Activtiy
Class Overview
An activity is a single, focused thing that the user can do. Almost all activities interact with the user, so the Activity class takes care of creating a window for you in which you can place your UI with setContentView(View). While activities are often presented to the user as full-screen windows, they can also be used in other ways: as floating windows (via a theme with windowIsFloating set) or embedded inside of another activity (usingActivityGroup). There are two methods almost all subclasses of Activity will implement:
onCreate(Bundle)is where you initialize your activity. Most importantly, here you will usually callsetContentView(int)with a layout resource defining your UI, and usingfindViewById(int)to retrieve the widgets in that UI that you need to interact with programmatically.onPause()is where you deal with the user leaving your activity. Most importantly, any changes made by the user should at this point be committed (usually to theContentProviderholding the data).
To be of use with Context.startActivity(), all activity classes must have a corresponding <activity> declaration in their package'sAndroidManifest.xml.
Topics covered here:
- Fragments
- Activity Lifecycle
- Configuration Changes
- Starting Activities and Getting Results
- Saving Persistent State
- Permissions
- Process Lifecycle
Developer Guides
The Activity class is an important part of an application's overall lifecycle, and the way activities are launched and put together is a fundamental part of the platform's application model. For a detailed perspective on the structure of an Android application and how activities behave, please read theApplication Fundamentals and Tasks and Back Stack developer guides.
You can also find a detailed discussion about how to create activities in the Activities developer guide.
Fragments
Starting with HONEYCOMB, Activity implementations can make use of the Fragment class to better modularize their code, build more sophisticated user interfaces for larger screens, and help scale their application between small and large screens.
Activity Lifecycle
Activities in the system are managed as an activity stack. When a new activity is started, it is placed on the top of the stack and becomes the running activity -- the previous activity always remains below it in the stack, and will not come to the foreground again until the new activity exits.
An activity has essentially four states:
- If an activity in the foreground of the screen (at the top of the stack), it is active or running.
- If an activity has lost focus but is still visible (that is, a new non-full-sized or transparent activity has focus on top of your activity), it is paused. A paused activity is completely alive (it maintains all state and member information and remains attached to the window manager), but can be killed by the system in extreme low memory situations.
- If an activity is completely obscured by another activity, it is stopped. It still retains all state and member information, however, it is no longer visible to the user so its window is hidden and it will often be killed by the system when memory is needed elsewhere.
- If an activity is paused or stopped, the system can drop the activity from memory by either asking it to finish, or simply killing its process. When it is displayed again to the user, it must be completely restarted and restored to its previous state.
The following diagram shows the important state paths of an Activity. The square rectangles represent callback methods you can implement to perform operations when the Activity moves between states. The colored ovals are major states the Activity can be in.
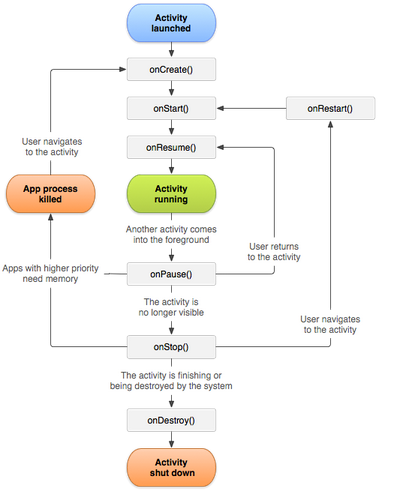
There are three key loops you may be interested in monitoring within your activity:
- The entire lifetime of an activity happens between the first call to
onCreate(Bundle)through to a single final call toonDestroy(). An activity will do all setup of "global" state in onCreate(), and release all remaining resources in onDestroy(). For example, if it has a thread running in the background to download data from the network, it may create that thread in onCreate() and then stop the thread in onDestroy(). - The visible lifetime of an activity happens between a call to
onStart()until a corresponding call toonStop(). During this time the user can see the activity on-screen, though it may not be in the foreground and interacting with the user. Between these two methods you can maintain resources that are needed to show the activity to the user. For example, you can register aBroadcastReceiverin onStart() to monitor for changes that impact your UI, and unregister it in onStop() when the user no longer sees what you are displaying. The onStart() and onStop() methods can be called multiple times, as the activity becomes visible and hidden to the user. - The foreground lifetime of an activity happens between a call to
onResume()until a corresponding call toonPause(). During this time the activity is in front of all other activities and interacting with the user. An activity can frequently go between the resumed and paused states -- for example when the device goes to sleep, when an activity result is delivered, when a new intent is delivered -- so the code in these methods should be fairly lightweight.
