Learn day8 re正则表达式\search函数\反射\tcp发送消息(循环)\udp发送消息
1.匹配单个字符
# ### 正则表达式 - 单个字符匹配
import re
'''
findall 把匹配的结果直接返回到列表中
lst = re.findall("正则表达式","要匹配的字符串")
''' # 预定义字符集
# (1) \d 匹配数字
lst = re.findall("\d","UIUI uuiui898(*(* 神秘男孩xboy")
print(lst) # (2) \D 匹配非数字
lst = re.findall("\D","UIUI uuiui898(*(* 神秘男孩xboy")
print(lst) # (3) \w 匹配字母或数字或下划线 (正则函数中,支持中文的匹配)
lst = re.findall("\w","UIUI uui!@#$$%%^%^898(*(* 神秘男孩xboy")
print(lst)#['U', 'I', 'U', 'I', 'u', 'u', 'i', '8', '9', '8', '神', '秘', '男', '孩', 'x', 'b', 'o', 'y'] # (4) \W 匹配非字母或数字或下划线
lst = re.findall("\W","UIUI uui!@#$$%%^%^898(*(* 神秘男孩xboy")
print(lst) #[' ', '!', '@', '#', '$', '$', '%', '%', '^', '%', '^', '(', '*', '(', '*', ' '] # (5)\s 匹配任意的空白符
lst = re.findall("\s","123 45 6")
print(lst) # (6) \S 匹配任意非空白符
lst = re.findall("\S","123 45 6")
print(lst) #['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6'] # (7) \n 匹配一个换行符
strvar = """
本来无一物,何处惹尘埃, 无住 生心 """
lst = re.findall("\n",strvar)
print(lst) # (8) \t 匹配制表符 缩进
lst = re.findall("\t","慎勿信汝意,汝意 不可信")
print(lst) # 字符组 []
# 默认必须从字符组当中选一个
lst =re.findall("[abc]","6767yuyua-=-=")
print(lst) print(re.findall('a[abc]b','aab abb acb adb')) print(re.findall('a[0123456789]b','a1b a2b a3b acb ayb'))
# 优化版 0-9 从0到9当中选一个 - 代表的是一个范围,是特殊字符
print(re.findall('a[0-9]b','a1b a2b a3b acb ayb')) print(re.findall('a[abcdefg]b','a1b a2b a3b acb ayb adb'))
# 优化版 a-z 代表的是26个小写字母
print(re.findall('a[a-g]b','a1b a2b a3b acb ayb adb')) print(re.findall('a[ABCDEFG]b','a1b a2b a3b aAb aDb aYb'))
# 优化版 A-Z 代表的是26个大写字母
print(re.findall('a[A-G]b','a1b a2b a3b aAb aDb aYb')) print(re.findall('a[0-9a-zA-Z]b','a-b aab aAb aWb aqba1b'))
# 注意事项 : 0-z 不但能表示大小写字母,数字,还包含了一些特殊的字符
print(re.findall('[0-z]','=')) print(re.findall('a[0-9][*#/]b','a1/b a2b a29b a56b a456b'))
# 字符组中的 ^ 代表的是除了... [^-+*/] 除了-+*/之外的所有符号都匹配
print(re.findall('a[^-+*/]b',"a%b ccaa*bda&bd")) # 如果就是想匹配特殊的符号,用\进行转义.
# 匹配^
print(re.findall('a[\^]b',"a^b")) # 匹配\ \b 代表退格 backspace
lst = re.findall(r'a\\b',r'a\b')
print(lst) # 显示为 ['a\\b']
print(lst[0]) # 当拿出来打印时,会变成原有的样子 lst = re.findall(r'a[\\]b',r'a\b')
print(lst)
print(lst[0])
2.匹配多个字符
# ### 正则表达式 - 多个字符匹配
import re
# ### 量词练习
'''1) ? 匹配0个或者1个a '''
print(re.findall('a?b','abbzab abb aab'))
# ab b ab ab b ab '''2) + 匹配1个或者多个a '''
print(re.findall('a+b','b ab aaaaaab abb'))
# ab aaaaaab ab '''3) * 匹配0个或者多个a '''
print(re.findall('a*b','b ab aaaaaab abbbbbbb'))
# b ab aaaaaab ab b b b b b b '''4) {m,n} 匹配m个至n个a '''
print(re.findall('a{1,3}b','aaab ab aab abbb aaz aabb'))# aaab ab aab ab aab
# {1} 必须只有1个
print(re.findall('a{1}b','aaab ab aab abbb aaz aabb'))# ab ab ab ab ab
# {1,} 至少有1个
print(re.findall('a{1,}b','aaab ab aab abbb aaz aabb'))# aaab ab aab ab aab # ### 贪婪匹配 和 非贪婪匹配
"""
贪婪匹配 : 默认向更多次匹配 (回溯算法)
非贪婪匹配: 默认向更少次匹配 (语法在量词的后面加?号) . 代表除了\n,可以匹配任意字符
.? .+ .* .{m,n} 回溯算法:从左到右进行匹配,直到再也匹配不到了,回头,拿离右边最近的一个值. 非贪婪匹配语法: (语法在量词的后面加?号)
.?? .+? .*? .{m,n}?
