PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)——二叉树,建树,层序遍历
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
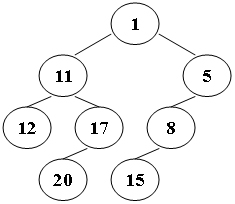
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
812 11 20 17 1 15 8 512 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <queue>
- using namespace std;
- const int maxn=;
- int pos[maxn],in[maxn];
- int n,m;
- vector<int> res[];
- struct node{
- int data;
- node* left,*right;
- int lvl;
- };
- node* create(int inl,int inr,int posl,int posr){
- if(inl > inr) return NULL;
- node* root = new node;
- root->data = pos[posr];
- int k;
- for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++){
- if(pos[posr]==in[k]) break;
- }
- int numleft=k-inl;
- root->left = create(inl,k-,posl,posl+numleft-);
- root->right = create(k+,inr,posl+numleft,posr-);
- return root;
- }
- void pr(node* root){
- queue<node*> q;
- root->lvl=;
- q.push(root);
- while(!q.empty()){
- node* now=q.front();
- q.pop();
- res[now->lvl].push_back(now->data);
- if(now->left!=NULL){
- now->left->lvl=now->lvl+;
- q.push(now->left);
- }
- if(now->right!=NULL){
- now->right->lvl=now->lvl+;
- q.push(now->right);
- }
- }
- }
- int main(){
- scanf("%d",&n);
- for(int i=;i<n;i++){
- scanf("%d",&in[i]);
- }
- for(int i=;i<n;i++){
- scanf("%d",&pos[i]);
- }
- node* root = create(,n-,,n-);
- pr(root);
- int cnt=;
- for(int i=;i<;i++){
- if(i%==){
- for(int j=res[i].size()-;j>=;j--){
- printf("%d",res[i][j]);
- cnt++;
- if(cnt<n)printf(" ");
- }
- }
- else{
- for(int j=;j<res[i].size();j++){
- printf("%d",res[i][j]);
- cnt++;
- if(cnt<n)printf(" ");
- }
- }
- if(cnt==n)break;
- }
- }
注意点:最简单的一道30分题了。只要会建树,再层序遍历,把每层的数据保存起来,再根据层数正着输出或是反向输出就ac了。
ps:也可以用deque双向队列更方便的实现。每层的输出其实可以不用开vector数组,一层遍历完后输出就好了。
PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)——二叉树,建树,层序遍历的更多相关文章
- PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can ...
- PAT甲级:1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)
PAT甲级:1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分) 题干 A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as ...
- PAT甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- pat 甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- PAT 甲级 1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)(不会做,重点复习,模拟中序遍历)
1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分) A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a bin ...
- PTA 04-树6 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/669 5-7 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分) A ...
- PAT-2019年冬季考试-甲级 7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)(最小堆的中序遍历求层序遍历,递归建树bfs层序)
7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分) A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct ...
- Leetcode 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal(二叉树的层序遍历)
Given a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, ...
- LeetCode:144_Binary Tree Preorder Traversal | 二叉树的前序遍历 | Medium
题目:Binary Tree Preorder Traversal 二叉树的前序遍历,同样使用栈来解,代码如下: struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left; ...
随机推荐
- 漫画 | Servlet属于线程安全的吗?
Servlet属于线程安全的吗? Servlet不是线程安全的 在JSP中,只有一行代码:<%=A+B %>,运行结果如何? jsp和servlet有什么关系? jsp一般被用在view层 ...
- vue中使用axios(异步请求)和mock.js 模拟虚假数据
一.使用axios 1.安装 npm install --save axios 2.引用 import Axios from 'axios' Vue.prototype.Axios = Axios 二 ...
- 【工具相关】Web-HTML特殊字符对照表
特殊符号 命名实体 十进制编码 特殊符号 命名实体 十进制编码 特殊符号 命名实体 十进制编码 Α Α Α Β Β Β Γ Γ Γ Δ Δ Δ Ε Ε Ε Ζ Ζ Ζ Η Η Η Θ Θ Θ Ι Ι ...
- 《Attention is All You Need》浅读(简介+代码)
2017年中,有两篇类似同时也是笔者非常欣赏的论文,分别是FaceBook的<Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning>和Google的< ...
- 基于Grafana的监控数据钻取功能应用实践
互联网企业中,随着机器规模以及业务量的爆发式增长,监控数据逐渐成为一种大数据,对监控大数据的分析,包括数据采集.数据缓存.数据聚合分析.数据存储.数据展现等几个阶段.不同阶段有不同的解决方案及支撑工具 ...
- MySQL四种隔离级别和MVCC
事务在一个数据库中的地位尤为重要,尤其是高并发的场合.保证数据库操作的原子性和错误出现情况下的回滚,对数据的安全性和可靠性提供了保障.事务有四大原则,即ACID原则.网上关于这个问题的文章有很多,读者 ...
- [20171031]rman xxx Failure.txt
[20171031]rman xxx Failure.txt --//简单测试 List Failure, Advise Failure and Repair Failure命令在11g下,也许以后工 ...
- python第七十九天--第十四周作业
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 监控.net 网站 Glimpse
使用Nuget 安装Glimpse 安装好后,config会默认添加几个节点 安装好之后 只需要浏览器输入 网站/Glimpse.axd 再次进入网站 就可以查看(ajax sql session ...
- ssh无法访问服务器报“ssh-dss”认证错误
故障描述: 在windows下的ssh客户端直接报错,内容为: Unable to negotiate with legacyhost: no matching host key type found ...
