Spring Security(三十):9.5 Access-Control (Authorization) in Spring Security
The main interface responsible for making access-control decisions in Spring Security is the AccessDecisionManager. It has a decide method which takes an Authentication object representing the principal requesting access, a "secure object" (see below) and a list of security metadata attributes which apply for the object (such as a list of roles which are required for access to be granted).
9.5.1 Security and AOP Advice
If you’re familiar with AOP, you’d be aware there are different types of advice available: before, after, throws and around. An around advice is very useful, because an advisor can elect whether or not to proceed with a method invocation, whether or not to modify the response, and whether or not to throw an exception. Spring Security provides an around advice for method invocations as well as web requests. We achieve an around advice for method invocations using Spring’s standard AOP support and we achieve an around advice for web requests using a standard Filter.
9.5.2 Secure Objects and the AbstractSecurityInterceptor
So what is a "secure object" anyway? Spring Security uses the term to refer to any object that can have security (such as an authorization decision) applied to it. The most common examples are method invocations and web requests.
Each supported secure object type has its own interceptor class, which is a subclass of AbstractSecurityInterceptor. Importantly, by the time the AbstractSecurityInterceptor is called, the SecurityContextHolder will contain a valid Authentication if the principal has been authenticated.
AbstractSecurityInterceptor provides a consistent workflow for handling secure object requests, typically:
- Look up the "configuration attributes" associated with the present request
查找与当前请求关联的“配置属性”
- Submitting the secure object, current
Authenticationand configuration attributes to theAccessDecisionManagerfor an authorization decision将安全对象,当前身份验证和配置属性提交给AccessDecisionManager以进行授权决策 - Optionally change the
Authenticationunder which the invocation takes place(可选)更改进行调用的身份验证 - Allow the secure object invocation to proceed (assuming access was granted)
允许安全对象调用继续(假设已授予访问权限)
- Call the
AfterInvocationManagerif configured, once the invocation has returned. If the invocation raised an exception, theAfterInvocationManagerwill not be invoked.调用返回后,调用AfterInvocationManager(如果已配置)。如果调用引发异常,则不会调用AfterInvocationManager。
What are Configuration Attributes?
A "configuration attribute" can be thought of as a String that has special meaning to the classes used by AbstractSecurityInterceptor. They are represented by the interface ConfigAttribute within the framework. They may be simple role names or have more complex meaning, depending on the how sophisticated the AccessDecisionManager implementation is. The AbstractSecurityInterceptor is configured with a SecurityMetadataSource which it uses to look up the attributes for a secure object. Usually this configuration will be hidden from the user.
<intercept-url pattern='/secure/**' access='ROLE_A,ROLE_B'/> in the namespace introduction, this is saying that the configuration attributes ROLE_A and ROLE_B apply to web requests matching the given pattern. In practice, with the default AccessDecisionManager configuration, this means that anyone who has a GrantedAuthority matching either of these two attributes will be allowed access. Strictly speaking though, they are just attributes and the interpretation is dependent on the AccessDecisionManager implementation. The use of the prefix ROLE_ is a marker to indicate that these attributes are roles and should be consumed by Spring Security’s RoleVoter. This is only relevant when a voter-based AccessDecisionManager is in use. We’ll see how the AccessDecisionManager is implemented in the authorization chapter.RunAsManager
Assuming AccessDecisionManager decides to allow the request, the AbstractSecurityInterceptor will normally just proceed with the request. Having said that, on rare occasions users may want to replace the Authentication inside the SecurityContext with a different Authentication, which is handled by the AccessDecisionManager calling a RunAsManager. This might be useful in reasonably unusual situations, such as if a services layer method needs to call a remote system and present a different identity. Because Spring Security automatically propagates security identity from one server to another (assuming you’re using a properly-configured RMI or HttpInvoker remoting protocol client), this may be useful.
AfterInvocationManager
Following the secure object invocation proceeding and then returning - which may mean a method invocation completing or a filter chain proceeding - the AbstractSecurityInterceptor gets one final chance to handle the invocation. At this stage the AbstractSecurityInterceptor is interested in possibly modifying the return object. We might want this to happen because an authorization decision couldn’t be made "on the way in" to a secure object invocation. Being highly pluggable, AbstractSecurityInterceptor will pass control to an AfterInvocationManager to actually modify the object if needed. This class can even entirely replace the object, or throw an exception, or not change it in any way as it chooses. The after-invocation checks will only be executed if the invocation is successful. If an exception occurs, the additional checks will be skipped.
AbstractSecurityInterceptor and its related objects are shown in Figure 9.1, “Security interceptors and the "secure object" model”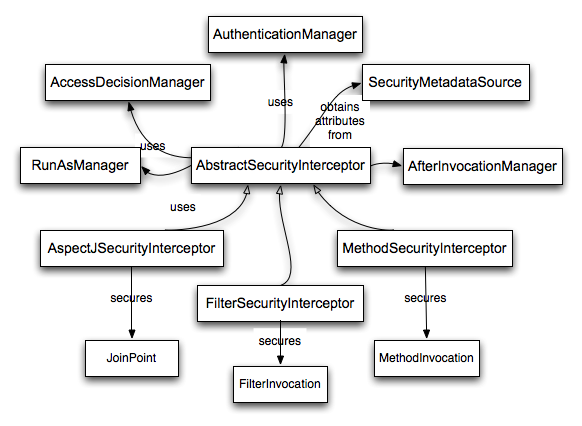
Extending the Secure Object Model
Only developers contemplating an entirely new way of intercepting and authorizing requests would need to use secure objects directly. For example, it would be possible to build a new secure object to secure calls to a messaging system. Anything that requires security and also provides a way of intercepting a call (like the AOP around advice semantics) is capable of being made into a secure object. Having said that, most Spring applications will simply use the three currently supported secure object types (AOP Alliance MethodInvocation, AspectJ JoinPoint and web request FilterInvocation) with complete transparency.
