Linux软件包管理和磁盘管理实践
一、自建yum仓库,分别为网络源和本地源
本地yum仓库的搭建就是以下三个步骤:
- 创建仓库目录结构
- 上传相应的包到目录下,或者直接挂载光盘也行,如果挂载光盘,第三步就可以省略,因为光盘默认里有repodata目录,且里面就是放的仓库元数据信息。
- 创建仓库元数据信息(createrepo 后面放包存放的目录路径)
网络仓库源的搭建就是在本地仓库搭建的步骤上多了一个安装http的过程,然后把对应的目录挂载到http 的工作目录下就可以,具体实现请参考本人博客https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/11487456.html
搭建好仓库就可以创建相应的配置文件,其客户端配置文件格式如下(/etc/yum.repo.d/xxx.repo)
[my_base]
name=this is test repo
baseurl=file:///rpm/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch
gpgcheck=0
说明:其中第一行中括号里的内容可以任意填写,就相当于仓库的名字,name表示仓库的说明信息,baseurl是仓库的路径,上面就是一个本地仓库的地址,如果是基于网络http的仓库,就要写http://仓库服务器地址/repodata文件夹的父目录,gpgcheck=0表示不开启gpg验证。
在客户端配置好repo文件后,可以查看我们搭建的仓库信息
yum clean all ##清除缓存
yum repolist ##列出仓库信息
二、编译安装http2.4,实现可以正常访问,并将编译步骤和结果提交。
编译安装,首先安装好编译环境包,比如:“development tools”,然后下载好源码包解压,然后进入到解压后的目录,然后查看README或者INSTALL说明文档,然后在解压后的目录下运行./configure --help查看编译选项说明,然后根据自己的需求定制编译选项,检查当前系统是否满足指定编译参数的环境,比如编译依赖的库是否存在呀,编译依赖的包是否存在呀等等,然后make && make install 如编译安装http2.4步骤如下:
1、yum安装 “development tools” 包组
[root@localhost ~]# yum groupinstall "development tools" -y
2、创建一个系统用户用于httpd的启动
[root@localhost ~]useradd -r -u 80 -d /data/www/ -s /sbin/nologin httpd
[root@localhost ~]# getent passwd httpd
httpd:x:80:80::/data/www/:/sbin/nologin
3、下载源码包
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache//httpd/httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz
--2019-11-05 20:11:40-- http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache//httpd/httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz
Resolving mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn (mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn)... 101.6.8.193, 2402:f000:1:408:8100::1
Connecting to mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn (mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn)|101.6.8.193|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 9267917 (8.8M) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: ‘httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz’ 100%[======================================>] 9,267,917 2.82MB/s in 3.1s 2019-11-05 20:11:43 (2.82 MB/s) - ‘httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz’ saved [9267917/9267917] [root@localhost ~]# ll
total 9052
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 9267917 Aug 13 07:37 httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz
4、解压源码包
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# ls
httpd-2.4.41 httpd-2.4.41.tar.gz
5、进入到解压后的目录
[root@localhost ~]# cd httpd-2.4.41/
6、查看README文件
Installation
------------ Please see the file called INSTALL. Platform specific notes can be
found in README.platforms.
说明:它上面说安装就去看INSTALL文件
7、查看INSTALL文件
Quick Start - Unix
------------------ For complete installation documentation, see [ht]docs/manual/install.html or
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/install.html $ ./configure --prefix=PREFIX
$ make
$ make install
$ PREFIX/bin/apachectl start
说明:INSTALL文件说快速安装就用以上命令就可以快速运行服务,当然快速安装,我们要指定安装软件的位置,很多选项都是默认的值。
For a short impression of what possibilities you have, here is a
typical example which configures Apache for the installation tree
/sw/pkg/apache with a particular compiler and flags plus the two
additional modules mod_rewrite and mod_speling for later loading
through the DSO mechanism: $ CC="pgcc" CFLAGS="-O2" \
./configure --prefix=/sw/pkg/apache \
--enable-rewrite=shared \
--enable-speling=shared The easiest way to find all of the configuration flags for Apache 2.4
is to run ./configure --help.