""" # (1)贪婪匹配
strvar = "刘能和刘老根和刘铁棍子123子456"
lst = re.findall("刘.?",strvar)
print(lst) # 刘能 刘老 刘铁 lst = re.findall("刘.+",strvar)
print(lst) # ['刘能和刘老根和刘铁棍子123子456'] lst = re.findall("刘.*",strvar)
print(lst) # ['刘能和刘老根和刘铁棍子123子456'] lst = re.findall("刘.{1,100}",strvar)
print(lst) # ['刘能和刘老根和刘铁棍子123子456'] # (2)非贪婪匹配
strvar = "刘能和刘老根和刘铁棍子123子456"
lst = re.findall("刘.??",strvar)
print(lst) # ['刘', '刘', '刘'] lst = re.findall("刘.+?",strvar)
print(lst) # 刘能 刘老 刘铁 lst = re.findall("刘.*?",strvar)
print(lst) # ['刘', '刘', '刘'] lst = re.findall("刘.{1,100}?",strvar)
print(lst) # 刘能 刘老 刘铁 # 贪婪
lst = re.findall("刘.*子",strvar)
print(lst)
# 非贪婪
lst = re.findall("刘.*?子",strvar)
print(lst) # # ### 边界符 \b ^ $
"""
卡住左边界:\bw
卡住右边界:d\b 任何的正则表达式,字符创左边都加上r,防止转义.
"""
strvar = "word pwd zef"
lst = re.findall(r"\bw.*",strvar)
print(lst)
lst = re.findall(r".*d\b",strvar)
print(lst)
lst = re.findall(r".*?d\b",strvar)
print(lst)
lst = re.findall(r"\bw.*?d\b",strvar)
print(lst)
# 单独匹配 word
lst = re.findall(r"\bw\S*",strvar)
print(lst) """
^ 必须以 .. 开头
$ 必须以 .. 结尾
无论是^ 还是 $ ,都需要把字符串看成一个整体;
"""
strvar = "大哥大嫂大爷"
# print(re.findall('大.',strvar)) # ['大哥', '大嫂', '大爷']
# print(re.findall('^大.',strvar)) #['大哥']
# print(re.findall('大.$',strvar)) # ['大爷']
# print(re.findall('^大.$',strvar)) # []
# print(re.findall('^大.*?$',strvar)) # 大哥大嫂大爷
# print(re.findall('^大.*?大$',strvar)) # 必须以大字开头,必须以爷字结尾,否则匹配不到;
print(re.findall('^大.*?爷$',strvar)) # ['大哥大嫂大爷'] # print(re.findall('^g.*? ' , 'giveme 1gfive gay')) # giveme
# print(re.findall('five$' , 'aassfive')) # ['five']
# print(re.findall('^giveme$' , 'giveme')) #giveme
# print(re.findall('^giveme$' , 'giveme giveme'))# []
# print(re.findall('giveme' , 'giveme giveme')) #['giveme', 'giveme']
print(re.findall("^g.*e",'giveme 1gfive gay')) #giveme 1gfive
3.匹配分组_函数
# ### 分组匹配
import re
"""
# 1.正常分组 ()
1) 正常情况下用()圆括号进行分组 可以用\1 反向引用第一个圆括号匹配的内容。
2) (?:正则表达式) 表示取消优先显示的功能
""" print(re.findall('.*?_good','wusir_good alex_good secret男_good'))
print(re.findall('(.*?)_good','wusir_good alex_good secret男_good'))
# ?: 取消优先显示括号的功能;
print(re.findall('(?:.*?)_good','wusir_good alex_good secret男_good')) # | 或 把长的字符串放到前面优先匹配,把短的容易匹配的放到后面;
strvar = "abcabcd"
lst = re.findall("abc|abcd",strvar)
print(lst)
lst = re.findall("abcd|abc",strvar)
print(lst) # 匹配小数
strvar = "3.14 56 89.78 78sdfs"
lst = re.findall("\d+\.\d+",strvar)
print(lst) # 匹配小数和整数
strvar = "3.14 56 89.78 78sdfs"
lst = re.findall("\d+\.\d+|\d+",strvar)
print(lst) # 用分组匹配小数和整数
lst = re.findall("\d+(\.\d+)?",strvar)
print(lst)
# 不优先显示小括号内容
lst = re.findall("\d+(?:\.\d+)?",strvar)
print(lst) # 匹配135或171的手机号
lst = re.findall("171[0-9]{8}|135\d{8}","17188886666 13566668888 13366668888")
print(lst)
# 加上^ 和 $ 意味着 只能写一组手机号,开头和结尾,不能是多个
lst = re.findall("^171[0-9]{8}$|^135\d{8}$","17188886666")
print(lst) # search 函数
"""
search 只匹配到一个就返回,返回的是对象
可以让分组的内容和正常匹配的结果同时显示; 想要拿到对象中的结果,使用group函数 findall 从左到右把所有符合条件的内容都返回到列表
不可以同时显示分组和正常匹配的结果
"""
obj = re.search("171[0-9]{8}|135\d{8}","17188886666 13566668888 13366668888")
print(obj)
# obj.group() 用来获取该对象匹配到的值
res = obj.group()
print(res) # 匹配www.baidu.com 或者 www.oldboy.com
strvar = "www.baidu.com www.oldboy.com"
obj = re.search("(www)\.(baidu|oldboy)\.(com)",strvar)
# 返回匹配的结果
res = obj.group()
print(res) # 显示分组里面的内容
res = obj.group(1) # 显示第一个小括号里的内容
res = obj.group(2) # 显示第二个小括号里的内容
