java中多线程 - 多线程中的基本方法
介绍一下线程中基本的方法使用
线程睡眠sleep()
Thread.sleep(毫秒);我们可以通过sleep方法设置让线程睡眠。可以看到sleep是个静态方法
public static native void sleep(long var0) throws InterruptedException;
try {System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());Thread.sleep(5000);System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
setDaemon守护线程
非守护线程停止,那么守护线程自动退出
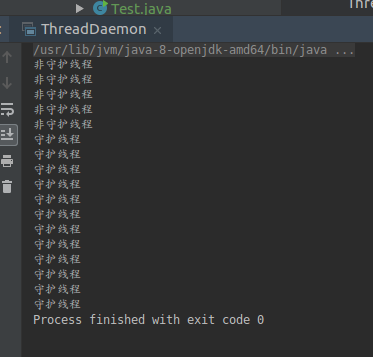
public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {System.out.println("非守护线程");}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {System.out.println("守护线程");}}};thread2.setDaemon(true);thread1.start();thread2.start();}
可以很明显的看到thread2本应该执行200次输出,但是这里只输出了几行。因为当thread1执行完毕后,thread2作为守护线程就自动停止了。
多线程join
如果执行了join方法,那么停止当前线程,先跑执行了join()的线程。相当于插队执行。如下,在执行thread2线程的时候,如果i==20的时候,则让thread1插队先执行
public static void main(String[] args) {final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {System.out.println("thread1---" + i);}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {if (i == 20) {try {//插队执行thread1.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(i);}}};thread1.start();thread2.start();}
join()方法也可以传参数long 毫秒 join(毫秒)
表示让执行join的线程,插队执行XXX毫秒,过了时间后,两个线程交替执行
public static void main(String[] args) {final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {System.out.println("thread1---" + i);}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {if (i == 20) {try {//插队执行1毫秒thread1.join(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(i);}}};thread1.start();thread2.start();}
yeild 礼让线程
yeild会让出cpu,让其他线程执行
public static void main(String[] args) {final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {if (i % 5 == 0) {Thread.yield();}System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);}}};thread1.start();thread2.start();}
setPriority给线程设置优先级
默认优先级是5 最小1,最大10
越大优先级越高
public static void main(String[] args) {final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);}}};//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);thread1.start();thread2.start();}
synchronized
同步代码块
当多线程并发,多段代码同时执行的时候。希望在执行其中代码的时候,cpu不切换线程
不用synchronized的情况
我们来看一下不用synchronized的情况会发生什么
public class ThreadSynchronied {public static void main(String[] args) {final Say say = new Say();Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say();}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say1();}}};//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);thread1.start();thread2.start();}}class Say {void say() {System.out.print("s ");System.out.print("a ");System.out.print("y ");System.out.print("h ");System.out.print("e ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.println("o");}void say1() {System.out.print("1 ");System.out.print("2 ");System.out.print("3 ");System.out.print("4 ");System.out.print("5 ");System.out.print("6 ");System.out.print("7 ");System.out.println("8");}}
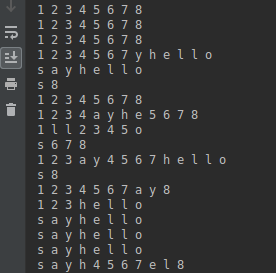
我们发现有些输出并没有打印全,在执行线程thread1的过程中,cpu被thread2抢占。这种情况下,肯定是不符合我们的业务逻辑的。所以我们要保证线程执行了一个完整的方法后,cpu才会被其他线程抢占
使用synchronized
public class ThreadSynchronied {public static void main(String[] args) {final Say say = new Say();Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say();}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say1();}}};//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);thread1.start();thread2.start();}}class Say {String s = "hahaah";void say() {synchronized (s) {System.out.print("s ");System.out.print("a ");System.out.print("y ");System.out.print("h ");System.out.print("e ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.println("o");}}void say1() {synchronized (s) {System.out.print("1 ");System.out.print("2 ");System.out.print("3 ");System.out.print("4 ");System.out.print("5 ");System.out.print("6 ");System.out.print("7 ");System.out.println("8");}}}
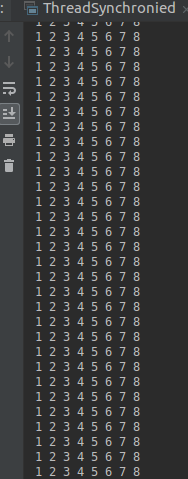
使用synchronized同步代码块后,就发现不会出现上述情况了
同步方法
public class ThreadSynchroniedMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {final Say say = new Say();Thread thread1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say();}}};Thread thread2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {say.say1();}}};//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);thread1.start();thread2.start();}}class Say {//在方法上加锁static synchronized void say() {System.out.print("s ");System.out.print("a ");System.out.print("y ");System.out.print("h ");System.out.print("e ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.print("l ");System.out.println("o");}static void say1() {synchronized (Say.class) {System.out.print("1 ");System.out.print("2 ");System.out.print("3 ");System.out.print("4 ");System.out.print("5 ");System.out.print("6 ");System.out.print("7 ");System.out.println("8");}}}
同步方法指的就是在方法上加锁
静态同步方法的所对象是该类的字节码对象
非静态的同步方法锁对象是this
多个线程使用同一资源锁,容易造成死锁
什么是死锁?