说明:INSTALL还告诉我们,如果我们需要编译安装额外的模块,我们用像它给我们举的例子这样用选项来指定。当然要查看更多选项信息,我们可以运行./configure --help来查看
8、查看./configure 选项帮助
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# ./configure --help
`configure' configures this package to adapt to many kinds of systems. Usage: ./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]... To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as
VAR=VALUE. See below for descriptions of some of the useful variables. Defaults for the options are specified in brackets. Configuration:
-h, --help display this help and exit
--help=short display options specific to this package
--help=recursive display the short help of all the included packages
-V, --version display version information and exit
-q, --quiet, --silent do not print `checking ...' messages
--cache-file=FILE cache test results in FILE [disabled]
-C, --config-cache alias for `--cache-file=config.cache'
-n, --no-create do not create output files
--srcdir=DIR find the sources in DIR [configure dir or `..'] Installation directories:
--prefix=PREFIX install architecture-independent files in PREFIX
[/usr/local/apache2]
--exec-prefix=EPREFIX install architecture-dependent files in EPREFIX
[PREFIX] By default, `make install' will install all the files in
`/usr/local/apache2/bin', `/usr/local/apache2/lib' etc. You can specify
an installation prefix other than `/usr/local/apache2' using `--prefix',
for instance `--prefix=$HOME'. For better control, use the options below. Fine tuning of the installation directories:
--bindir=DIR user executables [EPREFIX/bin]
--sbindir=DIR system admin executables [EPREFIX/sbin]
--libexecdir=DIR program executables [EPREFIX/libexec]
--sysconfdir=DIR read-only single-machine data [PREFIX/etc]
--sharedstatedir=DIR modifiable architecture-independent data [PREFIX/com]
--localstatedir=DIR modifiable single-machine data [PREFIX/var]
--runstatedir=DIR modifiable per-process data [LOCALSTATEDIR/run]
--libdir=DIR object code libraries [EPREFIX/lib]
--includedir=DIR C header files [PREFIX/include]
--oldincludedir=DIR C header files for non-gcc [/usr/include]
--datarootdir=DIR read-only arch.-independent data root [PREFIX/share]
--datadir=DIR read-only architecture-independent data [DATAROOTDIR]
--infodir=DIR info documentation [DATAROOTDIR/info]
--localedir=DIR locale-dependent data [DATAROOTDIR/locale]
--mandir=DIR man documentation [DATAROOTDIR/man]
--docdir=DIR documentation root [DATAROOTDIR/doc/PACKAGE]
--htmldir=DIR html documentation [DOCDIR]
--dvidir=DIR dvi documentation [DOCDIR]
--pdfdir=DIR pdf documentation [DOCDIR]
--psdir=DIR ps documentation [DOCDIR]
...省略部分显示
说明:我们可以看到.configure 的编译选项有很多,每个选项都代表着不同的功能和含义。
9、指定自己需要的功能选项,运行./configure +功能选项 检查系统都有指定功能说依赖的库和包。
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# ./configure --prefix=/application/httpd_2.4 --sysconfdir=/etc/httpd24 --enable-ssl --disable-status
checking for chosen layout... Apache
checking for working mkdir -p... yes
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking build system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking host system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking target system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
configure:
configure: Configuring Apache Portable Runtime library...
configure:
checking for APR... no
configure: error: APR not found. Please read the documentation.
