet跳转,另一处是DB+ActiveRecord的映射 ...
- Linux网络编程一步一步学【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-10747583-id-297982.html Linux网络编程一步一步学+基础 原文地址:http://blogold.chin ...
- ElasticSearch第四步-查询详解
ElasticSearch系列学习 ElasticSearch第一步-环境配置 ElasticSearch第二步-CRUD之Sense ElasticSearch第三步-中文分词 ElasticSea ...
- Centos7 配置网络步奏详解
Centos7 配置网络步奏详解 编辑网卡配置文件 vi /etc/sysconfig/network-script/ifcfg-ens01 备注:这里的ens01不是所有系统都叫这个,有的可能叫其他 ...
- 一步一步造个IoC轮子(二),详解泛型工厂
一步一步造个Ioc轮子目录 一步一步造个IoC轮子(一):Ioc是什么 一步一步造个IoC轮子(二):详解泛型工厂 一步一步造个IoC轮子(三):构造基本的IoC容器 详解泛型工厂 既然我说IoC容器 ...
- ElasticSearch第五步-.net平台下c#操作ElasticSearch详解
前面我们讲解了关于ElasticSearch的安装配置,以及CRUD 本章我将讲解怎么使用c#操作ElasticSearch. 首先你需要一定的技术储备,比如:asp.net webapi,mvc,j ...
- 一步一步使用ABP框架搭建正式项目系列教程之本地化详解
返回总目录<一步一步使用ABP框架搭建正式项目系列教程> 本篇目录 扯扯本地化 ABP中的本地化 小结 扯扯本地化 本节来说说本地化,也有叫国际化.全球化的,不管怎么个叫法,反正道理都是一 ...
- 【Devops】【docker】【CI/CD】关于jenkins构建成功后一步,执行的shell命令详解+jenkins容器运行宿主机shell命令的实现方法
1.展示这段shell命令 +详解 #================================================================================= ...
- “makefile”写法详解,一步一步写一个实用的makefile,详解 sed 's,$∗\.o[ :]*,\1.o $@ : ,g' < $@.
目的:编写一个实用的makefile,能自动编译当前目录下所有.c/.cpp源文件,支持二者混合编译.并且当某个.c/.cpp..h或依赖的源文件被修改后,仅重编涉及到的源文件,未涉及的不编译. 二要 ...
随机推荐
- FieldGroup绑定的日期类型存储格式的问题
问题 日期存储的时候,当前数据库中存储格式为 "2017-9-5 0:00:00", 而我实现了以后,看到数据库的存储格式为 "Mon Sep 04 00:00:00 C ...
- CSS覆盖公共样式中的某个属性
CSS如何覆盖公共样式中的某个属性?利用CSS样式的优先级. 如下例子: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transition ...
- day25 初始面向对象
类 有具体规范,无具体值对象 有具体的值 dict 类d = {"":""} 对象 自定义一个类格式: class 类名: # 可以跟()或者不跟 属性 = ' ...
- MT【51】一道三角求最值问题
[Genius is one percent inspiration and ninety-nine percent perspiration]--- 爱迪生 [Without the one per ...
- Deep Learning(深度学习)学习笔记整理系列 一
声明: 1)该Deep Learning的学习系列是整理自网上很大牛和机器学习专家所无私奉献的资料的.具体引用的资料请看参考文献.具体的版本声明也参考原文献. 2)本文仅供学术交流,非商用.所以每一部 ...
- 【模板】spfa
代码如下 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxv=1e4+10; const int maxe=5e5+1 ...
- CodeForces 纪念一下这个突破性的时刻
- 开启 Hyper-v 后如何使用 Android Emulator?
如果开启了 Hyper-v 时,当需要使用 Android Studio 中 Android Emulator 时,系统会出现蓝屏代码错误. 使用下面的方法,则可以解决冲突. 首先,你需要确保已经开启 ...
- maveb安装与配置(win10)
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/eagle6688/p/7838224.html 看了几篇博客,感觉这篇博客写的含金量最高了,因为我电脑的系统是win10的,所以配置有细微的差别 ...
- GTF文件
一.GTF文件格式 Fields must be tab-separated. Also, all but the final field in each feature line must cont ...