The entire lifecycle of an activity is defined by the following Activity methods. All of these are hooks that you can override to do appropriate work when the activity changes state. All activities will implement onCreate(Bundle) to do their initial setup; many will also implement onPause() to commit changes to data and otherwise prepare to stop interacting with the user. You should always call up to your superclass when implementing these methods.
public class Activity extends ApplicationContext {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState);
protected void onStart();
protected void onRestart();
protected void onResume();
protected void onPause();
protected void onStop();
protected void onDestroy();
}
In general the movement through an activity's lifecycle looks like this:
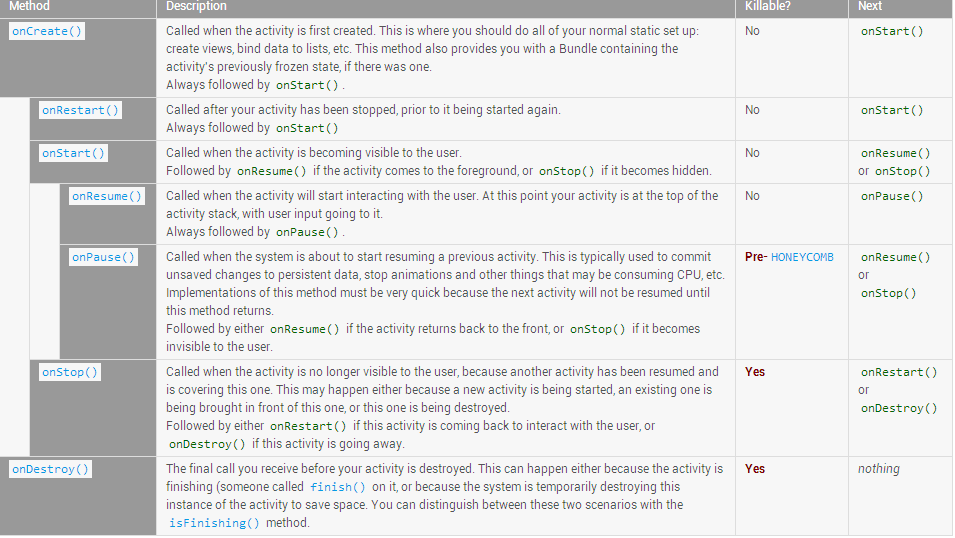
Note the "Killable" column in the above table -- for those methods that are marked as being killable, after that method returns the process hosting the activity may killed by the system at any time without another line of its code being executed. Because of this, you should use the onPause() method to write any persistent data (such as user edits) to storage. In addition, the method onSaveInstanceState(Bundle) is called before placing the activity in such a background state, allowing you to save away any dynamic instance state in your activity into the given Bundle, to be later received in onCreate(Bundle) if the activity needs to be re-created. See the Process Lifecycle section for more information on how the lifecycle of a process is tied to the activities it is hosting. Note that it is important to save persistent data in onPause() instead ofonSaveInstanceState(Bundle) because the latter is not part of the lifecycle callbacks, so will not be called in every situation as described in its documentation.
Be aware that these semantics will change slightly between applications targeting platforms starting with HONEYCOMB vs. those targeting prior platforms. Starting with Honeycomb, an application is not in the killable state until its onStop() has returned. This impacts when onSaveInstanceState(Bundle) may be called (it may be safely called after onPause() and allows and application to safely wait until onStop() to save persistent state.
