Matplotlib新手上路(下)
接上篇继续,这次来演示下如何做动画,以及加载图片
一、动画图
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import matplotlib.animation as animation
- fig, ax = plt.subplots()
- x = np.arange(0, 2 * np.pi, 0.01)
- line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
- def init():
- line.set_ydata([np.nan] * len(x)) # Y轴值归0,Mac上加不加这句,都一样
- return line,
- def animate(i):
- line.set_ydata(np.sin(x + i / 100)) # update the data.
- return line,
- ani = animation.FuncAnimation(
- # blit在Mac上只能设置False,否则动画有残影
- fig, animate, init_func=init, interval=2, blit=False, save_count=50)
- init()
- plt.show()
基本套路是:init()函数中给定图象的初始状态,然后animate()函数中每次对函数图象动态调整一点点,最后用FuncAnimation把它们串起来。
再来看一个官网给的比较好玩的示例:
- from numpy import sin, cos
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import scipy.integrate as integrate
- import matplotlib.animation as animation
- G = 9.8 # acceleration due to gravity, in m/s^2
- L1 = 1.0 # length of pendulum 1 in m
- L2 = 1.0 # length of pendulum 2 in m
- M1 = 1.0 # mass of pendulum 1 in kg
- M2 = 1.0 # mass of pendulum 2 in kg
- def derivs(state, t):
- dydx = np.zeros_like(state)
- dydx[0] = state[1]
- del_ = state[2] - state[0]
- den1 = (M1 + M2) * L1 - M2 * L1 * cos(del_) * cos(del_)
- dydx[1] = (M2 * L1 * state[1] * state[1] * sin(del_) * cos(del_) +
- M2 * G * sin(state[2]) * cos(del_) +
- M2 * L2 * state[3] * state[3] * sin(del_) -
- (M1 + M2) * G * sin(state[0])) / den1
- dydx[2] = state[3]
- den2 = (L2 / L1) * den1
- dydx[3] = (-M2 * L2 * state[3] * state[3] * sin(del_) * cos(del_) +
- (M1 + M2) * G * sin(state[0]) * cos(del_) -
- (M1 + M2) * L1 * state[1] * state[1] * sin(del_) -
- (M1 + M2) * G * sin(state[2])) / den2
- return dydx
- # create a time array from 0..100 sampled at 0.05 second steps
- dt = 0.05
- t = np.arange(0.0, 20, dt)
- # th1 and th2 are the initial angles (degrees)
- # w10 and w20 are the initial angular velocities (degrees per second)
- th1 = 120.0
- w1 = 0.0
- th2 = -10.0
- w2 = 0.0
- # initial state
- state = np.radians([th1, w1, th2, w2])
- # integrate your ODE using scipy.integrate.
- y = integrate.odeint(derivs, state, t)
- x1 = L1 * sin(y[:, 0])
- y1 = -L1 * cos(y[:, 0])
- x2 = L2 * sin(y[:, 2]) + x1
- y2 = -L2 * cos(y[:, 2]) + y1
- fig = plt.figure()
- ax = fig.add_subplot(111, autoscale_on=False, xlim=(-2, 2), ylim=(-2, 2))
- ax.set_aspect('equal')
- ax.grid()
- line, = ax.plot([], [], 'o-', lw=2)
- time_template = 'time = %.1fs'
- time_text = ax.text(0.05, 0.9, '', transform=ax.transAxes)
- def init():
- line.set_data([], [])
- time_text.set_text('')
- return line, time_text
- def animate(i):
- thisx = [0, x1[i], x2[i]]
- thisy = [0, y1[i], y2[i]]
- line.set_data(thisx, thisy)
- time_text.set_text(time_template % (i * dt))
- return line, time_text
- ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, np.arange(1, len(y)),
- interval=25, blit=False, init_func=init)
- plt.show()
甚至还可以创建一些艺术气息的动画:
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
- # Fixing random state for reproducibility
- np.random.seed(19680801)
- # Create new Figure and an Axes which fills it.
- fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
- ax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], frameon=False)
- ax.set_xlim(0, 1), ax.set_xticks([])
- ax.set_ylim(0, 1), ax.set_yticks([])
- # Create rain data
- n_drops = 50
- rain_drops = np.zeros(n_drops, dtype=[('position', float, 2),
- ('size', float, 1),
- ('growth', float, 1),
- ('color', float, 4)])
- # Initialize the raindrops in random positions and with
- # random growth rates.
- rain_drops['position'] = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (n_drops, 2))
- rain_drops['growth'] = np.random.uniform(50, 200, n_drops)
- # Construct the scatter which we will update during animation
- # as the raindrops develop.
- scat = ax.scatter(rain_drops['position'][:, 0], rain_drops['position'][:, 1],
- s=rain_drops['size'], lw=0.3, edgecolors=rain_drops['color'],
- facecolors='none')
- def update(frame_number):
- # Get an index which we can use to re-spawn the oldest raindrop.
- current_index = frame_number % n_drops
- # Make all colors more transparent as time progresses.
- rain_drops['color'][:, 3] -= 1.0/len(rain_drops)
- rain_drops['color'][:, 3] = np.clip(rain_drops['color'][:, 3], 0, 1)
- # Make all circles bigger.
- rain_drops['size'] += rain_drops['growth']
- # Pick a new position for oldest rain drop, resetting its size,
- # color and growth factor.
- rain_drops['position'][current_index] = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 2)
- rain_drops['size'][current_index] = 5
- rain_drops['color'][current_index] = (0, 0, 0, 1)
- rain_drops['growth'][current_index] = np.random.uniform(50, 200)
- # Update the scatter collection, with the new colors, sizes and positions.
- scat.set_edgecolors(rain_drops['color'])
- scat.set_sizes(rain_drops['size'])
- scat.set_offsets(rain_drops['position'])
- # Construct the animation, using the update function as the animation director.
- animation = FuncAnimation(fig, update, interval=10)
- plt.show()

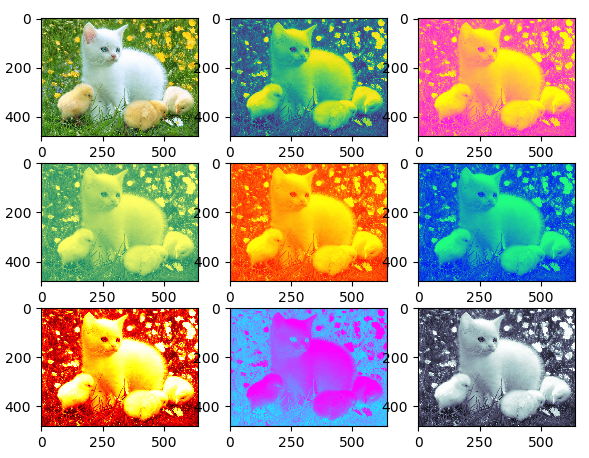
二、加载图片
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import matplotlib.image as mpimg
- img = mpimg.imread('cat.png') # 随便从网上捞的一张图片,保存到当前目录下
- lum_img = img[:, :, 0]
- # plt.figure()
- plt.subplot(331)
- plt.imshow(img)
- plt.subplot(332)
- plt.imshow(lum_img)
- plt.subplot(333)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="spring")
- plt.subplot(334)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="summer")
- plt.subplot(335)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="autumn")
- plt.subplot(336)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="winter")
- plt.subplot(337)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="hot")
- plt.subplot(338)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="cool")
- plt.subplot(339)
- plt.imshow(lum_img, cmap="bone")
- plt.show()
Matplotlib新手上路(下)的更多相关文章
- Matplotlib新手上路(中)
接上回继续 一.多张图布局(subplot) 1.1 subplot布局方式 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.figure() plt.subplot(3, 2 ...
- Matplotlib新手上路(上)
matplotlib是python里用于绘图的专用包,功能十分强大.下面介绍一些最基本的用法: 一.最基本的划线 先来一个简单的示例,代码如下,已经加了注释: import matplotlib.py ...
