python与mysql的数据交互
一 Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
1.1 安装pymysql命令
sudo pip3 install pymysql 安装软件:sudo apt-get install 软件名称 安装模块:sudo pip3 install 模块名称
1.2 通过pymysql操作数据库的步骤
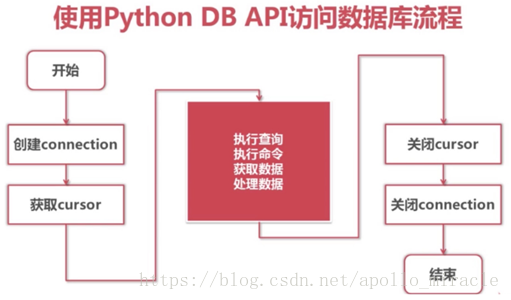
1.3 引入模块
在py文件中引入pymysql模块 from pymysql import * from pymasql import connect
1.4 建立连接对象
1.4.1 Connect 对象
#用于建立与数据库的连接 创建对象:调用connect()方法 # conn = connect(参数列表) conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")
参数host:连接的mysql主机,如:本机是”localhost”或”127.0.0.1” 参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306 参数database:数据库的名称 参数user:连接的用户名 参数password:连接的密码 参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
1.4.2 对象的方法
conn.close() # 关闭连接 conn.commit() # 提交 conn.cursor() # 返回Cursor游标对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果
1.5 创建游标对象
1.5.1 Cursor对象
用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete 获取Cursor对象:调用Connect对象的cursor()方法 cs = conn.cursor()
1.5.2 对象的方法
cs.close() # 关闭 # 执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
cs.execute(operation [, parameters ]) # 执行SQL语句 业务代码 查询操作返回记录数
count = cs.execute("select * from goods") # 获取查询结果集的下一行数据,返回一个元组
cs.fetchone() # 获取多条查询结果集,返回是一个元组,默认返回1条
cs.fetchmany(nums) # 获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
cs.fetchall()
1.6 对数据表的读操作
# 导入模块
from pymysql import * # 创建连接对象 连接数据库
conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong")
# 创建cursor游标对象
cs = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL语句 业务代码 查询操作返回记录数
count = cs.execute("select * from goods")
# 获取查询结果集的下一行数据,返回一个元组
cs.fetchone()
# 获取多条查询结果集,返回是一个元组,默认返回1条
cs.fetchmany(nums)
# 获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
cs.fetchall()
# 最近一次execute返回数据的行数或影响的行数
print(cs.rowcount)
# 使用完毕 先关闭游标
cs.close()
# 再关闭连接
conn.close()
二 增删改查
2.1 增删改
from pymysql import * def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, database="jing_dong", user="root", password="mysql", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor() # 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
# 增加
count = cs1.execute("insert into goods_cates(name) values('硬盘')")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("受影响的行数:%d" % count) # # 更新
# count = cs1.execute("update goods_cates set name='机械硬盘' where name='硬盘'") # # 删除
# count = cs1.execute("delete from goods_cates where id=6") # 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交
conn.commit() # 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.2 查询一行数据
from pymysql import * def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs = conn.cursor() # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs.execute("select id, name from goods where id>=4")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count) for i in range(count):
# 获取查询的结果
result = cs.fetchone()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 获取查询的结果 # 关闭Cursor对象
cs.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.3 查询多行数据
from pymysql import * def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs = conn.cursor() # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs.execute("select id,name from goods where id>=4")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count) result = cs.fetchall()
print(result) # 关闭Cursor对象
cs.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.4 用面向对象的思想来实现
from pymysql import * class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong",
charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close() def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp) def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql) @staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...") def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.5 添加一个商品分类
from pymysql import * class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close() def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp) def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit() @staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "":
# 商品品牌分类
self.add_brands()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...") def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.6 根据商品名称查询信息
from pymysql import * class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close() def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp) def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit() def get_info_by_name(self):
find_name = input("请输入要查询的商品的名字:") # 对 find_name 进行 判断,验证。 sql = """select * from goods where name='%s';""" % find_name """
find_name = ' or 1=1 '; insert into goods ..... ;or '
find_name = 老王牌电脑
select * from goods where name='' or 1=1 or '';
""" print("---->%s<----" % sql)
self.execute_sql(sql) @staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
print("5:根据名字查询一个商品")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "":
# 添加品牌分类
self.add_brands()
elif num == "":
# 根据名字查询商品
self.get_info_by_name()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...") def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3 防止SQL注入——参数化
sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
注意:此处不同于python的字符串格式化,全部使用%s占位
from pymysql import * class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close() def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp) def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql) def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit() def get_info_by_name(self):
find_name = input("请输入要查询的商品的名字:")
# sql = """select * from goods where name='%s';""" % find_name
# print("---->%s<----" % sql)
# self.execute_sql(sql)
sql = "select * from goods where name=%s"
self.cursor.execute(sql, [find_name])
print(self.cursor.fetchall()) @staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
print("5:根据名字查询一个商品")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "":
# 添加品牌分类
self.add_brands()
elif num == "":
# 根据名字查询商品
self.get_info_by_name()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...") def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
python与mysql的数据交互的更多相关文章
- python对MySQL进行数据的插入、更新和删除之后需要commit,数据库才会真的有数据操作。(待日后更新)
今天在尝试用下面的python代码对MySQL进行数据的插入.更新和删除时, 突然发现代码执行成功, 通过代码查询也显示数据已经插入或更新, 但是当我在MySQL客户端通过SQL语句查询时, 数据库中 ...
