PCL中使用FLANN库(2)
接着上一篇的介绍继续
关于在使用readHeader函数读取点云数据头的类型的代码(Read a point cloud data header from a PCD file.)
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
//读取PCD文件的头的基本信息
/*(in)path.string ()文件名
cloud 点云数据集 origin传感器的采集中心点 orientation传感器的方位 version为PCD版本
type数据类型(0 = ASCII,1 =二进制,2 =二进制压缩)(in)idx为在文件内的偏移点云数据*/
r.readHeader (path.string (), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);
查看PCD文件里的内容(其实对于如何生成这种高纬度的文件呢?)
# .PCD v. - Point Cloud Data file format 注释掉说明这是关于点云的文件格式
VERSION .7 PCD文件的版本号
FIELDS x y z rgb u v vx vy vz normal_x normal_y normal_z curvature 文件中点云的维度数
SIZE 4 每个维度数据的大小
TYPE F F F F F F F F F F F F F 数据的类型
COUNT 1
WIDTH 3484 点云大小
HEIGHT 1 无序点云
VIEWPOINT 0 视点
POINTS 3484 大小
DATA ascii 数据
-0.0042959 -0.041022 0.97549 7.3757e-39 -0.15142 0.63581 -0.75685 0.018435
-0.0031521 -0.040989 0.97472 7.0991e-39 -0.12262 0.63448 -0.76315 0.017282
-0.0042959 -0.03988 0.97549 5.9927e-39 -0.15385 0.62475 -0.76552 0.017079
-0.0020133 -0.03988 0.97549 5.3473e-39 -0.11114 0.62014 -0.77658 0.015706
-0.00087171 -0.039294 0.9751 5.6239e-39 277.5 261.5 -0.089597 0.61557 -0.78297 0.015285
另外一种PCD文件的比如VFH的PCD文件
# .PCD v. - Point Cloud Data file format
FIELDS vfh
SIZE
TYPE F
COUNT
WIDTH
HEIGHT
POINTS
DATA ascii
0.086133 0.31582 ........................................................
那么接下来我们就可以使用PCL给定的数据集,以及FLANN的库是实现对点云的识别,方法是按照(1)的思路来做的
首先我们是假设已经有了数据集,以及相应每个数据集的VFH全局表述子的PCD文件,这样我们就可以使用(1)中的思路把数据集训练并保存到数中,方便之后我们再输入给定的点云的VFH的PCD文件进行查找
那么其实这里面,我们如果是自己生成数据集,并对每个数据生成对应的VFH文件就会有点难度,毕竟这是对采集到的数据,对于一些无关点云需要剔除,
然后对有用的有价值的点云数据进行聚类,以及各个角度的点云聚类,然后对聚类的对象生成对应的VFH的特征PCD文件,这就是大致思路,
那么我们来看一下源代码是如何读取并训练数据源的,并生成可用于FLANN使用的文件,并存在磁盘中
源代码分析如下
#include <pcl/point_types.h> //点云的类型
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/console/print.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>
#include <flann/flann.h>
#include <flann/io/hdf5.h>
#include <fstream>
//pair的成员有两个first second两个,很明显第一个vfh_model.first就是std::string
//vfh_model.second就是存入的float的变量
typedef std::pair<std::string, std::vector<float> > vfh_model;//用于存储VFH模型的容器 /** \brief Loads an n-D histogram file as a VFH signature 以VFH作为特征直方图
* \param path the input file name 输入的文件的名称
* \param vfh the resultant VFH model //VFH的模型
*/
bool
loadHist (const boost::filesystem::path &path, vfh_model &vfh)
{
int vfh_idx;
// Load the file as a PCD
try
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin; //中心float的向量
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation; //方向
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type;
unsigned int idx;
r.readHeader (path.string (), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx); vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex (cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -)
return (false);
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != ) //点的数目不为0
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&) //抛出异常
{
return (false);
} // Treat the VFH signature as a single Point Cloud把相应的VFH特征代表单个点云
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> point; //申明VFH 的点云
pcl::io::loadPCDFile (path.string (), point);
vfh.second.resize (); //因为VFH有308个数据 std::vector <pcl::PCLPointField> fields;
pcl::getFieldIndex (point, "vfh", fields); for (size_t i = ; i < fields[vfh_idx].count; ++i)
{
vfh.second[i] = point.points[].histogram[i]; //每个点的直方图
}
vfh.first = path.string ();
return (true);
} /** \brief Load a set of VFH features that will act as the model (training data) //以VFH特征作为模型的训练数据集
* \param argc the number of arguments (pass from main ()) //输入参数的个数
* \param argv the actual command line arguments (pass from main ())
* \param extension the file extension containing the VFH features 文件名的后缀
* \param models the resultant vector of histogram models //特征模型的直方图向量
*/
void
