【21.28%】【codeforces 707D】Persistent Bookcase
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test512 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn’t take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1 to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got ‘A’ in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
Output
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
Examples
input
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2
4 0
output
1
4
0
input
4 2 6
3 2
2 2 2
3 3
3 2
2 2 2
3 2
output
2
1
3
3
2
4
input
2 2 2
3 2
2 2 1
output
2
1
Note
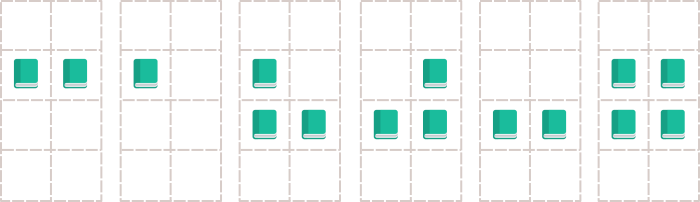
This image illustrates the second sample case.
【题解】
要用一个数据结构要求支持以下操作
1 i j 如果i,j没有书,则在这个位置放一本书
2 i j 如果i,j有书,把这本书给去掉
3 i 把第i行,有书的地方的书去掉,原来没书的地方放上书
4 i 把书柜的状态转换到第i次操作之后;

把一个一个询问看成是树的节点。
相当于从根节点开始进行dfs一直走到树的最低端。
然后往回再回溯。再找找其他的路径。
每次节点的答案往下传。然后在新的节点开始进行操作。再往下传。
一个节点有多个儿子节点也同理;
如果不是4号操作则前面一个询问和这个询问所代表的节点连起来;
这些修改操作和异或的操作都可以用bitset实现.
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1200;
const int MAXQ = 1e5 + 100;
int n, m, q, opt[MAXQ] = { 0 }, key[MAXQ][2] = { 0 };
int ans[MAXQ];
bitset <MAXN> book[MAXN] = { 0 };
bitset <MAXN> temp;
vector <int> a[MAXQ];
void input(int &r)
{
r = 0;
char t = getchar();
while (!isdigit(t)) t = getchar();
while (isdigit(t)) r = r * 10 + t - '0', t = getchar();
}
void dfs(int x)
{
int x1 = key[x][0], y1 = key[x][1],len = a[x].size();
if (x == 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= len - 1; i++)
{
ans[a[x][i]] = ans[x];//答案往下传
dfs(a[x][i]);
}
}
if (opt[x] == 1)
{
bool changed = false;
if (!book[x1][y1])//如果原来没书
{
changed = true;
book[x1][y1] = true;
ans[x]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= len - 1; i++)
{
ans[a[x][i]] = ans[x];//答案往下传
dfs(a[x][i]);
}
if (changed)
book[x1][y1] = false;
}
if (opt[x] == 2)
{
bool changed = false;
if (book[x1][y1])//如果原来有书
{
changed = true;
book[x1][y1] = false;
ans[x]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= len - 1; i++)
{
ans[a[x][i]] = ans[x];
dfs(a[x][i]);
}
if (changed)//回溯
book[x1][y1] = true;
}
if (opt[x] == 3)//相当于异或操作
{
ans[x] -= book[key[x][0]].count();
book[key[x][0]] ^= temp;
ans[x] += book[key[x][0]].count();
for (int i = 0; i <= len - 1; i++)
{
ans[a[x][i]] = ans[x];
dfs(a[x][i]);
}
book[key[x][0]] ^= temp;//一定要进行回溯操作
}
if (opt[x] == 4)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= len - 1; i++)
{
ans[a[x][i]] = ans[x];
dfs(a[x][i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("F:\\rush.txt", "r", stdin);
input(n); input(m); input(q);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
temp[i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++)
{
input(opt[i]);
if (opt[i] == 1)
input(key[i][0]), input(key[i][1]);
if (opt[i] == 2)
input(key[i][0]), input(key[i][1]);
if (opt[i] == 3)
input(key[i][0]);
if (opt[i] == 4)
{
input(key[i][0]);
a[key[i][0]].push_back(i);
}
else
a[i - 1].push_back(i);//如果操作是1或2或3就把当前这个操作接到前一个操作后面
}
ans[0] = 0;
dfs(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}【21.28%】【codeforces 707D】Persistent Bookcase的更多相关文章
- codeforces 707D:Persistent Bookcase
Description Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are d ...
- codeforces 707D D. Persistent Bookcase(dfs)
题目链接: D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input ...
- 【 BowWow and the Timetable CodeForces - 1204A 】【思维】
题目链接 可以发现 十进制4 对应 二进制100 十进制16 对应 二进制10000 十进制64 对应 二进制1000000 可以发现每多两个零,4的次幂就增加1. 用string读入题目给定的二进制 ...
- 【离线】【深搜】【树】Codeforces 707D Persistent Bookcase
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/707/D 题目大意: 一个N*M的书架,支持4种操作 1.把(x,y)变为有书. 2.把(x,y)变为没 ...
- 【21.37%】【codeforces 579D】"Or" Game
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- 【21.21%】【codeforces round 382D】Taxes
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- 【75.28%】【codeforces 764B】Decoding
time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard ou ...
- 【21.58%】【codeforces 746D】Green and Black Tea
time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard ou ...
- 【77.78%】【codeforces 625C】K-special Tables
time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standa ...
随机推荐
- Nginx TCP代理
nginx 在1.9.0 版本发布以前如果要想做到基于TCP的代理及负载均衡需要通过打名为nginx_tcp_proxy_module的第三方patch来实现,该模块的代码托管在github上 网址: ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor – Java Thread Pool Example(java线程池创建和使用)
Java thread pool manages the pool of worker threads, it contains a queue that keeps tasks waiting to ...
- BP神经网络公式推导及实现(MNIST)
BP神经网络的基础介绍见:http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/50274471,这里主要以公式推导为主. BP神经网络又称为误差反向传播 ...
- 基于Qt Assistant制作软件帮助文档
Qt Assistant是Qt自带的一款可定制.可重新发行的帮助文件浏览器.Qt Assistant支持HTML文件,用户可以利用其定制自己的功能强大的帮助文档浏览器.关于Qt Assistant定制 ...
- IQMath是什么 浮点转定点运算,dsp
[转帖注明出处:blog.csdn.net/lanmanck] 网上搜了一下没发现非常合适的,特写出来与大家分享. 大家都知道嵌入式系统里带浮点运算指令的CPU都比較少,TI的DSP也是定点的廉价. ...
- 用bootstrap做一个背景可轮转的登录界面
用bootstrap做一个背景可轮转的登录界面 一.总结 一句话总结:用css3的动画的 @keyframes 规则,制作轮转图. 1.用bootstrap做一个背景可轮转的登录界面? a.动画部分用 ...
- JAVA初始开发环境搭建
上午想在一台新电脑上搭建java开发环境,在没有之前备份的情况下,单靠网络还真有点麻烦.最主要的原因是貌似在我当前的网络环境下jdk无法下载,官网这个链接半天打不开,http://www.oracle ...
- ios 获取button所在的cell对象, 注意:ios7 =< System Version < ios8 获取cell对象的差别
ios7 =< System Version< ios8 : ios7 =< System Version < ios8 下 button.superview.supervi ...
- ZOJ Special AC String 水
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=3702 题目大意: 对于给定的一个字符串,满足如下要求输出AC,否则WA(好吧我 ...
- 洛谷 P4013 数字梯形问题
->题目链接 题解: 网络流. #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<queue> #include< ...