For those methods that are not marked as being killable, the activity's process will not be killed by the system starting from the time the method is called and continuing after it returns. Thus an activity is in the killable state, for example, between after onPause() to the start of onResume().
Configuration Changes
If the configuration of the device (as defined by the Resources.Configuration class) changes, then anything displaying a user interface will need to update to match that configuration. Because Activity is the primary mechanism for interacting with the user, it includes special support for handling configuration changes.
Unless you specify otherwise, a configuration change (such as a change in screen orientation, language, input devices, etc) will cause your current activity to be destroyed, going through the normal activity lifecycle process of onPause(), onStop(), and onDestroy() as appropriate. If the activity had been in the foreground or visible to the user, onceonDestroy() is called in that instance then a new instance of the activity will be created, with whatever savedInstanceState the previous instance had generated fromonSaveInstanceState(Bundle).
This is done because any application resource, including layout files, can change based on any configuration value. Thus the only safe way to handle a configuration change is to re-retrieve all resources, including layouts, drawables, and strings. Because activities must already know how to save their state and re-create themselves from that state, this is a convenient way to have an activity restart itself with a new configuration.
In some special cases, you may want to bypass restarting of your activity based on one or more types of configuration changes. This is done with theandroid:configChanges attribute in its manifest. For any types of configuration changes you say that you handle there, you will receive a call to your current activity'sonConfigurationChanged(Configuration) method instead of being restarted. If a configuration change involves any that you do not handle, however, the activity will still be restarted and onConfigurationChanged(Configuration) will not be called.
Starting Activities and Getting Results
The startActivity(Intent) method is used to start a new activity, which will be placed at the top of the activity stack. It takes a single argument, an Intent, which describes the activity to be executed.
Sometimes you want to get a result back from an activity when it ends. For example, you may start an activity that lets the user pick a person in a list of contacts; when it ends, it returns the person that was selected. To do this, you call the startActivityForResult(Intent, int) version with a second integer parameter identifying the call. The result will come back through your onActivityResult(int, int, Intent) method.
When an activity exits, it can call setResult(int) to return data back to its parent. It must always supply a result code, which can be the standard results RESULT_CANCELED, RESULT_OK, or any custom values starting at RESULT_FIRST_USER. In addition, it can optionally return back an Intent containing any additional data it wants. All of this information appears back on the parent's Activity.onActivityResult(), along with the integer identifier it originally supplied.
If a child activity fails for any reason (such as crashing), the parent activity will receive a result with the code RESULT_CANCELED.
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
...
static final int PICK_CONTACT_REQUEST = 0;
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER) {
// When the user center presses, let them pick a contact.
startActivityForResult(
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_PICK,
new Uri("content://contacts")),
PICK_CONTACT_REQUEST);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode,
Intent data) {
if (requestCode == PICK_CONTACT_REQUEST) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
// A contact was picked. Here we will just display it
// to the user.
startActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, data));
}
}
}
}
Saving Persistent State
There are generally two kinds of persistent state than an activity will deal with: shared document-like data (typically stored in a SQLite database using a content provider) and internal state such as user preferences.
For content provider data, we suggest that activities use a "edit in place" user model. That is, any edits a user makes are effectively made immediately without requiring an additional confirmation step. Supporting this model is generally a simple matter of following two rules:
When creating a new document, the backing database entry or file for it is created immediately. For example, if the user chooses to write a new e-mail, a new entry for that e-mail is created as soon as they start entering data, so that if they go to any other activity after that point this e-mail will now appear in the list of drafts.
When an activity's
onPause()method is called, it should commit to the backing content provider or file any changes the user has made. This ensures that those changes will be seen by any other activity that is about to run. You will probably want to commit your data even more aggressively at key times during your activity's lifecycle: for example before starting a new activity, before finishing your own activity, when the user switches between input fields, etc.