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]#
说明:我们指定httpd 安装到/application/httpd_2.4目录里 ,系统配置文件存放在/etc/httpd24目录下 ,开启ssl功能,关闭进程/线程监控。configure抱错,找不到APR,请阅读文档
10、安装依赖包
yum install apr-devel apr-util-devel pcre-devel openssl-devel
说明:安装依赖可以在第一步就可以做。在我们熟悉软件的情况下可以提前安装好它说依赖的包。
11、安装完依赖包后,我们在来用./configure +我们指定的选项 来检查我们当前系统是否符合编译选项功能
config.status: creating build/config_vars.sh
config.status: creating include/ap_config_auto.h
config.status: executing default commands
configure: summary of build options: Server Version: 2.4.41
Install prefix: /application/httpd_2.4
C compiler: gcc -std=gnu99
CFLAGS: -pthread
CPPFLAGS: -DLINUX -D_REENTRANT -D_GNU_SOURCE
LDFLAGS:
LIBS:
C preprocessor: gcc -E [root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]#
说明:安装依赖后,我们再次运行./configure +我们指定的编译选项,没有发现有ERROR的字样,说明我们指定的编译选项在当前系统环境是可以编译的
12、编译
usr/lib64/apr-1/build/libtool --silent --mode=link gcc -std=gnu99 -pthread -o mod_rewrite.la -rpath /application/httpd_2.4/modules -module -avoid-version mod_rewrite.lo
make[4]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41/modules/mappers”
make[3]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41/modules/mappers”
make[2]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41/modules”
make[2]: 进入目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41/support”
make[2]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41/support” make[1]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41”
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]#
说明:在我们执行make命令后,会出现一大片编译显示的信息,最后如果没有出现ERROR,说明我们的编译时没有问题的
13、安装
Installing configuration files
mkdir /etc/httpd24
mkdir /etc/httpd24/extra
mkdir /etc/httpd24/original
mkdir /etc/httpd24/original/extra
Installing HTML documents
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/htdocs
Installing error documents
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/error
Installing icons
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/icons
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/logs
Installing CGIs
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/cgi-bin
Installing header files
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/include
Installing build system files
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/build
Installing man pages and online manual
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/man
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/man/man1
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/man/man8
mkdir /application/httpd_2.4/manual
make[1]: 离开目录“/root/httpd-2.4.41”
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]#
说明:我们通过执行make install 可以了解到,安装就是把我们编译好的库和二进制文件复制到相应的目录下的过程
14、添加PATH环境变量,并加载环境变量
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# ll /application/httpd_2.4/bin/
总用量 1176
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 73808 11月 6 05:20 ab
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root 40 3449 11月 6 05:13 apachectl
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root 40 23519 11月 6 05:13 apxs
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8736 11月 6 05:20 checkgid
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root 40 8925 11月 6 05:13 dbmmanage
-rw-r--r-- 1 root 40 1081 11月 6 05:13 envvars
-rw-r--r-- 1 root 40 1081 11月 6 05:13 envvars-std
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 13848 11月 6 05:20 fcgistarter
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40984 11月 6 05:20 htcacheclean
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 28096 11月 6 05:20 htdbm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 18208 11月 6 05:20 htdigest
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 23456 11月 6 05:20 htpasswd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 867296 11月 6 05:20 httpd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 13800 11月 6 05:20 httxt2dbm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 14440 11月 6 05:20 logresolve
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 27432 11月 6 05:20 rotatelogs
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# echo 'export PATH=/application/httpd_2.4/bin/:$PATH' >/etc/profile.d/http24.sh
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# . /etc/profile.d/http24.sh
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# echo $PATH
/application/httpd_2.4/bin/:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]#
15、启动服务(启动服务前,把/etc/httpd24/httpd.conf里的User 更改为我们之前建立的用户httpd)
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# apachectl start
AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using ::1. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# ss -ntl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 80 :::3306 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
LISTEN 0 32 :::21 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::*
[root@localhost httpd-2.4.41]# ps axu |grep httpd
root 41401 0.0 0.1 72852 2956 ? Ss 05:28 0:00 /application/httpd_2.4/bin/httpd -k start
httpd 41583 0.0 0.3 427352 6256 ? Sl 05:39 0:00 /application/httpd_2.4/bin/httpd -k start
httpd 41584 0.0 0.3 361816 6264 ? Sl 05:39 0:00 /application/httpd_2.4/bin/httpd -k start
httpd 41585 0.0 0.3 361816 6264 ? Sl 05:39 0:00 /application/httpd_2.4/bin/httpd -k start
root 41668 0.0 0.0 112724 984 pts/0 R+ 05:40 0:00 grep --color=auto httpd
说明:可以看到80端口已经处于监听状态,httpd进程也相应起来了,况且是以我们指定的系统用户运行的。
16、用浏览器访问我们的服务器
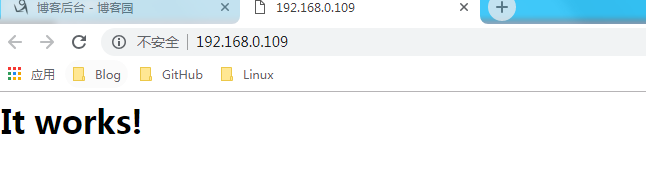
三、创建一个2G的文件系统,块大小为2048byte,预留1%可用空间,文件系统 ext4,卷标为test,要求此分区开机后自动挂载至/test目录,且默认有acl挂载选项
1、分区
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 3G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 16.8G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 40G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x7a888819.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only) Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4):
Value out of range.
