洛谷—— P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=3576
题目描述
The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food.
The ant hill has nn chambers and n-1n−1 corridors connecting them.
We know that each chamber can be reached via a unique path from every other chamber.
In other words, the chambers and the corridors form a tree.
There is an entrance to the ant hill in every chamber with only one corridor leading into (or out of) it.
At each entry, there are gg groups of m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg ants respectively.
These groups will enter the ant hill one after another, each successive group entering once there are no ants inside.
Inside the hill, the ants explore it in the following way:
Upon entering a chamber with dd outgoing corridors yet unexplored by the group,the group divides into dd groups of equal size. Each newly created group follows one of the d corridors.If d=0d=0, then the group exits the ant hill.
- If the ants cannot divide into equal groups, then the stronger ants eat the weaker until a perfect division is possible.Note that such a division is always possible since eventually the number of ants drops down to zero.Nothing can stop the ants from allowing divisibility - in particular, an ant can eat itself, and the last one remaining will do so if the group is smaller than dd.
The following figure depicts mm ants upon entering a chamber with three outgoing unexplored corridors, dividing themselves into three (equal) groups of \left \lfloor m/3 \right \rfloor⌊m/3⌋ ants each.
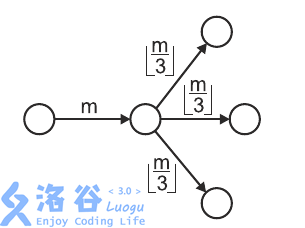
A hungry anteater dug into one of the corridors and can now eat all the ants passing through it.
However, just like the ants, the anteater is very picky when it comes to numbers.
It will devour a passing group if and only if it consists of exactly kk ants.
We want to know how many ants the anteater will eat.
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of the standard input contains three integers nn, gg, kk(2\le n,g\le 1\ 000\ 0002≤n,g≤1 000 000, 1\le k\le 10^91≤k≤109), separated by single spaces.
These specify the number of chambers, the number of ant groups and the number of ants the anteater devours at once. The chambers are numbered from 1 to nn.
The second line contains gg integers m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg (1\le m_i\le 10^91≤mi≤109), separated by single spaces, where m_imi gives the number of ants in the ii-th group at every entrance to the ant hill. The n-1n−1 lines that follow describe the corridors within the ant hill;the ii-th such line contains two integers a_iai,b_ibi (1\le a_i,b_i\le n1≤ai,bi≤n), separated by a single space, that indicate that the chambers no. a_iai and b_ibi are linked by a corridor. The anteater has dug into the corridor that appears first on input.
输出格式:
Your program should print to the standard output a single line containing a single integer: the number of ants eaten by the anteater.
输入输出样例
7 5 3
3 4 1 9 11
1 2
1 4
4 3
4 5
4 6
6 7
21
说明
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
从关键路的端点DFS,统计出到达每个点的最大和最小的蚂蚁数,(只有当最小值不比最大的蚁群数时,才继续搜下一层)
二分统计出每个点能得到的最大蚁群数、
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio> #define LL long long
const int N();
inline void read(LL &x)
{
x=; register char ch=getchar();
for(; ch>''||ch<''; ) ch=getchar();
for(; ch>=''&&ch<=''; ch=getchar()) x=x*+ch-'';
}
LL n,g,k,s1,s2,gi[N];
int head[N],sumedge;
struct Edge {
int v,next;
Edge(int v=,int next=):v(v),next(next){}
}edge[N<<];
inline void ins(int u,int v)
{
edge[++sumedge]=Edge(v,head[u]);
head[u]=sumedge;
edge[++sumedge]=Edge(u,head[v]);
head[v]=sumedge;
} #define min(a,b) (a<b?a:b)
#define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b)
int du[N],dad[N],minn[N],maxx[N];
void DFS(int u)
{
for(int v,i=head[u]; i; i=edge[i].next)
{
v=edge[i].v;
if(dad[u]==v) continue;
dad[v]=u; du[u]++;
}
for(int v,i=head[u]; i; i=edge[i].next)
{
v=edge[i].v;
if(dad[u]==v) continue;
minn[v]=minn[u]*du[u];
maxx[v]=(maxx[u]+)*du[u]-;
maxx[v]=min(maxx[v],gi[g]);
if(minn[v]<=gi[g]) DFS(v);
}
} LL l,r,mid,ans;
LL check(LL x)
{
LL ret=;
for(l=,r=g; l<=r; )
{
mid=l+r>>;
if(gi[mid]<x)
{
ret=mid;
l=mid+;
}
else r=mid-;
}
return ret;
} int Presist()
{
read(n),read(g),read(k);
for(int i=; i<=g; ++i) read(gi[i]);
read(s1);read(s2);
for(LL u,v,i=; i<n; ++i)
read(u),read(v),ins(u,v);
std::sort(gi+,gi+g+);
maxx[s1]=maxx[s2]=minn[s1]=minn[s2]=k;
DFS(s1); DFS(s2);
for(int i=; i<=n; ++i)
if(!du[i]) ans+=check(maxx[i]+)-check(minn[i]);
printf("%lld\n",ans*k);
return ;
} int Aptal=Presist();
int main(){;}
洛谷—— P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony的更多相关文章
- 洛谷——P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food. ...