- php大力力 [001节]2015-08-21.php在百度文库的几个基础教程新手上路日记 大力力php 大力同学 2015-08-21 15:28
php大力力 [001节]2015-08-21.php在百度文库的几个基础教程新手上路日记 大力力php 大力同学 2015-08-21 15:28 话说,嗯嗯,就是我自己说,做事认真要用表格,学习技 ...
- OpenGL教程之新手上路
Jeff Molofee(NeHe)的OpenGL教程- 新手上路 译者的话:NeHe的教程一共同拥有30多课,内容翔实,而且不断更新 .国内的站点实在应该向他们学习.令人吃惊的是,NeHe提供的例程 ...
- webpack4配置详解之新手上路初探
前言 经常会有群友问起webpack.react.redux.甚至create-react-app配置等等方面的问题,有些是我也不懂的,慢慢从大家的相互交流中,也学到了不少. 今天就尝试着一起来聊 ...
- 转-spring-boot 注解配置mybatis+druid(新手上路)-http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_36203615/article/details/53759935
spring-boot 注解配置mybatis+druid(新手上路) 转载 2016年12月20日 10:17:17 标签: sprinb-boot / mybatis / druid 10475 ...
- Ocelot 新手上路
新手上路,老司机请多多包含!Ocelot 在博园里文章特别多,但是按照其中一篇文章教程,如果经验很少或者小白,是没法将程序跑向博主的结果. 因此总结下 参考多篇文章,终于达到预期效果. Oce ...
- 新手上路——it人如何保持竞争力
新手上路——如何保持竞争力 JINGZHENGLI 套用葛大爷的一句名言:21世纪什么最贵,人才.哪你是人才还是人材?还是人财或人裁?相信大家都不是最后一种.何如保持住这个光环呢?就需要我们保持我们独 ...
- Dart语言快速学习上手(新手上路)
Dart语言快速学习上手(新手上路) // 声明返回值 int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } // 不声明返回值 add2(int a, int b) { r ...
随机推荐
- Day6------------磁盘用满的两种情况
1.文件包含元数据和写入的内容 元数据:存在硬盘中的inode ls -i /etc/passwd.bak 查看inode df -i 查看inode 2.磁盘用满的两种情况 1).内容太多 2).空 ...
- Spark的HA部署
一.安装JDK.Scala 二.安装zookeeper 三.安装Hadoop 四.安装Spark 1.修改spark/conf/spark-env.sh export JAVA_HOME=/usr/j ...
- LeetCode(59):螺旋矩阵 II
Medium! 题目描述: 给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵. 示例: 输入: 3 输出: [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 8, 9, ...
- 性能测试九:jmeter进阶之beanshell的使用+断言
一.使用 BeanShell使用方式一 BeanShell面板上写脚本 // 从vars中获取用户定义的参数,并转换为int类型 int p_skuId = Integer.parseInt(vars ...
- pytest十三:配置文件 pytest.ini
pytest 配置文件可以改变 pytest 的运行方式,它是一个固定的文件 pytest.ini 文件,读取配置信息,按指定的方式去运行. ini 配置文件pytest 里面有些文件是非 test ...
- python 全栈开发,Day135(爬虫系列之第2章-BS和Xpath模块)
一.BeautifulSoup 1. 简介 简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据.官方解释如下: ''' Beautiful Soup提供一些简单 ...
- python 全栈开发,Day132(玩具管理页面,控制玩具通讯录,基于请求的好友关系建立)
先下载github代码,下面的操作,都是基于这个版本来的! https://github.com/987334176/Intelligent_toy/archive/v1.5.zip 注意:由于涉及到 ...
- python 全栈开发,Day64(视图,触发器,函数,存储过程,事务)
昨日内容回顾 pymysql:属于python的一个模块 pip3 install pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(...,charset = 'uft8') 创建游标 ...
- myeclipse启动错误:org.eclipse.swt.SWTError: No more handles
myeclipse启动错误,生成日志: !SESSION 2014-11-06 09:13:16.296 ----------------------------------------------- ...
- day17--JQuery选择器
操作HTML标签的时候,我们首先要找到HTML标签的位置,然后进行操作,下面来看看集中查找标签的方法,如下: 1.Id选择器 -- Id在HTML中是唯一的,通过Id进行查找,Id ...