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-5221, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-5221, default 5221): +2G Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x7a888819 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
2、创建文件系统
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs.ext4 -b 2048 -m 1 -L "test" /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=test
OS type: Linux
Block size=2048 (log=1)
Fragment size=2048 (log=1)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
131560 inodes, 1052240 blocks
10522 blocks (1.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=538968064
65 block groups
16384 blocks per group, 16384 fragments per group
2024 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
16384, 49152, 81920, 114688, 147456, 409600, 442368, 802816 Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 39 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
说明:centos6自己手动创建的文件系统默认没有ACL功能,需要用tune2fs -o acl /dev/sdb1来添加默认挂载选项具有acl功能
3、添加默认挂载选项具有acl功能
[root@localhost ~]# tune2fs -l /dev/sdb1
tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem volume name: test
Last mounted on: <not available>
Filesystem UUID: be76ff36-e949-4434-9925-af60ce4e155a
Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53
Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic)
Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype extent flex_bg sparse_super huge_file uninit_bg dir_nlink extra_isize
Filesystem flags: signed_directory_hash
Default mount options: (none)
Filesystem state: clean
Errors behavior: Continue
Filesystem OS type: Linux
Inode count: 131560
Block count: 1052240
Reserved block count: 10522
Free blocks: 998252
Free inodes: 131549
First block: 0
Block size: 2048
Fragment size: 2048
Reserved GDT blocks: 512
Blocks per group: 16384
Fragments per group: 16384
Inodes per group: 2024
Inode blocks per group: 253
Flex block group size: 16
Filesystem created: Tue Oct 22 02:45:40 2019
Last mount time: n/a
Last write time: Tue Oct 22 02:45:40 2019
Mount count: 0
Maximum mount count: 39
Last checked: Tue Oct 22 02:45:40 2019
Check interval: 15552000 (6 months)
Next check after: Sun Apr 19 02:45:40 2020
Lifetime writes: 97 MB
Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root)
Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root)
First inode: 11
Inode size: 256
Required extra isize: 28
Desired extra isize: 28
Journal inode: 8
Default directory hash: half_md4
Directory Hash Seed: 2c750580-3dd9-4af4-a1e9-581761cd9559
Journal backup: inode blocks
[root@localhost ~]# tune2fs -o acl /dev/sdb1
tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
[root@localhost ~]# tune2fs -l /dev/sdb1
tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem volume name: test
Last mounted on: <not available>
Filesystem UUID: be76ff36-e949-4434-9925-af60ce4e155a
Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53
Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic)
Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype extent flex_bg sparse_super huge_file uninit_bg dir_nlink extra_isize
Filesystem flags: signed_directory_hash
Default mount options: acl
Filesystem state: clean
Errors behavior: Continue
Filesystem OS type: Linux
Inode count: 131560
Block count: 1052240
Reserved block count: 10522
Free blocks: 998252
Free inodes: 131549
First block: 0
Block size: 2048
Fragment size: 2048
Reserved GDT blocks: 512
Blocks per group: 16384
Fragments per group: 16384
Inodes per group: 2024
Inode blocks per group: 253
Flex block group size: 16
Filesystem created: Tue Oct 22 02:45:40 2019
Last mount time: n/a
Last write time: Tue Oct 22 02:46:53 2019
Mount count: 0
Maximum mount count: 39
Last checked: Tue Oct 22 02:45:40 2019
Check interval: 15552000 (6 months)
Next check after: Sun Apr 19 02:45:40 2020
Lifetime writes: 97 MB
Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root)
Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root)
First inode: 11
Inode size: 256
Required extra isize: 28
Desired extra isize: 28
Journal inode: 8
Default directory hash: half_md4
Directory Hash Seed: 2c750580-3dd9-4af4-a1e9-581761cd9559