loadFeatureModels (const boost::filesystem::path &base_dir, const std::string &extension,
std::vector<vfh_model> &models)
{
if (!boost::filesystem::exists (base_dir) && !boost::filesystem::is_directory (base_dir))
return; for (boost::filesystem::directory_iterator it (base_dir); it != boost::filesystem::directory_iterator (); ++it) //对文件下每一个VFH的PCD文件计数
{
if (boost::filesystem::is_directory (it->status ()))
{
std::stringstream ss; //输入
ss << it->path ();
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Loading %s (%lu models loaded so far).\n", ss.str ().c_str (), (unsigned long)models.size ());
loadFeatureModels (it->path (), extension, models);
}
if (boost::filesystem::is_regular_file (it->status ()) && boost::filesystem::extension (it->path ()) == extension)
{
vfh_model m;
if (loadHist (base_dir / it->path ().filename (), m))
models.push_back (m); //装进容器中
}
}
} int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
if (argc < ) //对输入命令行的解析
{
PCL_ERROR ("Need at least two parameters! Syntax is: %s [model_directory] [options]\n", argv[]);
return (-);
} std::string extension (".pcd");
transform (extension.begin (), extension.end (), extension.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); std::string kdtree_idx_file_name = "kdtree.idx";
std::string training_data_h5_file_name = "training_data.h5";
std::string training_data_list_file_name = "training_data.list"; std::vector<vfh_model> models; //VFH的模型 // Load the model histograms 载入模型的直方图
loadFeatureModels (argv[], extension, models);
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Loaded %d VFH models. Creating training data %s/%s.\n",
(int)models.size (), training_data_h5_file_name.c_str (), training_data_list_file_name.c_str ()); // Convert data into FLANN format 把数据转为FLANN格式
flann::Matrix<float> data (new float[models.size () * models[].second.size ()], models.size (), models[].second.size ()); for (size_t i = ; i < data.rows; ++i)
for (size_t j = ; j < data.cols; ++j)
data[i][j] = models[i].second[j]; // Save data to disk (list of models)保存数据集到本地
flann::save_to_file (data, training_data_h5_file_name, "training_data");
std::ofstream fs;
fs.open (training_data_list_file_name.c_str ()); //打开训练数据集的文件
for (size_t i = ; i < models.size (); ++i)
fs << models[i].first << "\n";
fs.close (); // Build the tree index and save it to disk 建立树索引并保存
pcl::console::print_error ("Building the kdtree index (%s) for %d elements...\n", kdtree_idx_file_name.c_str (), (int)data.rows);
flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index (data, flann::LinearIndexParams ());
//flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index (data, flann::KDTreeIndexParams (4));
index.buildIndex ();
index.save (kdtree_idx_file_name);
delete[] data.ptr (); return ();
}
这里面就很明显的生成了两个可用于FLANN进行搜索匹配的文件,以及模型的名称的列表,就是会生成以下三个文件
kdtree.idx(这个是kdtree模型的索引)
training_data.h5(用于FLANN库中的一种高效的文件格式,上一章有介绍),
training_data.list(这是训练数据集的列表)
(2)那么对于已经生成好的点云的数据集,我们就需要使用写一个程序来实现给定一个点云的VFH的PCD文件来寻找这个点云所在位置并且是什么角度拍照的结果,闲话少说明,直接就上程序
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/common/common.h>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/console/print.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <flann/flann.h>
#include <flann/io/hdf5.h>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp> typedef std::pair<std::string, std::vector<float> > vfh_model; /** \brief Loads an n-D histogram file as a VFH signature
* \param path the input file name
* \param vfh the resultant VFH model
*/
bool
loadHist (const boost::filesystem::path &path, vfh_model &vfh)
{
int vfh_idx;
// Load the file as a PCD
try
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
//读取PCD文件的头的基本信息
/*(in)path.string ()文件名
cloud 点云数据集 origin传感器的采集中心点 orientation传感器的方位 version为PCD版本