- 使用Connector / Python连接MySQL/查询数据
使用Connector / Python连接MySQL connect()构造函数创建到MySQL服务器的连接并返回一个 MySQLConnection对象 在python中有以下几种方法可以连接到M ...
- Python将MySQL表数据写入excel
背景:将mysql表查询结果写入excel. 1.使用sqlyog工具将查询结果导出到Excel.xml中,用excel打开发现:因为text字段中有回车换行操作,显示结果行是乱的. 2.用mysql ...
- python 向mysql插入数据
生成随机内容用到的方法: substr是一个字符串函数,从第二个参数1,开始取字符,取到3 + floor(rand() * 75)结束 floor函数代表的是去尾法取整数. rand()函数代表的是 ...
- SpringMVC4+thymeleaf3的一个简单实例(篇五:页面和MySql的数据交互-展示以及存储)
这一篇将介绍怎样把页面数据保存的MySQL数据库,并将数据库内容展示到页面上.首先做一个基础工作,添加以下jar到lib:1: mysql-connector-Java-5.1.40-bin.jar ...
- 使用spark与MySQL进行数据交互的方法
在项目中,遇到一个场景是,需要从Hive数据仓库中拉取数据,进行过滤.裁剪或者聚合之后生成中间结果导入MySQL. 对于这样一个极其普通的离线计算场景,有多种技术选型可以实现.例如,sqoop,MR, ...
- Python Django 前后端数据交互 之 HttpRequest、HttpResponse、render、redirect
在使用三神装的时候,首先当然是得要导入它们: from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse, render, redirect 一.HttpRequest捕获 ...
- Python Django 前后端数据交互 之 前端向后端发送数据
Python Django 之 前端向后端发送数据
- Python数据库MySQL之数据备份、pymysql模块
一 IDE工具介绍 生产环境还是推荐使用mysql命令行,但为了方便我们测试,可以使用IDE工具 下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bpo5mqj 掌握: #1. 测试+链接 ...
随机推荐
- django.db.utils.OperationalError: (1251, 'Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server; consider upgrading MySQL client')
1.打开MySQL: cmd里 net start mysql mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p回车 进入mysql数据库 2. 命令如下: 1.use mysql; 2.alt ...
- 【物联网】arduino wifi
https://www.arduino.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=49561 http://dy.163.com/v2/article/detail/DC ...
- Swift编码总结1
1. fileprivate (set) var hasSetDiscount = false中fileprivate (set)表示什么意思: //设置setter私有,但是getter为publi ...
- LODOP关联后眉脚条码的遮挡的一种情况
前面的博文中,有介绍层级关系,最先输出的打印项在下层,后输出的在上层,但是最近发现了一种例外,就是前面有关联的情况下,后面把一个条码设置为页眉页脚项,眉脚项和前面关联其他的项的那个项位置重合,虽然这个 ...
- 【err】开启Persistence-M模式-Check failed: err == CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS (1 vs. 0) : Create cublas handle failed
前言 安装好CUDA.CUDNN.NVIDIA driver之后,使用mxnet框架的时候出现该错误,本文记录该问题的解决方法. 环境 ubuntu 16.04 MxNet Cuda9.0 Nvidi ...
- iOS-UIPasteboard的使用
剪贴板的使用以及自定义剪贴板. 系统剪贴板的直接调用 其实整个过程非常的简单,我就用我写的一个自定义UILable来说明调用系统剪贴板. 首先,因为苹果只放出来了 UITextView,UITextF ...
- mac upgrade node and npm
一直以来, 我们都可以很轻松的更新npm: npm install npm -g 而Node我却是很久没有更新了, 记得当时好像是使用安装包安装的, 实际上有更加简单的安装方法. 实际上Mac上有一个 ...
- [bzoj4345][POI2016]Korale_堆_贪心_线段树_dfs
bzoj4345 POI2016 Korale 题目链接:https://lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4345 数据范围:略. 题解: 由于$k$的范围问 ...
- Python 数据处理库pandas教程(最后附上pandas_datareader使用实例)
0 简单介绍 pandas是一个Python语言的软件包,在我们使用Python语言进行机器学习编程的时候,这是一个非常常用的基础编程库.本文是对它的一个入门教程. pandas提供了快速,灵活和富有 ...
- Python 解LeetCode:394 Decode String
题目描述:按照规定,把字符串解码,具体示例见题目链接 思路:使用两个栈分别存储数字和字母 注意1: 数字是多位的话,要处理后入数字栈 注意2: 出栈时过程中产生的组合后的字符串要继续入字母栈 注意3: ...