Journal backup: inode blocks
[root@localhost ~]#
说明:可以看到Default mount options: acl 表示:具有了acl挂载选项,块大小为2048,Block count: 1052240和Reserved block count: 10522的比例是100:1,Filesystem volume name: test 表示卷标名为test
4、查看/dev/sdb1的卷标
[root@localhost ~]# e2label /dev/sdb1
test
5、设置开机挂载至/test目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /test
[root@localhost ~]# echo '/dev/sdb1 /test ext4 defaults,acl 0 0 ' >> /etc/fstab
[root@localhost ~]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 17187708 1915396 14392544 12% /
tmpfs 953456 0 953456 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 194241 40472 143529 22% /boot
[root@localhost ~]# mount -a
[root@localhost ~]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 17187708 1915396 14392544 12% /
tmpfs 953456 0 953456 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 194241 40472 143529 22% /boot
/dev/sdb1 2005740 9236 1975460 1% /test
[root@localhost ~]# mount
/dev/sda3 on / type ext4 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw)
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext4 (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
/dev/sdb1 on /test type ext4 (rw,acl)
[root@localhost ~]#
说明:可以看到/dev/sdb1的文件系统类型是ext4,并且以读写,acl挂载至/test
四、创建一个至少有两个PV组成的大小为20G的名为testvg的VG;要求PE大小 为16MB, 而后在卷组中创建大小为5G的逻辑卷testlv;挂载至/users目录
1、创建分区并分别指定大小为10G,并把分区类型改为Linux LVM类型
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only) Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x7a888819 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 2
First cylinder (263-5221, default 263):
Using default value 263
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (263-5221, default 5221): +10G Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 3
First cylinder (1569-5221, default 1569):
Using default value 1569
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1569-5221, default 5221): +10G Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x7a888819 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 263 1568 10490445 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 1569 2874 10490445 83 Linux Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-4): 2
Hex code (type L to list codes): L 0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 41 PPC PReP Boot 85 Linux extended c7 Syrinx
5 Extended 42 SFS 86 NTFS volume set da Non-FS data
6 FAT16 4d QNX4.x 87 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 88 Linux plaintext de Dell Utility
8 AIX 4f QNX4.x 3rd part 8e Linux LVM df BootIt
9 AIX bootable 50 OnTrack DM 93 Amoeba e1 DOS access
a OS/2 Boot Manag 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O
b W95 FAT32 52 CP/M 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor
c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a0 IBM Thinkpad hi eb BeOS fs
e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a5 FreeBSD ee GPT
f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 55 EZ-Drive a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
10 OPUS 56 Golden Bow a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC b
11 Hidden FAT12 5c Priam Edisk a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor
12 Compaq diagnost 61 SpeedStor a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor
14 Hidden FAT16 <3 63 GNU HURD or Sys ab Darwin boot f2 DOS secondary
16 Hidden FAT16 64 Novell Netware af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 65 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 70 DiskSecure Mult b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 80 Old Minix be Solaris boot ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e
Changed system type of partition 2 to 8e (Linux LVM) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-4): 3
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e
Changed system type of partition 3 to 8e (Linux LVM) Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x7a888819 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 262 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 263 1568 10490445 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb3 1569 2874 10490445 8e Linux LVM Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.