type数据类型(0 = ASCII,1 =二进制,2 =二进制压缩)(in)idx为在文件内的偏移点云数据*/
r.readHeader (path.string (), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx); vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex (cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -)
return (false);
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != )
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&)
{
return (false);
} // Treat the VFH signature as a single Point Cloud
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> point;
pcl::io::loadPCDFile (path.string (), point);
vfh.second.resize (); std::vector <pcl::PCLPointField> fields;
getFieldIndex (point, "vfh", fields); for (size_t i = ; i < fields[vfh_idx].count; ++i)
{
vfh.second[i] = point.points[].histogram[i];
}
vfh.first = path.string ();
return (true);
} /** \brief Search for the closest k neighbors搜索最近的K邻域
* \param index the tree 树 的索引
* \param model the query model //给定的模型
* \param k the number of neighbors to search for
* \param indices the resultant neighbor indices
* \param distances the resultant neighbor distances
*/
inline void
nearestKSearch (flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > &index, const vfh_model &model,
int k, flann::Matrix<int> &indices, flann::Matrix<float> &distances)
{
// Query point 给定的点云
flann::Matrix<float> p = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[model.second.size ()], , model.second.size ());
memcpy (&p.ptr ()[], &model.second[], p.cols * p.rows * sizeof (float)); indices = flann::Matrix<int>(new int[k], , k);
distances = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[k], , k);
index.knnSearch (p, indices, distances, k, flann::SearchParams ());
delete[] p.ptr ();
} /** \brief Load the list of file model names from an ASCII file 载入模型文件名
* \param models the resultant list of model name
* \param filename the input file name
*/
bool
loadFileList (std::vector<vfh_model> &models, const std::string &filename)
{
ifstream fs;
fs.open (filename.c_str ());
if (!fs.is_open () || fs.fail ())
return (false); std::string line;
while (!fs.eof ())
{
getline (fs, line);
if (line.empty ())
continue;
vfh_model m;
m.first = line;
models.push_back (m);
}
fs.close ();
return (true);
} int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
int k = ; double thresh = DBL_MAX; // No threshold, disabled by default if (argc < )
{
pcl::console::print_error
("Need at least three parameters! Syntax is: %s <query_vfh_model.pcd> [options] {kdtree.idx} {training_data.h5} {training_data.list}\n", argv[]);
pcl::console::print_info (" where [options] are: -k = number of nearest neighbors to search for in the tree (default: ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%d", k); pcl::console::print_info (")\n");
pcl::console::print_info (" -thresh = maximum distance threshold for a model to be considered VALID (default: ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%f", thresh); pcl::console::print_info (")\n\n");
return (-);
} std::string extension (".pcd");
transform (extension.begin (), extension.end (), extension.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); // Load the test histogram 载入测试的直方图
std::vector<int> pcd_indices = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd");
vfh_model histogram;
if (!loadHist (argv[pcd_indices.at ()], histogram))
{
pcl::console::print_error ("Cannot load test file %s\n", argv[pcd_indices.at ()]);
return (-);
} pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "-thresh", thresh);
// Search for the k closest matches 设置K邻域的个数
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "-k", k);
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Using "); pcl::console::print_value ("%d", k); pcl::console::print_info (" nearest neighbors.\n"); std::string kdtree_idx_file_name = "kdtree.idx";