死锁是指两个或两个以上的进程在执行过程中,由于竞争资源或者由于彼此通信而造成的一种阻塞的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去。此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁,这些永远在互相等待的进程称为死锁进程。
线程安全类
Vector
StringBuffer
HashTable
线程不安全
ArrayList
StringBuilder
HashSet
java.util.Collections中有synchronizedList等方法,支持我们把线程不安全的集合转成线程安全的

学习笔记
多次启动一个线程是非法的
java中多线程 - 多线程中的基本方法的更多相关文章
- Java线程和多线程(二)——对象中的wait,notify以及notifyAll方法
Java对象中的wait,notify以及notifyAll方法 在Java的Object类中包含了3个final的方法,这三个方法允许线程来交流资源是否被锁定.这三个方法就是wait(),notif ...
- java多线程中wait/notify/sleep/join/yield方法以及多线程的六种状态
刚开始学线程的时候也是被这几个方法搞的云里雾里的,尤其是一开始看的毕老师的视频,老师一直在强调执行权和执行资格,看的有点懵逼,当然不是说毕老师讲的不好,就是自己有点没听明白,后来复习看了一些其他的博客 ...
- Java多线程中join、yield、sleep方法详解
在Java多线程编程中,Thread类是其中一个核心和关键的角色.因此,对该类中一些基础常用方法的理解和熟练使用是开发多线程代码的基础.本篇主要总结一下Thread中常用的一些静态方法的含义及代码中的 ...
- 详细分析 Java 中实现多线程的方法有几种?(从本质上出发)
详细分析 Java 中实现多线程的方法有几种?(从本质上出发) 正确的说法(从本质上出发) 实现多线程的官方正确方法: 2 种. Oracle 官网的文档说明 方法小结 方法一: 实现 Runnabl ...
- Java多线程入门中几个常用的方法
一.currentThread()方法 currentThread方法就是返回当前被调用的线程. 该方法为一个本地方法,原码如下: /** * Returns a reference to the c ...
- 黑马程序员_ JAVA中的多线程
------- android培训.java培训.期待与您交流! ---------- 尽管线程对象的常用方法可以通过API文档来了解,但是有很多方法仅仅从API说明是无法详细了解的. 本来打算用一节 ...
- 【转】Java多线程编程中易混淆的3个关键字( volatile、ThreadLocal、synchronized)总结
概述 最近在看<ThinKing In Java>,看到多线程章节时觉得有一些概念比较容易混淆有必要总结一下,虽然都不是新的东西,不过还是蛮重要,很基本的,在开发或阅读源码中经常会遇到,在 ...
- java中的多线程——进度1
import java.util.*;public static void main(String[] args) {/*final可以修饰类,方法,变量.final修饰的类不可以被继承.final修 ...
- JAVA并发七(多线程环境中安全使用集合API)
在集合API中,最初设计的Vector和Hashtable是多线程安全的.例如:对于Vector来说,用来添加和删除元素的方法是同步的.如果只有一个线程与Vector的实例交互,那么,要求获取和释放对 ...
- Java多线程编程中Future模式的详解
Java多线程编程中,常用的多线程设计模式包括:Future模式.Master-Worker模式.Guarded Suspeionsion模式.不变模式和生产者-消费者模式等.这篇文章主要讲述Futu ...
随机推荐
- Anaconda、TensorFlow安装和Pycharm配置详细教程,亲测有效!
目录 1.Anaconda下载与安装 2.Anaconda安装成功与否测试 3.安装python 4.检查TensorFlow环境添加成功与否 5.TensorFlow安装 6.测试TensorFlo ...
- Python网络爬虫实战(五)批量下载B站收藏夹视频
我们除了爬取文本信息,有的时候还需要爬媒体信息,比如视频图片音乐等.就拿B站来说,我的收藏夹内的视频可能随时会失效,所以把它们下载到本地是非常保险的一件事. 对于这种大量列表型的数据,可以猜测B站收藏 ...
- vue中关于滚动条的那点事
vue中关于滚动条的那点事 不知道你有没有遇到过这种情况,有时当页面切换时,滚动条不在页面的顶端.最近半路加入一个项目,就遇到这种情况.(若只是为了解决此问题,可直接翻到最下方)下面谈谈解决此问题的过 ...
- 站内搜索(ELK)之数据目录
在使用elasticsearch建设站内搜索时,随着数据不断丰富,为了数据管理更加精细化,必须建立并实时维护“数据目录”(在程序设计中对应的叫法“数据字典”). 数据目录需要包含以下几个维度:数据名称 ...
- redis分布式锁-自动超时锁(在用)
1.加锁代码结构 2.解锁代码结构 3.java实例 4.测试类 5.测试日志 加锁代码结构 def acquire_lock_with_timeout(conn,lockname,acquire_t ...
- Linux mint 启动文本模式(不启动图形界面)
Linux Mint 系统用了很久,很顺手,赞一个! 有一天想同时运行多个虚拟机linux系统做实验,想着只启动文本模式可以省点内存资源,结果试了多种方法都不成功,网上现有针对Ubuntu原版和Cen ...
- ubuntu13启动屏幕亮度0解决方法
在终端输入: sudo gedit /etc/default/grub 找到 GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash" GRUB_CMDL ...
- volatile 关键字的作用
简介Java 语言提供了一种稍弱的同步机制,即 volatile 变量,用来确保将变量的更新操作通知到其他线程.volatile 变量具备两种特性:变量可见性.禁止重排序. 作为同步锁在访问 vola ...
- Python爬虫(三):BeautifulSoup库
BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从 HTML 或 XML 文件中提取数据的 Python 库,它能够将 HTML 或 XML 转化为可定位的树形结构,并提供了导航.查找.修改功能,它会自动将输入 ...
- vmware上安装centos7虚拟机
1.1 Linux 的安装 安 装 采 用 在 虚 拟 机 中 安 装 , 以 方 便 不 同 班 级 授 课 时 , 需 要 重 复 安装的情况. 1.1.1 配置虚拟机 1. 在 VMware W ...