[root@localhost ~]#
说明:可以看到/dev/sdb1和/dev/sdb2的分区类型为Linux LVM
2、创建pv
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 3G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 16.8G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 40G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part /test
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb
BLKPG: Device or resource busy
error adding partition 1
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 3G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 16.8G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 40G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part /test
├─sdb2 8:18 0 10G 0 part
└─sdb3 8:19 0 10G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb2 /dev/sdb3
Physical volume "/dev/sdb2" successfully created
Physical volume "/dev/sdb3" successfully created
[root@localhost ~]# pvs
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
/dev/sdb2 lvm2 --- 10.00g 10.00g
/dev/sdb3 lvm2 --- 10.00g 10.00g
[root@localhost ~]# pvdisplay
"/dev/sdb2" is a new physical volume of "10.00 GiB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sdb2
VG Name
PV Size 10.00 GiB
Allocatable NO
PE Size 0
Total PE 0
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID Yxsoub-DQJt-5g3T-uSca-839U-vmVV-A2t8Gl "/dev/sdb3" is a new physical volume of "10.00 GiB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sdb3
VG Name
PV Size 10.00 GiB
Allocatable NO
PE Size 0
Total PE 0
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID ChnbDg-DaSx-BhKz-a427-qEjc-VneO-A6V2jl [root@localhost ~]#
说明:在我们分区后,用lsblk可能会出现分区表不同步的现象,我们可以用partx -a /dev/sdb命令来通知内核同步,这样我们就可以看到我们之前的分区,然后用pvcreate命令 来创建pv,用pvs或者pvdisplay来查看我们创建的物理卷的信息
3、创建vg(卷组),并设置pe大小为16m
root@localhost ~]# vgcreate "testvg" -s 16m /dev/sdb{2,3}
Volume group "testvg" successfully created
[root@localhost ~]# vgs
VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree
testvg 2 0 0 wz--n- 20.00g 20.00g
[root@localhost ~]# vgdisplay
--- Volume group ---
VG Name testvg
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 2
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 2
Act PV 2
VG Size 20.00 GiB
PE Size 16.00 MiB
Total PE 1280
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 1280 / 20.00 GiB
VG UUID XgjjlR-jg4D-iOpA-W65s-S4WF-Qq8r-UaBjPW
说明:可以看到我们已经很顺利的创建了testvg,大小为20G,pe的大小是16m,pe是逻辑卷中最小分配单位,类似磁盘的block大小,只有创建了VG 才可以看到pe的大小,若不指定默认为4m
4、创建大小为5G的逻辑卷testlv
[root@localhost ~]# lvs
[root@localhost ~]# lvdisplay
[root@localhost ~]# lvcreate -n "testlv" -L 5G testvg
Logical volume "testlv" created.
[root@localhost ~]# lvs
LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convert
testlv testvg -wi-a----- 5.00g
[root@localhost ~]# lvdisplay
--- Logical volume ---
LV Path /dev/testvg/testlv
LV Name testlv
VG Name testvg
LV UUID RPUlTS-fVfA-etlO-Rzqz-KzMD-6xS1-dszf8F
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time localhost, 2019-10-22 03:55:08 +0800
LV Status available
# open 0
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 320
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:0 [root@localhost ~]#
说明:lvcreate -n 表示指定要创建的逻辑卷名称,-L 表示指定逻辑卷的大小,当然还有-l 指定逻辑卷大小的方式,小l指定的是pe的个数。最后指定在那个卷组里分配,创建好的lvs 它的真正路径在/dev/dm-0,因为dm-0没有实质的意义,就是我们看到名字不知道这个逻辑卷到底是那个卷组里创建的,所以系统就给我们做了一个软连接,/dev/testvg/testlv,我们一看这个名字这个逻辑卷是从testvg里分配的。
5、在创建好的lvs上创建文件系统
root@localhost ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/testvg/testlv
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
327680 inodes, 1310720 blocks
65536 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280
40 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736 Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 39 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
6、挂载创建好文件系统的lvs
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/testvg/testlv /users/
[root@localhost ~]# df -Th
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 ext4 17G 1.9G 14G 12% /
tmpfs tmpfs 932M 0 932M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 ext4 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot
/dev/sdb1 ext4 2.0G 9.1M 1.9G 1% /test
/dev/mapper/testvg-testlv
ext4 4.8G 10M 4.6G 1% /users
[root@localhost ~]#
说明:若要开机自动挂载需要在/etc/fstab文件中加上 /dev/testvg/testlv /users ext4 defaults 0 0 这条记录就可以实现开机自动挂载。
Linux软件包管理和磁盘管理实践的更多相关文章
- Linux 指令篇:磁盘管理--tree
Linux 指令篇:磁盘管理--tree 功能说明:以树状图列出目录的内容. 语 法:tree [-aACdDfFgilnNpqstux][-I <范本样式>][-P <范本样式&g ...
- Linux基本命令——系统管理和磁盘管理
转: Linux基本命令--系统管理和磁盘管理 Linux命令--系统管理和磁盘管理 一.系统管理 1.1 时间相关指令 <1> 查看当前日历: cal <2> 显示或设置时间 ...
- linux的基本操作(磁盘管理)
磁盘管理 [查看磁盘或者目录的容量 df 和 du] df 查看已挂载磁盘的总容量.使用容量.剩余容量等,可以不加任何参数,默认是按k为单位显示的 df常用参数有 –i -h -k –m等 -i 使用 ...