std::string training_data_h5_file_name = "training_data.h5";
std::string training_data_list_file_name = "training_data.list"; std::vector<vfh_model> models;
flann::Matrix<int> k_indices; //索引
flann::Matrix<float> k_distances; //距离
flann::Matrix<float> data;
// Check if the data has already been saved to disk
if (!boost::filesystem::exists ("training_data.h5") || !boost::filesystem::exists ("training_data.list"))
{
pcl::console::print_error ("Could not find training data models files %s and %s!\n",
training_data_h5_file_name.c_str (), training_data_list_file_name.c_str ());
return (-);
}
else
{
loadFileList (models, training_data_list_file_name); //载入模型的文件名
flann::load_from_file (data, training_data_h5_file_name, "training_data");
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Training data found. Loaded %d VFH models from %s/%s.\n",
(int)data.rows, training_data_h5_file_name.c_str (), training_data_list_file_name.c_str ());
} // Check if the tree index has already been saved to disk
if (!boost::filesystem::exists (kdtree_idx_file_name))
{
pcl::console::print_error ("Could not find kd-tree index in file %s!", kdtree_idx_file_name.c_str ());
return (-);
}
else
{
flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index (data, flann::SavedIndexParams ("kdtree.idx"));
index.buildIndex ();
nearestKSearch (index, histogram, k, k_indices, k_distances); //搜索K邻域
} // Output the results on screen
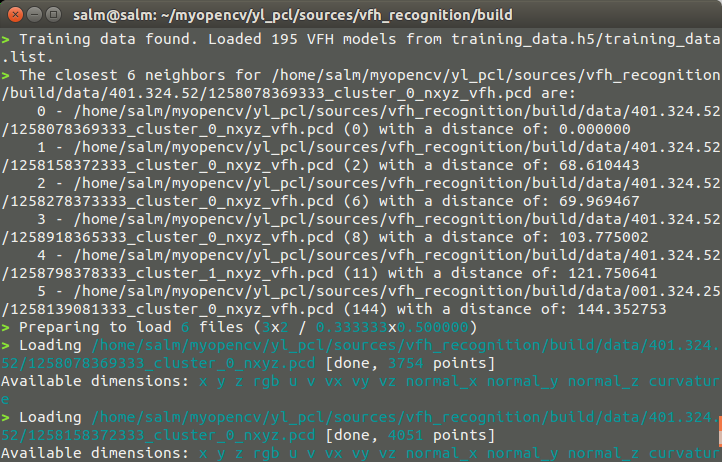
pcl::console::print_highlight ("The closest %d neighbors for %s are:\n", k, argv[pcd_indices[]]);
for (int i = ; i < k; ++i)
pcl::console::print_info (" %d - %s (%d) with a distance of: %f\n",
i, models.at (k_indices[][i]).first.c_str (), k_indices[][i], k_distances[][i]); // Load the results可视化结果
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer p (argc, argv, "VFH Cluster Classifier");
int y_s = (int)floor (sqrt ((double)k));
int x_s = y_s + (int)ceil ((k / (double)y_s) - y_s);
double x_step = (double)( / (double)x_s);
double y_step = (double)( / (double)y_s);
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Preparing to load ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%d", k);
pcl::console::print_info (" files (");
pcl::console::print_value ("%d", x_s);
pcl::console::print_info ("x");
pcl::console::print_value ("%d", y_s);
pcl::console::print_info (" / ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%f", x_step);
pcl::console::print_info ("x");
pcl::console::print_value ("%f", y_step);
pcl::console::print_info (")\n"); int viewport = , l = , m = ;
for (int i = ; i < k; ++i)
{
std::string cloud_name = models.at (k_indices[][i]).first;
boost::replace_last (cloud_name, "_vfh", ""); p.createViewPort (l * x_step, m * y_step, (l + ) * x_step, (m + ) * y_step, viewport);
l++;
if (l >= x_s)
{
l = ;
m++;
} pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
pcl::console::print_highlight (stderr, "Loading "); pcl::console::print_value (stderr, "%s ", cloud_name.c_str ());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (cloud_name, cloud) == -)
break; // Convert from blob to PointCloud
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_xyz;
pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2 (cloud, cloud_xyz); if (cloud_xyz.points.size () == )
break; pcl::console::print_info ("[done, ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%d", (int)cloud_xyz.points.size ());
pcl::console::print_info (" points]\n");
pcl::console::print_info ("Available dimensions: ");
pcl::console::print_value ("%s\n", pcl::getFieldsList (cloud).c_str ()); // Demean the cloud
Eigen::Vector4f centroid;
pcl::compute3DCentroid (cloud_xyz, centroid);//Compute the 3D (X-Y-Z) centroid of a set of points and return it as a 3D vector.