This model is designed to prevent data loss when a user is navigating between activities, and allows the system to safely kill an activity (because system resources are needed somewhere else) at any time after it has been paused. Note this implies that the user pressing BACK from your activity does not mean "cancel" -- it means to leave the activity with its current contents saved away. Canceling edits in an activity must be provided through some other mechanism, such as an explicit "revert" or "undo" option.
See the content package for more information about content providers. These are a key aspect of how different activities invoke and propagate data between themselves.
The Activity class also provides an API for managing internal persistent state associated with an activity. This can be used, for example, to remember the user's preferred initial display in a calendar (day view or week view) or the user's default home page in a web browser.
Activity persistent state is managed with the method getPreferences(int), allowing you to retrieve and modify a set of name/value pairs associated with the activity. To use preferences that are shared across multiple application components (activities, receivers, services, providers), you can use the underlying Context.getSharedPreferences()method to retrieve a preferences object stored under a specific name. (Note that it is not possible to share settings data across application packages -- for that you will need a content provider.)
Here is an excerpt from a calendar activity that stores the user's preferred view mode in its persistent settings:
public class CalendarActivity extends Activity {
...
static final int DAY_VIEW_MODE = 0;
static final int WEEK_VIEW_MODE = 1;
private SharedPreferences mPrefs;
private int mCurViewMode;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
SharedPreferences mPrefs = getSharedPreferences();
mCurViewMode = mPrefs.getInt("view_mode", DAY_VIEW_MODE);
}
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
SharedPreferences.Editor ed = mPrefs.edit();
ed.putInt("view_mode", mCurViewMode);
ed.commit();
}
}
Permissions
The ability to start a particular Activity can be enforced when it is declared in its manifest's <activity> tag. By doing so, other applications will need to declare a corresponding <uses-permission> element in their own manifest to be able to start that activity.
When starting an Activity you can set Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION and/or Intent.FLAG_GRANT_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION on the Intent. This will grant the Activity access to the specific URIs in the Intent. Access will remain until the Activity has finished (it will remain across the hosting process being killed and other temporary destruction). As of GINGERBREAD, if the Activity was already created and a new Intent is being delivered to onNewIntent(Intent), any newly granted URI permissions will be added to the existing ones it holds.
See the Security and Permissions document for more information on permissions and security in general.
Process Lifecycle
The Android system attempts to keep application process around for as long as possible, but eventually will need to remove old processes when memory runs low. As described in Activity Lifecycle, the decision about which process to remove is intimately tied to the state of the user's interaction with it. In general, there are four states a process can be in based on the activities running in it, listed here in order of importance. The system will kill less important processes (the last ones) before it resorts to killing more important processes (the first ones).
The foreground activity (the activity at the top of the screen that the user is currently interacting with) is considered the most important. Its process will only be killed as a last resort, if it uses more memory than is available on the device. Generally at this point the device has reached a memory paging state, so this is required in order to keep the user interface responsive.
A visible activity (an activity that is visible to the user but not in the foreground, such as one sitting behind a foreground dialog) is considered extremely important and will not be killed unless that is required to keep the foreground activity running.
A background activity (an activity that is not visible to the user and has been paused) is no longer critical, so the system may safely kill its process to reclaim memory for other foreground or visible processes. If its process needs to be killed, when the user navigates back to the activity (making it visible on the screen again), its
onCreate(Bundle)method will be called with the savedInstanceState it had previously supplied inonSaveInstanceState(Bundle)so that it can restart itself in the same state as the user last left it.An empty process is one hosting no activities or other application components (such as
ServiceorBroadcastReceiverclasses). These are killed very quickly by the system as memory becomes low. For this reason, any background operation you do outside of an activity must be executed in the context of an activity BroadcastReceiver or Service to ensure that the system knows it needs to keep your process around.
Sometimes an Activity may need to do a long-running operation that exists independently of the activity lifecycle itself. An example may be a camera application that allows you to upload a picture to a web site. The upload may take a long time, and the application should allow the user to leave the application will it is executing. To accomplish this, your Activity should start a Service in which the upload takes place. This allows the system to properly prioritize your process (considering it to be more important than other non-visible applications) for the duration of the upload, independent of whether the original activity is paused, stopped, or finished.