res = obj.group(3) # 显示第三个小括号里的内容
# res = obj.group(4) # 显示第三个小括号里的内容 error
print(res) # 一次性显示分组里所有内容 groups
res = obj.groups()
print(res) # 用findall 来做 分组内容和正常匹配的内容2者之间不能同时显示,只能同一时间显示一个;
lst = re.findall("(?:www)\.(?:baidu|oldboy)\.(?:com)",strvar)
print(lst) # "5*6-7/3" 匹配 5*6 或者 7/3 search
strvar = "5*6-9/3" # 27
obj = re.search("\d+[*/]\d+",strvar) # 返回匹配的结果
def calc(strvar):
if '*' in strvar:
num1,num2 = strvar.split('*')
return float(num1) * float(num2) if '/' in strvar:
num1,num2 = strvar.split('/')
return float(num1) / float(num2) res = obj.group()
print(res)
num = str(calc(res)) # 30.0 # 把最后得出的结果取代原来的5*6字符串
res2 = strvar.replace(res,num)
print(res2,type(res2)) #30.0-9/3 <class 'str'> # 把剩下的字符串在匹配一遍即可
obj = re.search("\d+[*/]\d+",res2)
res3 = obj.group()
num = str(calc(res3))
print(num) # 3.0 # 把最后得出的结果取代原来的9/3字符串
res4 = res2.replace(res3,num)
print(res4,type(res)) #30.0-3.0 <class 'str'> # ### 反向引用
strvar = "<h1>大标题</h1>"
obj = re.search("<.*?>.*?<.*?>",strvar)
print(obj.group()) #<h1>大标题</h1> obj = re.search("<(.*?)>.*?<(.*?)>",strvar)
print(obj.groups()) #('h1', '/h1') # 反向引用 \1 表达把第一个括号里面的内容在使用一次;
print("<==========>")
strvar = "<h1>大标题</h1>"
obj = re.search(r"<(.*?)>.*?</(\1)>",strvar)
print(obj.groups()) #('h1', '/h1')
4.反射\魔术方法
# ### 类相关的魔术属性
class Human():
pass
class Man():
pass
class Woman():
pass class Children(Man,Woman):
'''
成员属性: hair skin
成员方法: cry eat __drink
功能:描述小孩的特征
'''
hair = "black"
skin = "yellow" # 绑定方法
def cry(self):
print("小孩会哭") # 普通方法
def eat():
print("小孩下生会吃饼干") def smile(self,func):
# __name__ 获取函数名
res = func.__name__
print(res) #ceshi
# 私有方法
def __drink(self):
print("小孩喜欢喝奶奶") obj = Children()
obj.abc = 10
# __dict__ 获取对象或类的内部成员结构
print(obj.__dict__)
print(Children.__dict__) # __doc__ 获取对象或类的内部文档
print(Children.__doc__)
print(obj.__doc__) # __name__ 获取类名函数名
def ceshi():
print(123)
obj.smile(ceshi) # __class__ 获取当前对象所属的类
print(obj.__class__) # __bases__ 获取一个类直接继承的所有父类,返回元组
res = Children.__bases__
print(res) # (<class '__main__.Man'>, <class '__main__.Woman'>) # ### 反射
"""
# 概念:通过字符串去操作类对象 或者 模块中的 属性方法
""" # (1)hasattr() 检测对象/类是否有指定的成员
res = hasattr(obj,"hair")
res = hasattr(obj,"cry")
print(res) # True
res = hasattr(Children,"hair")
res = hasattr(Children,"eat123")
print(res) # (2)getattr() 获取对象/类成员的值
res = getattr(obj,"hair")
func = getattr(obj,"cry")
print(res)
func() #小孩会哭 res = getattr(Children,"skin")
print(res)
func = getattr(Children,"eat")
func() """
def cry(self):
print("小孩会哭")
如果通过对象反射出来的绑定方法,里面的self 这个参数自动传递
如果通过类 反射出来的方法,里面的self 这个参数手动传递
"""
print("<==start==>")
# 通过对象反射的
func = getattr(obj,"cry") # self 系统自动传递
func() # 通过类反射的
func = getattr(Children,"cry")
func(13213213131212) # 让形参实参保持一致,self需要手动传递
print("<==end==>") # 综合案例
'''
res = input("请用户输入要调用的方法")
if hasattr(Children,res):
func = getattr(Children,res)
func()
''' # (3)setattr() 设置对象/类成员的值
setattr(obj,"eye","蓝色的眼睛")
print(obj.eye)
setattr(Children,"ceshi111",lambda : print("ceshi111"))
Children.ceshi111() """
# 一般在类外创建的都是静态方法,无论是对象还是类都可以调用 # 在类外创建绑定方法的过程
import types
types.MethodType(函数,obj)
""" # (4)delattr() 删除对象/类成员的值
delattr(obj,"eye")
# obj.eye
delattr(Children,"ceshi111")
# Children.ceshi111() # ### 关于模块的反射 import sys
# sys.modules 返回一个字典,这个字典存放的都是系统的模块
print(sys.modules)
"""
{'builtins': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>,
'sys': <module 'sys' (built-in)>,
