C# 类型转换的开销
先来个测试:
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Stopwatch stopwatch;
- string strStr = "string";
- object objStr = strStr;
- string strTarget;
- object objTarget;
- int count = int.MaxValue;
- stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
- for (int i = ; i < count; i++)
- strTarget = strStr;
- stopwatch.Stop();
- Console.WriteLine("string to string: " + stopwatch.Elapsed);
- stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
- for (int i = ; i < count; i++)
- strTarget = (string)objStr;
- stopwatch.Stop();
- Console.WriteLine("object to string: " + stopwatch.Elapsed);
- stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
- for (int i = ; i < count; i++)
- objTarget = strStr;
- stopwatch.Stop();
- Console.WriteLine("string to object: " + stopwatch.Elapsed);
- stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
- for (int i = ; i < count; i++)
- objTarget = objStr;
- stopwatch.Stop();
- Console.WriteLine("object to object: " + stopwatch.Elapsed);
- }
结果:
- string to string: ::00.8043824
- object to string: ::03.9572322
- string to object: ::00.8029497
- object to object: ::00.8057540
结论:
- .向上转(子转父)与直接添加引用一样,基本没什么消耗
- .向下转(父转子),由于父不知道子的某些特性,需要新生成,因此会生成新的对象,非常耗时。
参考文章:
Type casting impact over execution performance in C#
Introduction
Explicit and implicit type casting is a common programming topic for almost any imperative programming language. Most C, C++, or Pascal programmers care about efficiency and speed of their code; but those who use managed programming environments, such as Java, Visual Basic, or C# rely all the optimizing tasks on the compiler and the runtime environment.
This can be a good approach in many cases, but managed languages are becoming more and more popular also for high-performance applications where the knowledge of the language, compiler, and runtime environment can enhance a program's quality and speed.
This article analyzes the most common type casting situations and the compiler behavior in them. We are going to study the MSIL generated code, but not the machine-specific instruction sequences due to the implementation and vendor dependency.
Casting primitive types
Primitive types are those non-composed types which can be handled directly by the (virtual) machine instructions, i.e., int, long, float, etc... Those types doesn't have inner structure, and are always passed by value if the programmer doesn't specify explicitly other behavior (using the out and ref modifiers). Let's see a simple example about using and casting primitive types:
- int z = 10;
- double r = 3.4;
- uint n = 20;
- r = z; // Implicit conversion from int to double (1)
- z = (int)r; // Explicit conversion from double to int (2)
- n = (uint)z; // Explicit conversion from int to uint (3)
This sample performs some conversions in the set of primitive types, leaving in some cases the casting tasks to the compiler and marking conversions explicitly in some other cases.
OK, time to dive into the MSIL generated code and check the impact of type casts in our code:
- .locals init ([0] int32 z,
- [1] float32 r,
- [2] unsigned int32 n)
- IL_0000: ldc.i4.s 10
- IL_0002: stloc.0
- IL_0003: ldc.r4 (9A 99 59 40)
- IL_0008: stloc.1
- IL_0009: ldc.i4.s 20
- IL_000b: stloc.2 //(1)
- IL_000c: ldloc.0
- IL_000d: conv.r4
- IL_000e: stloc.1
- IL_000f: ldloc.1 //(2)
- IL_0010: conv.i4
- IL_0011: stloc.0
- IL_0012: ldloc.0 //(3)
- IL_0013: stloc.2
- IL_0014: ret
As we can see, there are several Conv.XY instructions in the code, whose function is to convert the value at the top of the stack to the type designed in the opcode (r4, i4, etc...). From now, we know that the "innocent" explicit and implicit conversions between primitive types generate instructions which can be avoided with a consistent type usage. The same conversions are applied in 64-bit data types, such as double, long and ulong.
Note that the last type cast doesn't need an explicit "Conv" opcode due to the nature of the involved types: intand uint; these types have a very close storage structure (big endian bit order with a sign bit in the signed type) and conversion sign issues must be controlled by the programmer.
A special kind of primitive type is bool (handled internally as an int), whose conversions to numeric types (and backward) are not allowed in C#, so we will not study them.
