CodeForces - 631C (截取法)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Technologies". There are n commodities produced by the company. For each of them there is exactly one integer in the final report, that denotes corresponding revenue. Before the report gets to Blake, it passes through the hands of m managers. Each of them may reorder the elements in some order. Namely, the i-th manager either sorts first ri numbers in non-descending or non-ascending order and then passes the report to the manager i + 1, or directly to Blake (if this manager has number i = m).
Employees of the "Blake Technologies" are preparing the report right now. You know the initial sequence ai of length n and the description of each manager, that is value ri and his favourite order. You are asked to speed up the process and determine how the final report will look like.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of commodities in the report and the number of managers, respectively.
The second line contains n integers ai (|ai| ≤ 109) — the initial report before it gets to the first manager.
Then follow m lines with the descriptions of the operations managers are going to perform. The i-th of these lines contains two integers ti and ri (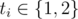 , 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
, 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
Print n integers — the final report, which will be passed to Blake by manager number m.
3 1
1 2 3
2 2
2 1 3
4 2
1 2 4 3
2 3
1 2
2 4 1 3
In the first sample, the initial report looked like: 1 2 3. After the first manager the first two numbers were transposed: 2 1 3. The report got to Blake in this form.
In the second sample the original report was like this: 1 2 4 3. After the first manager the report changed to: 4 2 1 3. After the second manager the report changed to: 2 4 1 3. This report was handed over to Blake.
题意:先输入两个数n,m,再输入一个长度为n的数列,输入m个有先后关系的操作(后面的操作建立在前面操作的基础上),每个操作有两个数 t,r,t==1代表把当前前 r 个数按照非递减(递增)顺序排序,t==2代表把当前前 r 个数按照非递增(递减)顺序排序。
思路:通过题意我们可以知道,如果后面的操作中如果有 r 大于等于前面操作中的 r ,则前面的操作就相当于没有作用(假设当你递增排序排好了前r个,我如果后面再递减排序前r+1个,你前面的排序就没有用),这样可以减少部分的不必要的操作,但是如果你就按照你优化后的操作来 一 一排序,还是会超时的。
我们还要考虑怎么再去减少不必要的操作,当我们优化操作之后,得到的操作一定是递减(因为当当前的操作大于前面的操作时,前面的操作就失效了,所有当前面的操作是有效的时,当前的操作一定是小于前面所有的操作的)。当我们执行当前操作时(假设它是对前面 a 个数进行排序的),它后面一个操作(假设它是对前面 b个数进行排序的)就会对前 b 个数造成影响,那我们当前就不必对所有前 a 个数进行排序,直接对前(b+1----->a)个数进行排序就可以了(因为没有别的操作再会改变它们的顺序),这样就极大的减少了程序要运行的次数。
我们还可以对他更加的优化。
我们先对前(1--->rx)个数进行递增的排序{( rx 为操作数中最大的那个 r ),(假设我们已经把所有的操作存到数组 v 里面了,则v[i].r一定是大于v[i+1].r的,因为它是递减的 )},我们可以先直接把(rx--->n)个数直接放入答案数组(因为没有操作会对它进行影响),然后我们遍历数组 v ,
每次把位序为( v[i+1].r+1)----->v[i].r的数排序后放入答案数组,我们可以直接利用排序好的数组通过截取前面( v[i].r - v[i+1].r )个数 (如果它是递减的),或者是后面( v[i].r - v[i+1].r )个数 (如果它是递增的)。(因为每次的排序都会把当前最小的或者最大的数放在数组最后)具体请看代码。
对于这个样例
6 4
1 5 3 7 6 8
2 2
2 5
1 3
2 2
进行操作优化后得到的操作数组为
v[0].r=5;
v[1].r=3;
v[2].r=2
对于v[0]
它先对前5个要进行递减排序,而第六个数可以直接写进答案数组
ans= _ _ _ _ _ 8
我们可以直接先对前五个数先进行递增排序
有序数组= 1 3 5 6 7 因为v[1].r==3,则第4,5个数不会被影响,而v[0]又是递减排序的,所以我们可以倒着截取有序数组前面第一和第二个数
ans= _ _ _ 3 1 8 有序数组= 1 3 5 6 7(红色代表已经使用的数字)
然后对于v[1].r=3,v[2].r=2,则第3个数不会被影响,而v[1]又是递增排序的,所以我们可以直接截取有序数组后面第一个数
ans= _ _ 7 1 3 8 有序数组= 1 3 5 6
对于v[2].r==2,它后面已经没有操作可以影响它,而它又是递减排序的,,所以我们可以倒着把有序数组剩下的两个数字放入答案数组
我们可以直接把它放入答案数组
ans= 6 5 7 1 3 8
有序数组= 1 3 5 6 7
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct st{
int t;
int r;
};
vector<st> v;
int s[200010];
int ans[200010];
int main(){
int n,m;
int i,j,k;
int mx=0;
st a;
int lg;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&a.t,&a.r);
lg=1;
for(j=v.size()-1;j>=0&≶j--){//优化操作数
if(v[j].r<=a.r)//优化的条件
v.pop_back();
else
lg=0;//如果a.r现在就比v[j].r小了,那它一定比前面的v[j].r小,因为数组v是递减的,这样可以避免多余的计算而导致超时
}
v.push_back(a);
}
for(i=v[0].r;i<n;i++){//先放入不会被排序影响的数字
ans[i]=s[i];
}
int l=0,r=v[0].r;//表示有序数组还没被截取的那段数列的右端 ,初始左边为0,右边为v[0].r
sort(s,s+v[0].r);//有序数组
for(i=0;i<v.size()-1;i++){
if(v[i].t==1){//递增
k=0;
for(j=v[i+1].r;j<v[i].r;j++){
ans[j]=s[r-v[i].r+v[i+1].r+k];
k++;
}
r-=k;//表示有序数组还没被截取的那段数列的右端
}
else if(v[i].t==2){//递减
k=0;
for(j=v[i].r-1;j>=v[i+1].r;j--){
ans[j]=s[l+k];
k++;
}
l+=k;//表示有序数组还没被截取的那段数列的左端
}
}
k=0;
//printf("%d %d\n",l,r);
if(v[i].t==1)//处理最小的那组操作
for(j=0;j<v[i].r;j++){
ans[j]=s[r-v[i].r+k];
k++;
}
else
for(j=v[i].r-1;j>=0;j--){
ans[j]=s[l+k];
k++;
} printf("%d",ans[0]);
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
printf(" %d",ans[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
CodeForces - 631C (截取法)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 631C. Report 模拟