'_frozen_importlib': <module '_frozen_importlib' (frozen)>,
'_imp': <module '_imp' (built-in)>,
'_warnings': <module '_warnings' (built-in)>, '_thread': <module '_thread' (built-in)>, '_weakref': <module '_weakref' (built-in)>, '_frozen_importlib_external': <module '_frozen_importlib_external' (frozen)>, '_io': <module 'io' (built-in)>, 'marshal': <module 'marshal' (built-in)>, 'nt': <module 'nt' (built-in)>, 'winreg': <module 'winreg' (built-in)>, 'zipimport': <module 'zipimport' (built-in)>, 'encodings': <module 'encodings' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\__init__.py'>, 'codecs': <module 'codecs' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\codecs.py'>, '_codecs': <module '_codecs' (built-in)>, 'encodings.aliases': <module 'encodings.aliases' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\aliases.py'>, 'encodings.utf_8': <module 'encodings.utf_8' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\utf_8.py'>, '_signal': <module '_signal' (built-in)>,
'__main__': <module '__main__' from 'D:/周末四期/L008/mymodule4.py'>,
'encodings.latin_1': <module 'encodings.latin_1' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\latin_1.py'>, 'io': <module 'io' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\io.py'>, 'abc': <module 'abc' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\abc.py'>, '_weakrefset': <module '_weakrefset' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\_weakrefset.py'>, 'site': <module 'site' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\site.py'>, 'os': <module 'os' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\os.py'>, 'errno': <module 'errno' (built-in)>, 'stat': <module 'stat' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\stat.py'>, '_stat': <module '_stat' (built-in)>, 'ntpath': <module 'ntpath' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\ntpath.py'>, 'genericpath': <module 'genericpath' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\genericpath.py'>, 'os.path': <module 'ntpath' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\ntpath.py'>, '_collections_abc': <module '_collections_abc' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\_collections_abc.py'>, '_sitebuiltins': <module '_sitebuiltins' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\_sitebuiltins.py'>, '_bootlocale': <module '_bootlocale' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\_bootlocale.py'>, '_locale': <module '_locale' (built-in)>, 'encodings.gbk': <module 'encodings.gbk' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\gbk.py'>, '_codecs_cn': <module '_codecs_cn' (built-in)>, '_multibytecodec': <module '_multibytecodec' (built-in)>, 'sysconfig': <module 'sysconfig' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\sysconfig.py'>, 'encodings.cp437': <module 'encodings.cp437' from 'C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\lib\\encodings\\cp437.py'>,
'sitecustomize': <module 'sitecustomize' from 'C:\\Program Files\\JetBrains\\PyCharm 2019.1.3\\helpers\\pycharm_matplotlib_backend\\sitecustomize.py'>}
""" # 通过__main__ 字典的键,直接获取的是当前的模块对象 mymodule4
mod = sys.modules['__main__'] #<module '__main__' from 'D:/周末四期/L008/mymodule4.py'> def func1():
print("这是func1方法")
def func2():
print("这是func2方法")
def func3():
print("这是func3方法") # 通过用户输入,不停的反射模块当中的方法.
