循环神经网络-LSTM进阶
基础的LSTM模型,单隐层,隐层单神经元,而实际中一般需要更为复杂的网络结构,
下面借用手写数字的经典案例构造比较复杂的LSTM模型,并用代码实现。
单隐层,隐层多神经元
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data # 导入数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot = True) training_iters = 50001
batch_size = 100 # 批量大小 n_inputs = 28
n_steps = 28 # 序列长度
n_hidden_number = 128 # 隐藏层神经元个数
n_outputs = 10 # 输出层神经元个数 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_steps,n_inputs]) # 输入3维 样本数*序列长度*每个元素长度
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_outputs]) weights = {
# 权重设定同全连接,这是单步权重
# 每步权重共享
# shape = (28,128)
'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_inputs,n_hidden_number])),
# shape = (128,10)
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_number,n_outputs]))} biases = {
# shape = (128,)
'in':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [n_hidden_number,])),
# shape = (10,)
'out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [n_outputs,]))} def RNN(X,weights,biases):
""" 这里是整个RNN的网络
1. 输入x是整个序列的,即 [x1,x2,..xt]*samples
2. 隐层的输出包含了序列中每个时间的输出
"""
### 输入层到核运算 ###
# X shape = (100batch,28steps,28inputs) ==> (100batch*28steps,28inputs)
X = tf.reshape(X,[-1,n_inputs]) # 之所以转成2维,是要与weight相乘
# X_in shape ==> (100batch*28steps,128hidden)
X_in = tf.matmul(X,weights['in'])+biases['in']
# 这是所有样本每个时序都乘以weight,每个时序都变成了hidden_num长度,结果是所有样本每个时序的hidden_num长,此时所有样本混在一起 # X_in shape ==> (100batch,28steps,128hidden)
# 然后要重新划分成样本,每个样本有n_steps个时序,每个时序是hidden_num长,按样本送给隐层
X_in = tf.reshape(X_in,[-1,n_steps,n_hidden_number]) ### cell核内运算 ###
## 构建单个rnn cell,单隐层,n_hidden_number个神经元,横向网络会根据输入(n_steps)自动构建
lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden_number,forget_bias = 1.0) # LSTM cell is divided into two parts-->(c_state,m_state)
