1018 Public Bike Management
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
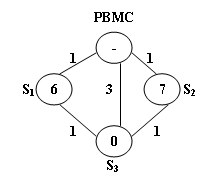
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex S is the current number of bikes stored at S. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
PBMC -> S1 -> S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
PBMC -> S2 -> S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: Cmax (≤100), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; N(≤500), the total number of stations; Sp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to N, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and M, the number of roads. The second line contains N non-negative numbers Ci (i=1,⋯,N) where each Ci is the current number of bikes at Si respectively. Then Mlines follow, each contains 3 numbers: Si, Sj, and Tijwhich describe the time Tij taken to move betwen stations Si and Sj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0−>S1−>⋯−>Sp. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of Sp is adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
思路:
Dijkstra求出所有最短路 + DFS求出min need的路
在DFS中回溯的时候,注意:从起点(PBMC)开始走,先前的back可以抵消后面的need,但是后面的back不能抵消先前的need
前面的need也不影响后面的back;
也就是说,每个点的不足,由PBMC或者其先前的站点补足,与下游站点无关
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int inf = ;
const int maxn = ; int cmax,n,sp,m;
int dismap[maxn][maxn];
int w[maxn],dis[maxn];
vector<int> pre[maxn];
vector<int> path,tmppath;
int minneed=inf ,minback=inf; void dijkstra(int s){
int vis[maxn]; fill(vis,vis+maxn,);
fill(dis,dis+maxn,inf);
dis[s]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int minv,mind=inf;
for(int v=;v<=n;v++){
if(!vis[v]&&dis[v]<mind){
mind=dis[v];
minv=v;
}
}
if(mind==inf) break;
vis[minv]=;
for(int v=;v<=n;v++){
if(!vis[v]&&dismap[minv][v]!=inf){
if(dis[v]>mind+dismap[minv][v]){
dis[v]=mind+dismap[minv][v];
//printf("# %d %d %d\n",dis[v],minv,v);
pre[v].clear();
pre[v].push_back(minv);
}else if(dis[v]==mind+dismap[minv][v]){
pre[v].push_back(minv);
}
}
}
}
} void dfs(int v){
tmppath.push_back(v);
if(v==){
int back=,need=;
for(int i=tmppath.size()-;i>=;i--){
int id=tmppath[i]; if(w[id]>=){
back+=w[id]; }else{
if(-w[id]<back){
back+=w[id];
}else{
need+=(-w[id])-back;
back=;
//printf("# %d %d %d\n",id,w[id],need);
}
}
}
if(need<minneed){
path=tmppath;
minneed=need;
minback=back;
}else if(need==minneed&&back<minback){
path=tmppath;
minback=back;
}
tmppath.pop_back();
return;
}
for(int i=;i<pre[v].size();i++){
dfs(pre[v][i]);
}
tmppath.pop_back();
} int main(){
fill(dismap[],dismap[]+maxn*maxn,inf); scanf("%d %d %d %d",&cmax,&n,&sp,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&w[i]);
w[i]-=cmax/;
}
int a,b,tmpd;
for(int i=;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&tmpd);
dismap[a][b]=dismap[b][a]=tmpd;
}
//printf("# %d\n",w[3]);
dijkstra();
dfs(sp);
printf("%d ",minneed);
for(int i=path.size()-;i>=;i--){
printf("%d",path[i]);
if(i!=) printf("->");
}
printf(" %d",minback);
}
1018 Public Bike Management的更多相关文章
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management[难]
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/4b20ed271e864f06ab77a984e71c090f来源:牛客网PAT 1018 Public ...
- PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management
PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management 题意: 杭州市有公共自行车服务,为世界各地的游客提供了极大的便利.人们可以在任何一个车站租一辆自行车,并将其送回城市的任何其他车站. ...
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management(Dijkstra 最短路)
1018. Public Bike Management (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yu ...
- PAT 甲级 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(dijstra+dfs,dfs记录路径,做了两天)
1018 Public Bike Management (30 分) There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
- 1018. Public Bike Management (30)
时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue There is a public bike service i ...
- PAT 1018. Public Bike Management
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- PTA (Advanced Level) 1018 Public Bike Management
Public Bike Management There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenie ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30)(30 分)
时间限制400 ms 内存限制65536 kB 代码长度限制16000 B There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
- PAT Advanced 1018 Public Bike Management (30) [Dijkstra算法 + DFS]
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
随机推荐
- List 的add()与addAll()的区别
add 是将传入的参数作为当前List中的一个Item存储,即使你传入一个List也只会另当前的List增加1个元素addAll 是传入一个List,将此List中的所有元素加入到当前List中,也就 ...
- ETL讲解(很详细!!!)
ETL讲解(很详细!!!) ETL是将业务系统的数据经过抽取.清洗转换之后加载到数据仓库的过程,目的是将企业中的分散.零乱.标准不统一的数据整合到一起,为企业的决策提供分析依据. ETL是BI项目重要 ...
- dubbo使用简介
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- Python第2天
今天学习的主要内容: pycharm专业版的安装和注册,采用注册码的方式注册. 运算符,+ — * / // % < > <= >= != <> . 基本数据类型 ...
- kaggle首秀之intel癌症预测(续篇)
之前写了这篇文章.现在把他搬到知乎live上了.书非借不能读也,因此搞了点小费用,如果你觉得贵,加我微信我给你发红包返回给你. 最近的空余时间拿去搞kaggle了, 好久没更新文章了.今天写写kagg ...
- BASIC GIT WORKFLOW
BASIC GIT WORKFLOW Generalizations You have now been introduced to the fundamental Git workflow. You ...
- LevelDB源码分析-TableBuilder生成sstable
TableBuilder生成sstable(include/table_builder.h table/table_builder.cc) LevelDB使用TableBuilder来构建sstabl ...
- 用命令生成Webservice 对应的代理类
wsdl /language:C# /namespace:Camstar.WebPortal.WebPortlets.Shopfloor.SAP.GreatWall /out:gwSAPService ...
- java文件转发
实际开发情景中,有时会遇到文件需要从一台服务器发到另一台服务器的情况,比如外网发到内网,服务器之间文件同步的情况. 就可以用文件转发. 转发端代码: /** * * @param fileName 保 ...
- 替换php remi源
检查当前安装的PHP包 yum list installed | grep php 如果有安装的PHP包,先删除他们 这里一定要把上一步列出来的所有php包删除干净 yum remove php.x8 ...