while True:
res = input("请选择要调用的函数")
# 判断是否存在当前方法
if hasattr(mod,res):
# 通过字符串反射该方法
func = getattr(mod,res)
func()
else:
print("没有当前方法")
5.tcp发送消息
tcp三次握手过程
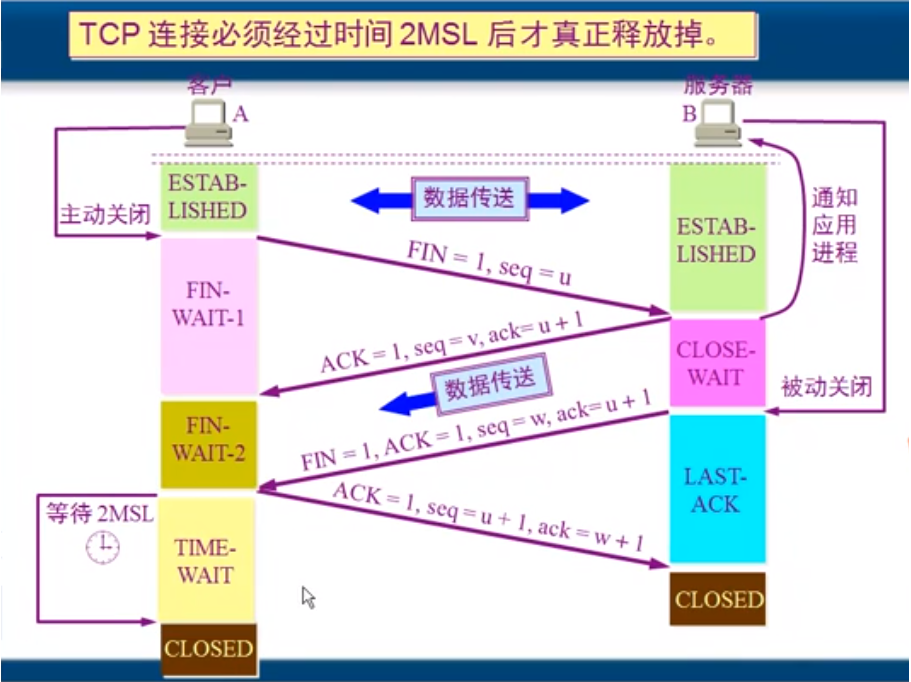
tcp四次挥手过程
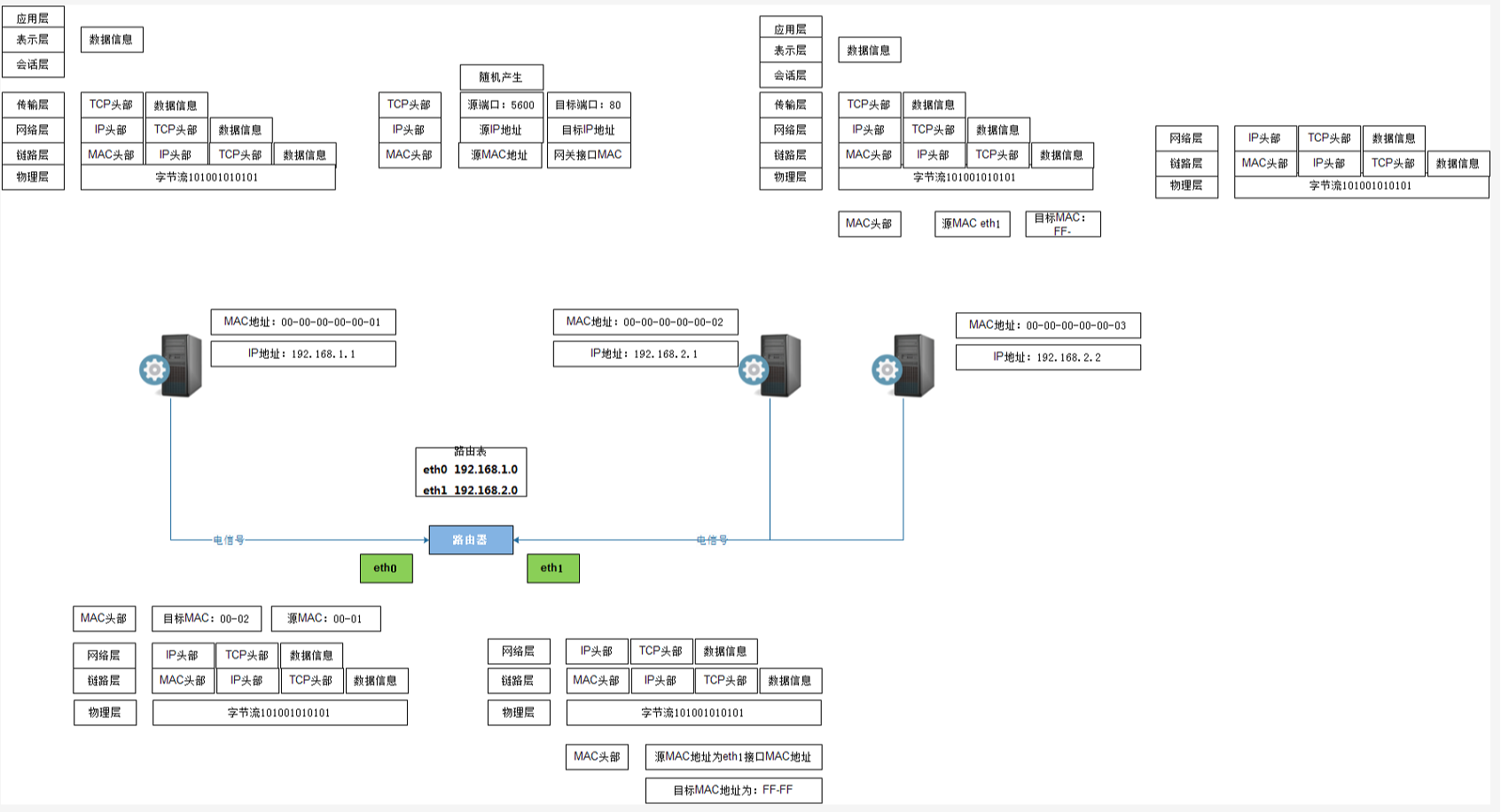
网络中包的传输过程
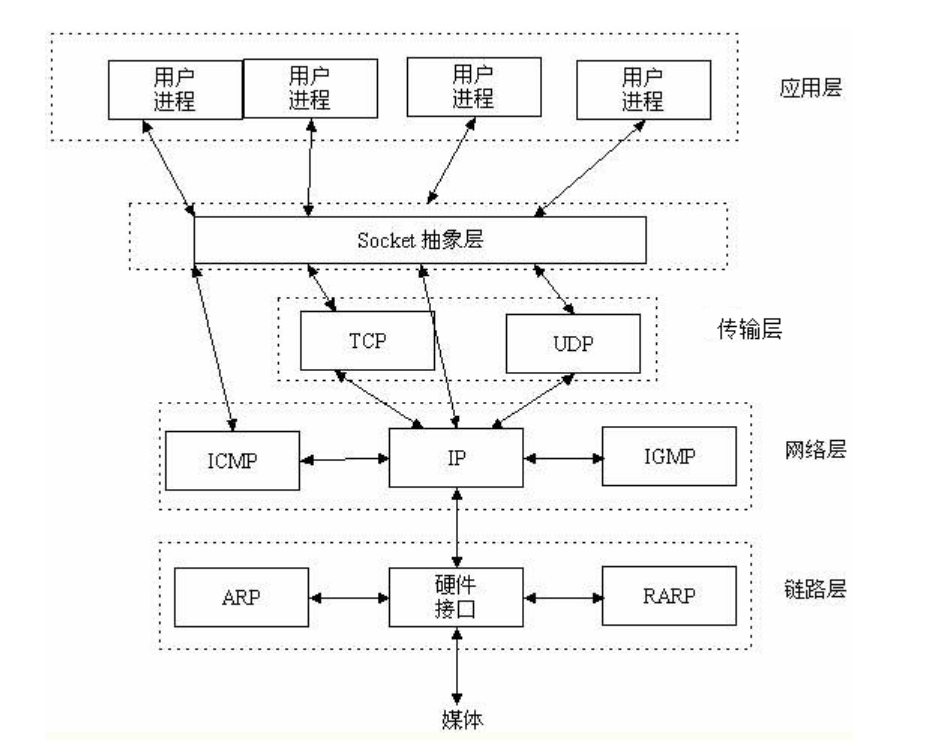
socket所在位置
[server端]
# ### 服务端
import socket
# 1.创建一个socket对象 , 默认按照tcp协议创建
sk = socket.socket()
# 2.绑定ip 和 端口 (在网络上注册该主机,让其他主机找到你)
'''bind( 元组 ) 默认本地ip 127.0.0.1 (ip,端口) '''
sk.bind( ("127.0.0.1",9000) )
# 3.开启监听
sk.listen() # 4.三次握手
'''conn 是三次握手后的连接对象,addr是对方的ip和端口号'''
conn,addr = sk.accept() # <socket.socket fd=476, family=AddressFamily.AF_INET, type=SocketKind.SOCK_STREAM, proto=0, laddr=('127.0.0.1', 9000), raddr=('127.0.0.1', 51123)>
print(conn)
# ('127.0.0.1', 51123)
print(addr) # 5.写收发数据的逻辑
"""
1kb = 1024B
1024kb = 1024 * 1024B
1mb = 1100000000
一发一收是一对,发和收要一一匹配
recv(字节)
""" # 接收数据 recv后面的字节数,是一次性最大接收这么多个字节;
msg = conn.recv(1024)
print(msg.decode("utf-8")) # 发送数据
conn.send("你是个好人..".encode()) # 6.四次挥手