# 初始化s
init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size,dtype=tf.float32) # outputs states 都是隐层的输出,整个RNN所有时序的输出,但只是h,还没到o o=vh+c(c是bias,不同于states的c,这是记忆单元)
# outputs 是以三维矩阵的形式记录了所有样本所有时序的所有隐层神经元的输出,shape为[batch_size, timestep_size, hidden_size]
# states 是最后时刻的c 和 h,c是记忆,shape为 [batch_size, 2, hidden_size]
# 当然通常顺序是这样的[2, batch_size, hidden_size]
outputs,states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm_cell,X_in,initial_state=init_state,time_major=False) ### 核内运算到输出层 ###
# states[1]就是所有样本最后时刻的h, 实际上 states[1] == outputs[:,-1,:]
result = tf.matmul(states[1],weights['out'])+biases['out'] # result就是o
return result prediction = RNN(x,weights,biases) ### 后面所有的神经网络都大同小异
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=prediction))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(loss)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1), tf.argmax(Y,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 0
while step*batch_size < training_iters:
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# batch_xs shape = [100,28,28]
batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size,n_steps,n_inputs])
train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch_xs,Y:batch_ys,})
if step%50 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch_xs,Y:batch_ys,})
print("step", step, "training accuracy", train_accuracy)
step += 1
上面的网络大概是这样
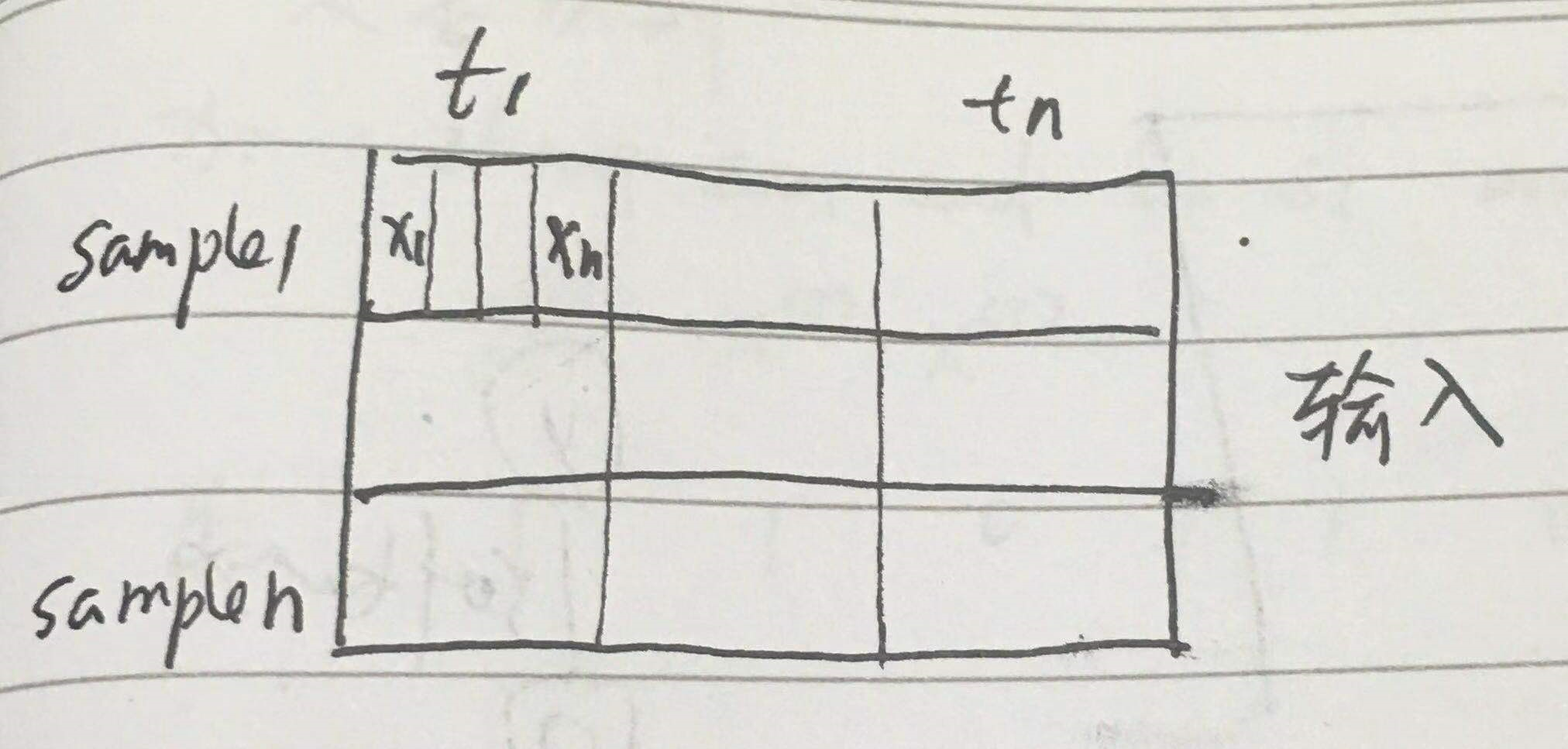
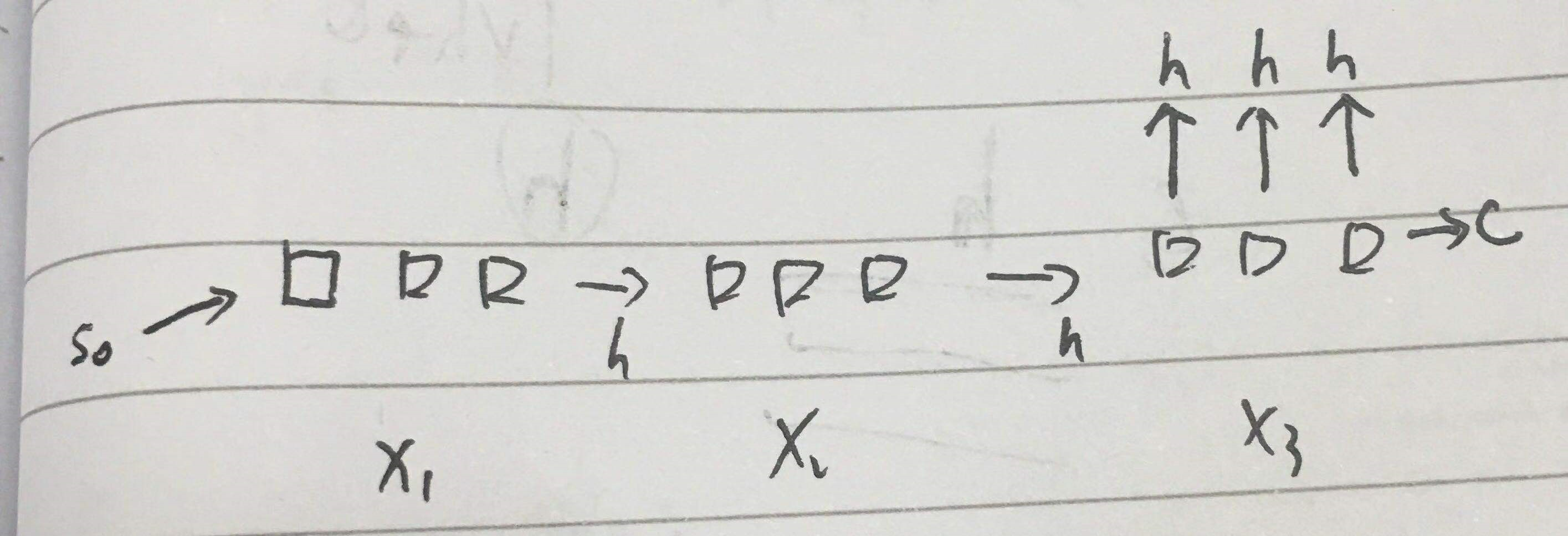
x1 x2 其实应该是 xt1 xt2
多层隐层,隐层多节点
layer_num = 2 # 隐层数 def clstm():
lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=hidden_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
lstm_cell = rnn.DropoutWrapper(cell=lstm_cell, input_keep_prob=1.0, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
