【原创】Android开发之ADB及ADB SHELl命令的应用
adb的全称为Android Debug Bridge,就是起到调试桥的作用。通过adb我们可以在Eclipse中方面通过DDMS来调试Android程序,说白了就是debug工具。adb的工作方式比较特殊,采用监听Socket TCP 5554等端口的方式让IDE和Qemu通讯,默认情况下adb会daemon相关的网络端口,所以当我们运行Eclipse时adb进程就会自动运行。
adb是Android SDK里的一个工具, 用这个工具可以直接操作管理android模拟器或者真实的android设备(如G1手机). 它的主要功能有:
* 运行设备的shell(命令行)
* 管理模拟器或设备的端口映射
* 计算机和设备之间上传/下载文件
* 将本地apk软件安装至模拟器或android设备
ADB是一个 客户端-服务器端 程序, 其中客户端是你用来操作的电脑, 服务器端是android设备.
查看帮助:adb help
一、ADB命令
1、显示当前运行的全部模拟器
adb devices
2、对某一模拟器执行命令
adb –s 模拟器编号 命令
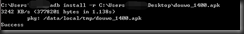
3、安装应用程序:
adb install –r 路径+应用名称(记得加上后缀)
4、卸载应用(暂时没成功)
adb uninstall
5、从电脑发送文件至设备
adb push <本地路径> <设备路径>

(在adb shell中通过pwd查看路径)
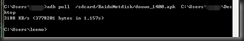
6、从手机至电脑
adb pull <设备路径> <本地路径>
7、获取管理员权限
adb root
8、获取设备的ID和序列号
adb get-product //个人表示使用没效果
adb get-serialno
9、无线调试
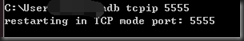
首先用数据线连接手机和电脑 执行以下命令
adb tcpip 5555
接下来断开数据线
查看手机ip地址
执行命令:adb connect 192.168.1.105:5555

即可远程调试设备
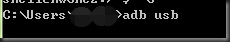
如果需要恢复到USB数据线,可以在命令行输入adb usb
我们也可以现在款adbwireless软件进行远程调试
10、重启、关机、进入recovery模式
重启 adb reboot
关机
进入recovery模式 adb reboot recovery
11、屏幕录像
开始录像 adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/demo.mp4
结束录像 ctrl+c