Downcasting object references
C# provides two ways for casting object references (note that all types, unless those studied in the previous section, are reference types):
- object myClass = new MyClass();
- ((MyClass)myClass).DoSome(); //(1)
- (myClass as MyClass).DoSome(); //(2)</CODE>
The previous is a good example of downcasting (casting from the top to the bottom of the class hierarchy). The method used to perform the cast appears to be the same, but the generated MSIL sequences are a bit different:
- .locals init ([0] object myClass)
- IL_0000: newobj instance void Sample.MyClass::.ctor()
- IL_0005: stloc.0
- IL_0006: ldloc.0 //(1)
- IL_0007: castclass Sample.MyClass
- IL_000c: callvirt instance void Sample.MyClass::DoSome()
- IL_0011: ldloc.0 //(2)
- IL_0012: isinst Sample.MyClass
- IL_0017: callvirt instance void Sample.MyClass::DoSome()
- IL_001c: ret
In the first line of code, the compiler emits a "Castclass" opcode, which converts the reference to the type specified between the parenthesis if possible (if not, an InvalidCastException exception is thrown).
In the second case, the as operator is translated as an "IsInst" opcode, which works much faster, because it only checks the reference type but doesn't perform any sort of cast (nor throws any exception).
In performance terms, we prefer the second option, because the "IsInst" speeds up much more the code execution, avoiding type casts and exception throwing. Here is a sample of the speed increment obtained using the "as" operator:
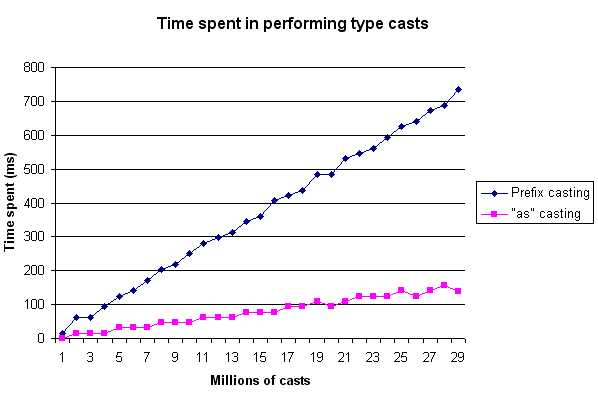
In the other hand, parenthesized casts give a better error control to programmers, avoiding the null-reference errors obtained when invalid typecasts happen using the "as" operator.
Upcasting object references
Let's make the opposite! Now it's time for climbing up into the class hierarchy, and see how slow (or fast) are these sort of casts. The following example creates an object of the type MyDerivedClass and stores its reference in a MyClass type variable:
- MyDerivedClass myDerivedClass = new MyDerivedClass();
- MyClass myClass = myDerivedClass;
And the produced code is:
- .locals init ([0] class Sample.MyDerivedClass myDerivedClass,
- [1] class Sample.MyClass myClass)
- IL_0000: newobj instance void Sample.MyDerivedClass::.ctor()
- IL_0005: stloc.0
- IL_0006: ldloc.0
- IL_0007: stloc.1
- IL_0008: ret
As we can see, there are no conversion opcodes, just reference loading and storing. This is good for out efficiency purposes... as expected, upcasting type checks are made at compile time and the runtime costs are as cheap as a simple assign between variables of the same type.
Casting operators
C# language contains a great feature which allows to define implicit and explicit conversion operators. The efficiency of these casting methods depends on the casting method implementation. Anyway, these functions are always static and have only one parameter, so the procedure call overhead is small (no "this" parameter should be passed). Anyway, it seems to be that the Microsoft C# compiler doesn't inline those methods, so arranging parameters and return addresses in the stack may slow your code execution speed.
Putting it all together
Here are some general tips for optimizing your programs based on the results obtained in the previous sections:
- Numeric type conversions are usually expensive, take them out of the loops and recursive functions and use the same numeric types when possible.
- Downcasting is a great invention but the type checks involved have a great impact on execution performance, check the object types out of loops and recursive functions, and use the "
as" operator into them. - Upcasting is cheap!, use it everywhere you need.
- Build lightweight conversion operators to make custom casts faster.
Tools used
All the tests and disassemblies have been made using the tools included in the .NET Framework SDK. ILDasm can tell you much about your program's performance flaws, so play with it.
C# 类型转换的开销的更多相关文章
- SAM4E单片机之旅——23、在AS6(GCC)中使用FPU
浮点单元(Floating Point Unit,FPU),是用于处理浮点数运算的单元. 为使用FPU,除了需要启用FPU外,还需要对编译器进行设置,以使其针对浮点运算生成特殊的指令.虽然在Atmel ...