More information please refer to: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
Activtiy的更多相关文章
- Activtiy完全解析(三、View的显示过程measure、layout、draw)
转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/xmxkf/article/details/52840065 本文出自:[openXu的博客] 在Activity完全解析的第一篇文章A ...
- Activtiy完全解析(二、layout的inflate过程)
转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/xmxkf/article/details/52457893 本文出自:[openXu的博客] 在上一篇文章<Activtiy完全 ...
- Activtiy完全解析(一、Activity的创建过程)
转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/xmxkf/article/details/52452218 本文出自:[openXu的博客] 在Android开发过程中,我们几乎每天 ...
- KeyBord事件从Activtiy层往下分发详细过程代码示例
step1:调用Activity成员函数dispatchKeyEvent public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) { // Let action ...
- [虾扯蛋] android界面框架-Window
从纯sdk及framwork的角度看,android中界面框架相关的类型有:Window,WindowManager,View等.下面就以这几个类为出发点来概览下安卓开发的"界面架构&quo ...
- Workflow笔记1——工作流介绍
什么是工作流? 工作流(Workflow),是对工作流程及其各操作步骤之间业务规则的抽象.概括.描述.BPM:是Business Process Management的英文字母缩写.即业务流程管理,是 ...
- android:使用Messenger进行进程间通信(二)
//继续完善音乐播放器demo 相关文章: android:使用Messenger进行进程间通信(一):http://www.cnblogs.com/happyhacking/p/5318418.ht ...
- 跳转到某个Activity
跳转 Activity之间的跳转 可以依靠Intent 简单粗暴的办法是 Intent intent= new Intent(*.this, MainActivity.class); startAct ...
- Android开发之---Activity启动模式
在Android开发中,启动一个新的activity我们可以使用startActivity或startActivityForResult,Android系统使用栈的方式来管理一个APP的页面显示与保存 ...
随机推荐
- android使用其他应用打开文件
根据文件的MIME类型来判断,手机中有哪些应用可以打开这个文件,然后把应用在弹窗列表中显示 /** * 打开文件 * * @param file */ public static void openF ...
- [BIM]案例
以下是中建三局BIM小组的项目,用以参考: BIM协同设计与质量控制 现实建筑物实体都是以三维空间状态存在,若用三维设计表达更具有优势.如复杂管综设计,一般情况下,二维AutoCAD设计是在建筑.结构 ...
- Gson心得小笔记
又和往常一样看项目的时候遇到了点新的东西,至少对我来说是个新的东西吧.Gson 废话不多说.个人认为Gson主要用来实现对象和json之间的转换. 例如有个person对象,想要把这个对象转化为jso ...
- BLOB:大数据,大对象,在数据库中用来存储超长文本的数据,例如图片等
将一张图片存储在mysql中,并读取出来(BLOB数据:插入BLOB类型的数据必须使用PreparedStatement,因为插入BLOB类型的数据无法使用字符串拼写): -------------- ...
- Pie(二分POJ3122)
Pie Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 12985 Accepted: 4490 Special Ju ...
- ZOJ 3593 One Person Game
One Person Game Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB There is an interesting and simple ...
- reactjs入门到实战(一)---- hello world例子
React 起源于 Facebook 的内部项目,因为该公司对市场上所有 JavaScript MVC 框架,都不满意,就决定自己写一套,用来架设 Instagram 的网站.做出来以后,发现这套东西 ...
- Codeforces Round #373 (Div. 2) B
Description Anatoly lives in the university dorm as many other students do. As you know, cockroaches ...
- int转多进制
char buf[4]; int len=100; _itoa(len,buf_len,16);//16代表十六进制,可用其他进制
- WinForm窗体及其控件的自适应
3步骤: 1.在需要自适应的Form中实例化全局变量 AutoSizeFormClass.cs源码在下方 AutoSizeFormClass asc = new AutoSizeFormClass ...