- 洛谷 P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food. ...
- 洛谷P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony [二分答案,树形DP]
题目传送门 MRO-Ant colony 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food. The ant h ...
- 洛谷 P3580 - [POI2014]ZAL-Freight(单调队列优化 dp)
洛谷题面传送门 考虑一个平凡的 DP:我们设 \(dp_i\) 表示前 \(i\) 辆车一来一回所需的最小时间. 注意到我们每次肯定会让某一段连续的火车一趟过去又一趟回来,故转移可以枚举上一段结束位置 ...
- 洛谷 P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally 解题报告
P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally 题意: 给定一个\(N\)个点\(M\)条边的有向无环图,每条边长度都是\(1\). 请找到一个点,使得删掉这个点后剩余的图中的最长路径最短. 输入输 ...
- 洛谷P3572 [POI2014]PTA-Little Bird
P3572 [POI2014]PTA-Little Bird 题目描述 In the Byteotian Line Forest there are nn trees in a row. On top ...
- 2018.09.14 洛谷P3567 [POI2014]KUR-Couriers(主席树)
传送门 简单主席树啊. 但听说有随机算法可以秒掉%%%(本蒟蒻并不会) 直接维护值域内所有数的出现次数之和. 当这个值不大于区间总长度的一半时显然不存在合法的数. 这样在主席树上二分查值就行了. 代码 ...
- 洛谷P3567[POI2014]KUR-Couriers(主席树+二分)
题意:给一个数列,每次询问一个区间内有没有一个数出现次数超过一半 题解: 最近比赛太多,都没时间切水题了,刚好日推了道主席树裸题,就写了一下 然后 WA80 WA80 WA0 WA90 WA80 ?? ...
- 【刷题】洛谷 P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally
题目描述 An annual bicycle rally will soon begin in Byteburg. The bikers of Byteburg are natural long di ...
随机推荐
- springMVC与freemarker整合
准备好的环境:Maven工程整合好了ssm,即spring+springMVC+mybatis.接下来准备将springMVC与freemarker整合,以html文件为模板. 一,加入freemar ...
- maven的pom.xml文件错误
来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shihujiang/p/3492864.html
- POJ3070Fibonacci
矩阵乘法裸题 求快速幂 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #define ll long long #define Mod 10000 u ...
- 【BZOJ3527】[ZJOI2014] 力(FFT)
题目: BZOJ3527 分析: FFT应用第一题-- 首先很明显能把\(F_j\)约掉,变成: \[E_j=\sum _{i<j} \frac{q_i}{(i-j)^2}-\sum_{i> ...
- nginx深入
1.编译安装配置完成 /opt/nginx11/html/index.html 这是网页的首页文件 2. nginx.conf主配置文件学习 ############################# ...
- Android内存管理(13)常见产生内存泄漏的原因
1.集合类泄漏 集合类如果仅仅有添加元素的方法,而没有相应的删除机制,导致内存被占用.如果这个集合类是全局性的变量 (比如类中的静态属性,全局性的 map 等即有静态引用或 final 一直指向它), ...
- 【转】基于linux下的变量声明declare的用法
转自:http://techcurtman.iteye.com/blog/1249512 declare 功能介绍:声明变量的属性,如果使用declare,后面没有任何参数,那么bash就会主动将所有 ...
- Hadoop Hive概念学习系列之hive里的桶(十一)
不多说,直接上干货! Hive还可以把表或分区,组织成桶.将表或分区组织成桶有以下几个目的: 第一个目的是为看取样更高效,因为在处理大规模的数据集时,在开发.测试阶段将所有的数据全部处理一遍可能不太 ...
- [转]android 获取 imei号码
核心代码: Imei = ((TelephonyManager) getSystemService(TELEPHONY_SERVICE)) .getDeviceId(); 1.加入权限 在manife ...
- D3.js 力导向图(小气泡围绕中心气泡)
html <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3 ...