- Collections你用对了吗?
.Net有两类基础的集合类型:List和Dictionary.List是基于Index的,Dictionary是基于key的.集合类型一般实现了IEnumberable,ICollection或者Il ...
- 第四章-shceme和数据类型优化
选择数据类型的原则: 1.更小通常更好.因为占用更少磁盘,内存和cpu缓存.但是要确保没有低估,因为进行alter时,是很耗时和头疼的操作.所以当无法确定数据类型的时候,选择不会超过范围的最小类型. ...
- C#高级编程第11版 - 第六章 索引
[1]6.2 运算符 1.&符在C#里是逻辑与运算.管道符号|在C#里则是逻辑或运算.%运算符用来返回除法运算的余数,因此当x=7时,x%5的值将是2. [2]6.2.1 运算符的简写 1.下 ...
- C++强制类型转换操作符 dynamic_cast
dynamic_cast是四个强制类型转换操作符中最特殊的一个,它支持运行时识别指针或引用. >>>>>>>>>>>编译器的RTTI设 ...
- 尽量采用as操作符而不是旧式C风格做强制类型转换
http://www.cnblogs.com/JiangSoney/archive/2009/08/07/1541488.html MSDN: https://msdn.microsoft.com/z ...
- 从零开始学C++之从C到C++(二):引用、内联函数inline、四种类型转换运算符
一.引用 (1).引用是给一个变量起别名 定义引用的一般格式:类型 &引用名 = 变量名: 例如:int a=1; int &b=a;// b是a的别名,因此a和b是同一个单元 注 ...
- C++进阶--显式类型转换(casting)
//############################################################################ /* * 显式类型转换 * * 类型转换 ...
- 从Qt谈到C++(一):关键字explicit与隐式类型转换
转载:果冻虾仁 提出疑问 当我们新建了一个Qt的widgets应用工程时.会自动生成一个框架,包含了几个文件. 其中有个mainwindow.h的头文件.就是你要操纵的UI主界面了.我们看看其中的一段 ...
随机推荐
- SQL SERVER-创建Alwayson
Failover Custer(AlwaysOn) 创建Failover Cluster和启动AlwaysOn 创建Failover Cluster 节点的个数要是奇数如果是偶数则要加一个仲裁磁盘.在 ...
- NT路径,DOS路径和Device路径互相转换
项目中遇到的比较奇葩的问题,从网上找到一份源码,https://blog.csdn.net/qq125096885/article/details/70766206 稍微整理了下,VS可以直接编译 # ...
- C++一些基本数据结构:字面常量、符号常量、枚举常量
常量:C++包括两种常量,字面常量和符号常量. 字面常量:指的是直接输入到程序中的值 比如:in myAge=26: myAge是一个int类型变量,而26是一个字面常量. 符号常量:指的是用名称表示 ...
- 如何配置jenkins 与代理服务器吗?
0 我们面临一些问题使用代理服务器(即缓存服务器)和詹金斯是希望有人可以提供如果他们有类似的设置. Herea年代简要描述的设置: 在主站点反向代理,JTS & CCM服 ...
- django.core.exceptions.ImproperlyConfigured: Error loading MySQLdb module: No module named 'MySQLdb'. Did you install mysqlclient or MySQL-python?
Error msg: Unhandled exception in thread started by <function check_errors.<locals>.wrapper ...
- BigDecimal比较大小,BigDecimal判断是否为0
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34926773/article/details/83419004 BigDecimal类型的数据,需要比较大小:声明BigDescimal: ...
- JQuery滚动分页查询功能
//获取滚动条的高度 function getScrollTop() { var scrollTop = 0; if (document.documentElement && docu ...
- sql 语句中as的用法和作用
我们的Sql语句在很多数据库中都是通用的,比如像Mysql数据库 Access数据库. Oracle数据库. Sqlite数据库 .甚至在我们的Excel中也可以使用Sql语句. 在我的数据库中有u ...
- servlet(1)
servlet类分级: 1.ServletConfig接口类:理解为读取servlet配置的类,里面有四个抽象方法如下: ①getServletName:获取servlet在web.xml中的名字 ② ...
- nginx 项目部署
一.nginx 想必我们大多数人都是通过访问网站而开始接触互联网的吧.我们平时访问的网站服务 就是 Web 网络服务,一般是指允许用户通过浏览器访问到互联网中各种资源的服务. Web 网络服务是一种被 ...