return lstm_cell # 调用 MultiRNNCell 来实现多层 LSTM
mlstm_cell = rnn.MultiRNNCell([clstm() for i in range(layer_num)], state_is_tuple=True) init_state = mlstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32) outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(mlstm_cell, inputs=X, initial_state=init_state, time_major=False)
h_state = outputs[:, -1, :]
其他代码雷同
预测
看看rnn是如何预测的
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
current_y= mnist.train.labels[5]
current_x=mnist.train.images[5]
print(current_y)
# 计算h
current_x.shape = [-1, 784]
current_y.shape = [-1, class_num]
current_outputs = np.array(sess.run(outputs, feed_dict={_X: current_x, y:current_y, keep_prob: 1.0, batch_size: 1}))
print(current_outputs.shape) # (1, timesteps, hidden_size)
current_outputs.shape = [28, hidden_size] # 计算出参数
h_W = sess.run(W, feed_dict={_X:current_x, y: current_y, keep_prob: 1.0, batch_size: 1})
h_bias = sess.run(bias, feed_dict={_X:current_x, y: current_y, keep_prob: 1.0, batch_size: 1})
h_bias.shape = [-1, 10] bar_index = range(class_num)
# 识别过程
for i in range(current_outputs.shape[0]): # current_outputs.shape[0] 是 squence_length
plt.subplot(7, 4, i+1)
current_h_shate = current_outputs[i, :].reshape([-1, hidden_size]) # 每个时刻的h current_formula=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(current_h_shate, h_W) + h_bias) # 每个时刻的y
pro = sess.run(current_formula)
plt.bar(bar_index, pro[0], width=0.2 , align='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
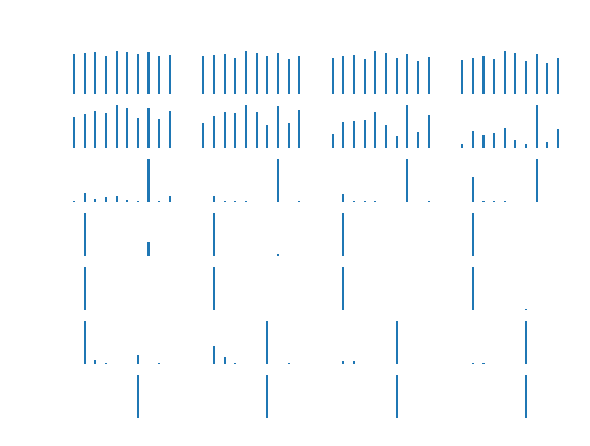
每一行显示了 4 个图,共有 7 行,每个图是一个y,表示了一行一行读取过程中,模型对字符的识别。
可以看到,在只看到前面的几行像素时,模型根本认不出来是什么字符,随着看到的像素越来越多,最后就基本确定了它是字符 4.
循环神经网络-LSTM进阶的更多相关文章
- 十 | 门控循环神经网络LSTM与GRU(附python演练)
欢迎大家关注我们的网站和系列教程:http://panchuang.net/ ,学习更多的机器学习.深度学习的知识! 目录: 门控循环神经网络简介 长短期记忆网络(LSTM) 门控制循环单元(GRU) ...