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_xyz_demean (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::demeanPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud_xyz, centroid, *cloud_xyz_demean);
// Add to renderer*
p.addPointCloud (cloud_xyz_demean, cloud_name, viewport); // Check if the model found is within our inlier tolerance
std::stringstream ss;
ss << k_distances[][i];
if (k_distances[][i] > thresh)
{
p.addText (ss.str (), , , , , , ss.str (), viewport); // display the text with red // Create a red line
pcl::PointXYZ min_p, max_p;
pcl::getMinMax3D (*cloud_xyz_demean, min_p, max_p);
std::stringstream line_name;
line_name << "line_" << i;
p.addLine (min_p, max_p, , , , line_name.str (), viewport);
p.setShapeRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_LINE_WIDTH, , line_name.str (), viewport);
}
else
p.addText (ss.str (), , , , , , ss.str (), viewport); // Increase the font size for the score*
p.setShapeRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_FONT_SIZE, , ss.str (), viewport); // Add the cluster name
p.addText (cloud_name, , , cloud_name, viewport);
}
// Add coordianate systems to all viewports
p.addCoordinateSystem (0.1, "global", ); p.spin ();
return ();
}
这里面就涉及到FLANN的库的函数的使用,执行的结果
打印的结果,这里面会显示最接近的六个数据集,并且计算这六个最近点云与给定点云之间的“距离”,这也是衡量两者之间的相似度的大小
可视化的结果

很明显左下角就是我们给定的数据点云,而且运行查找的速度非常快~
好了就这样了
关注微信公众号,欢迎大家的无私分享

PCL中使用FLANN库(2)的更多相关文章
- PCL中使用FLANN库(1)
FLANN库全称是Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors,它是目前最完整的(近似)最近邻开源库.不但实现了一系列查找算法,还包含了一种自动选取最快 ...
- 基于传统方法点云分割以及PCL中分割模块
之前在微信公众号中更新了以下几个章节 1,如何学习PCL以及一些基础的知识 2,PCL中IO口以及common模块的介绍 3,PCL中常用的两种数据结构KDtree以及Octree树的介绍 ...
- PCL中的OpenNI点云获取框架(OpenNI Grabber Framework in PCL)
从PCL 1.0开始,PCL(三维点云处理库Point Cloud Library)提供了一个通用采集接口,这样可以方便地连接到不同的设备及其驱动.文件格式和其他数据源.PCL集成的第一个数据获取驱动 ...
- PCL中可用的PointT类型
PCL中可用的PointT类型: PointXYZ——成员变量:float x,y,z; PointXYZ是使用最常见的一个点数据类型,因为他之包含三维XYZ坐标信息,这三个浮点数附加一个浮点数来满足 ...
- PCL中异常处理机制
博客转载自:http://www.pclcn.org/study/shownews.php?lang=cn&id=287 本节我们主要讨论PCL在编写和应用过程中如何利用PCL的异常机制,提高 ...