conn.close() # 7.退还端口
sk.close()
[client端]
# ### 客户端
import socket
# 创建tcp对象
sk = socket.socket()
# 直接与服务器主机建立连接
'''connect( 元组 ) (ip,端口号)'''
sk.connect( ("127.0.0.1" , 9000) )
# send 用来发送消息,recv 用来接收消息
'''send(二进制字节流)'''
sk.send("我爱你".encode("utf-8"))
# 接收数据
# res = sk.recv(1024)
# print(res.decode())
# 关闭连接
sk.close()
6.tcp循环发送消息
[server端]
# ### 服务端
import socket
# 1.创建一个socket对象 , 默认按照tcp协议创建
sk = socket.socket()
# 2.绑定ip 和 端口 (在网络上注册该主机,让其他主机找到你)
'''bind( 元组 ) 默认本地ip 127.0.0.1 (ip,端口) '''
sk.bind( ("127.0.0.1",9000) )
# 3.开启监听
sk.listen() # listen accept recv 都是阻塞;如果不满足条件,程序不会往下执行; # 5.收发数据 quit while True:
# 4.三次握手
'''conn 是三次握手后的连接对象,addr是对方的ip和端口号'''
conn,addr = sk.accept()
while True:
# 收消息
msg = conn.recv(1024)
print(msg.decode())
# 发消息
message = input("老弟,要发什么?>>>")
conn.send(message.encode("utf-8"))
if message == "q":
break # 6.四次挥手
conn.close() # 7.退还端口
sk.close() [client端]
# ### 客户端
import socket
# 创建tcp对象
sk = socket.socket()
# 直接与服务器主机建立连接
'''connect( 元组 ) (ip,端口号)'''
sk.connect( ("127.0.0.1" , 9000) ) while True:
# 发消息
message = input(">>>:")
sk.send(message.encode("utf-8"))
# 收消息
res = sk.recv(1024)
if res == b'q':
break
print(res.decode("utf-8")) # 关闭连接
sk.close()
7.udp发送消息
[server端]
# ### 服务端
""" 如果是udp的服务端 ,只能先接收数据 ,tcp服务端可以先发也可以先收 """
import socket # 1.创建udp对象 type = SOCK_DGRAM 代表udp协议
sk = socket.socket(type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# 2.绑定ip和端口 (在网络中注册该主机)
sk.bind( ("127.0.0.1",9000) ) # 3.udp服务器,第一次启动时,一定是先接收数据,在发送数据
msg,cli_addr = sk.recvfrom(1024)
print(msg.decode("utf-8"))
print(cli_addr) # 4.关闭udp连接
sk.close() [client端] # ### 客户端
import socket
# 1.创建udp对象 type = SOCK_DGRAM 代表udp协议
sk = socket.socket(type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# 2.sendto(要发的消息,(ip,端口号))
sk.sendto( "你好".encode("utf-8") , ("127.0.0.1",9000) ) # 3.关闭udp连接
sk.close()
Learn day8 re正则表达式\search函数\反射\tcp发送消息(循环)\udp发送消息的更多相关文章
- win32编程中消息循环和WndProc()窗口过程函数
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zxxSsdsd/article/details/45504383 在win32程序的消息循环函数中 while (GetMessage (&a ...