- 循环神经网络LSTM RNN回归:sin曲线预测
摘要:本篇文章将分享循环神经网络LSTM RNN如何实现回归预测. 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] 十四.循环神经网络LSTM RNN回归案例之sin曲线预测 丨[百变AI秀]& ...
- Pytorch循环神经网络LSTM时间序列预测风速
#时间序列预测分析就是利用过去一段时间内某事件时间的特征来预测未来一段时间内该事件的特征.这是一类相对比较复杂的预测建模问题,和回归分析模型的预测不同,时间序列模型是依赖于事件发生的先后顺序的,同样大 ...
- 循环神经网络-RNN进阶
这部分许多内容要类比CNN来进行理解和解释,所以需要对CNN比较熟悉. RNN的特点 1. 权值共享 CNN权值共享,RNN也有权值共享,在入门篇可以看到RNN结构图中,权重使用的是同样的字母 为什么 ...
- 循环神经网络-LSTM
LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)是长短期记忆网络,是一种时间递归神经网络,适合于处理和预测时间序列中间隔和延迟相对较长的重要事件. LSTM能够很大程度上缓解长期依赖的问题. ...
- 深度学习 循环神经网络 LSTM 示例
最近在网上找到了一个使用LSTM 网络解决 世界银行中各国 GDP预测的一个问题,感觉比较实用,毕竟这是找到的唯一一个可以正确运行的程序. #encoding:UTF-8 import pandas ...
- [ DLPytorch ] 循环神经网络进阶&拟合问题&梯度消失与爆炸
循环神经网络进阶 BPTT 反向传播过程中,训练模型通常需要模型参数的梯度. \[ \frac{\partial L}{\partial \boldsymbol{W}_{qh}} = \sum_{t= ...
- 循环神经网络之LSTM和GRU
看了一些LSTM的博客,都推荐看colah写的博客<Understanding LSTM Networks> 来学习LSTM,我也找来看了,写得还是比较好懂的,它把LSTM的工作流程从输入 ...
- 通过keras例子理解LSTM 循环神经网络(RNN)
博文的翻译和实践: Understanding Stateful LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks in Python with Keras 正文 一个强大而流行的循环神经 ...
随机推荐
- Create a Hadoop Build and Development Environment
Create a Hadoop Build and Development Environment http://vichargrave.com/create-a-hadoop-build-and-d ...
- android--------自定义控件 之 基本实现篇
前面简单的讲述了Android中自定义控件中的几个方法,今天通过代码来实现一个简单的案例 自定义一个扇形图 自定义控件示例: 这里先介绍继承View的方式为例 public class Circula ...
- 『TensorFlow』分布式训练_其一_逻辑梳理
1,PS-worker架构 将模型维护和训练计算解耦合,将模型训练分为两个作业(job): 模型相关作业,模型参数存储.分发.汇总.更新,有由PS执行 训练相关作业,包含推理计算.梯度计算(正向/反向 ...
- Matlab-5:牛顿迭代法工具箱
function [f,L]=Newton(f,a) %this is newton teration whic is used for solving implicit One-dimensiona ...
- 【IDEA】【7】Git更新及提交
如果是Git管理的项目,顶部会出现这样的按钮 绿色代表commit到本地 蓝色代表update最新代码 Push:推送到远程服务器:右键项目->Git->Repository->Pu ...
- css中伪类与伪元素的区别
一:伪类:1:定义:css伪类用于向某些选择器添加特殊效果. 伪类其实与普通的css类相类似,可以为已有的元素添加样式,但是他只有处于dom无法描述的状态下才能为文档树中的元素添加样式,所以将其称为伪 ...
- leetcode-algorithms-28 Implement strStr()
leetcode-algorithms-28 Implement strStr() mplement strStr(). Return the index of the first occurrenc ...
- CF-787D-线段树建图+最短路
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/787/D 题目大意是给出一个有向图,有N个节点,初始节点在S,询问S到所有点最短路.边的读入方式有三种, 1 u v ...
- 不安装Oracle数据库使用plsqldevloper
1.Oracle官网下载instantclient 解压到D:\zl\instantclient_11_2 2.配置环境变量 ORACLE_HOME = D:\zl\instantclient_11_ ...
- Fastjson, Gson, org.json.JSON三者对于JSONObject及JSONArray的判断
1.Fastjson 我们通常在已知格式的情况下直接使用JSONObject,JSONArray,但是如果遇到需要判断格式呢? try{ Object object = JSON.parse(a); ...