12、屏幕截图
截图 adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/1.png
复制到本地电脑 adb shell pull /sdcard/1.png 本地路径
二、ADB SHELL常用命令
输入adb shell命令后即可使用Linux系统下的一些命令像ls、cd、cat、mkdir等等
1、ls命令
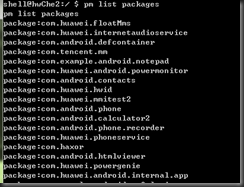
2、列出安装程序列表
pm list packages
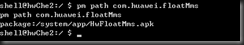
3、查看一个apk所在的路径
pm path 包名
4、
三、ADB HELP
1: Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
2:
3: -a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
4: -d - directs command to the only connected USB device returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
5: -e - directs command to the only running emulator.returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
6: -s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL environment variable.
7: -p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or a relative/absolute path to a product
8: out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
9: If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
10: environment variable is used, which must
11: be an absolute path.
12: -H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
13: -P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
14: devices [-l] - list all connected devices
15: ('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
16: connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
17: Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
18: disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
19: Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
20: Using this command with no additional arguments
21:
22: will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
23:
24: device commands:
25: adb push <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device
26: adb pull <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device
27: adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
28: (-l means list but don't copy)
29: (see 'adb help all')
30: adb shell - run remote shell interactively
31: adb shell <command> - run remote shell command
32: adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
33: adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
34: adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
35: the format is a list of lines with the following format:
36: <serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
37: adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
38: forward specs are one of:
39: tcp:<port>
40: localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
41: localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
42: localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
43: dev:<character device name>
44: jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
45: adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
46: - same as 'adb forward <local> <remote>' but fails
47: if <local> is already forwarded
48: adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection
49: adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
50: adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
51:
52: adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <file>
53: - push this package file to the device and install it
54: ('-l' means forward-lock the app)
55: ('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
56: ('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
57: ('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
58: adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
59: ('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
60: adb bugreport - return all information from the device
61: that should be included in a bug report.
62:
63: adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all]
64: [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>]
65: - write an archive of the device's data to <file>
66: .
67: If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
68: to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
69: (-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
70: in the archive; the default is noapk.)
71: (-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
72: (aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
73: is noobb.)
74: (-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
75: shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
76: (-all means to back up all installed applications)
77: (-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
78: system applications; the default is to include system apps)
79: (<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If
80: the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
81: list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
82: command line will be included even if -nosystem would
83: ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
84:
85: adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive
86:
87: adb help - show this help message
88: adb version - show version num
89:
90: scripting:
91: adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
92: adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
93: adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
94: adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
95: adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
96: adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path>
97: adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
98: adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
99: adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
100: adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
101: adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
102: adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
103: adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port networking:
104: adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
105: Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
106: <tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
107: [parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
108:
109: adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
110: <localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
111:
112: - If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
113:
114: - If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
115: is updated.
116:
117: environmental variables:
118: ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
119: 1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
120: ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
121: ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.
【原创】Android开发之ADB及ADB SHELl命令的应用的更多相关文章
- Android开发之Java集合类性能分析
对于Android开发者来说深入了解Java的集合类很有必要主要是从Collection和Map接口衍生出来的,目前主要提供了List.Set和 Map这三大类的集合,今天Android吧(ard8. ...
- Android开发之InstanceState详解
Android开发之InstanceState详解 本文介绍Android中关于Activity的两个神秘方法:onSaveInstanceState() 和 onRestoreInstanceS ...
- Android开发之Git配置
Android开发之Git配置 1.首先git配置: 输入命令: git config --global user.name "xxx.xx" git config --globa ...
- 【Android UI】Android开发之View的几种布局方式及实践
引言 通过前面两篇: Android 开发之旅:又见Hello World! Android 开发之旅:深入分析布局文件&又是“Hello World!” 我们对Android应用程序运行原理 ...
- Android开发之旅: Intents和Intent Filters(理论部分)
引言 大部分移动设备平台上的应用程序都运行在他们自己的沙盒中.他们彼此之间互相隔离,并且严格限制应用程序与硬件和原始组件之间的交互. 我们知道交流是多么的重要,作为一个孤岛没有交流的东西,一定毫无意义 ...
- Android开发之ViewPager+ActionBar+Fragment实现响应式可滑动Tab
今天我们要实现的这个效果呢,在Android的应用中十分地常见,我们可以看到下面两张图,无论是系统内置的联系人应用,还是AnyView的阅读器应用,我们总能找到这样的影子,当我们滑动屏幕时,Tab可 ...
- Android开发之Java必备基础
Android开发之Java必备基础 Java类型系统 Java语言基础数据类型有两种:对象和基本类型(Primitives).Java通过强制使用静态类型来确保类型安全,要求每个变量在使用之前必须先 ...
- Android开发之PopupWindow
/* * Android开发之PopupWindow * * Created on: 2011-8-8 * Author: blueeagle * Email: liujiaxiang@g ...
- [置顶] Android开发之MediaPlayerService服务详解(一)
前面一节我们分析了Binder通信相关的两个重要类:ProcessState 和 IPCThreadState.ProcessState负责打开Binder 驱动,每个进程只有一个.而 IPCThre ...
- Android 开发之旅:深入分析布局文件&又是“Hello World!”
http://www.cnblogs.com/skynet/archive/2010/05/20/1740277.html 引言 上篇可以说是一个分水岭,它标志着我们从Android应用程序理论进入实 ...
随机推荐
- Redis在PHP中的基本使用案例
下载http://www.oschina.net/p/redis 解压后里面有:lib 源文件 .examples 例子.test测试 将lib目录拷贝到你的项目中,就可以开始你的predis操作了. ...
- 教程-Delphi操作快捷键
************************************************************** Delphi快捷键-全-高手用-南山古桃(新手)-同学共进 ******* ...
- A Tour of Go Exercise: Loops and Functions
As a simple way to play with functions and loops, implement the square root function using Newton's ...
- light oj 1297 Largest Box
1297 - Largest Box PDF (English) Statistics Forum Time Limit: 2 second(s) Memory Limit: 32 MB In t ...
- iOS网络编程(三) 异步加载及缓存图片---->SDWebImage
@SDWebImage提供一个UIImageView的类别以支持加载来自网络的远程图片.具有缓存管理.异步下载.同一个URL下载次数控制和优化等特征. @SDWebImage的导入1.https:// ...
- [一]初识SpringMVC
是什么? web开发框架 为什么用? 功能强大 怎么做? 1.导入jar包 2.配置web.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UT ...
- JS----JS调试技巧
骨灰级调试大师Alert 那还是互联网刚刚起步的时代,网页前端还主要以内容展示为主,浏览器脚本还只能为页面提供非常简单的辅助功能的时候.那个时候,网页主要运行在以IE6为主的浏览器中,JS的调试功能还 ...
- Android两个控件叠在一起,如何让被挡住的控件显示出来
Android两个控件叠在一起,如何让被挡住的控件显示出来 问题 : 两个控件叠在一起,如何让被挡住的控件显示出来? 比如A,B两个控件,A被B挡住,目前A要显示出来,B不能被隐藏,A的高度只有那么一 ...
- Android开发_Gson解析
//转换器 GsonBuilder builder = new GsonBuilder(); // 不转换没有 @Expose 注解的字段 builder.excludeFieldsWithoutEx ...
- BLE 广播数据解析
从上一篇GATT Profile 简介中提到过,BLE 设备工作的第一步就是向外广播数据.广播数据中带有设备相关的信息.本文主要说一下 BLE 的广播中的数据的规范以及广播包的解析. 广播模式 BLE ...