C. Report time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input out ...
- Codeforces 631C
题意:给定n和m. 给定一个长度为n的序列,m次操作. 接下来m次操作,每行第一个数若为1,则增序排列,若为2则降序排列,第二个数是排列的范围,即从第一个数排序到第某个数. 思路: 首先,对于其中范围 ...
- codeforces 631C. Report
题目链接 按题目给出的r, 维护一个递减的数列,然后在末尾补一个0. 比如样例给出的 4 21 2 4 32 31 2 递减的数列就是3 2 0, 操作的时候, 先变[3, 2), 然后变[2, 0) ...
- CodeForces 631C Print Check
排序+构造+预处理 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm ...
- Report CodeForces - 631C (栈)
题目链接 题目大意:给定序列, 给定若干操作, 每次操作将$[1,r]$元素升序或降序排列, 求操作完序列 首先可以发现对最后结果有影响的序列$r$一定非增, 并且是升序降序交替的 可以用单调栈维护这 ...
- CodeForces - 631C ——(思维题)
Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Tech ...
- codeforces 631C C. Report
C. Report time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces 631C Report【其他】
题意: 给定序列,将前a个数进行逆序或正序排列,多次操作后,求最终得到的序列. 分析: 仔细分析可以想到j<i,且rj小于ri的操作是没有意义的,对于每个i把类似j的操作删去(这里可以用mult ...
- PHP 手机号中间4位加密
/** * 中间加密 字符串截取法 */ public static function encryptTel($tel) { $new_tel = substr($tel, 0, 3).'****'. ...
随机推荐
- org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException: Failed to parse multipart servlet request; nested exception is java.io.IOException: The temporary upload location [/tmp/tomcat.1428942566812653608
一.异常信息 org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException: Failed to parse multipart servlet reque ...
- sgu 191 Exhibition
题意:开始只有某一展台(设为A),有2种操作.1.A展台上放B产品(或者B展台放A产品).2.A展台左边1位放B展台,左边2位放A产品.给出最终产品的排列,问能否实现. 考虑最后一个用2操作的展台,因 ...
- 关于Android如何创建空文件夹,以及mkdir和mkdirs的区别
File().mkdir 和File().mkdirs的区别 mkdir是只能建立一级目录 比如 /sdcard/test/pp 就只能建立test 而mkdirs 则可以全部建立
- dcoker 安装mysql和数据持久化
# mysql 镜像下载 docker pull mysql ( 版本自己选择) # run 服务 docker run --name mysql.5.5 -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQ ...
- ddt 实例
from :https://blog.csdn.net/wushuai150831/article/details/78453549
- 第二类Stirling数
第二类斯特林数 第二类Stirling数:S2(p, k) 1.组合意义:第二类Stirling数计数的是把p个互异元素划分为k个非空集合的方法数 2.递推公式: S2(0, 0) = 1 S2(p, ...
- Oracle11g温习-第十八章:role管理
2013年4月27日 星期六 10:52 role 的功能:简化用户的权限管理 建立角色——给角色授权——将角色授予用户/角色 2.查看系统建立的role SYS @ prod > selec ...
- CSS text-decoration 属性
定义和用法 text-decoration 属性规定添加到文本的修饰. 注释:修饰的颜色由 "color" 属性设置. 说明 这个属性允许对文本设置某种效果,如加下划线.如果后代元 ...
- springcloud之eureka配置——eureka.instance
1.在springcloud中服务的 Instance ID 默认值是: ${spring.cloud.client.hostname}:${spring.application.name}:${sp ...
- 浏览器行为模拟之requests、selenium模块
requests模块 前言: 通常我们利用Python写一些WEB程序.webAPI部署在服务端,让客户端request,我们作为服务器端response数据: 但也可以反主为客利用Python的re ...