Spring Security(三十):9.5 Access-Control (Authorization) in Spring Security的更多相关文章
- 精选Spring Boot三十五道必知必会知识点
Spring Boot 是微服务中最好的 Java 框架. 我们建议你能够成为一名 Spring Boot 的专家.本文精选了三十五个常见的Spring Boot知识点,祝你一臂之力! 问题一 Spr ...
- Browser security standards via access control
A computing system is operable to contain a security module within an operating system. This securit ...
- SpringBoot:三十五道SpringBoot面试题及答案
SpringBoot面试前言今天博主将为大家分享三十五道SpringBoot面试题及答案,不喜勿喷,如有异议欢迎讨论! Spring Boot 是微服务中最好的 Java 框架. 我们建议你能够成为一 ...
- Oracle Applications Multiple Organizations Access Control for Custom Code
档 ID 420787.1 White Paper Oracle Applications Multiple Organizations Access Control for Custom Code ...
- spring boot / cloud (十五) 分布式调度中心进阶
spring boot / cloud (十五) 分布式调度中心进阶 在<spring boot / cloud (十) 使用quartz搭建调度中心>这篇文章中介绍了如何在spring ...
- Spring Security(三十五):Part III. Testing
This section describes the testing support provided by Spring Security. 本节介绍Spring Security提供的测试支持. ...
- Spring Security(三十六):12. Spring MVC Test Integration
Spring Security provides comprehensive integration with Spring MVC Test Spring Security提供与Spring MVC ...
- spring boot 常见三十四问
Spring Boot 是微服务中最好的 Java 框架. 我们建议你能够成为一名 Spring Boot 的专家. 问题一 Spring Boot.Spring MVC 和 Spring 有什么区别 ...
- SELINUX、Security Access Control Strategy && Method And Technology Research - 安全访问控制策略及其方法技术研究
catalog . 引言 . 访问控制策略 . 访问控制方法.实现技术 . SELINUX 0. 引言 访问控制是网络安全防范和客户端安全防御的主要策略,它的主要任务是保证资源不被非法使用.保证网络/ ...
- Spring Security(十九):6. Security Namespace Configuration
6.1 Introduction Namespace configuration has been available since version 2.0 of the Spring Framewor ...
随机推荐
- .NET Core2.1获取自定义配置文件信息
前言 .net core来势已不可阻挡.既然挡不了,那我们就顺应它.了解它并学习它.今天我们就来看看和之前.net版本的配置文件读取方式有何异同,这里不在赘述.NET Core 基础知识. ps:更新 ...
- ELK-log4j2异步输出+logstash
1.pom.xml配置文件 <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</ar ...
- 【ASP.NET Core快速入门】(四)在CentOS上安装.NET Core运行时、部署到CentOS
下载.NET Core SDK 下载地址:https://www.microsoft.com/net/download/windows 第一步:Add the dotnet product feed( ...
- .NET Core下的Spring Cloud——前言和概述
前言 前几年一直在写类似dubbo,Srping Cloud的微服务框架辗辗转转重复了多次,也重构推翻了很多次,其中诞生了"Rabbit.Rpc","Go",& ...
- 滚动 docker 中的 nginx 日志
Nginx 自己没有处理日志的滚动问题,它把这个球踢给了使用者.一般情况下,你可以使用 logrotate 工具来完成这个任务,或者如果你愿意,你可以写各式各样的脚本完成同样的任务.本文笔者介绍如何滚 ...
- 第2章 术语 - Identity Server 4 中文文档(v1.0.0)
规范.文档和对象模型等都使用特定的术语来表述. 2.1 IdentityServer IdentityServer是OpenID Connect提供程序 - 它实现OpenID Connect和OAu ...
- 常见MQTT服务器搭建[转载]
简介 MQTT(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport,消息队列遥测传输)是IBM开发的一个即时通讯协议,它比较适合于在低带宽.不可靠的网络的进行远程传感器和控制设备通 ...
- Java消息中间件----ActiveMQ入门①
一 首先到ActiveMQ下载安装包 Active官网地址http://activemq.apache.org/activemq-5150-release.html 如图所示,有两个下载的链接,我们下 ...
- 零基础学Python--------第7章 面向对象程序设计
第7章 面向对象程序设计 7.1 面向对象概述 面向对象(Object Oriented)的英文缩写是OO,它是一种设计思想.从20世纪60年代提出面向对象的概念到现在,它已经发展成为一种比较成熟的编 ...
- iOS----------教你如何使用 GitHub Desktop
1.先创建一个工程项目Test 2.创建一个仓库Repository 3.提交到master(记得写标题) 4.推送到github上 5.创建仓库Respository成功