- [C++] C++中的常用库
转载自:C++常用库 C++ 资源大全 关于 C++ 框架.库和资源的一些汇总列表,内容包括:标准库.Web应用框架.人工智能.数据库.图片处理.机器学习.日志.代码分析等. 标准库 C++标准库,包 ...
- PCL中outofcore模块---基于核外八叉树的大规模点云的显示
写在前面 最近公众号的活动让更多的人加入交流群,尝试提问更多的我问题,群主也在积极的招募更多的小伙伴与我一起分享,能够相互促进. 这里总结群友经常问,经常提的两个问题,并给出我的回答: (1) ...
- WebGIS中基于控制点库进行SHP数据坐标转换的一种查询优化策略
文章版权由作者李晓晖和博客园共有,若转载请于明显处标明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/naaoveGIS/ 1.前言 目前项目中基于控制点库进行SHP数据的坐标转换,流程大致为:遍 ...
- Linux中的动态库和静态库(.a/.la/.so/.o)
Linux中的动态库和静态库(.a/.la/.so/.o) Linux中的动态库和静态库(.a/.la/.so/.o) C/C++程序编译的过程 .o文件(目标文件) 创建atoi.o 使用atoi. ...
随机推荐
- class.forName的作用?
调用该访问 返回一个以字符串指定类名的类的对象. 返回字节码,返回字节码的方式有几种: ①:这份字节码曾经被加载过已经存在java虚拟机中了直接返回. ②:java虚拟机中还没有这份字节码,用类加载器 ...
- CocosCreator弹窗处理
目前我所用的也就两种方法, 放置一个几近透明的sprite,作为遮罩,防止弹窗出现后,作为背景的UI上的按钮类的响应: 2,将上述遮罩作为弹窗的背景或者弹窗的子对象[此时,需要作为子对象的第一个,防止 ...
- U3D面试题系列二
高频问题: 一.什么是渲染管道? 是指在显示器上为了显示出图像而经过的一系列必要操作. 渲染管道中的很多步骤,都要将几何物体从一个坐标系中变换到另一个坐标系中去. 主要步骤有: 本地坐标->视图 ...
- dockerfile安装php遇到的坑
fetch http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.7/main/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz fetch http://dl-cdn.alpi ...
- 伪造请求IP
//随机IP function Rand_IP(){ $ip2id= round(rand(600000, 2550000) / 10000); //第一种方法,直接生成 $ip3id= round( ...
- 转载一篇关于toString和valueOf
可以这样说,所有JS数据类型都拥有valueOf和toString这两个方法,null除外.它们俩解决javascript值运算与显示的问题.在程序应用非常广泛.下面我们逐一来给大家介绍下. Java ...
- ITxlab倡议启动“互联网X大脑”计划
导语:"互联网X大脑"计划由ITxlab(互联网X实验室)联合科学院相关机构.基于7年以来取得的研究成果,倡议建立的互联网与脑科学前沿研究平台,吸引不同领域专家进行科学研究和成果交 ...
- HDU4655【题意+分析】
哎这题有点意思.. 一开始肿么看都不理解题意,发现好多ACM题都这样,好多英文意思不能完全理解,只得照样例猜啦,猜不出来?? 那就靠神队友解释了,囧. 就是排列,涂色使结果最大化. 反正别人的博客把这 ...
- 修改Unity中Lua文件的默认打开程序
项目中引用了XLua,而Lua文件又是以txt文件结尾的,当修改系统的扩展脚本编辑器为vs后双击lua文件(xx.txt)默认也使用vs打开了,无提示的黑白文本编辑 昨办? -. 后来看到网上有写Un ...
- Java代码常见的十种错误
每一个程序员在编写代码的过程中都免不了出现错误或是小的失误,这些小的错误和失误往往使得程序员还得返工.那么,如何才能尽量避免这些错误的发生呢?笔者总结只有在日常的编写代码中总结出经验,在这篇文章中,笔 ...