- Linux学习笔记12—磁盘管理
一.查看磁盘或目录的容量 1. df命令 作用:查看已挂载磁盘的总容量.使用容量.剩余容量等,可以不加任何参数,默认是按k为单位显示的 参数: -I : 查看inodes使用状况 -h: 使用合适的 ...
- linux常用命令之--磁盘管理命令
linux的磁盘管理命令 1.查看磁盘空间 df:用于显示磁盘空间的使用情况 其命令格式如下: df [-option] 常用参数: -i:使用inodes显示结果 -k:使用KBytes显示结果 - ...
- Linux:Day7(下) 磁盘管理、文件系统管理
Linux入门 Linux系统管理: 磁盘管理.文件系统管理 RAID基本原理.LVM2 网络管理:TCP/IP协议.Linux网络属性配置 程序包管理:rpm,yum 进程管理:htop,glanc ...
- linux学习3-简单磁盘管理
简单的磁盘管理 下面涉及的命令具有一定的危险性,操作不当可能会丢失你的个人数据,初学者建议在虚拟环境中进行操作 通常情况下,这一小节应该直接将如何挂载卸载磁盘,如何格式化磁盘,如何分区,但如你所见,我 ...
- linux下玩转磁盘管理与挂载硬盘
前言 本文将带来linux下的磁盘管理中的硬盘挂载,Linux操作系统挂载硬盘需要了解的一些知识.这可能是迄今为止介绍的最最最实用的linux硬盘挂载的文章了,比较详细.由于工作原因,平时使用的比较多 ...
- Linux(6)文件和磁盘管理
文件和磁盘管理 1. 文件管理ls ls : 查看文件信息. 列出目录的内容 -a :显示指定目录下的所有文件, 包括以.开头的隐藏文件 -l :以列表方式显示文件的详细信息 -h :配合-l显示文件 ...
随机推荐
- django模型中有外键关系的表删除相关设置
0904自我总结 django模型中有外键关系的表删除相关设置 一.一对一 例如有Author.AuthorDetail两表 author = models.OneToOneField(to='Aut ...
- python学习(数据类型)
基本数据类型 (1)numbers 数字 %d 整型 int 长整型 Long 布尔型 boor True False %f 浮点型 float 3.1415926 4.2E-10 复数 comple ...
- js 变量与常量
编辑器:Sublime Text 3 <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charse ...
- 爬虫4:pdf页面+pdfminer模块+demo
本文介绍下pdf页面的爬取,需要借助pdfminer模块 demo一般流程: 1)设置url url = 'http://www.------' + '.PDF' 2)requests模块获取url ...
- 利用git工具将自己的代码文件上传到Github
GitHub 是一个面向开源及私有软件项目的托管平台,作为开源代码库以及版本控制系统,Github拥有超过900万开发者用户.随着越来越多的应用程序转移到了云上,Github已经成为了管理软件开发以及 ...
- python2与3实际中遇到的区别
1.type(1/2) python2是向下取整,0,为int:python3是正常除法,0.5,为float 2.
- Redis 集群搭建(基于Linux)
一.基础环境 1.虚拟机 VMware 15.x 2.Linux系统,用的是Centos7的Linux系统 3.Redis数据库版本 5.0.3 二.Redis集群简介 1.背景 Redis在3.0版 ...
- 谢宝友: 手把手教你给Linux内核发patch
本文系转载,著作权归作者所有. 商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处. 作者: 谢宝友 来源: 微信公众号 linux阅码场 (id: linuxdev) 本文简介 本文一步一 ...
- python3 requests_html 爬取智联招聘数据(简易版)
PS重点:我回来了-----我回来了-----我回来了 1. 基础需要: python3 基础 html5 CS3 基础 2.库的选择: 原始库 urllib2 (这个库早些年的用过,后来淡忘了) ...
- redis之PubSub
前面我们讲了 Redis 消息队列的使用方法,但是没有提到 Redis 消息队列的不足之处,那就是它不支持消息的多播机制. 消息多播 消息多播允许生产者生产一次消息,中间件负责将消息复制到多个消息队列 ...