- python中,有关正则表达式re函数:compile、match、search、findall
1.全局匹配函数 re.compile(pattern=pattern,re.S).findall(text)函数: compile 函数根据一个模式字符串和可选的标志参数生成一个正则表达式对象.该对 ...
- Python_常用的正则表达式处理函数
正则表达式就是用查找字符串的,它能查找规则比较复杂的字符串反斜杠:正则表达式里面用"\"作为转义字符. s='<a class="h3" href=&qu ...
- python笔记-正则表达式常用函数
1.re.findall()函数 语法:re.findall(pattern,string,flags=0) --> list(列表) 列出字符串中模式的所有匹配项,并作为一个列表返回.如果无匹 ...
- Python3中正则模块re.compile、re.match及re.search函数用法详解
Python3中正则模块re.compile.re.match及re.search函数用法 re模块 re.compile.re.match. re.search 正则匹配的时候,第一个字符是 r,表 ...
- Python中正则模块re.compile、re.match及re.search函数用法
import rehelp(re.compile)'''输出结果为:Help on function compile in module re: compile(pattern, flags=0) C ...
- Python 正则表达式 search vs match
search()和match()函数都是正则表达式中的匹配函数,二者有何区别呢? 1.match()从string的开始位置进行正则匹配,即从0位置开始匹配,若匹配上则返回一个match对象,否则返回 ...
- Python常用的正则表达式处理函数
Python常用的正则表达式处理函数 正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列,用于简洁表达一组字符串特征,检查一个字符串是否与某种模式匹配,使用起来十分方便. 在Python中,我们通过调用re库来使用re模 ...
- python3笔记二十二:正则表达式之函数
一:学习内容 re.match函数 re.search函数 re.findall函数 二:re.match函数 需要导入包:import re 1.格式:match(pattern,string,fl ...
随机推荐
- JavaEE的核心API与组件
JAVAEE Java ee 平台由一整套服务(Services).应用程序接口(APIs)和协议构成,它对开发基于Web的多层应用提供了功能支持,下面对JAVAEE中的13种技术规范进行简单的描述( ...
- idea如何通过数据库生成实体类
---恢复内容开始--- https://blog.csdn.net/liu_yulong/article/details/72910588 ---恢复内容结束---
- CentOS7的下载及虚拟机的创建
一.CentOS的安装 1,首先打开开源镜像网站:www.mirrors.163.com(网易开源镜像网站),www.mirrors.aliyun.com(阿里云开源镜像网站) 以网易为例 2.点击进 ...
- P4915 帕秋莉的魔导书(动态开点线段树)
题目背景 帕秋莉有一个巨大的图书馆,里面有数以万计的书,其中大部分为魔导书. 题目描述 魔导书是一种需要钥匙才能看得懂的书,然而只有和书写者同等或更高熟练度的人才能看得见钥匙.因此,每本魔导书都有它自 ...
- 【题解】[JSOI2007]字符加密
Link \(\text{Solution:}\) 后缀数组第一题祭-- 观察一下,这个是让求一个环形的原字符串的后缀,我们可以考虑一下断环为链. 对于\(aba\)我们扩展成\(abaaba,\)则 ...
- php curl 获取请求头与DNS解析
1 php-curl方法相关设置具体方法在最下方的示例函数有相关编著, 这里主要描述两个小众需求a 设置访问DNS解析问题点: get请求网页获取返回值速度很快, 但是使用curl请求数据时, 响应速 ...
- bash 在指定目录查找包含特定关键字的文件
比如我们要在目录/usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/下查找baidu.com这个关键字的文件 方法1: find /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/ -exe ...
- 多测师讲解_ 高级自动化测试selenium_001基本学习
高级自动化测试python+selenium教程手册 --高级讲师肖sir 第 1 章webdriver 环境搭建好了,我们正式学习 selenium 的 webdriver 框架,它不像 QTP 之 ...
- 增强for循环的用法
一.增强for循环 增强for循环的作用: 简化迭代器的书写格式.(注意:增强for循环的底层还是使用了迭代器遍历.)增强for循环的适用范围: 如果是实现了Iterable接口的对象或者是数组对象都 ...
- day05 Pyhton学习
1字典 字符串"" 列表[,] 元祖(,) 字典{:,} 集合{,} 2.增加 dic={} dic['name'] = '周润发' dic.setdefault() 如果dict ...
